Research Highlights
Oceanus Magazine
News Releases
Long-awaited event sets the stage for scientists to learn more about physical, chemical and biological processes in the deep ocean East Pacific Rise, Pacific Ocean (May 2, 2025) – Scientists diving in the human-occupied vehicle Alvin recently witnessed a rare…
New research on single-celled organisms sheds light on deep-sea energy sources
Research offers potential understanding of habitability on ocean worlds in the outer solar system
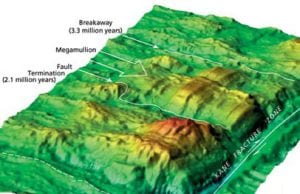
Scientists unravel the role of our planet’s mantle in volcanism and global cycles
A new study investigates how the influence of low gravity, as found on ocean worlds in our solar system, impacts flow of water and heat below their seafloors.
News & Insights
This week, NASA’s Perseverance Rover lands on Mars to continue the search for life on the Red Planet. At the same time, WHOI scientists and engineers are applying their experience exploring the deepest parts of planet Earth to the quest…
As glaciers melt at unprecedented rates, WHOI’s Simon Pendleton is looking back to historical records to predict whether this new cool runoff will slow ocean circulation and cool the northern hemisphere––findings which could mean adjustments to some climate predictions.
WHOI looks back at the legacy of co-founder of MIT-WHOI Joint Program, former Director of Research and Provost at WHOI, Art Maxwell
As I reached the end of April, I realized that too much of my time was getting consumed by zoom calls and email in a bid to over-compensate for not being able to interact with people on-site at WHOI. So…