Research Highlights
Oceanus Magazine
News Releases
An international research team discovered a human skeleton during its ongoing excavation of the famous Antikythera Shipwreck (circa 65 B.C.) this month. The shipwreck, which holds the remains of a Greek trading or cargo ship, is located off the Greek island of Antikythera in the Aegean Sea. The first skeleton recovered from the wreck site during the era of DNA analysis, this find could provide insight into the lives of people who lived 2100 years ago.
On the first trip to study great white sharks in the wild off Guadalupe Island in 2013, the REMUS SharkCam team returned with an autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) tattooed with bite marks and some of the most dramatic footage ever seen on Discovery Channel’s Shark Week: large great white sharks attacking the underwater robot, revealing previously unknown details about strategies sharks use to hunt and interact with their prey.
An international research team led by archaeologists and technical experts from the Hellenic Ministry of Culture and Sports and WHOI has discovered spectacular artifacts during its ongoing excavation of the famous ancient Antikythera Shipwreck off the Greek island of Antikythera in the Aegean Sea.
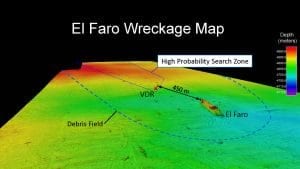
Technology and vehicles developed and operated by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists and engineers were instrumental in assisting the NTSB in locating the voyage data recorder (VDR) of El Faro.
Steve Elgar, a senior scientist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), has been selected as a 2016 National Security Science and Engineering Faculty Fellow (NSSEFF) by the Department of Defense.
News & Insights
An investigative report this week in the LA Times features the work of WHOI’s marine geochemistry lab in identifying the discarded barrels and analyzing samples from the discovery.