Marine Chemistry & Geochemistry
Marshes, Mosquitoes, and Sea Level Rise
In the 1930s, the Cape Cod Mosquito Control Project dug approximately 1,500 miles of ditches across marshes on the Cape to drain their water and reduce the number of ponds…
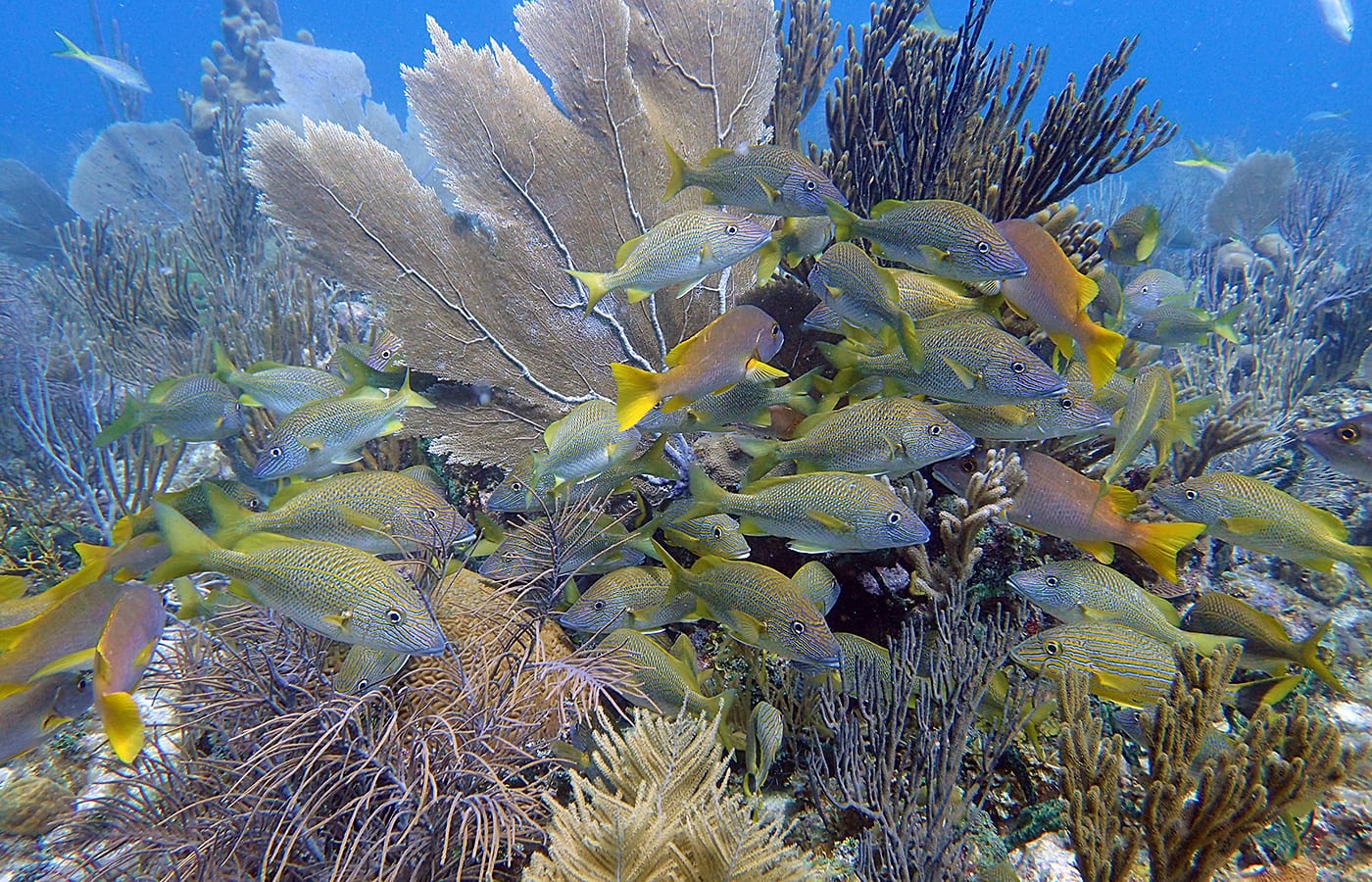
Read MoreThe Unseen World on Coral Reefs
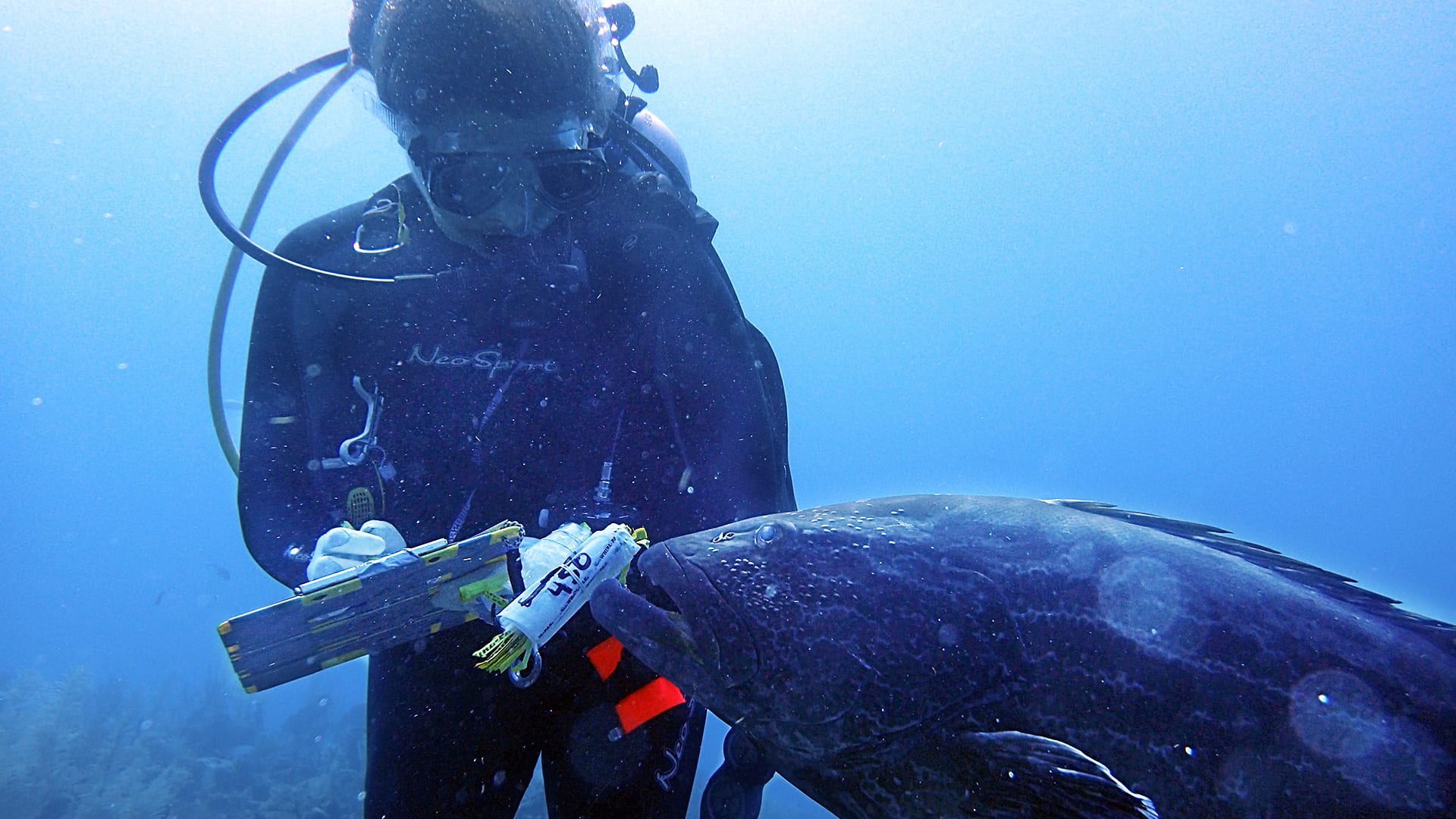
We have learned that microbial communities on and within us—a microbiome—keep people healthy. Corals reefs also have their own microbiomes that they couldn’t function without.
