Featured Project
How historic hurricanes can help predict storm intensity
Research into past hurricanes could help predict the strength of future storms, and inform infrastructure planning and emergency management decisions in southern New England
Read MoreUnderwater robot offers new insight into mid-ocean “twilight zone”
Woods Hole, MA (June 16, 2021) — An innovative underwater robot known as Mesobot is providing researchers with deeper insight into the vast mid-ocean region known as the “twilight zone.”…
Read MoreIcebergs drifting from Canada to Southern Florida
A newly developed iceberg computer model helped the researchers understand the timing and circulation of meltwater and icebergs through the global oceans during glacial periods, which is crucial for deciphering how past changes in high-latitude freshwater forcing influenced shifts in climate.
Read MorePapers Explore Massive Plankton Blooms with Very Different Ecosystem Impacts
Two papers explore the distribution and abundance of plankton and what conditions lead to big plankton blooms with vastly different potential impacts on the ecosystem.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution Wants Everyone to “Keep it Weird”
Campaign raises awareness of the ocean twilight zone by celebrating the “weird” in all of us Woods Hole, Mass. (May 27, 2021) — Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) wants to…
Read MoreSome Forams Could Thrive with Climate Change, Metabolism Study Finds
Oceanic deoxygenation is increasingly affecting marine ecosystems. A new paper that examines two foram species found that they demonstrated great metabolic versatility to flourish in hypoxic and anoxic sediments where there is little or no dissolved oxygen, inferring that the forams’ contribution to the marine ecosystem will increase with the expansion of oxygen-depleted habitats.
Read MoreFive things to know about NOAA’s 2021 Tech Demo
Researchers prepare WHOI’s autonomous underwater vehicle, Orpheus for its first deep dive of 2021Tech Demo.
