Featured Project
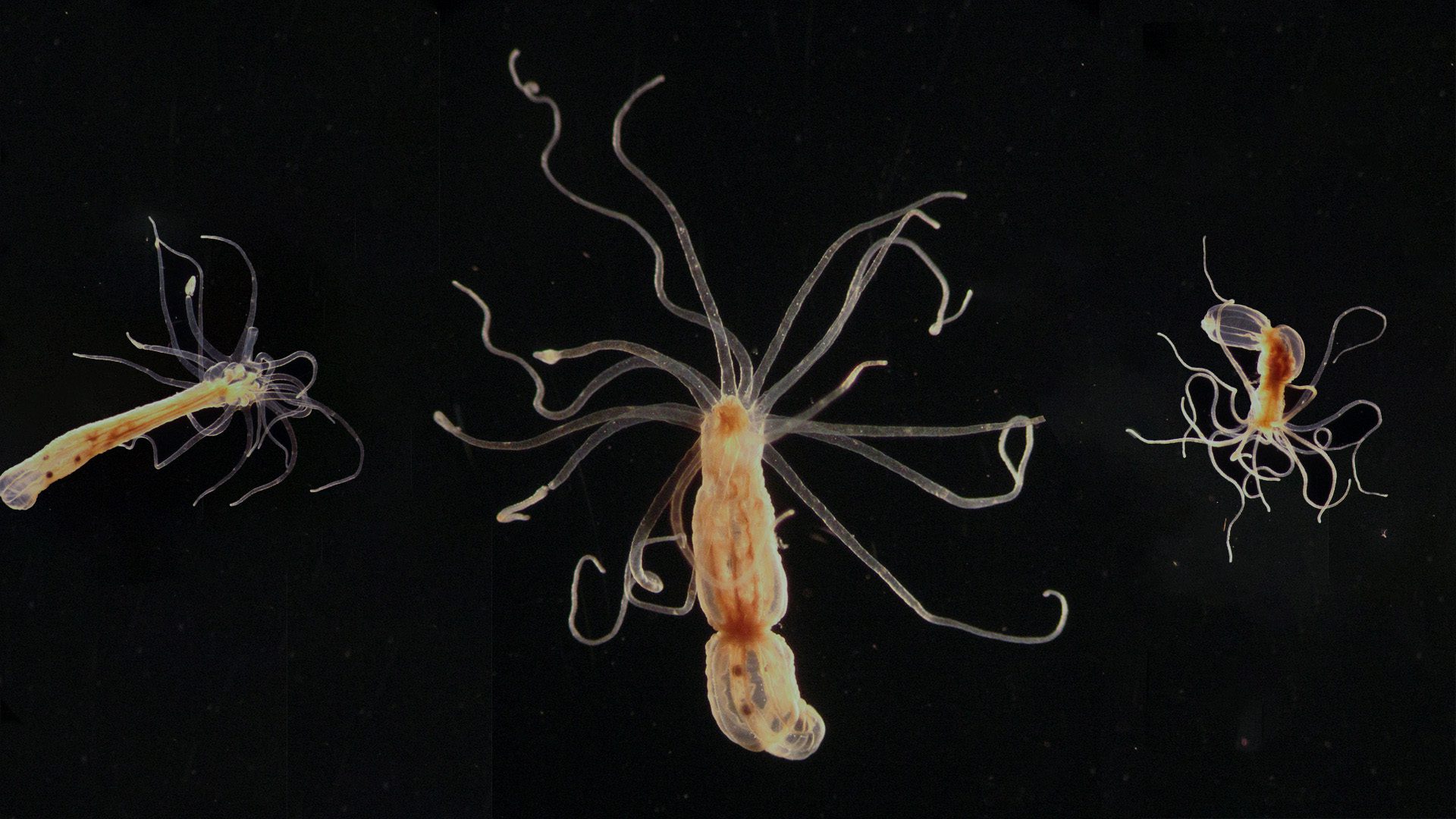
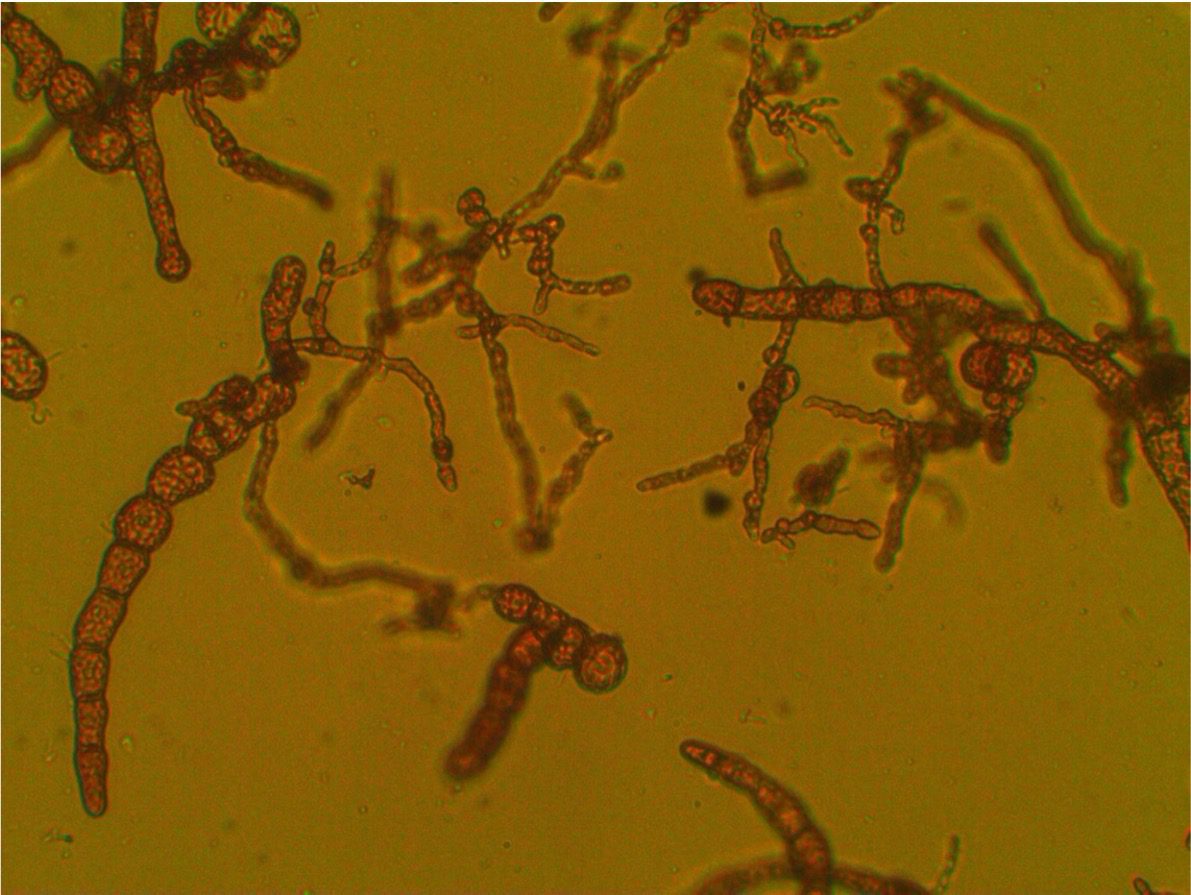
A toxic double whammy for sea anemones
Exposure to both oil and sunlight can be harmful to sea anemones
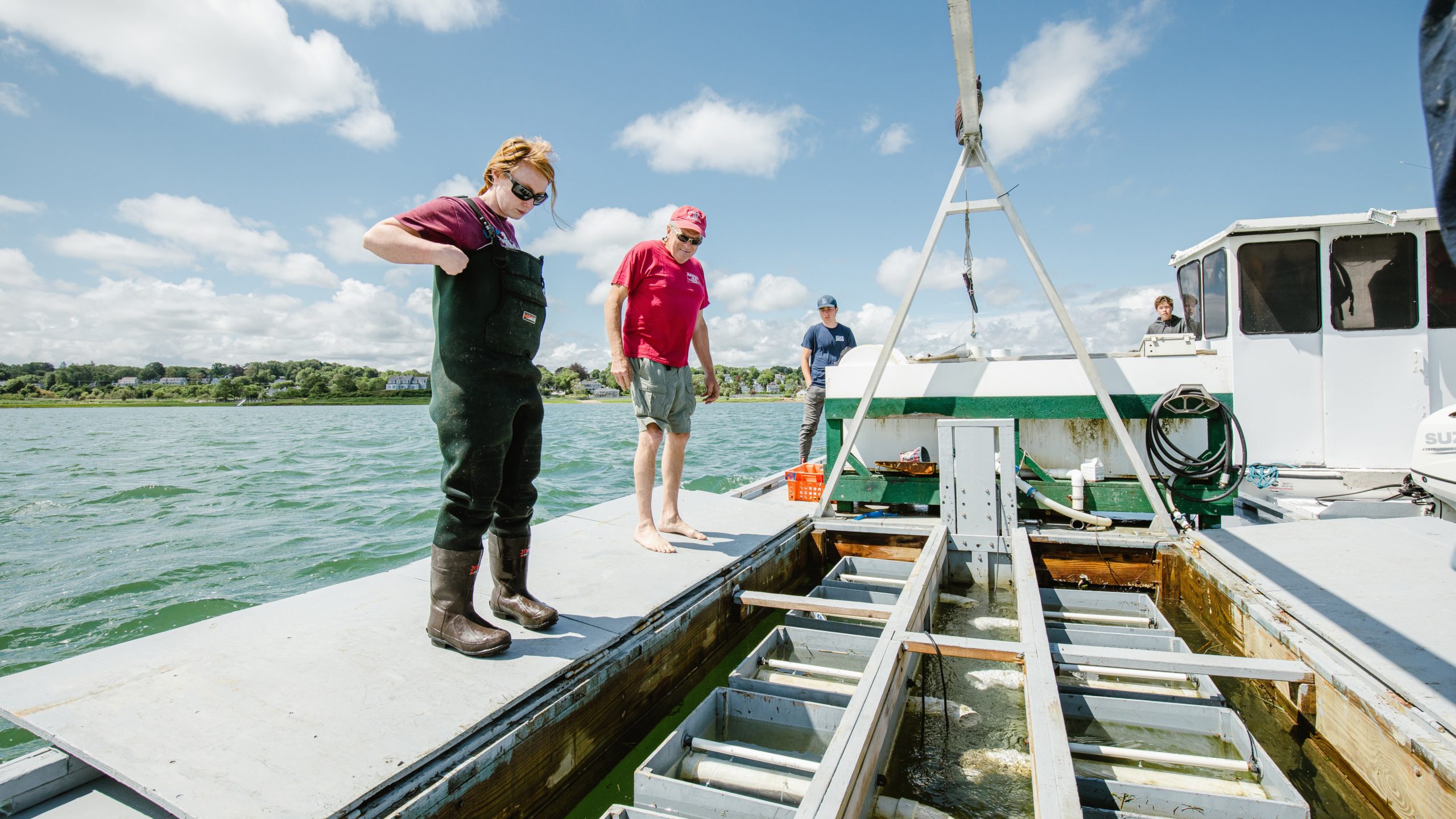
Read MoreInvasive tunicates have shellfish farmers crying “foul”
As shellfish farmers struggle with invasive tunicate invasions, scientists are trying to gain insight into the thermal tolerances for these strange critters and determine where they might show up next
Read MoreInnovative, new “road map” for kelp crop improvement
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the University of Connecticut, and Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences have executed a license agreement for a kelp germplasm, or collection of microscopic cells called gametophytes, containing more than 1,200 samples all developed and isolated by WHOI and UConn-led teams. Bigelow Laboratory’s National Center for Marine Algae and Microbiota plans to maintain, market, and distribute the germplasm collection for broad use.
Read MoreCreating synergy through art and science
A collaboration between the Art League of Rhode Island and WHOI scientists transforms abstract concepts into engaging perspectives on our ocean world.
