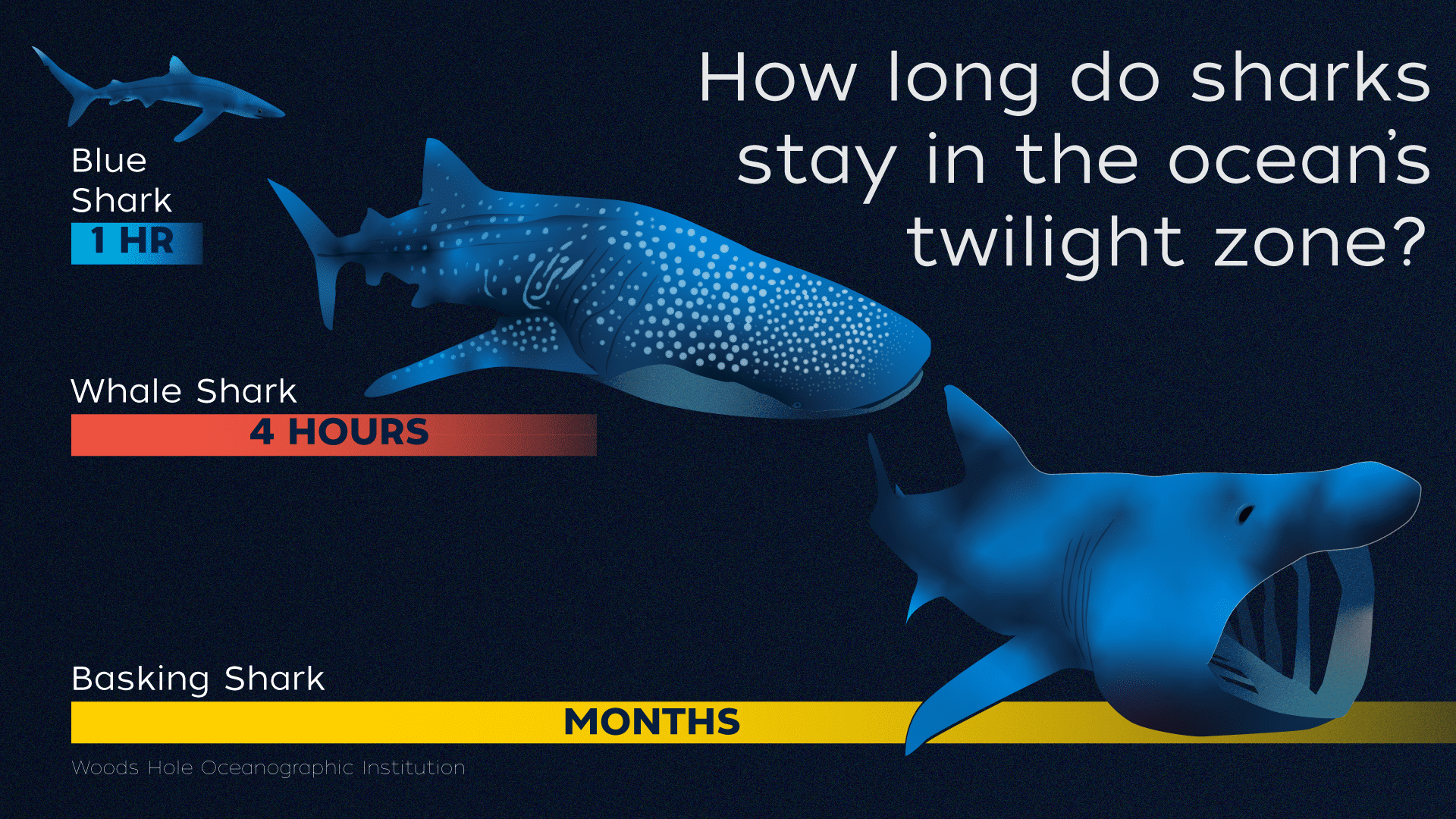News Releases
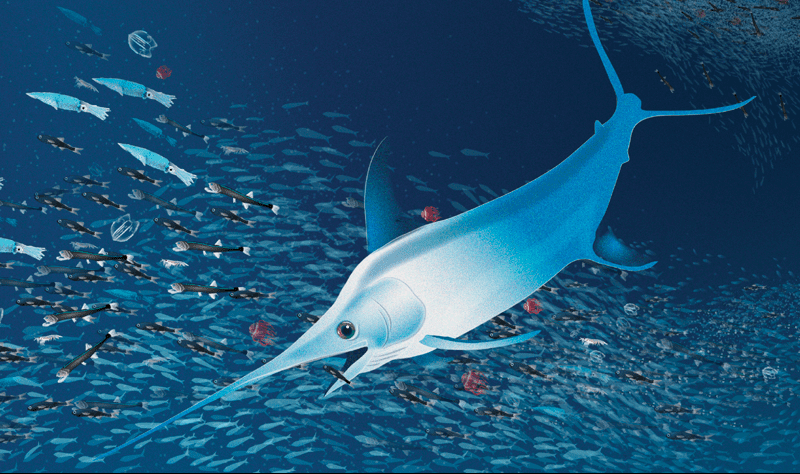
The ocean twilight zone’s role in climate change
A new report from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Ocean Twilight Zone (OTZ) project team offers a detailed look at the climate-altering processes that take place within the zone, in particular those that are driven by animals that migrate between the twilight zone and the surface each night to feed. This phenomenon is likely the biggest migration on Earth—yet it remains incredibly vulnerable to human exploitation.