Read MoreA new ocean soundscape
Combining his passions for marine chemistry and music, an MIT-WHOI Joint Program student converts data into songs that reveal the chemical nuances of the ocean.
Read MoreStudy Finds 6⁰C Cooling on Land during the Last Ice Age, With Implications about Future Global Warming
A recent report shows that prior studies have underestimated the cooling in the last glacial period, which has low-balled estimates of the Earth’s climate sensitivity to greenhouse gases. The rather high climate sensitivity is not good news regarding future global warming, which may be stronger than expected using previous best estimates.
Read MoreRemote Learning Takes on New Meaning with the Launch of Dive and Discover ™ Expedition 17
Dive and Discover Expedition 17 will look more closely at the middle of the ocean, also known as the mesopelagic or the ocean’s twilight zone.
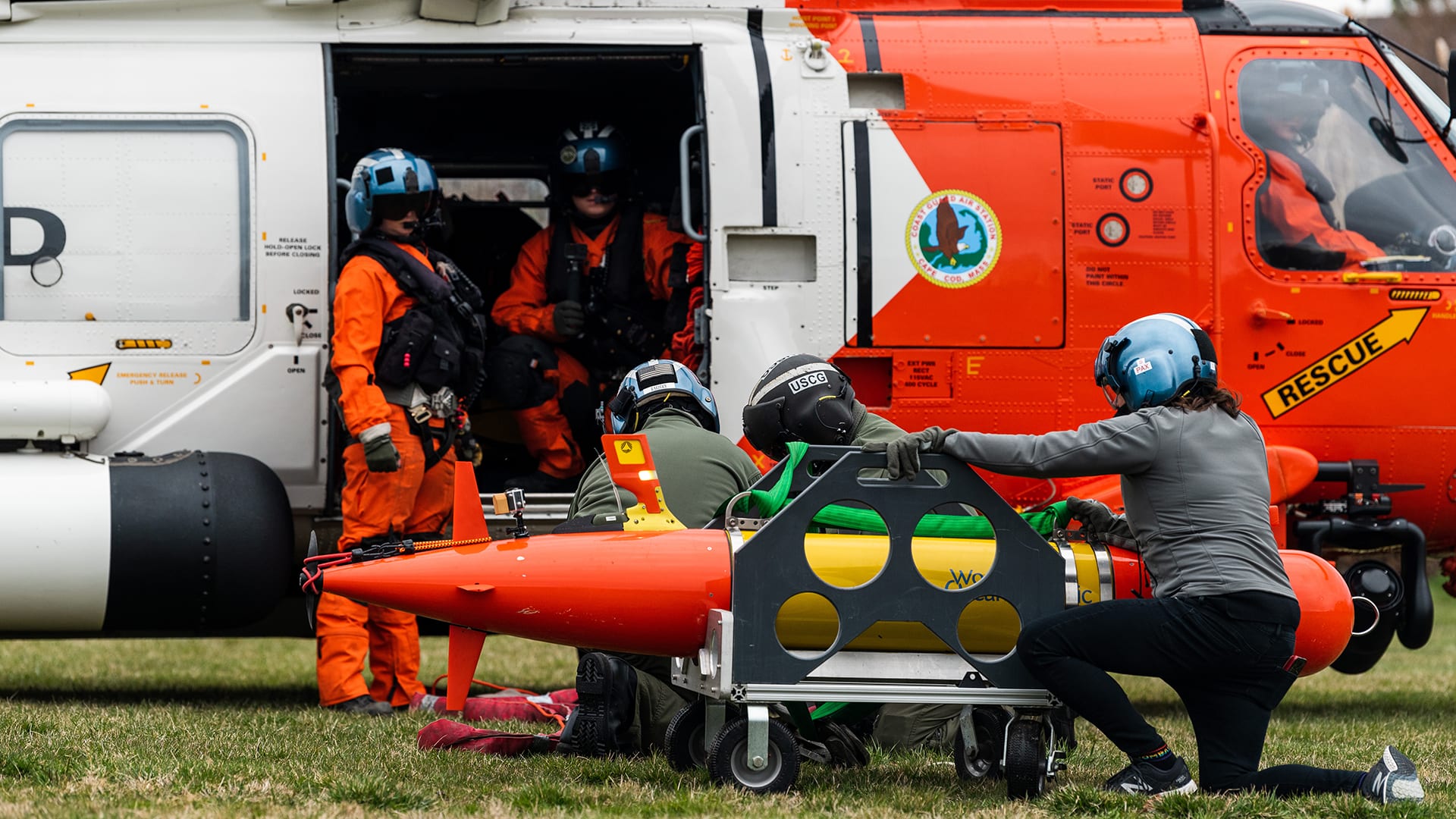
Read MoreOil spill response beneath the ice