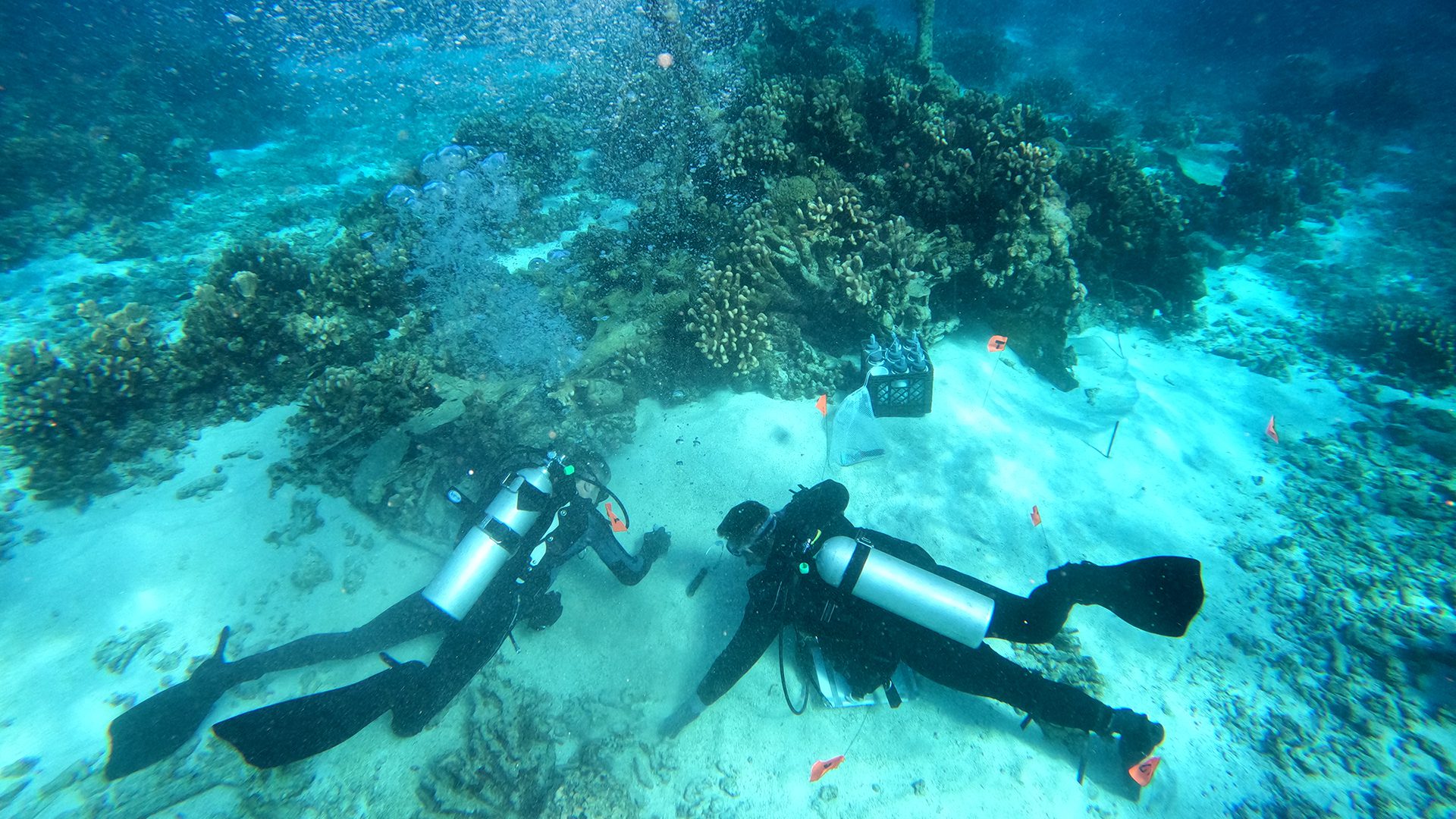
Read MoreWHOI campaign sheds light on new strategies and solutions for the coral reef crisis
In advance of World Ocean Day on June 8, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is launching its Give Reefs a Chance campaign, aimed at raising awareness of what WHOI scientists and engineers are doing to tackle the corals crisis, the importance of coral reefs, and what we can all do to give reefs a chance to survive.
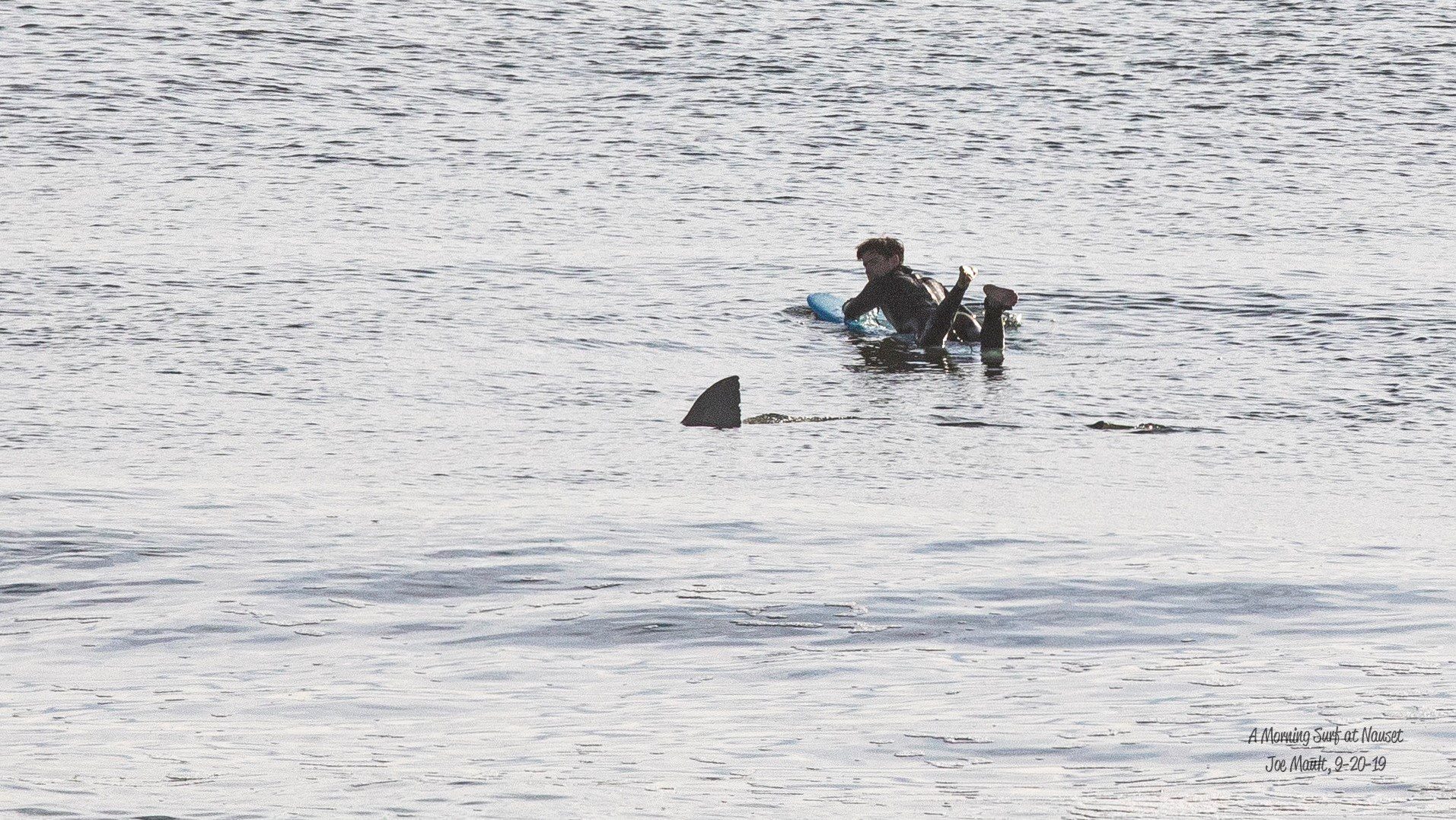
Read MorePartly cloudy with a chance of sharks
Researchers develop ‘heat map’ shark forecast system to improve beachgoer safety
Read MoreCan environmental DNA help us find lost US service members?