Read MoreEnvironmental DNA is a reliable way to learn about migration from the twilight zone
Woods Hole, MA — The mid-ocean “twilight zone” holds the key to several tantalizing questions about the marine food web and carbon-sequestering capacity of the ocean. But studying this vast…
Read MoreShark Week 2021: Sharks and the Ocean’s Twilight Zone
How large marine predators use the twilight zone to thrive, and survive Woods Hole, MA (July 11, 2021) — Sharks are some of the largest fish in the ocean, known…
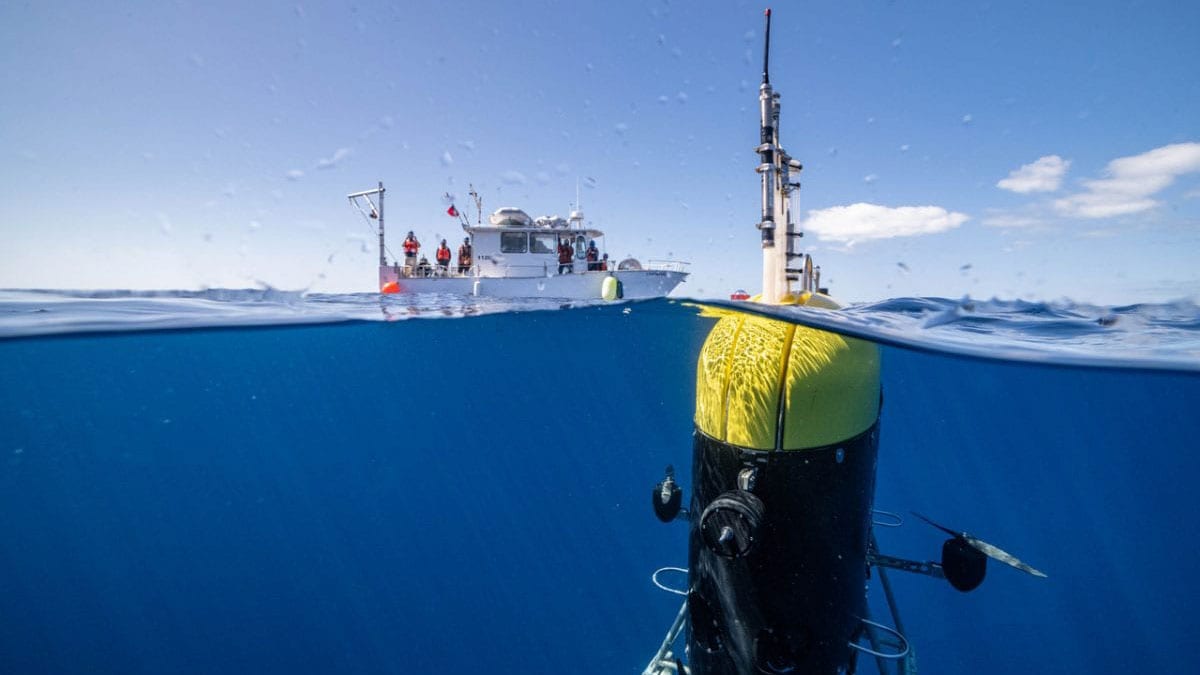
Read MoreUnderwater robot offers new insight into mid-ocean “twilight zone”