Successful test deployment of WHOI vehicle Polaris expands U.S. Coast Guard response to oil spills in the Arctic
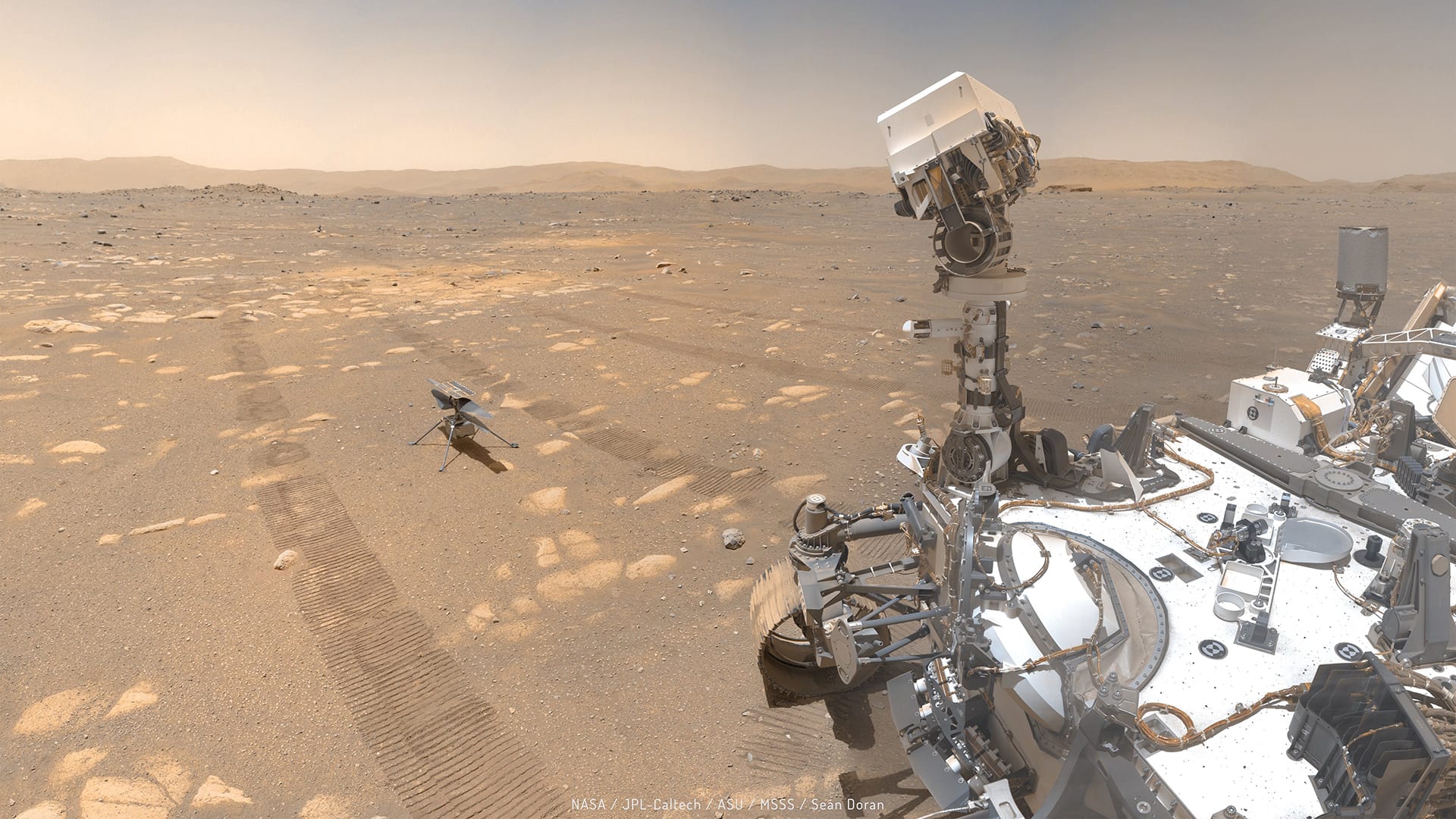
Read MoreFrom Mars to the deep
Navigation technology that helped NASA’s Perseverance rover land safely on Mars could guide robots in another unexplored terrain that’s much closer to home: the deepest trenches of the ocean.
Read MorePlate Tectonics Fuels a Vast Underground Ecosystem
The subsurface is among Earth’s largest biomes, but the extent to which microbial communities vary across tectonic plate boundaries or interact with subduction-scale geological processes remains unknown. In a recently published study, scientists compare bacterial community composition with deep-subsurface geochemistry from 21 hot springs across the Costa Rican convergent margin.
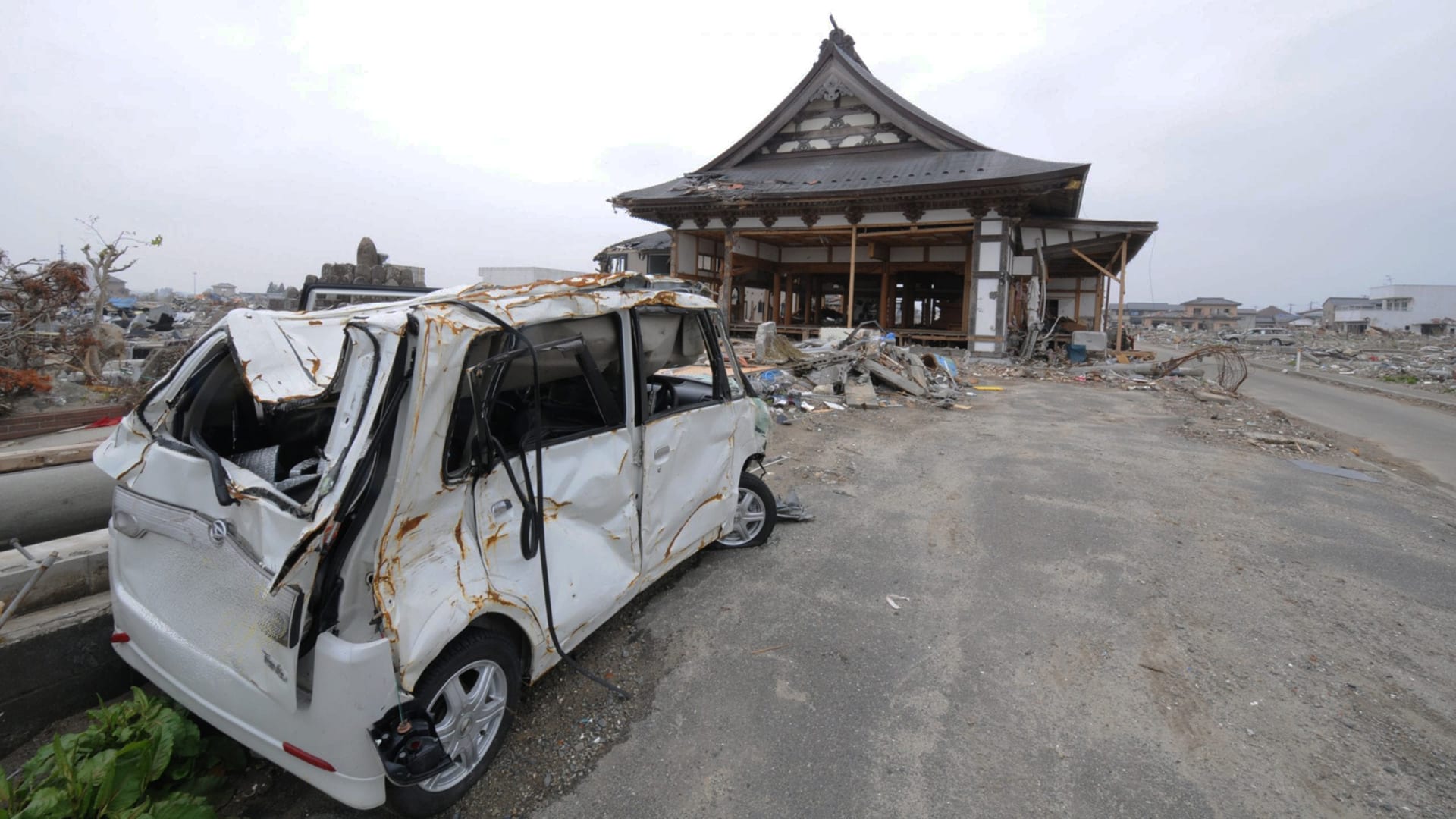
Read MoreFukushima and the Ocean: A decade of disaster response
One decade since explosions rocked Japan’s Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant, researchers look back at how the ocean was impacted by the radioactivity fallout from the event, and discuss how the situation continues to evolve.