Ocean scientists explore how eDNA may be able to help find and identify lost military personnel in the ocean
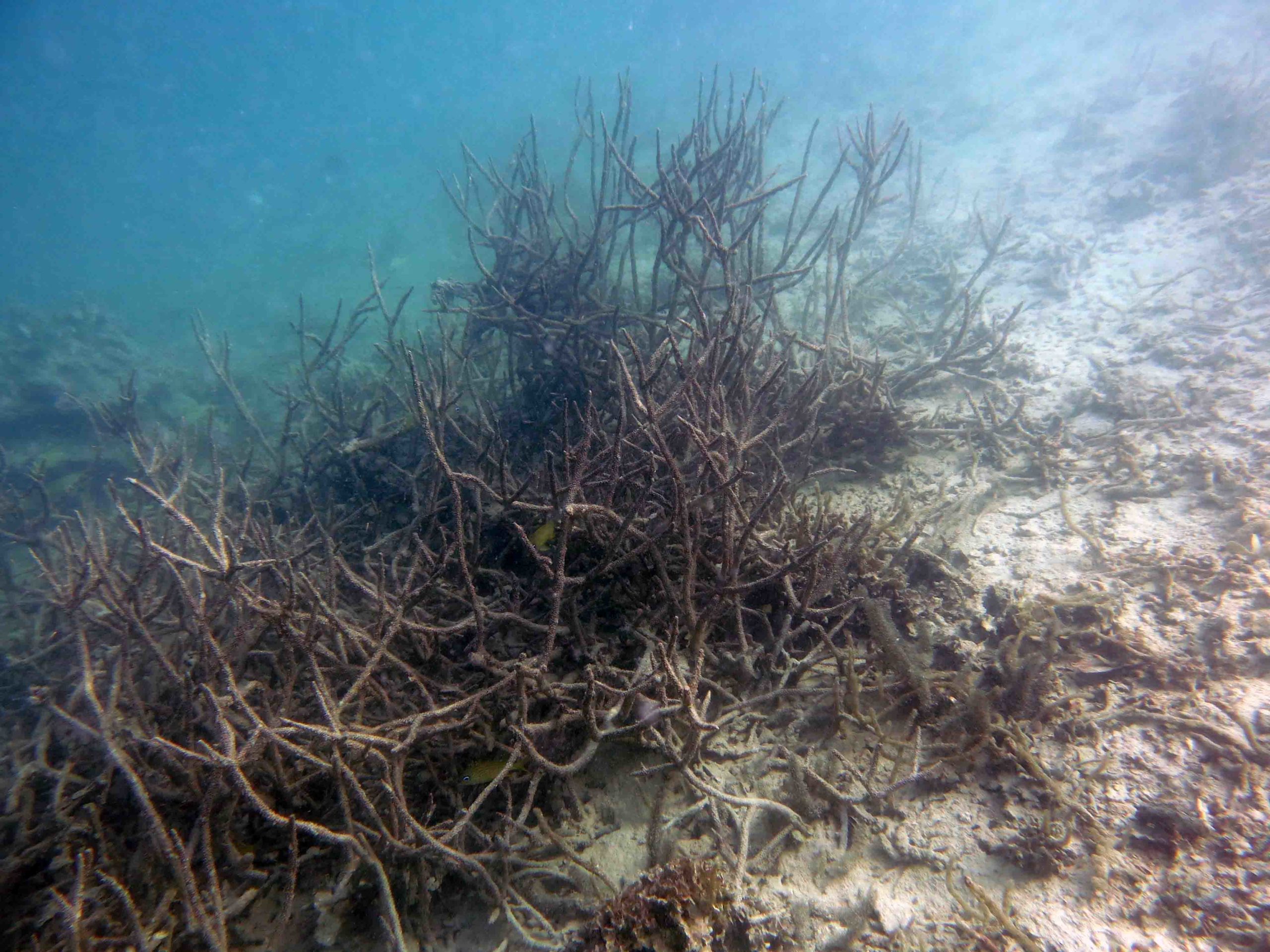
Read MoreThe hypoxic reef
Scientists say a lack of oxygen might be stressing tropical reefs even more than warming temperatures, acidification, and pollution. But the combination of these factors spells disaster for coral.