Read MoreA Change Has Come in the Arctic
On a long voyage across the Arctic Ocean, an MIT-WHOI graduate students finds chemical clues that climate change has already had impacts on the region.
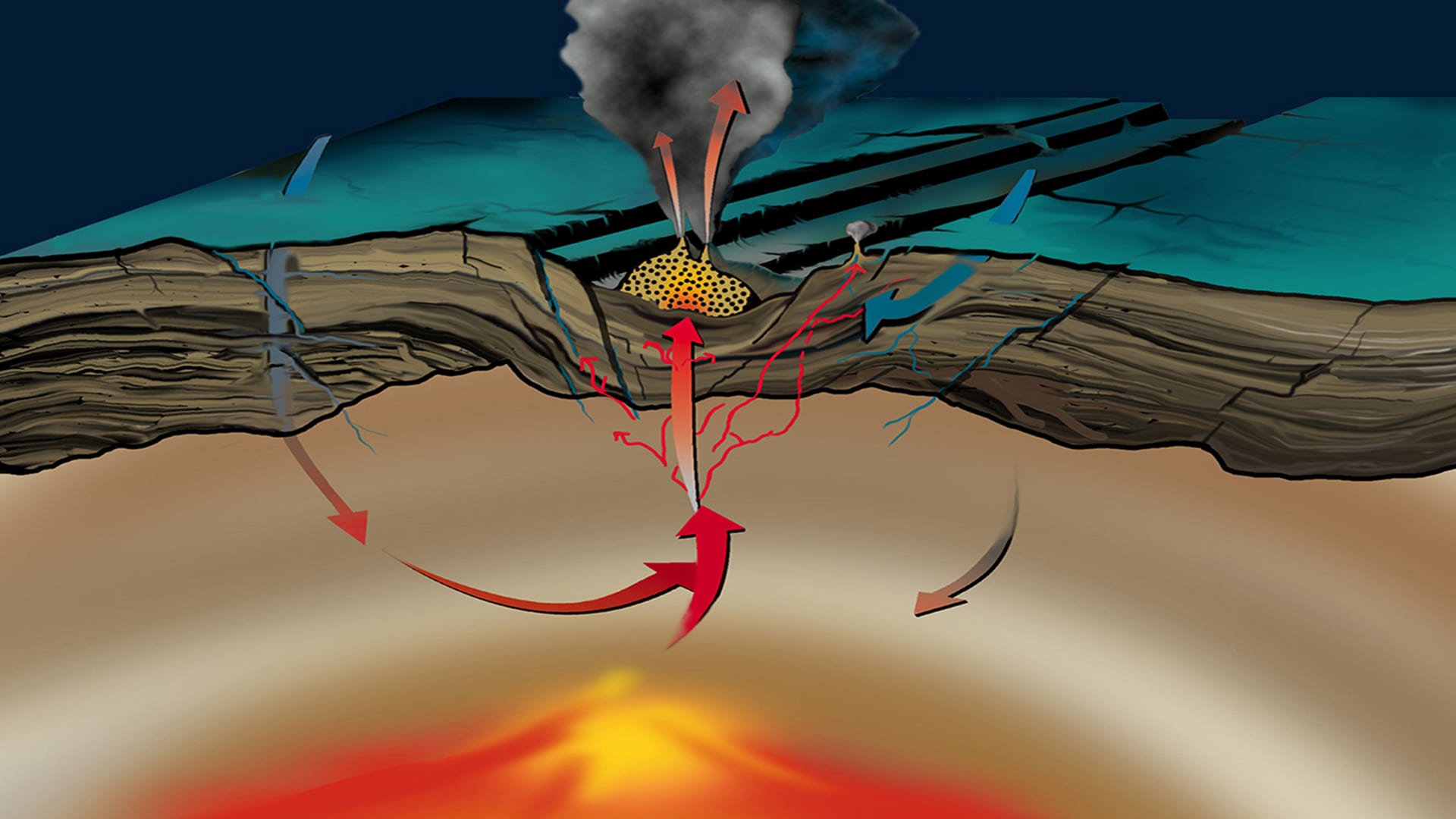
Read MoreThe Discovery of Hydrothermal Vents
In 1977, WHOI scientists made a discovery that revolutionized our understanding of how and where life could exist on Earth and other planetary bodies.