Read MoreClimate Change Can Destabilize the Global Soil Carbon Reservoir, New Study Finds
The vast reservoir of carbon that is stored in soils probably is more sensitive to destabilization from climate change than has previously been assumed, according to a new study by…
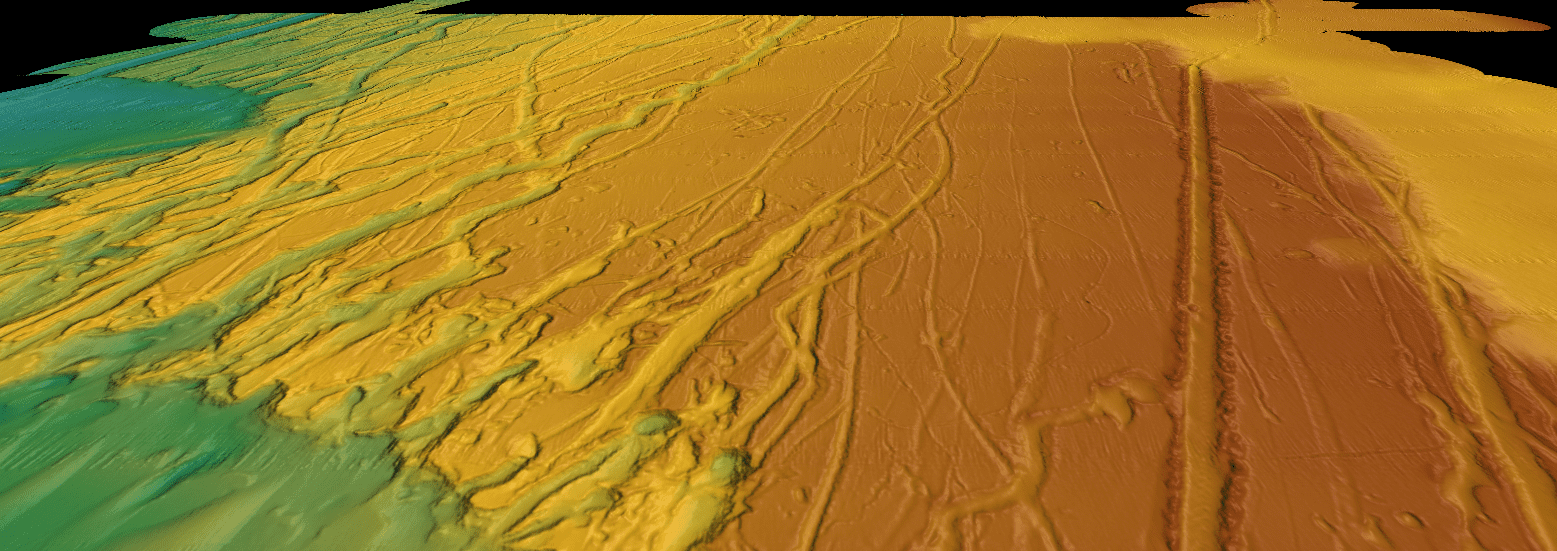
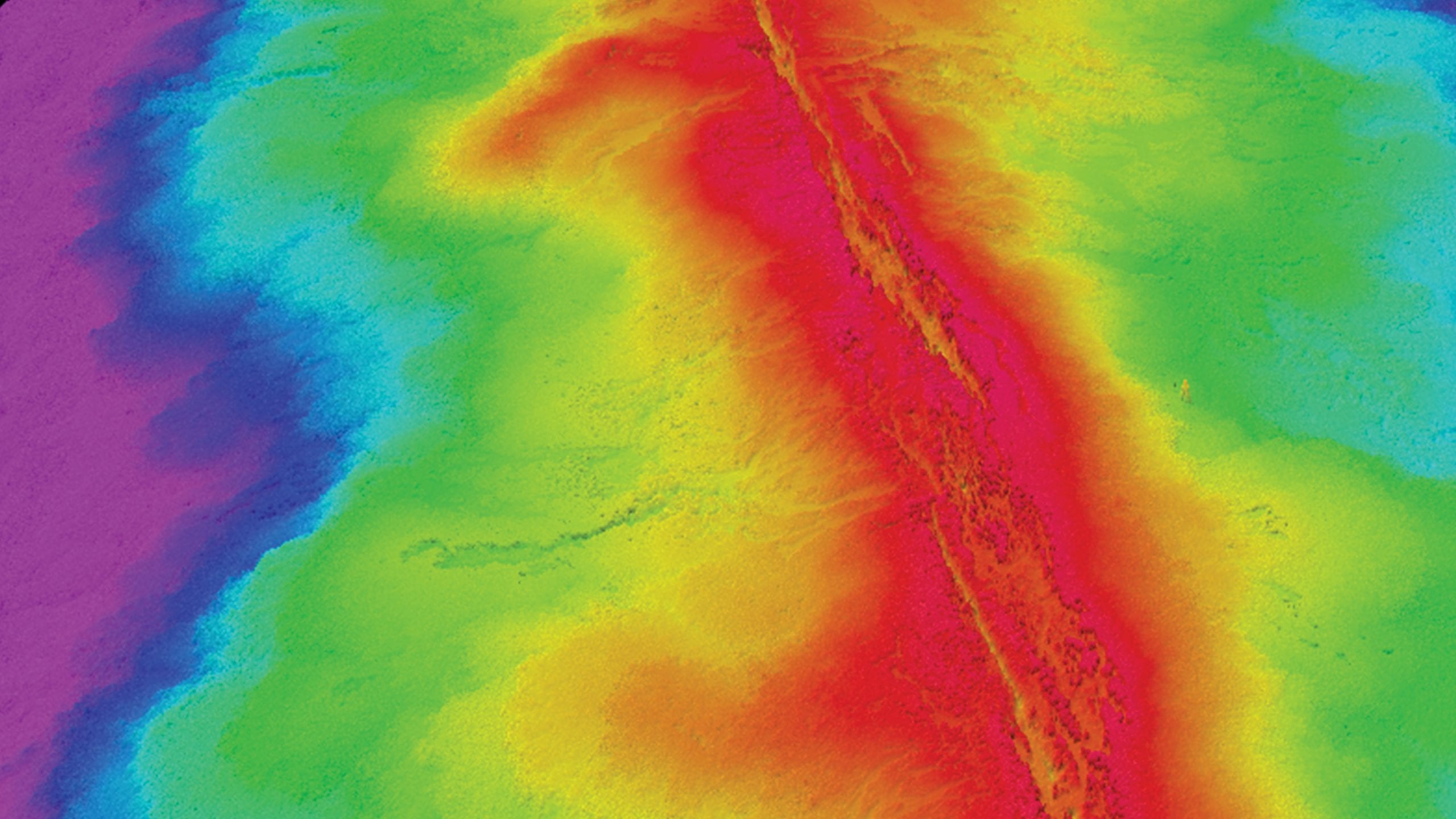
Read MoreRacing an undersea volcano
Using AUV Sentry to make a high-resolution, near-bottom, seafloor map before the next volcanic eruption at the East Pacific Rise
Read MoreAmidst pandemic, researchers deploy new monitoring station in tropical Pacific
After two attempts in 2020 to replace a monitoring station of the coast of Chile, WHOI researchers and colleagues successfully deployed the moored system despite pandemic-related challenges. This extends a 20-year ongoing presence of a monitoring buoy in this otherwise data-sparse area of the Pacific.
