Marine Chemistry & Geochemistry
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Marine Chemist Authors ‘A Kids Book About Being a Scientist’
In his new book, A Kids Book About Being a Scientist, award-winning author and WHOI chemist Chris Reddy encourages young people to explore the world around them
Read MoreHuman Activity Is Causing Toxic Thallium to Enter the Baltic Sea, According to New Study
Human activities account for a substantial amount – anywhere from 20% to more than 60% – of toxic thallium that has entered the Baltic Sea over the past 80 years, according to new research by scientists affiliated with WHOI and other institutions.
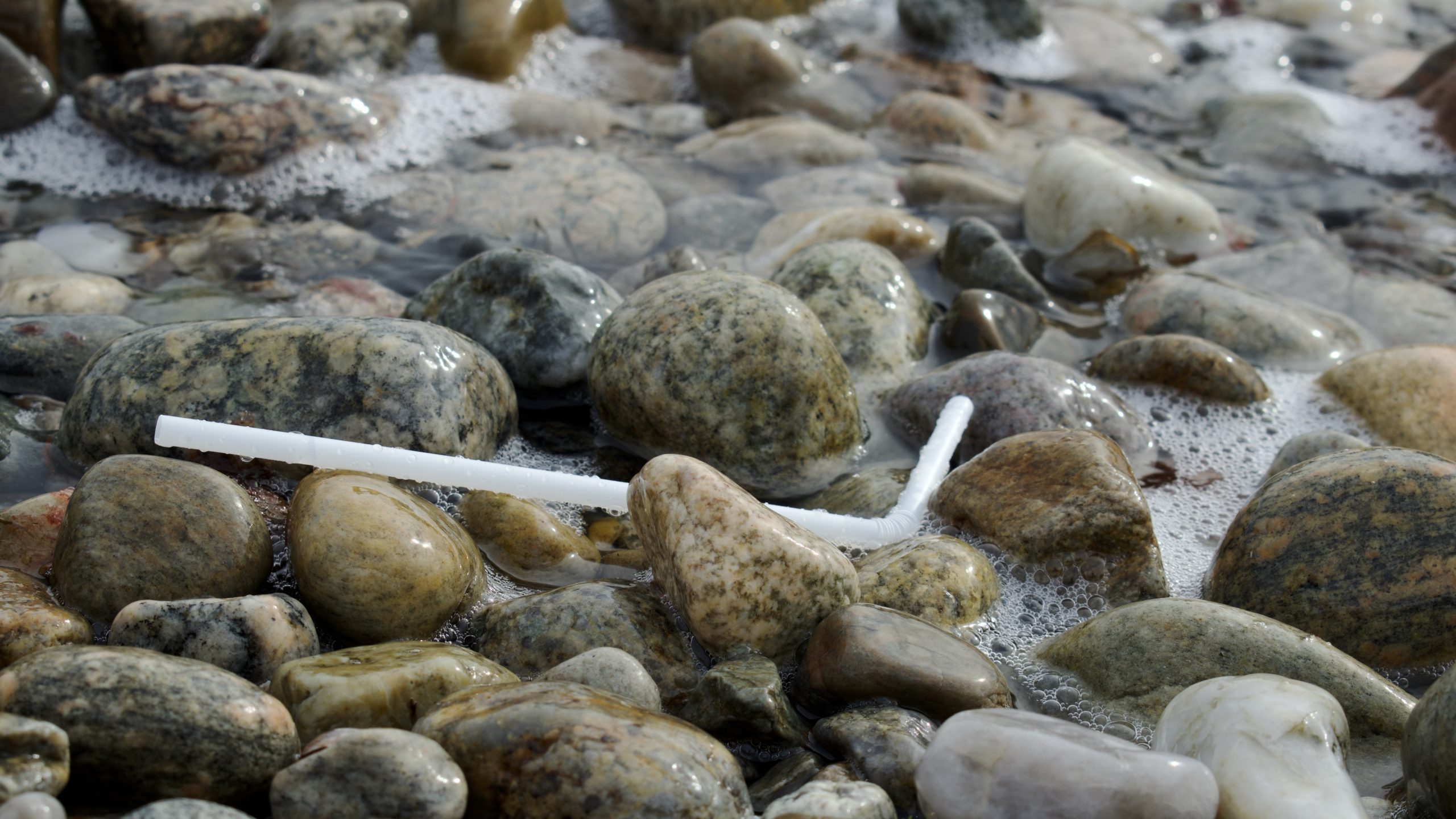
Read MoreDo all plastics degrade the same?