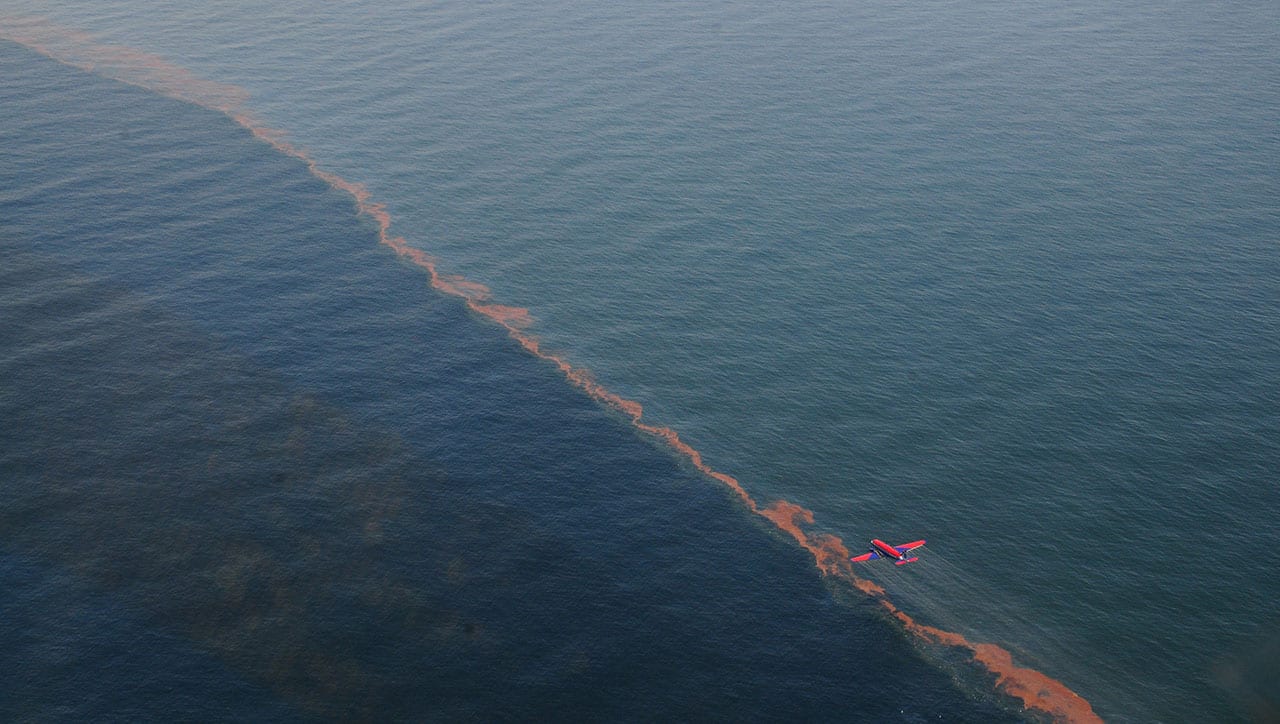
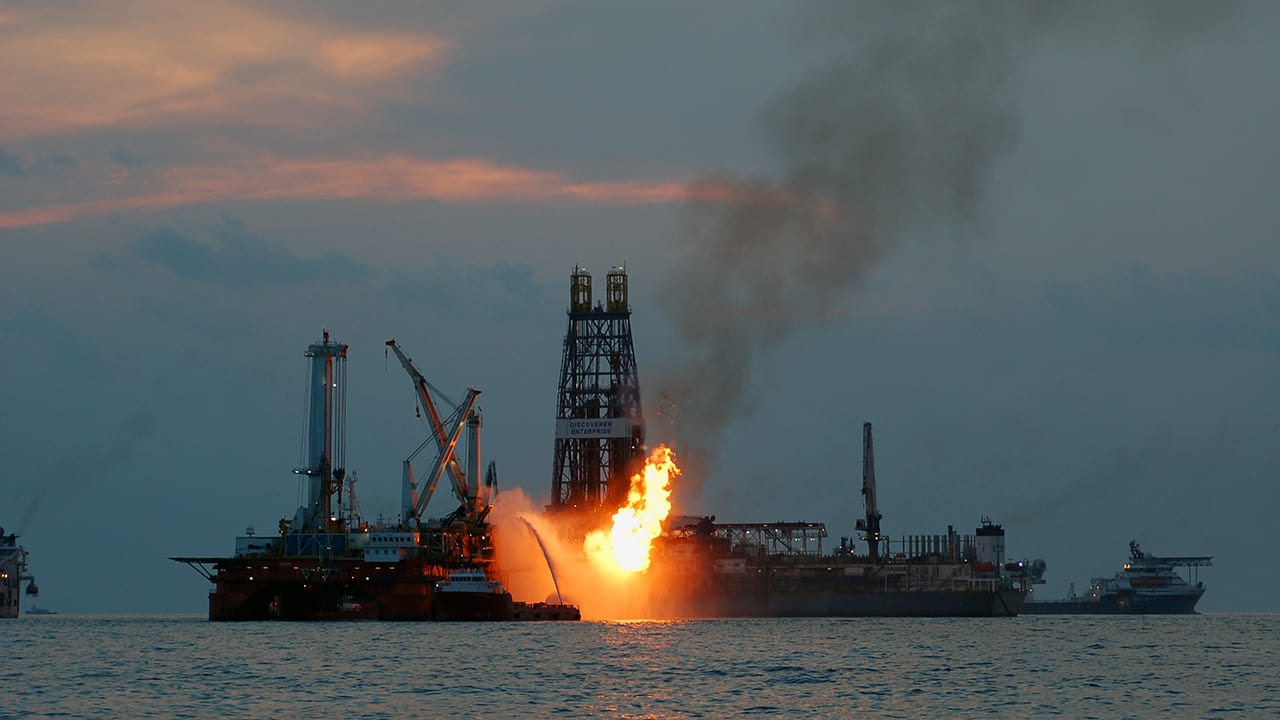
Read MoreA Long Trail of Clues Leads to a Surprise About Oil Spills
Scientists followed evidence from the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill to discover an unexpected phenomenon.
Read MoreReassessing Guidelines for Oil Spill Cleanups
A new discovery could change the way officials approach oil spill cleanups.
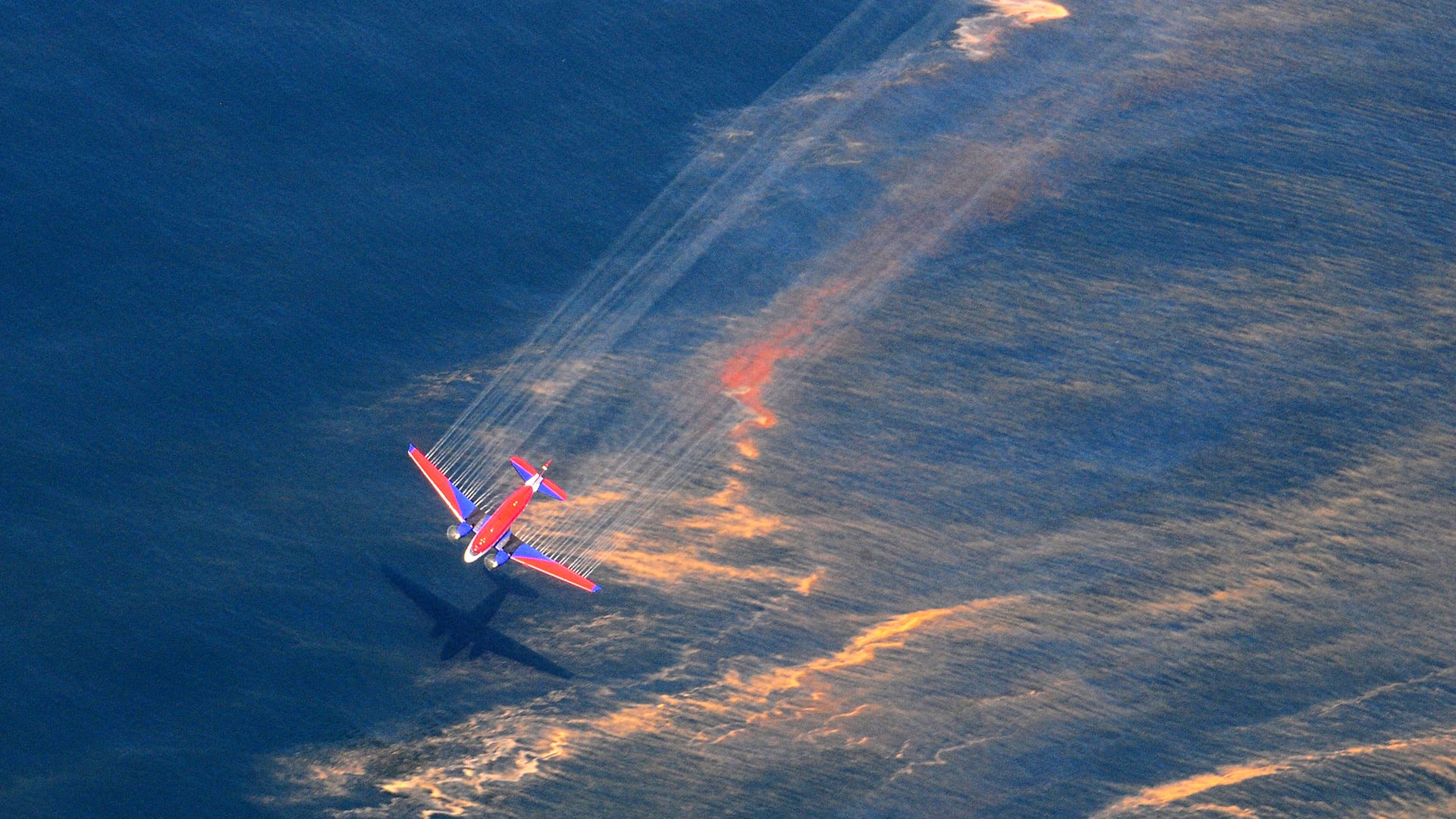
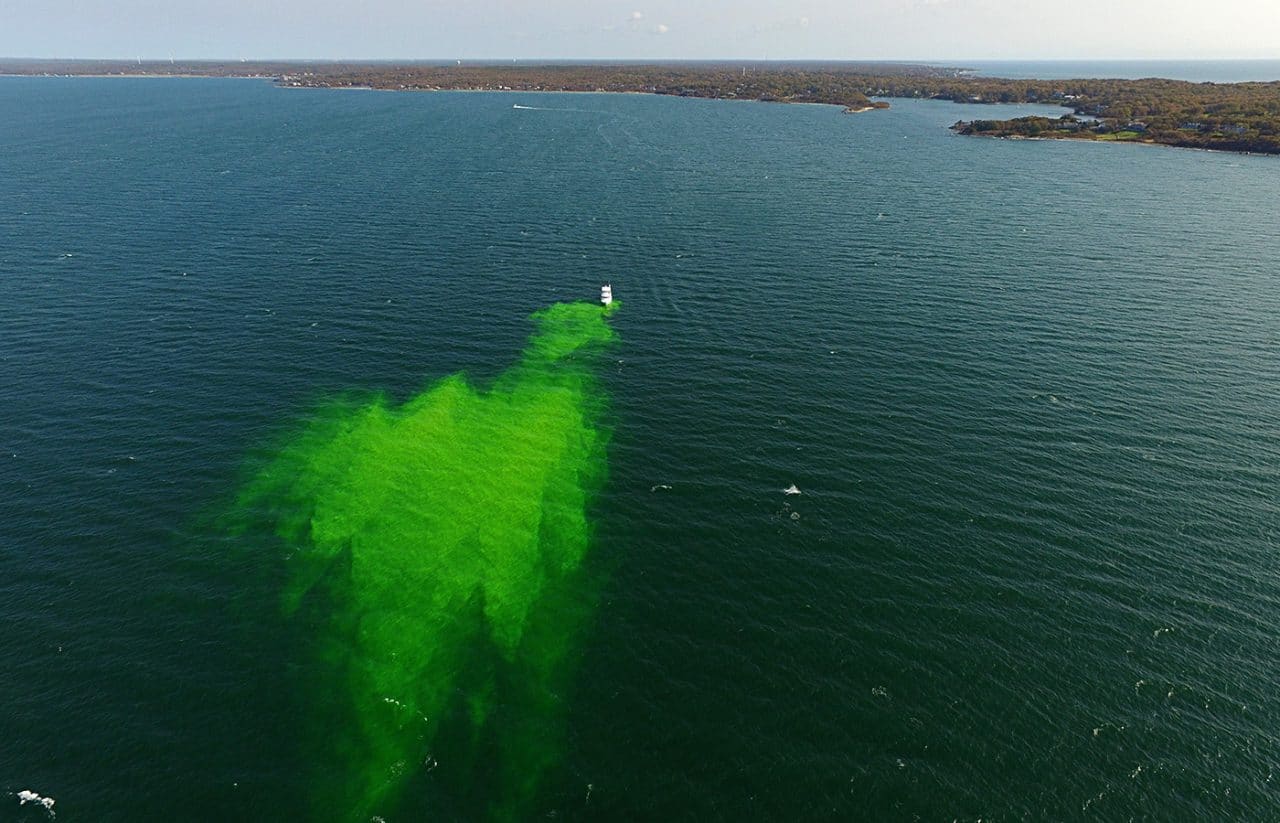