Read MoreMicrobial Methane – New Fuel for Ocean Robots?
Researchers are developing on an energy harvesting platform that converts marine methane to electricity. The system could be an answer to power-hungry robots that are being asked to explore increasingly larger swaths of the ocean.
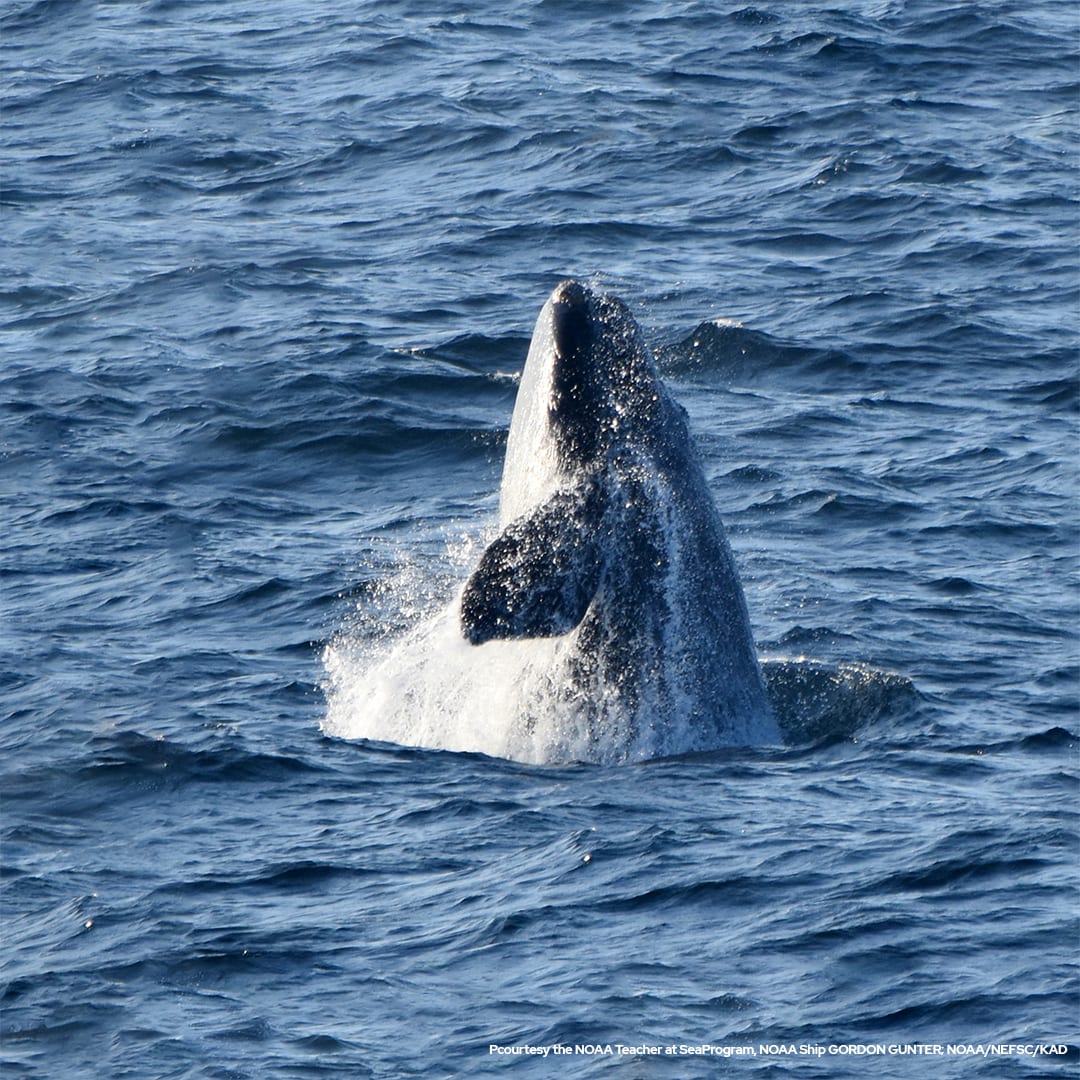
Read MoreWHOI and NOAA Fisheries Release New North Atlantic Right Whale Health Assessment Review
North Atlantic right whales are critically endangered and declining. Climate change, vessel strikes, entanglements and noise engender poor health and reproductive failure, and are major threats to individuals and the species. Trauma reduction measures and applying new tools to assess and enhance their health, are critically important.
