Research Highlights
Oceanus Magazine
News Releases
The study shows that large-scale harvesting of mesopelagic fish that live hundreds of meters below the surface could reduce the food available to bigeye tuna
CMA CGM, which has long been committed to preserving biodiversity through multiple initiatives in the U.S. and worldwide, will support two key WHOI projects
Coral reefs support more than 25 percent of all marine life and underpin the livelihoods of roughly one billion people globally.
A first of its kind study links drone-collected respiratory microbes with health assessments, offering hope for protecting vulnerable populations
WHOI scientists delve into the elusive fish’s role in the food web
News & Insights
WHOI’s Dennis McGillicuddy on why ocean life matters deeply to the Sunshine State
April 24 marks the first-ever Right Whale Day in Massachusetts. WHOI biologist and veterinarian Michael Moore recently met with the resident who brought this special recognition about– and explains why it’s important to raise awareness about the critically endangered North Atlantic right whale.
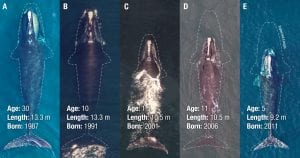
A report out this week in Current Biology reveal that critically endangered North Atlantic right whales are up to three feet shorter than 40 years ago. This startling conclusion reinforces what scientists have suspected: even when entanglements do not lead directly to the death of North Atlantic right whales, they can have lasting effects on the imperiled population that may now number less than 400 animals. Further, females that are entangled while nursing produce smaller calves.
May 10, 2021 During a joint research trip on February 28 in Cape Cod Bay, Mass., WHOI whale trauma specialist Michael Moore, National Geographic photographer Brian Skerry, and scientists from New England Aquarium, witnessed a remarkable biological event: North…