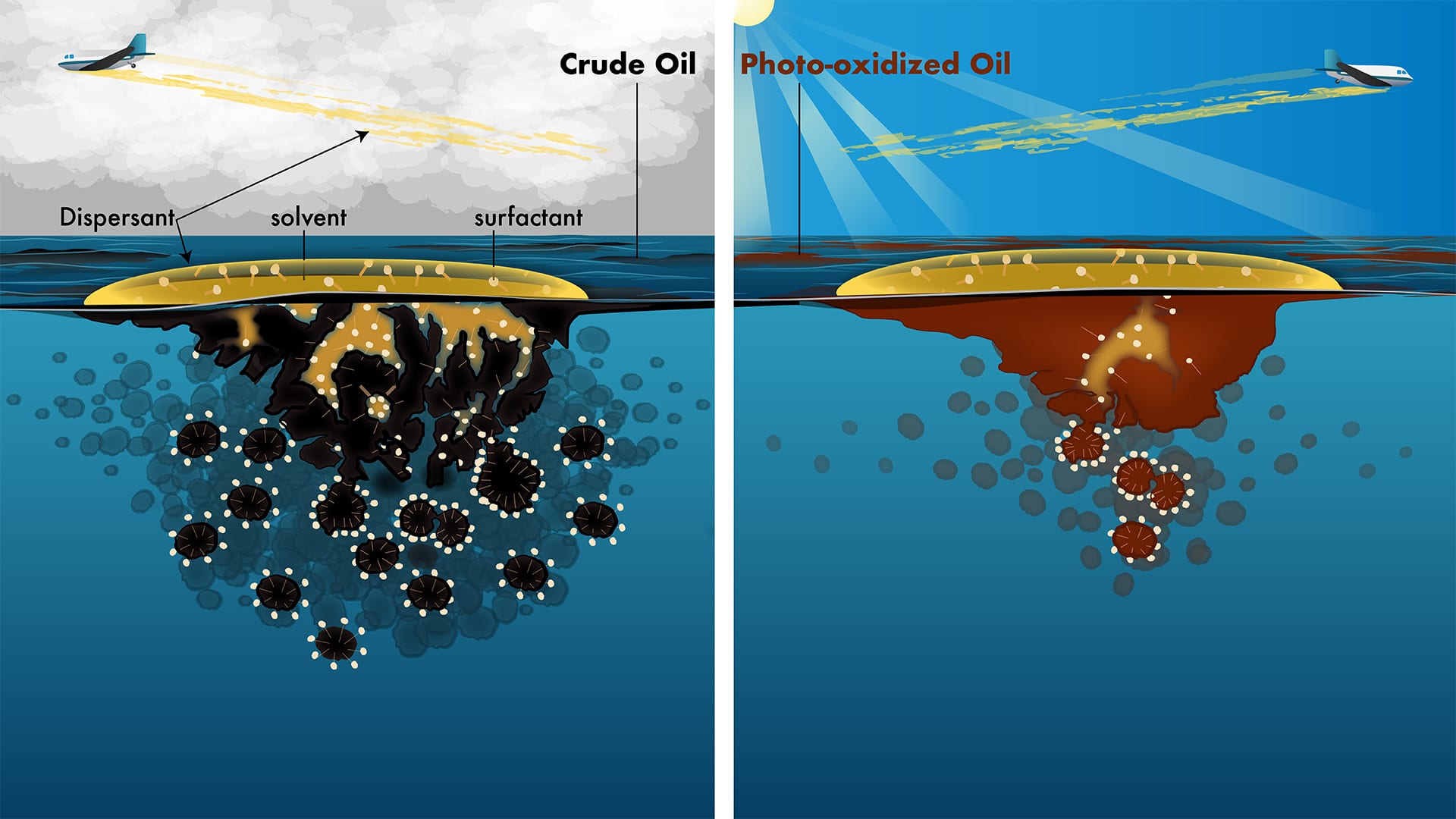
Read MoreSunlight Reduces Effectiveness of Dispersants Used in Oil Spills
A research team led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) found that sunlight chemically alters crude oil floating on the sea surface within hours or days. In a follow-up study the team reported that sunlight changes oil into different compounds that dispersants cannot easily break up. The results of these two studies could affect how responders decide when, where, and how to use dispersants.