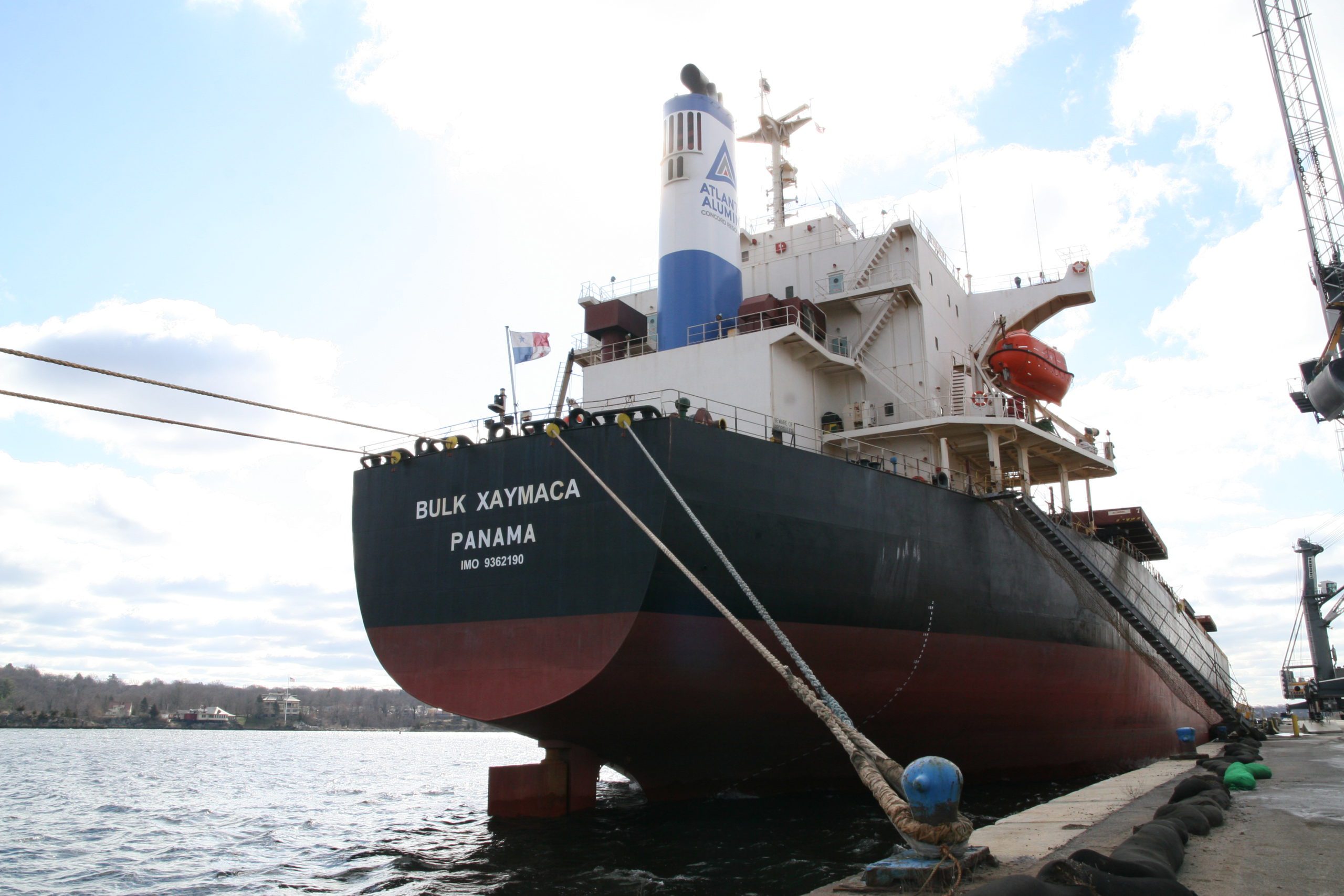
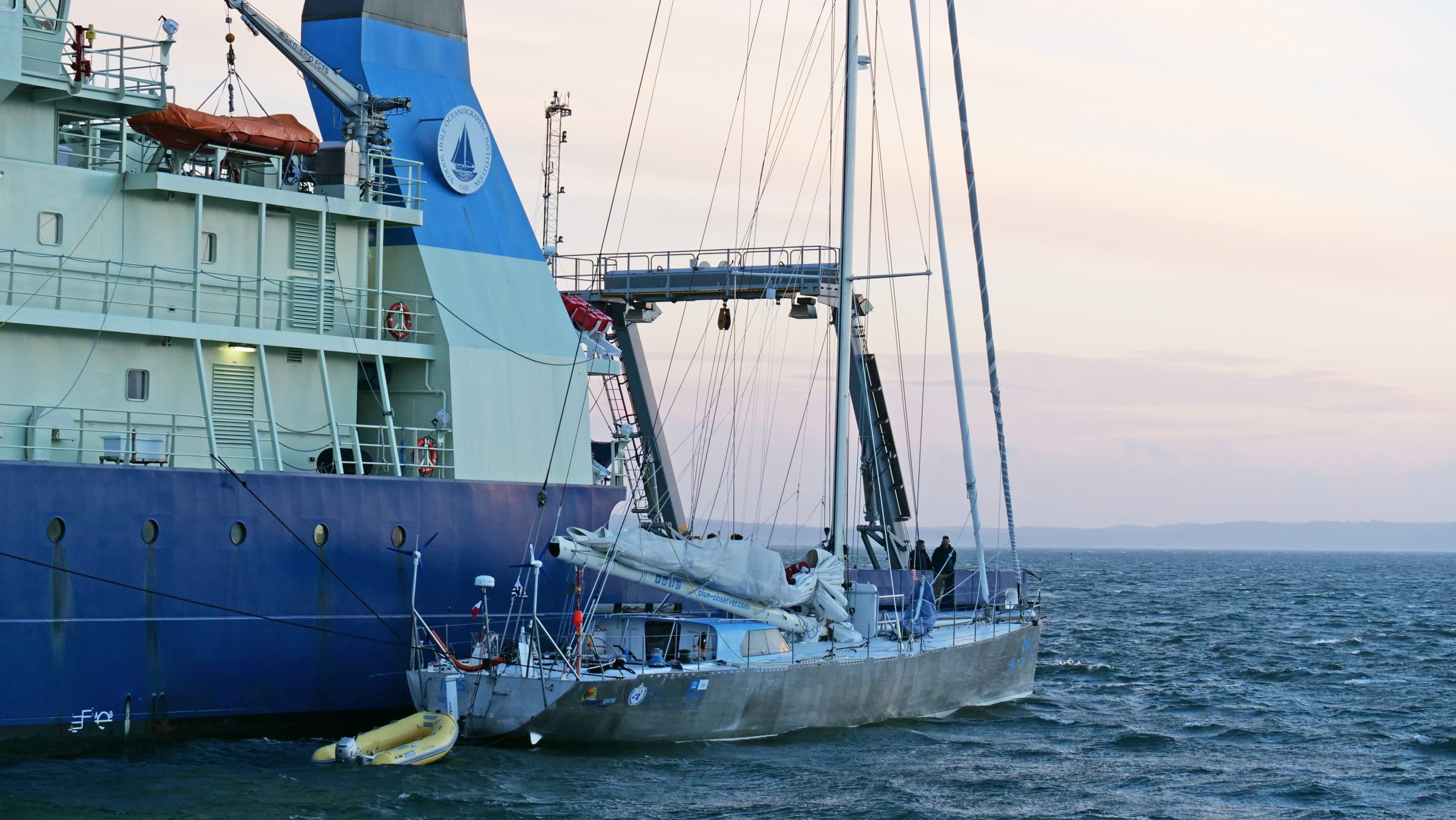
Read MoreWHOI & Pangaea Logistics Solutions to advance ocean science data acquisition through Science RoCS program
WHOI and Pangaea Logistics Solutions (Pangaea), a U.S. based, international maritime and logistics transportation company, today announced the launch of a new science program aboard Pangaea’s fleet of ships. Science RoCS (Science Research on Commercial Ships) is an innovative program pairing scientists with commercial vessels to regularly monitor the vast and open ocean, particularly along repeat routes in hard-to-reach areas where critical gaps in monitoring exist.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution and collaborators launch world’s largest kelp map
To further investigate and track kelp growth and survival over time, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, The Nature Conservancy, University of California Los Angeles, and the University of California Santa Barbara have launched the world’s largest map of kelp forest canopies extending from Baja California, Mexico to the Oregon-Washington border.