Woods Hole, MA (June 16, 2021) — An innovative underwater robot known as Mesobot is providing researchers with deeper insight into the vast mid-ocean region known as the “twilight zone.”…
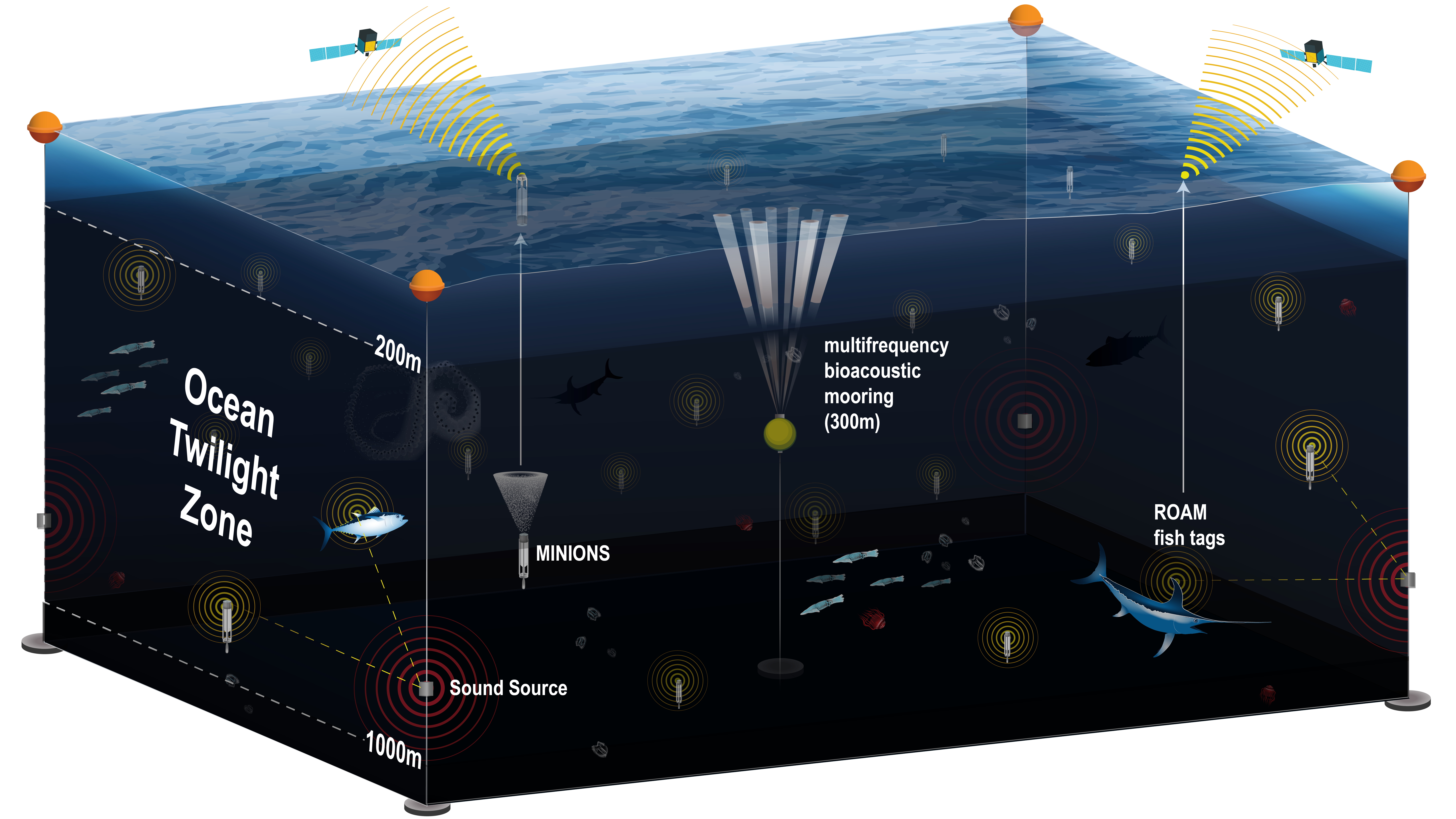
Read MoreNew observation network will provide unprecedented, long-term view of life in the ocean twilight zone
A new observation network under development by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will offer round-the-clock data about the ocean twilight zone – a dimly lit region roughly 200–1000 meters (650–3200 feet) below the surface, containing the largest amount of fish biomass on Earth.