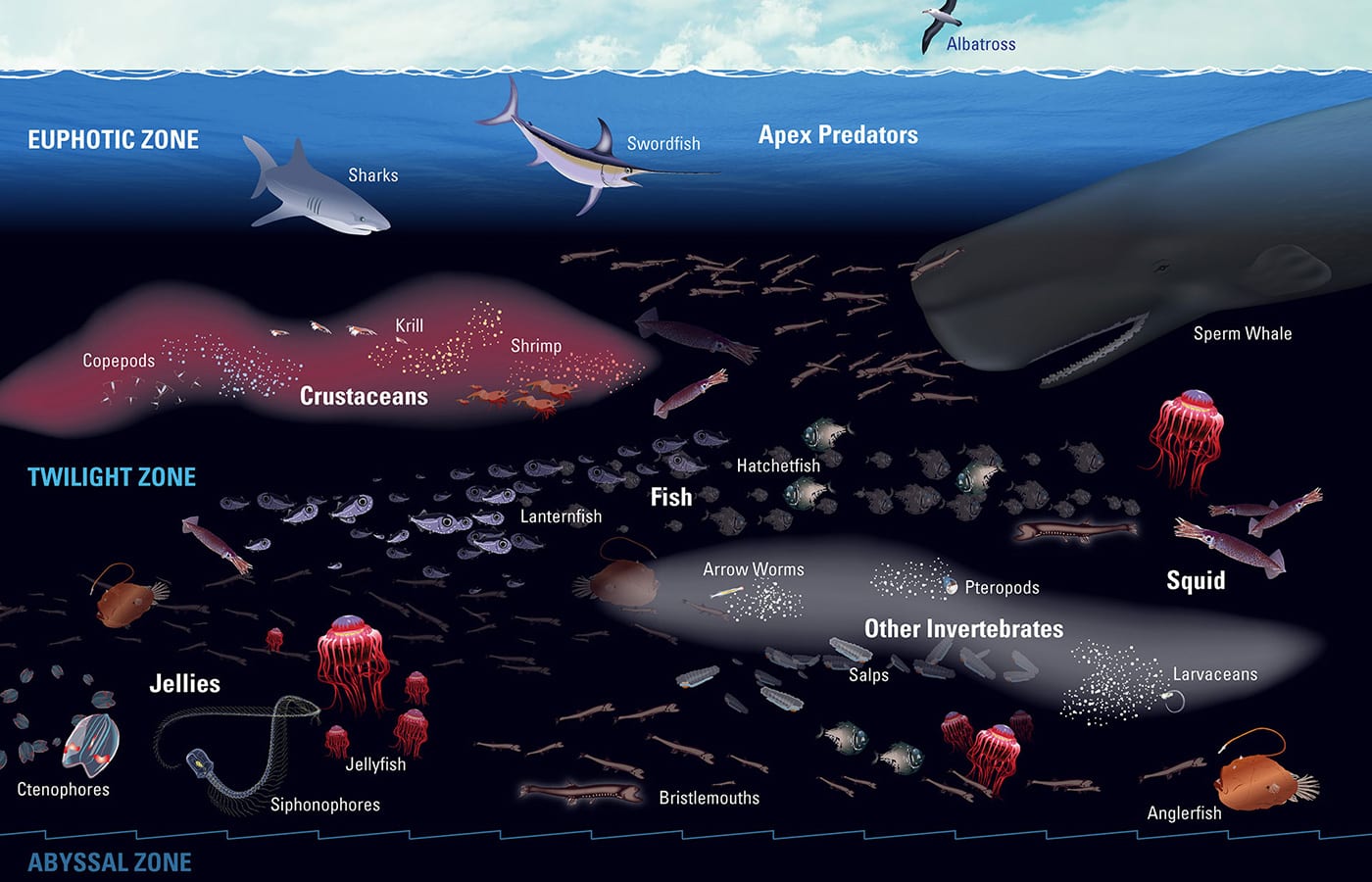
Read MoreMission to the Ocean Twilight Zone
The twilight zone is a part of the ocean 660 to 3,300 feet below the surface, where little sunlight can reach. It is deep and dark and cold, and the pressures there are enormous. Despite these challenging conditions, the twilight zone teems with life that helps support the ocean’s food web and is intertwined with Earth’s climate. Some countries are gearing up to exploit twilight zone fisheries, with unknown impacts for marine ecosystems and global climate. Scientists and engineers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution are poised to explore and investigate this hidden frontier.
Read MoreTo Track an Oil Spill
WHOI scientists are helping to develop a robotic underwater vehicle that can track oil spills and help responders mitigate damage in remote or ice-covered areas such as the Arctic Ocean and the Great Lakes.
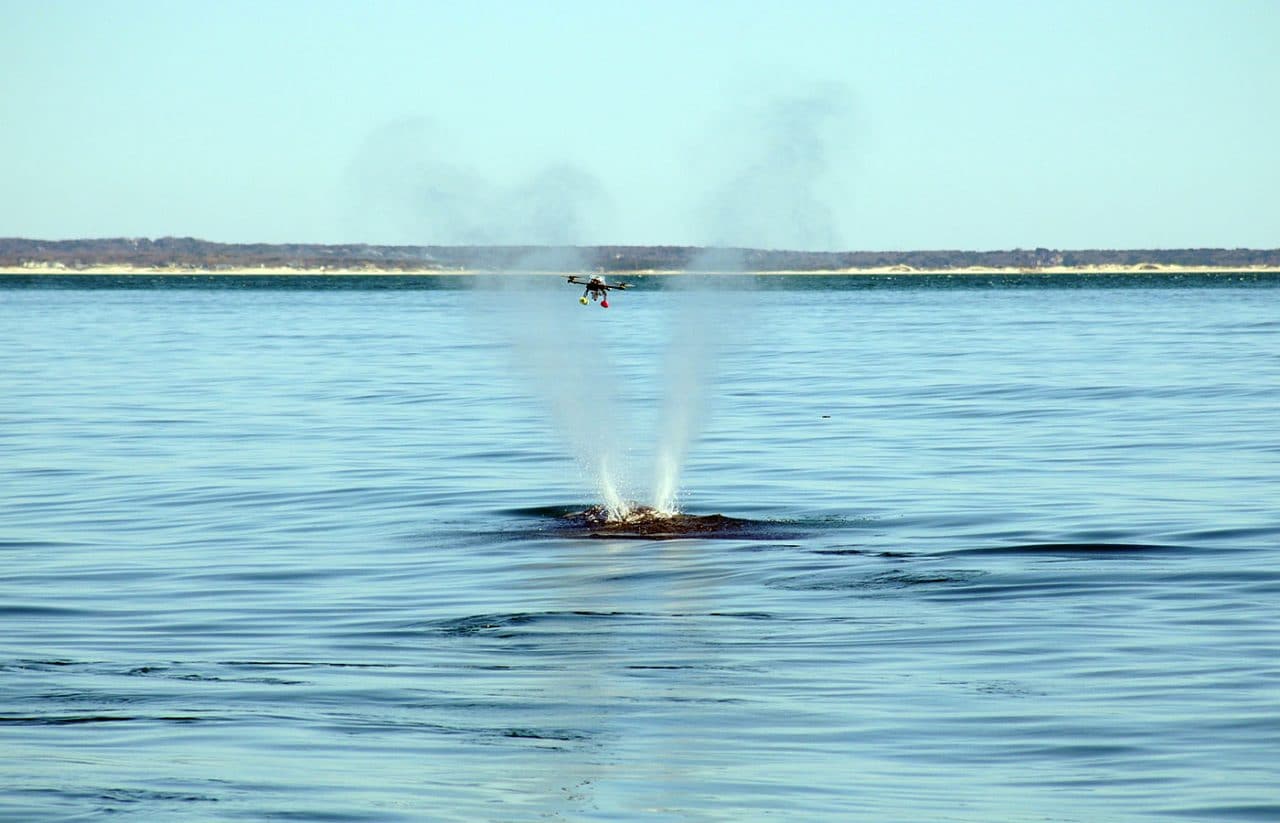
Read MoreUp in the Sky!