Read MoreTracking change in the Arctic Ocean
Changes in the Arctic Ocean are becoming clearer, thanks to an ocean monitoring network maintained by WHOI researchers in the Beaufort Gyre since 2003.
Read MoreThe Search for Life
WHOI researchers featured in episode of news program Full Measure February 17, 2021 This week, NASA’s Perseverance Rover lands on Mars to continue the search for life on the Red…
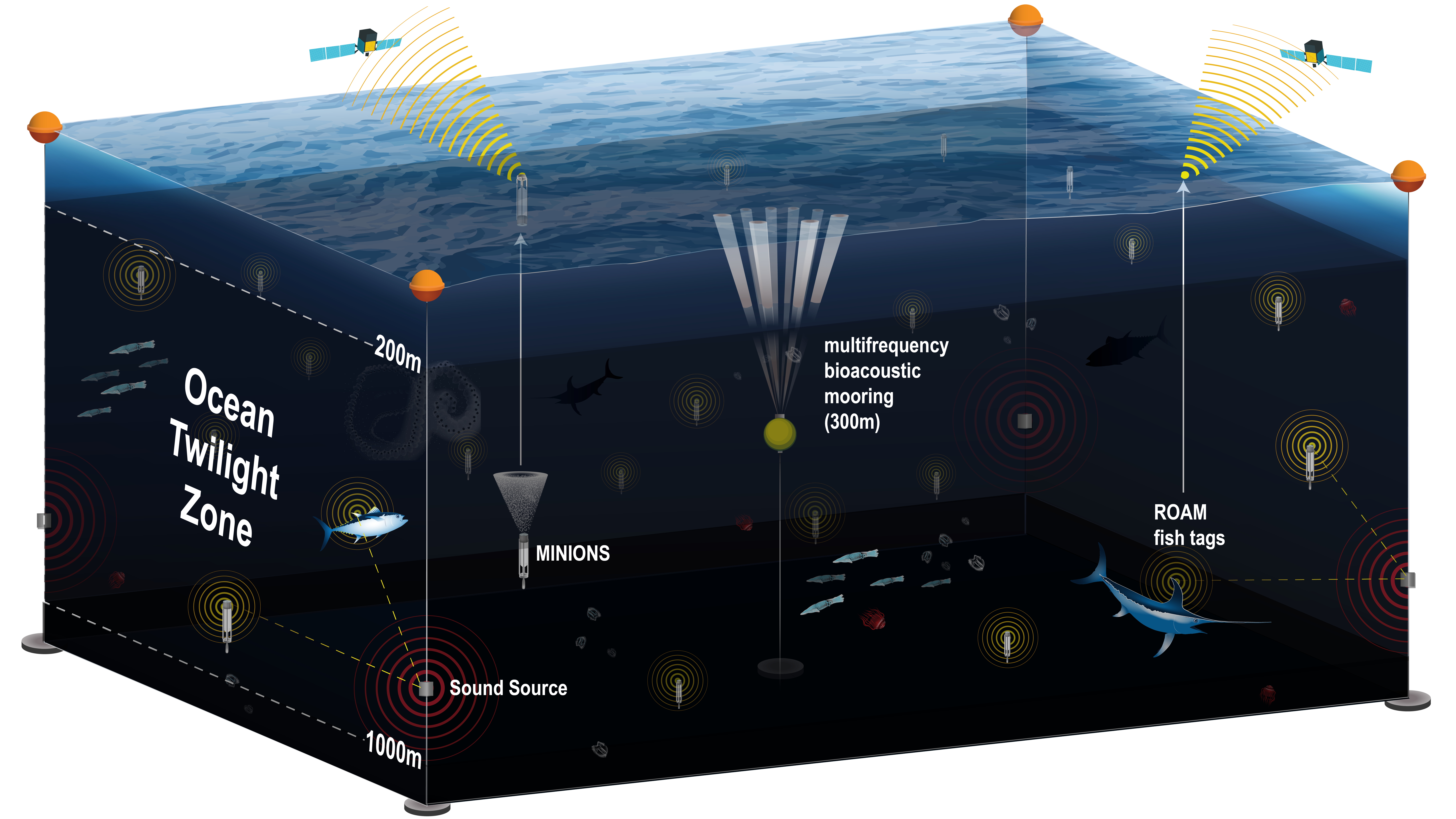
Read MoreNew observation network will provide unprecedented, long-term view of life in the ocean twilight zone
A new observation network under development by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will offer round-the-clock data about the ocean twilight zone – a dimly lit region roughly 200–1000 meters (650–3200 feet) below the surface, containing the largest amount of fish biomass on Earth.
