Physical Oceanography
Two WHOI Scientists Recognized with Endowed Positions
Two scientists have been recognized by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) for their contributions to ocean sciences research. Drs. Daniel J. Fornari of the Geology and Geophysics Department and Rui Xin Huang of the Physical Oceanography Department have been named recipients of a W. Van Alan Clark Chair for Excellence in Oceanography at the Institution. Each endowed chair brings financial support for a period of five years, allowing the recipient the freedom to pursue a variety of career interests. The awards were announced today during the Institution’s fall meeting of the Board of Trustees and Members of the Corporation and are effective January 1, 2002.
Read MoreOutposts in the Ocean
Oceanographers and climatologists have something in common with politicians and stock market analysts: They are all trying to get a grasp on a complex, ever-shifting system.
Read MoreLaunching the Argo Armada
The Argo program proposes to disperse 3,000 floats, like the one below, throughout the oceans to collect data on oceanic conditions that can be periodically transmitted to shore via satellite.
Read MoreU.S. Navy Honors Two WHOI Scientists
The Office of Naval Research (ONR) has named Senior Scientist Robert A. Weller and Associate Scientist Steven P. Anderson of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) as recipients of its…
Read MoreMonsoon Winds and Carbon Cycles in the Arabian Sea
The monsoon, a giant sea breeze between the Asian massif and the Indian Ocean, is one of the most significant natural phenomena that influences the everyday life of more than 60 percent of the world’s population.
Read MoreA New Way to Catch the Rain
The carbon budget of the upper ocean includes an important loss to the deep ocean due to a very slowly falling rain of organic particles, usually called sediment. As this sediment falls through the upper water column it is consumed, mainly by bacteria, and the carbon is recycled into nonsinking forms (dissolved or colloidal organic carbon or inorganic forms). Thus the sediment rain decreases with increasing depth in the water column, and only a tiny fraction reaches the deep sea floor, less than about one percent.
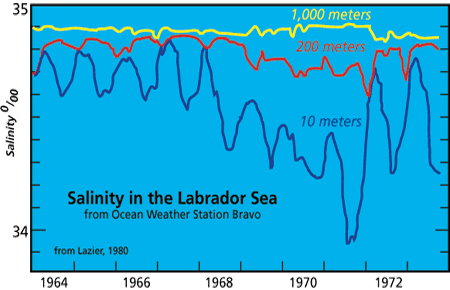
Read MoreAdventure in the Labrador Sea
The sound of the general alarm bell reverberated through the ship. At 2:30 AM, this couldn’t be a drill. Even more puzzling, we were still dockside in Halifax, four hours from our scheduled departure for the Labrador Sea.
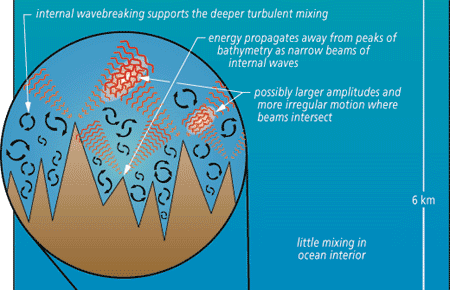
Read MoreNew Data on Deep Sea Turbulence Shed Light on Vertical Mixing
The global thermohaline circulation is basically a wholesale vertical overturning of the sea, driven by heating and cooling, precipitation and evaporation.
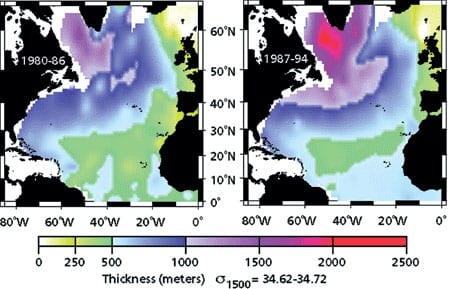
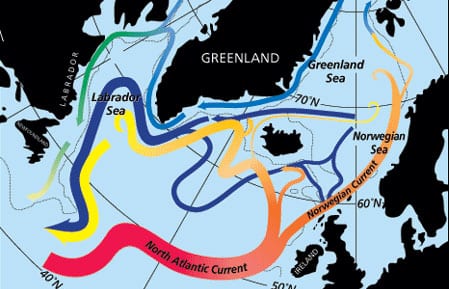
Read MoreLabrador Sea Water Carries Northern Climate Signal South
Changes in wind strength, humidity, and temperature over the ocean affect rates of evaporation, precipitation, and heat transfer between ocean and air. Long-term atmospheric climate change signals are imprinted onto the sea surface layer, a thin skin atop an enormous reservoirA? and subsequently communicated to the deeper water masses. Labrador Sea Water is a subpolar water mass shaped by air-sea exchanges in the North Atlantic. It is a major contributor to the deep water of the Atlantic, and changes of conditions in its formation area can be read several years later at mid-depths in the subtropics. Mapping these changes through time is helping us to understand the causes of significant warming and cooling patterns we have observed at these depths in the North Atlantic and links the subtropical deep signals back to the subpolar sea surface conditions.
Read MoreNorth Atlantic’s Transformation Pipeline Chills and Redistributes Subtropical Water
Warm and salty waters from the upper part of the South Atlantic flow northward across the equator and then progress through the tropical and subtropical North Atlantic to reach high latitudes. Beginning with the intense northward flow of the Gulf Stream off the East Coast of the United States, these waters are exposed to vigorous cooling, liberating considerable oceanic heat to the atmosphere. This is the first stage of “warm water transformation within the North Atlantic, a process that culminates in the high latitude production of cold and fresh waters that return to the South Atlantic in deep reaching currents beneath the warm waters of the subtropics and tropics.
Read MoreIf Rain Falls on the OceanDoes It Make a Sound?
As with similar questions about a tree in the forest or a grain of sand on the beach, it may be hard to imagine that a few inches of rain matters to the deep ocean.
Read MoreComputer Modelers Stimulate Real and Potential Climate, Work Toward Prediction
Although weather forecasting is accepted by the public as part of daily life, oceanic forecasting is not yet so advanced. There are, however, successful examples of oceanic forecasting—one is the newly developed skill to predict El Nino/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events, largely due to improvements in ocean modeling.
Read MoreOceans & Climate
The past decade has brought rapid scientific progress in understanding the role of the ocean in climate and climate change. The ocean is involved in the climate system primarily because it stores heat, water, and carbon dioxide, moves them around on the earth, and exchanges these and other elements with the atmosphere.
Read MoreThe Bermuda Station SA Long-Running Oceanographic Show
A time series of hydrographic measurements was initiated at Bermuda in 1954 and continues to the present. It began under the banner of the International Geophysical Year (1957-1958) with the scientific support of Henry Stommel of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and William Sutcliffe, director of the Bermuda Biological Station (BBS). The scientists and personnel of the originating institutions have been the most active participants over the years, but the data have been widely used by the international oceanographic community. While other long time series of measurements in the North Atlantic began in association with weather ships, only the Bermuda measurements have a strong oceanographic focus.
Read More