Read MoreReport reveals ‘unseen’ human benefits from ocean twilight zone
A new report from researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) reveals for the first time the unseen—and somewhat surprising—benefits that people receive from the ocean’s twilight zone. Also known as the “mesopelagic,” this is the ocean layer just beyond the sunlit surface.
Read MoreOcean’s “Twilight Zone” Plays Important Role in Climate Change
A major study has shed new light on the dim layer of the ocean called the “twilight zone”where mysterious processes affect the ocean’s ability to absorb and store carbon dioxide…
Read MoreVERTIGO: Carbon Cycling in the Twilight Zone
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists and their international colleagues will be at sea off Hawaii in June trying to learn more about the ocean’s ability to store atmospheric carbon…
Read MoreNew Technologies Revise Scientists’ Understanding of the Oxygen Minimum Zone
A new technology detects trace amounts of oxygen in an environment where previously these life-supporting molecules were below the limit of detection.
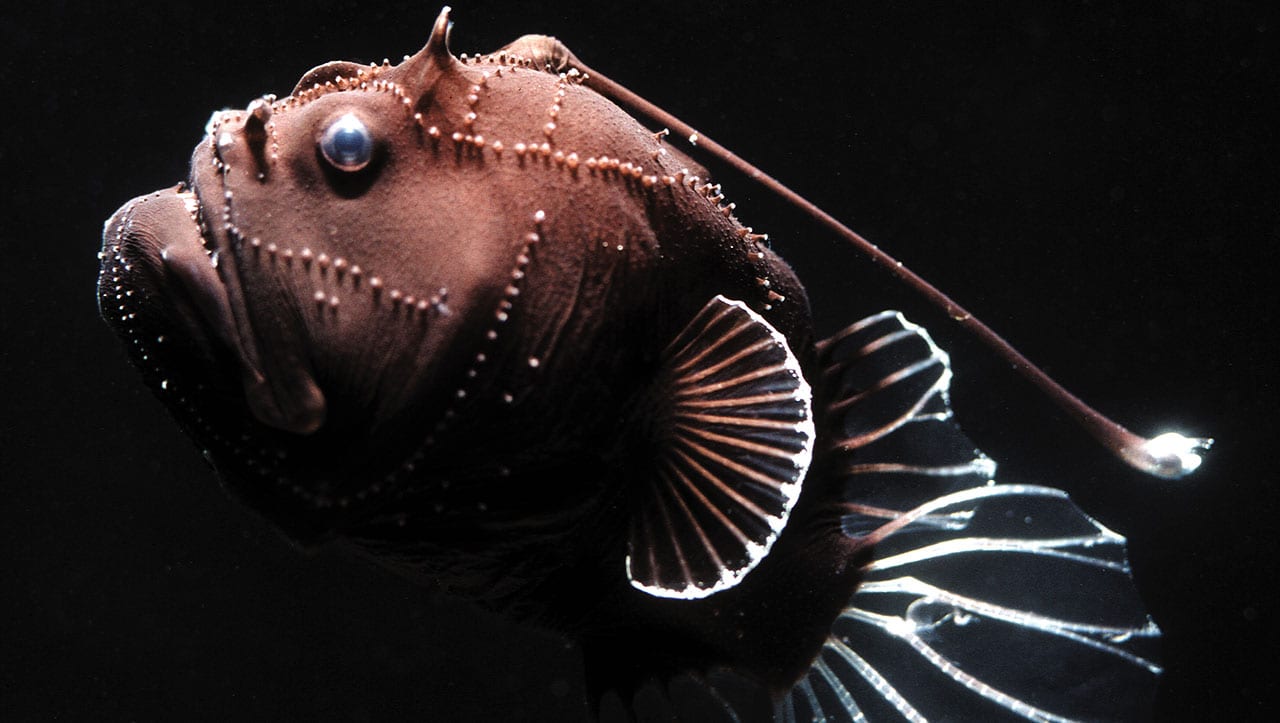
Read MoreNew Study Sheds Light on Why Some Animals Dive to The Dark, Deep Sea