Nope, it’s not a bird or a plane. It’s a drone on a scientific mission to restore a river long impaired by dams and to help bring back populations of…
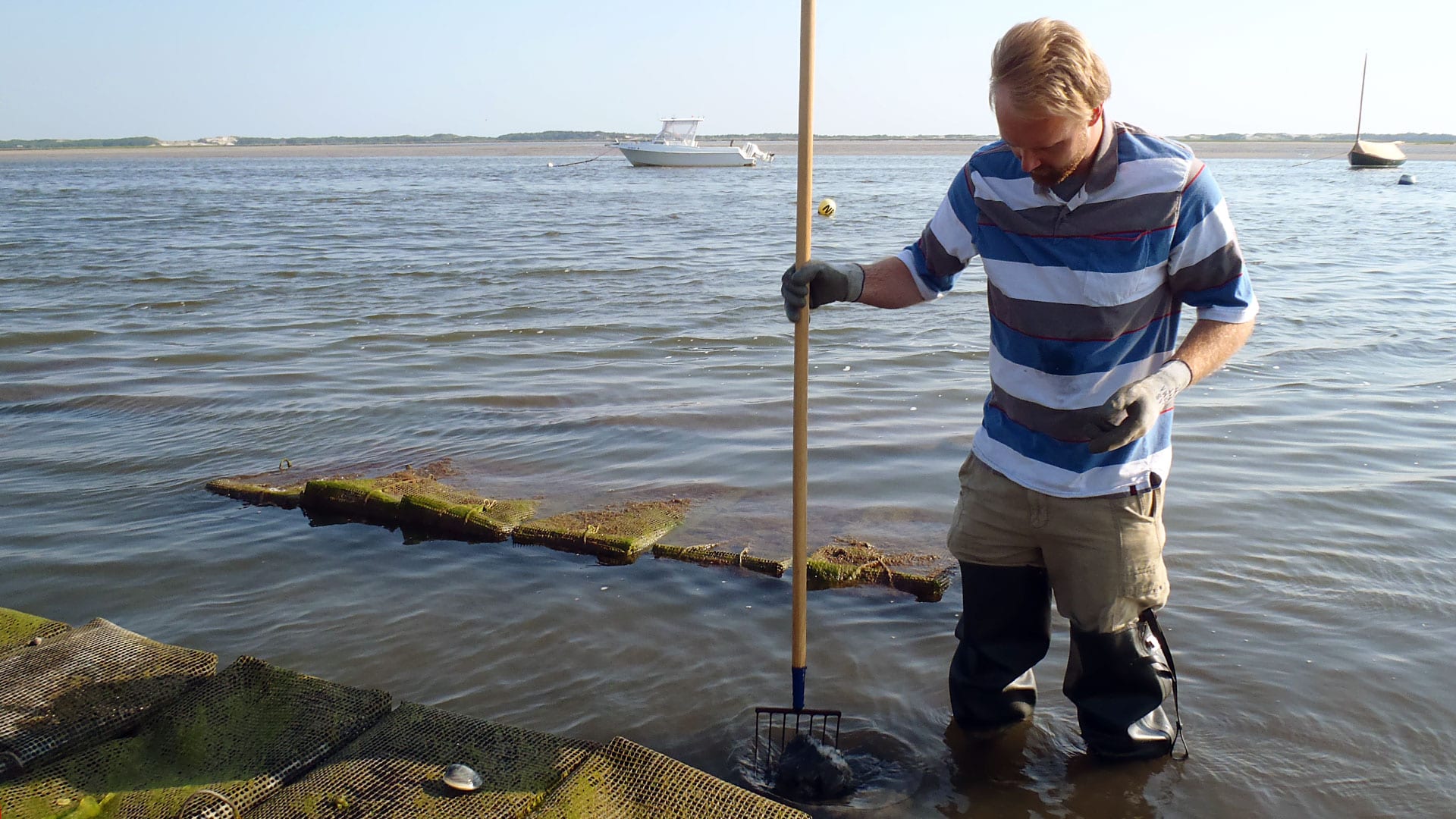
Read MoreCan Clams and Oysters Help Clean Up Waterways?
Towns in Cape Cod are looking to shellfish not only as culinary treats, but as a way to help clean up waters suffering from excess nitrogen. Nitrogen is an essential…
Read MoreDid Dispersants Help During Deepwater Horizon?
In the heat of the 2010 Deepwater Horizon disaster, U.S. government and industry responders had to make a crucial decision. They were facing an enormous oil spill, gushing uncontrollably from…
Read MoreScientists Reveal Secrets of Whales
Researchers have known for decades that whales create elaborate songs. But a new study has revealed a component of whale songs that has long been overlooked—sort of a booming baseline…
Read MoreIn the Gardens of the Queen
An unprecedented research cruise investigated one of the most beautiful and unexplored coral reefs in the Caribbean and fostered collaboration between U.S. and Cuban scientists.