Read MoreWHOI-led team awarded $7.6M to support Gulf of Mexico Loop Current research
A Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution-led research team has been awarded $7.6 million from the Gulf Research Program (GRP) of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM).
Read MoreOCIA: Accelerating the pace of ocean-climate research
The first five projects funded by the Ocean Climate Innovation Accelerator (OCIA) are set to advance research at the intersection of oceans and climate.
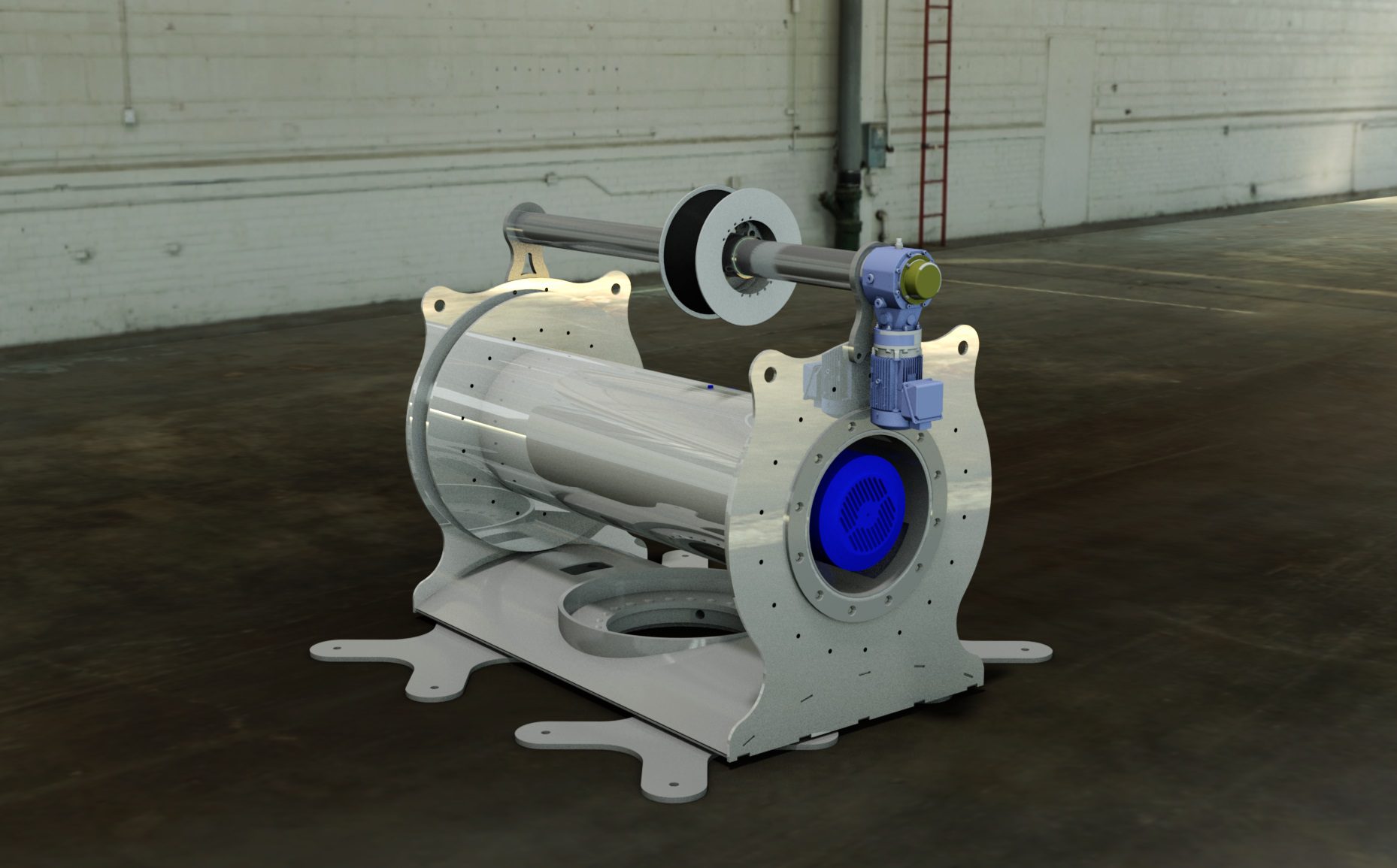
Read MoreWHOI engineers invent adjustable, compact marine winch, offering flexibility and improved vessel operations
Engineers with the UNOLS East Coast Winch Pool, at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), spent a decade working on a product that offers a lightweight, compact winch model, designed specifically to make for an easier and more efficient experience for crews onboard vessels.
Read MoreWith worsening storms, can the Outer Banks protect its shoreline?
The double-whammy of more intense storms and a COVID-era real estate boom has scientists and planners focused on resiliency
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution-led study explores effects of noise on marine life
New research shows turtles can experience temporary hearing loss from an excess of underwater noise. This high volume of sound, referred to as underwater noise pollution, can be caused by passing ships and offshore construction. These preliminary findings were part of a Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution-led study that is being presented at the 2022 Ocean Sciences Meeting..