Data from over 300 tags on large marine predators, along with shipboard sonar, point to the ecological importance of the ocean’s twilight zone
Read MoreWHOI’s first children’s book “Where the Weird Things Are” now available
By Zoleka Filander and llustrated by Patricia Hooning
Where the Weird Things Are is the first children’s book from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and is inspired by the groundbreaking work of the Ocean Twilight Zone (OTZ) project, and Mesobot, an innovative hybrid robot designed specifically to study life in the ocean twilight zone.
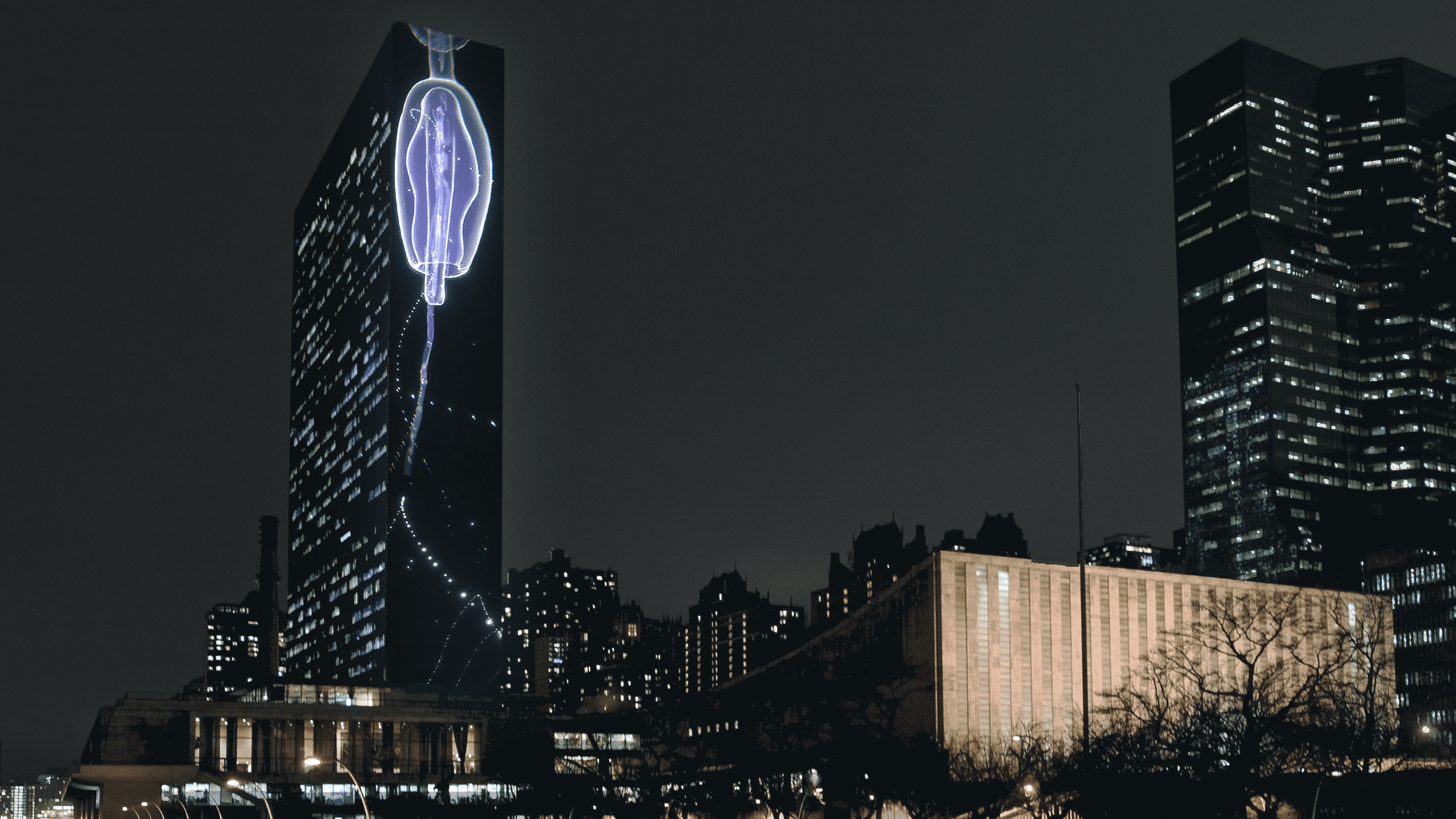
WHOI collaborates to bring video installation to United Nation Headquarters
Vertical Migration by artist group SUPERFLEX will be projected onto the facade of the United Nations’ 505-foot tower in New York, on 21-24 September 2021, coinciding with the 76th General Assembly and Climate Week NYC. The projection seeks to draw global attention to the critical role of the ocean in global climate, a primary focus of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Ocean Twilight Zone Project.
Read MoreRemote Learning Takes on New Meaning with the Launch of Dive and Discover ™ Expedition 17