Read MoreSmart cameras keep lookout for endangered whales
A ship-mounted thermal imaging system provides real-time detection of whales, which could reduce the number of endangered marine mammals killed by vessels each year.
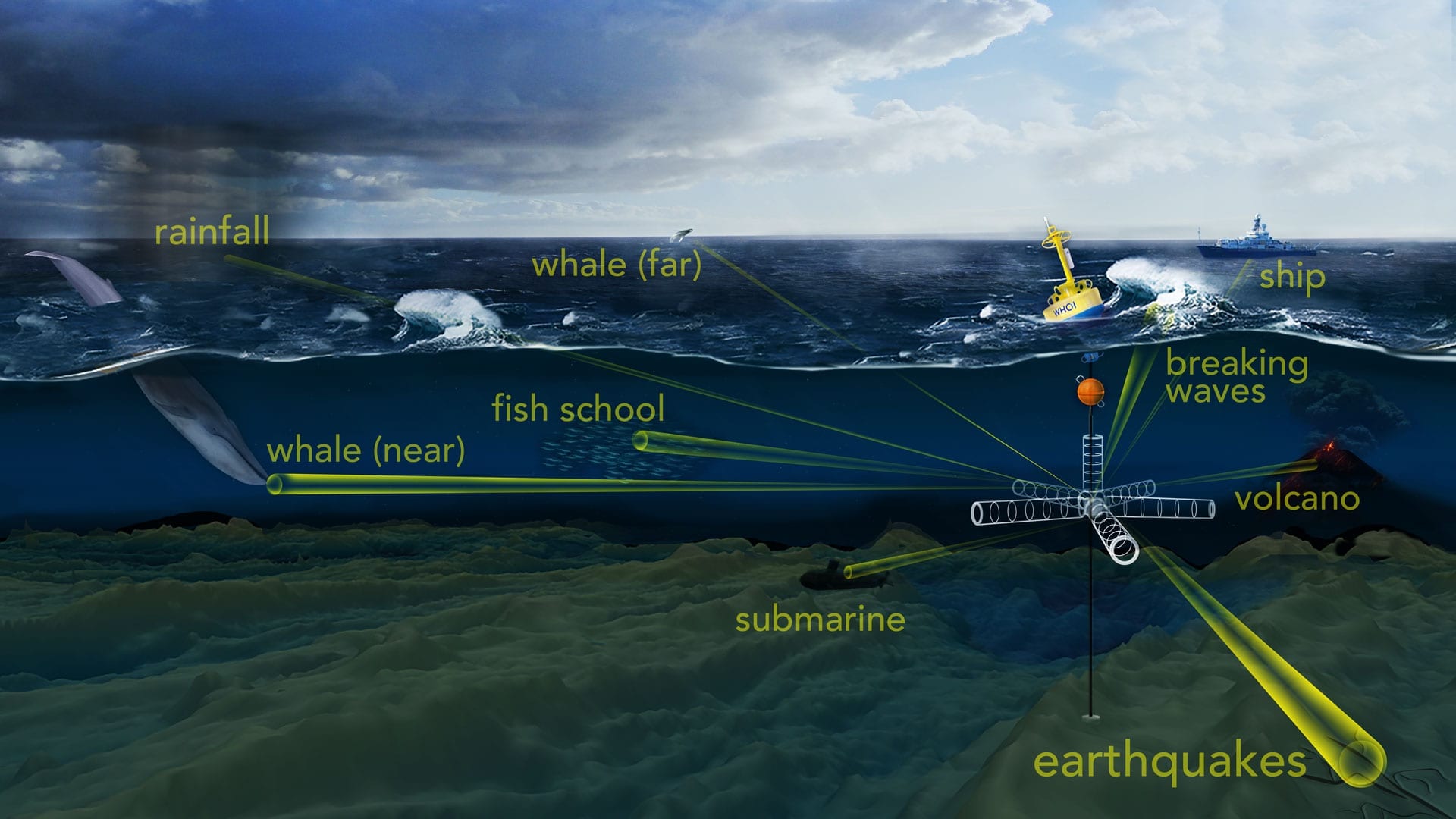
Read MoreCould listening to the deep sea help save it?
A recent New York Times article about sound in the deep ocean briefly mentions the work by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) acoustic scientist Ying-Tsong “YT” Lin and his work developing an “acoustic telescope.”
Read More