Read MoreResilient Woods Hole releases new, interactive tools to prepare for climate change
ResilientWoodsHole (RWH) initiative releases new interactive website tools to further engage the local community in its collective goal of securing a climate-resilient future for the coastal village of Woods Hole
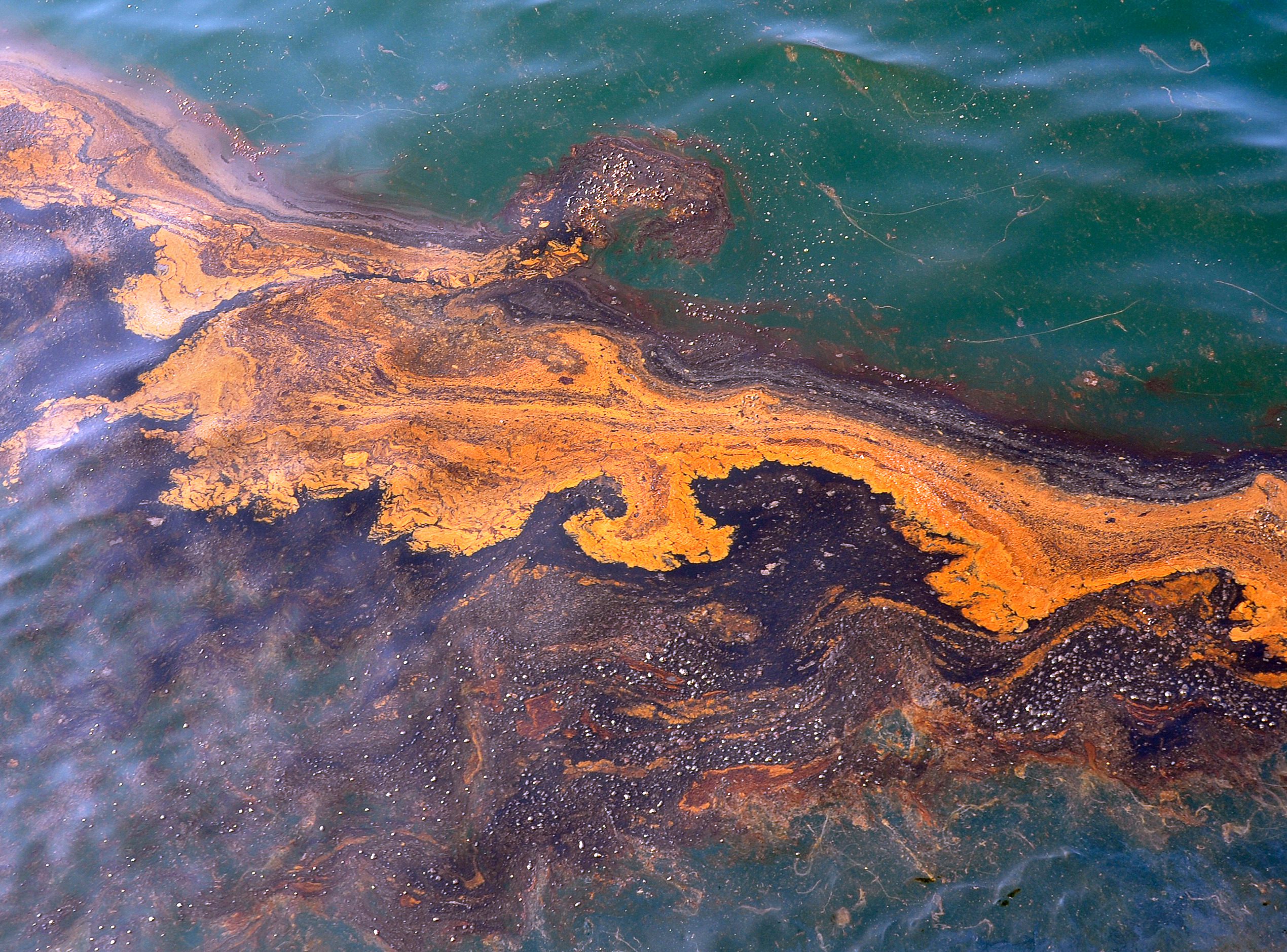
Read MoreDissolving oil in a sunlit sea
A team of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) researchers discovered that nearly 10 percent of the oil floating on the Gulf after the Deepwater Horizon disaster was dissolved into seawater by sunlight – a process called “photo-dissolution”. The findings were published today in the paper “Sunlight-driven dissolution is a major fate of oil at sea” in Science Advances.
Read MoreThe ocean twilight zone’s role in climate change
A new report from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Ocean Twilight Zone (OTZ) project team offers a detailed look at the climate-altering processes that take place within the zone, in particular those that are driven by animals that migrate between the twilight zone and the surface each night to feed. This phenomenon is likely the biggest migration on Earth—yet it remains incredibly vulnerable to human exploitation.
Read MoreSniffing out methane in the deep sea
Scientists cruise the Gulf of California’s Guaymas Basin to test out new tech for detecting and measuring methane in the deep
Read MoreWHOI shares details on microplastic detection project
A project led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Chemical Sensors Lab is moving researchers closer to an in-field microplastics sensor that measures the amount of plastic particles in water.
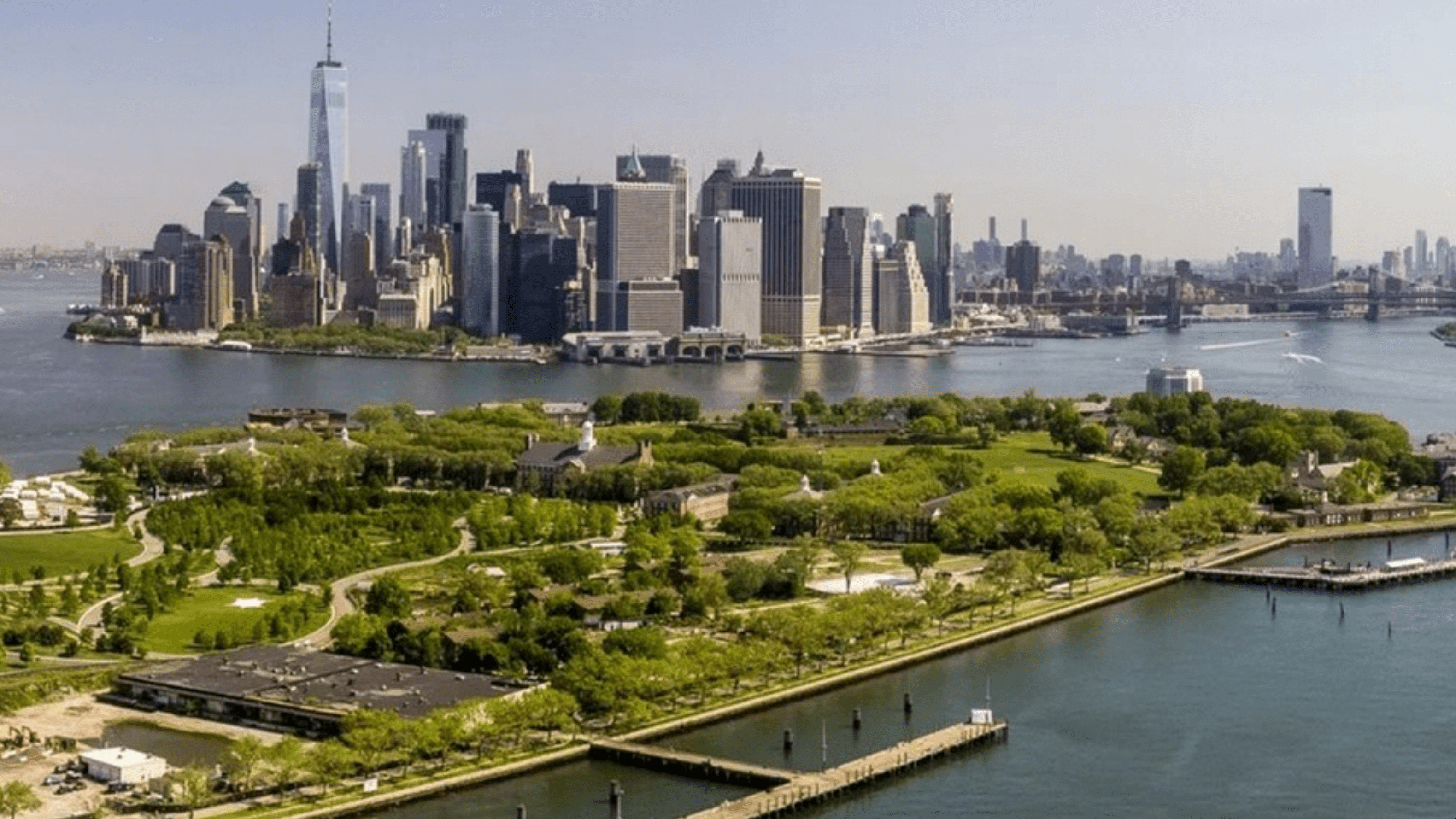
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution selected as finalist for Governors Island Climate Solutions Center
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI, a global leader in ocean research and exploration, is partnering with two teams selected as finalists in the development of the new Governors Island Climate Solutions Center in New York City. The announcement was recently made by former New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio and The Trust for Governors Island.