Dive and Discover Expedition 17 will look more closely at the middle of the ocean, also known as the mesopelagic or the ocean’s twilight zone.
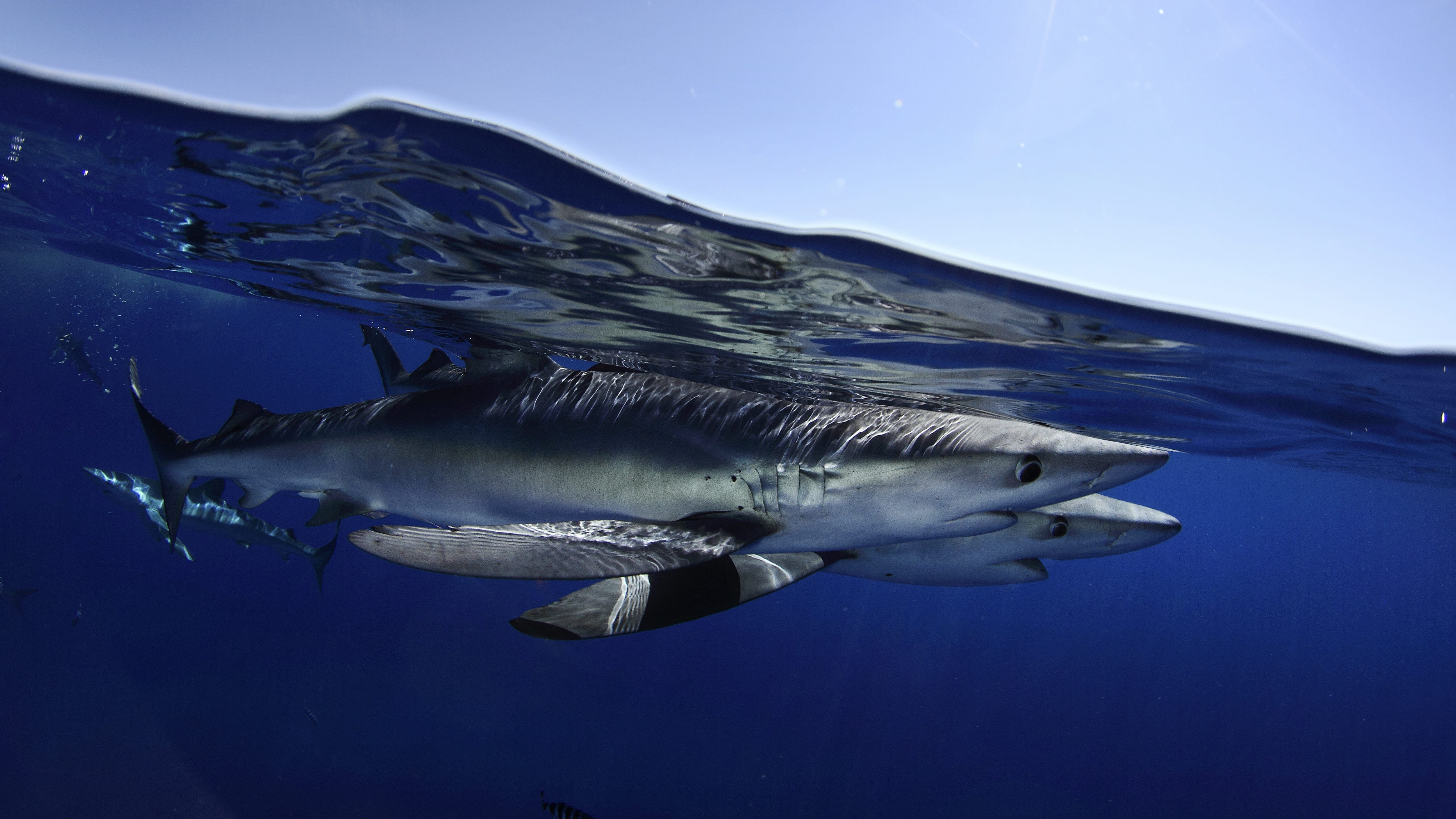
Read MoreBlue sharks use eddies for fast track to food
Blue sharks use large, swirling ocean currents, known as eddies, to fast-track their way down to feed in the ocean twilight zone—a layer of the ocean between 200 and 1000 meters deep containing the largest fish biomass on Earth, according to new research by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and the Applied Physics Lab at the University of Washington (UW).
Read MoreWHOI Among First Funding Recipients of The Audacious Project
What if we explored the ocean’s vast twilight zone, teeming with undiscovered life? Today, the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) was awarded $35 million – the largest philanthropic gift in the Institution’s history – to do just that. The award comes from The Audacious Project, a bold new philanthropic collaboration housed at TED to fund critical ideas that have potential to create massive, global change.
Read MoreSummer adventures await at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Discovery Center
New, interactive exhibits and fun learning experiences await visitors to Woods Hole, Mass.
Read MoreWHOI vehicles go to extreme sides of the globe
Simultaneous missions near Greenland and American Samoa support critical research about ocean life and sea level rise
Read MoreYawkey Foundation and WHOI present: Ocean & Climate Outreach Series
Looking for a fun, free, interactive way to learn more about the mysteries of the ocean? WHOI & the Yawkey Foundation present the 2024 Ocean and Climate Outreach Series.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution takes home four Communicator Awards
The Communicator Awards recognizes organizations committed to excellence, effectiveness, and innovation across all areas of communication.
Read MoreHow marine predators find food hot spots in open ocean “deserts”
A new study led by scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and University of Washington Applied Physics Laboratory (UW APL) finds that marine predators, such as tunas, billfishes and sharks, aggregate in anticyclonic, clockwise-rotating ocean eddies (mobile, coherent bodies of water). As these anticyclonic eddies move throughout the open ocean, the study suggests that the predators are also moving with them, foraging on the high deep-ocean biomass contained within.
Read More