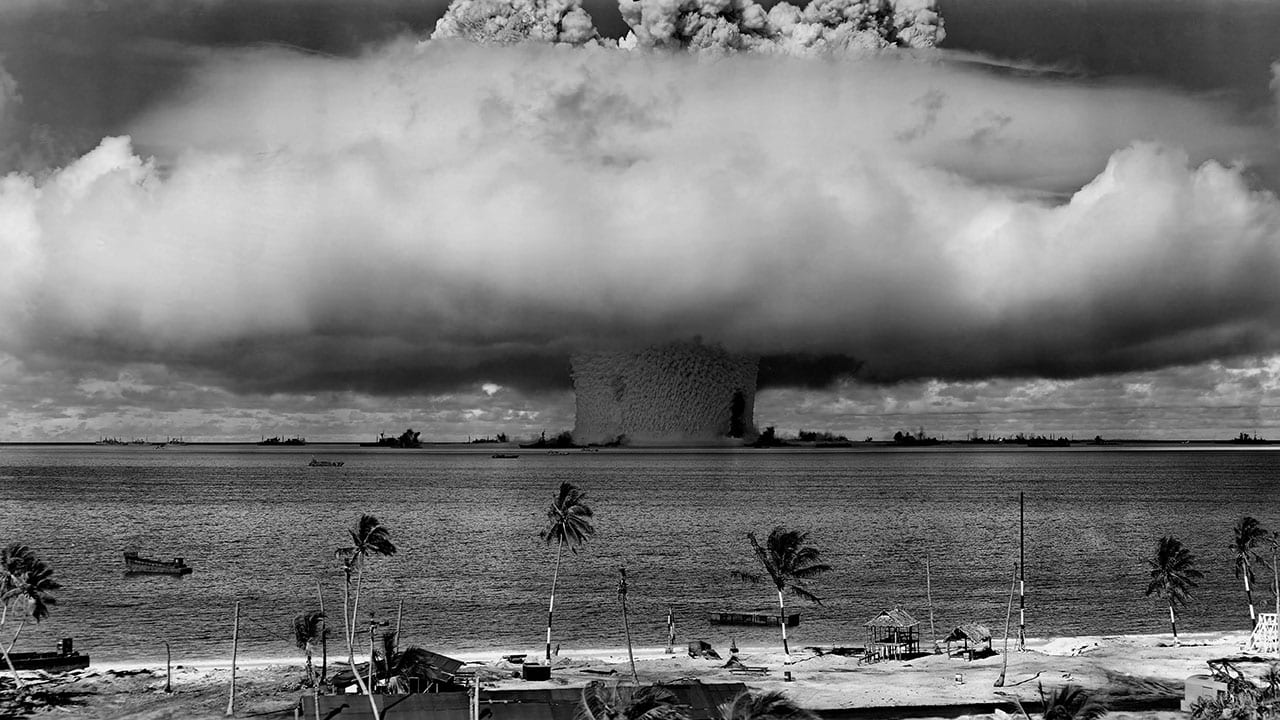
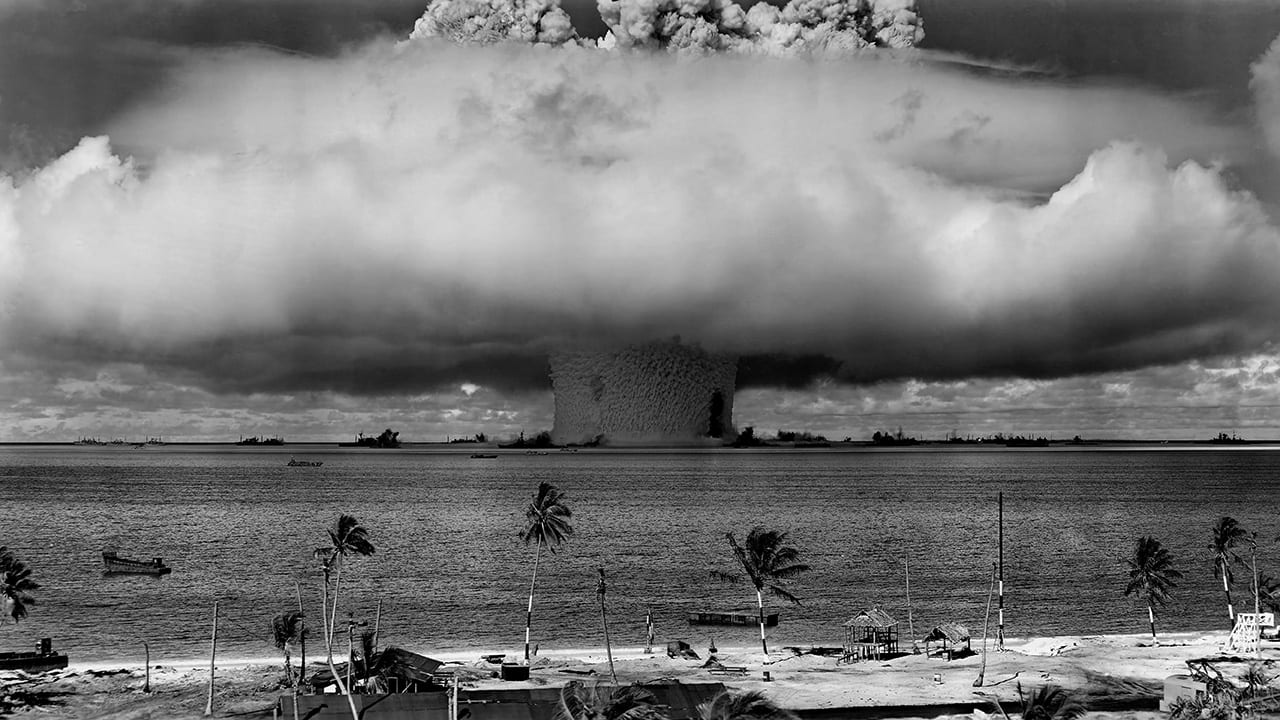
Read MoreRadioactivity Lingers from 1946-1958 Nuclear Bomb Tests
Scientists have found lingering radioactivity in the lagoons of remote Marshall Island atolls in the Pacific Ocean where the United States conducted 66 nuclear weapons tests in the 1940s and…
Read MoreDid Dispersants Help Responders Breathe Easier?
Seven years after the disastrous Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico, the decision to inject chemical dispersants into the deep ocean has remained contentious. New evidence reveals an unexpected benefit.
Read MoreDispersants Improved Air Quality for Responders at Deepwater Horizon
A study published Aug. 28, 2017, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences adds a new dimension to the controversial decision to inject large amounts of chemical dispersants immediately above the crippled oil well at the seafloor during the Deepwater Horizon disaster in 2010. The dispersants may have significantly reduced the amount of harmful gases in the air at the sea surface’diminishing health risks for emergency responders and allowing them to keep working to stop the uncontrolled spill and clean up the spilled oil sooner.
Read MorePop Goes the Seafloor Rock
WHOI scientists used the human-occupied submersible Alvin and the autonomous underwater vehicle Sentry to explore a surprising discovery: gas-filled volcanic rocks on the seafloor that “pop” when brought up to the surface.
Read MoreBack to Bikini
WHOI scientists returned to the Pacific islands of Bikini and Enewetak in 2015 to study radioactive contamination nearly 70 years after the U.S. used the islands for nuclear weapons testing. What they learned could also be applied to a more recent nuclear disaster: the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi reactor meltdown in Japan.