Read MoreNew ocean floats to boost global network essential for weather, climate research
WHOI and partners join together to launch approximately 100 new Argo floats across the Atlantic Ocean to collect data that supports ocean, weather and climate research and prediction
Read MoreHow to speak “Ocean”
Major communications initiative aims to bridge gaps in ocean literacy and awareness
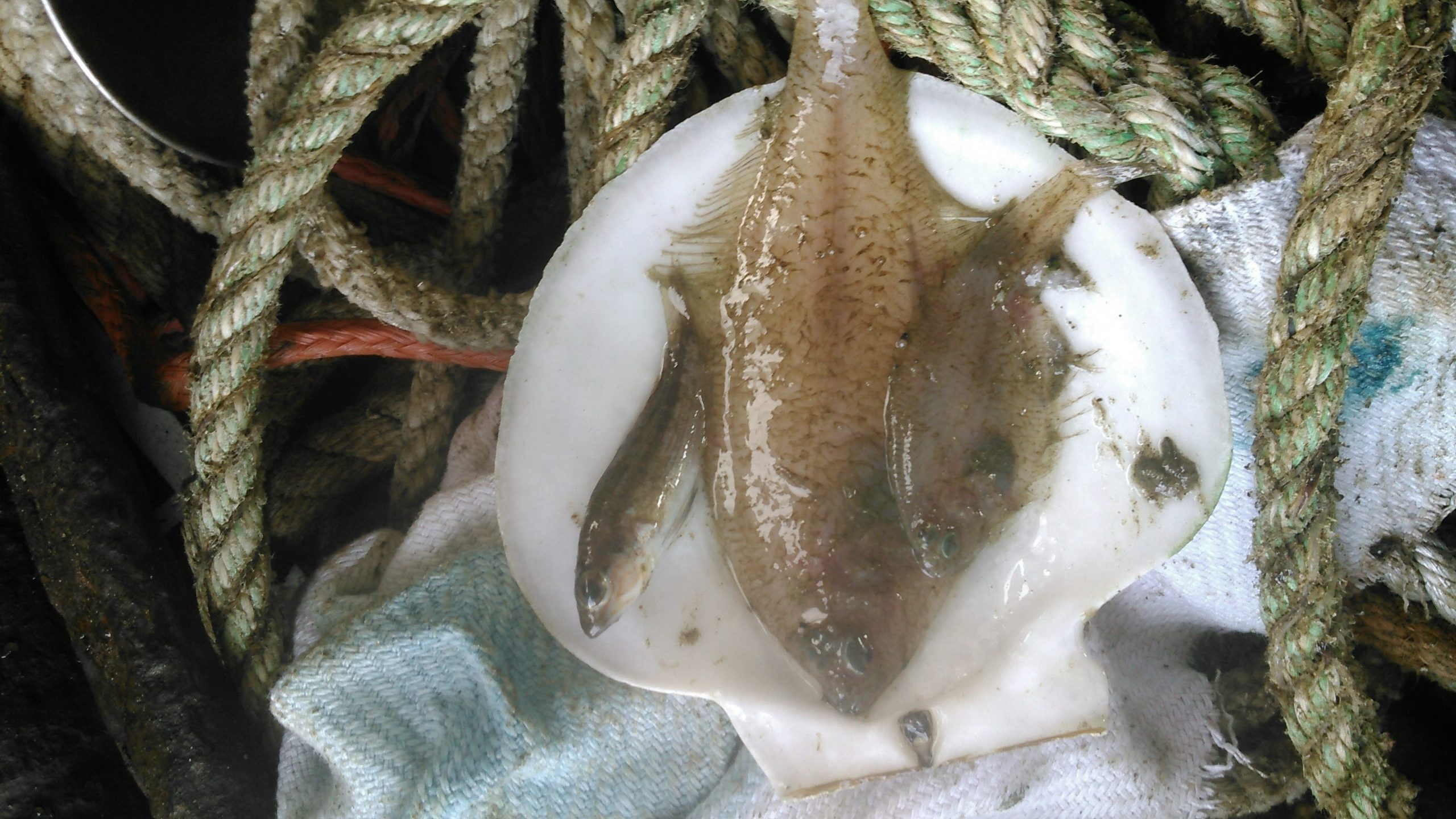
Read MoreTropical fish…up north? How ocean physics play a role in altering water temperature and salinity
A study led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution scientists is explaining why warm and salty water along with warm water fish species, such as the deep-sea dwelling Gulf Stream flounder and Black Sea bass, were found far inshore in New England in the middle of winter 2017. How did this happen? Researchers say it is due to an intrusion of offshore water from the open ocean onto the Northeast U.S. Shelf, caused by eddies (a circular current of water) and wind.
Read More