Research Highlights
Oceanus Magazine
News Releases
While the impacts of plastic pollution on human health and the environment are growing, the report finds, increasing harm due to plastics is not inevitable.
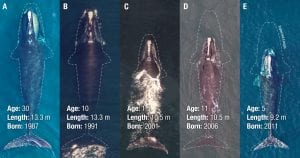
Filter-feeding whales sample the Arctic food web, tracking decades of change
Differences in brain structure between echolocating and non-echolocating marine mammals offers insight into auditory processing
WHOI researchers part of collaborative, international effort to increase Marine Protected Areas and other strategies
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and partners take home prestigious award
News & Insights
WHOI’s Dennis McGillicuddy on why ocean life matters deeply to the Sunshine State
April 24 marks the first-ever Right Whale Day in Massachusetts. WHOI biologist and veterinarian Michael Moore recently met with the resident who brought this special recognition about– and explains why it’s important to raise awareness about the critically endangered North Atlantic right whale.
A report out this week in Current Biology reveal that critically endangered North Atlantic right whales are up to three feet shorter than 40 years ago. This startling conclusion reinforces what scientists have suspected: even when entanglements do not lead directly to the death of North Atlantic right whales, they can have lasting effects on the imperiled population that may now number less than 400 animals. Further, females that are entangled while nursing produce smaller calves.
May 10, 2021 During a joint research trip on February 28 in Cape Cod Bay, Mass., WHOI whale trauma specialist Michael Moore, National Geographic photographer Brian Skerry, and scientists from New England Aquarium, witnessed a remarkable biological event: North…