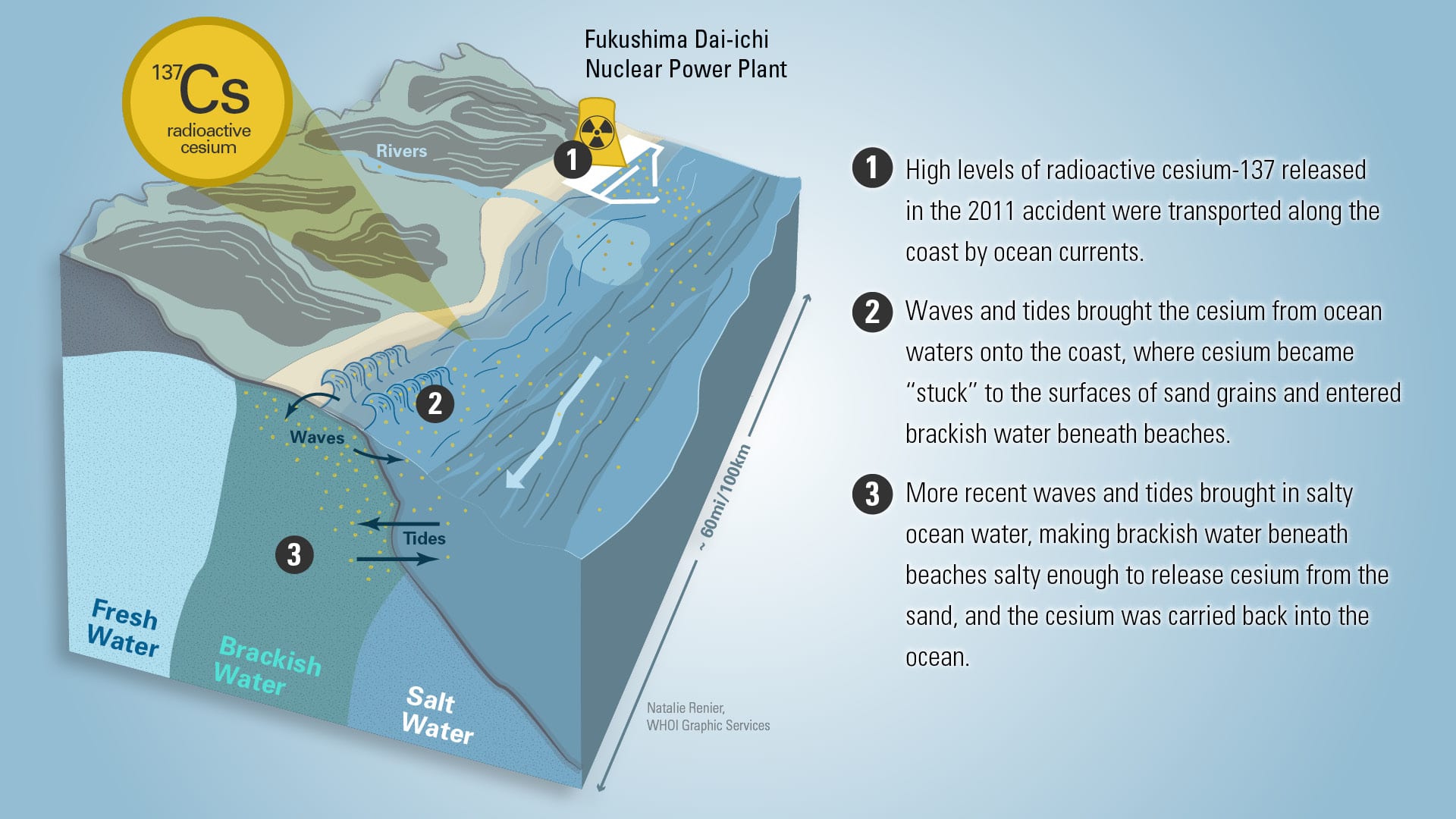
Read MoreRadioactivity Under the Beach?
Scientists have found a previously unsuspected place where radioactive material from the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant disaster has accumulated—in sands and brackish groundwater beneath beaches up to 60 miles away.
Read MoreScientists and Navy Join Forces
When U.S. Navy were preparing a major NATO military exercise, they solicited help from WHOI scientists to plan how to mitigate potential environmental damage from oil spills.
Read MoreWhat Happened to Deepwater Horizon Oil?
Officials pumped a huge amount of chemicals into the deep ocean during the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill in an effort to disperse the oil. A study published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences offers evidence that the dispersant may helped microbes break down the oil.
Read MoreNew Device Reveals What Ocean Microbes Do
Whether you’re a plant, animal, or even a microbe, you generally can’t conduct the business of living without exchanging oxygen. So just as you can figure out what’s going on…
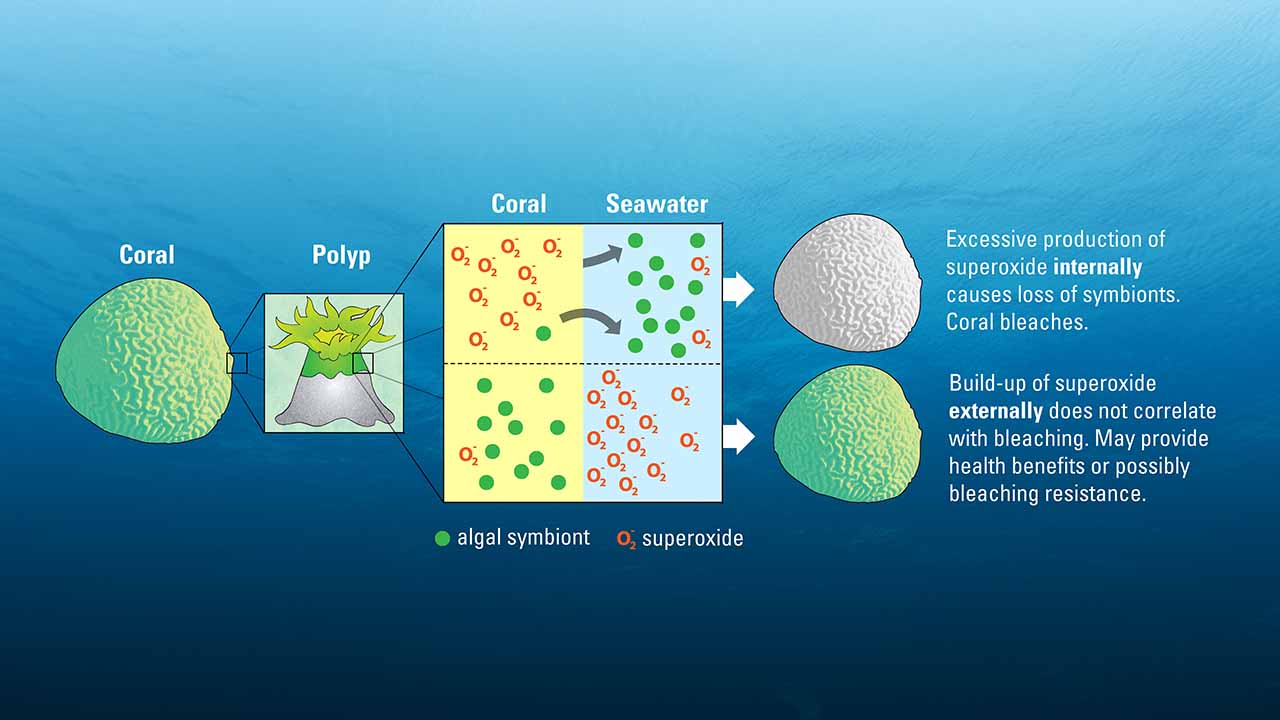
Read MoreNew Studies Take a Second Look at Coral Bleaching Culprit
A new study from WHOI indicates that superoxide’a natural toxin believed to be the main culprit behind coral bleaching’may actually play a beneficial role in coral health and resilience.
Read More