WHOI and Eastman created a wood-based straw that breaks down faster than paper—showing how science and industry can team up to fight ocean plastic.
Read MoreASLO honors Elizabeth B. Kujawinski with the 2024 G. Evelyn Hutchinson Award
Woods Hole, Mass. — Each year, the Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography (ASLO) honors scientists for their outstanding achievements in aquatic science research, service, and education. The…
Read MoreResearchers Studying Ocean Transform Faults, Describe a Previously Unknown Part of the Geological Carbon Cycle
Woods Hole, Mass. – Studying a rock is like reading a book. The rock has a story to tell, says Frieder Klein, an associate scientist in the Marine Chemistry &…
Read MoreVitamin B12 adaptability in Antarctic algae has implications for climate change
Woods Hole, Mass. — Vitamin B12 deficiency in people can cause a slew of health problems and even become fatal. Until now, the same deficiencies were thought to impact certain…
Read MoreSome Plastic Straws Degrade Quicker Than Others, New Study Shows
WHOI researchers determine lifetimes of drinking straws in the coastal ocean and develop a prototype bioplastic straw that degrades even faster than paper
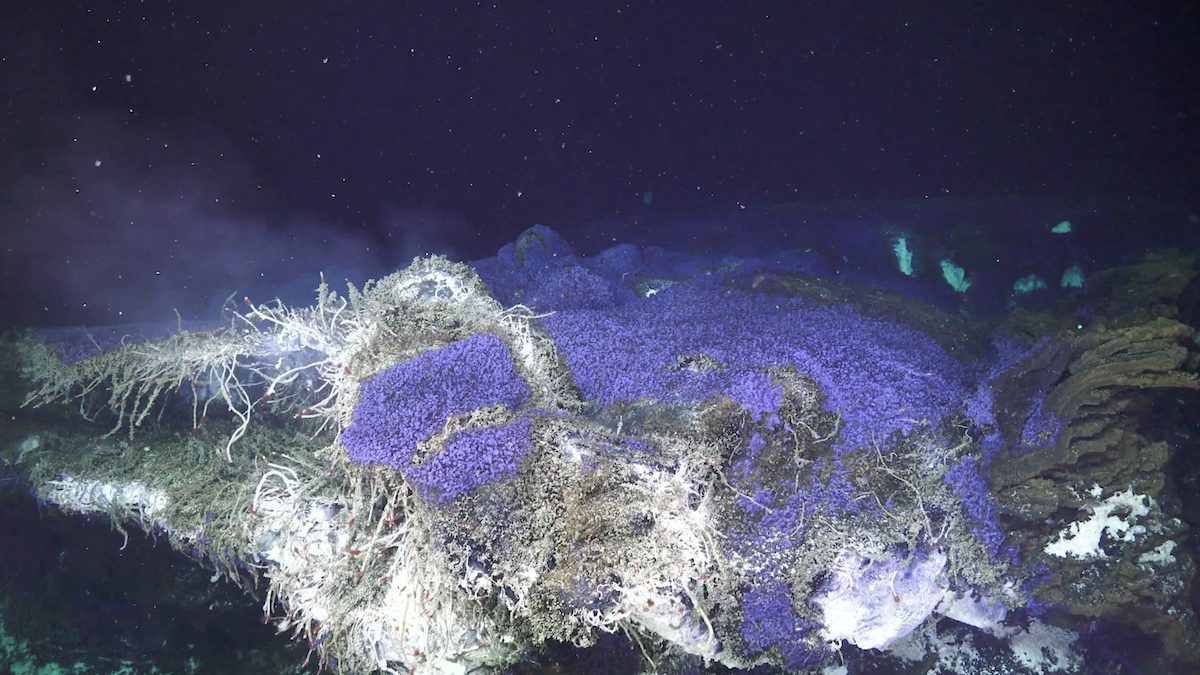
Read MoreInvestigating the world of microbes with ROV Jason
At Axial Seamount, WHOI scientists filmed vibrant life at deep-sea vents—ecosystems powered by chemosynthetic microbes in total darkness.
Read MoreA new way of looking at plastics
WHOI researchers develop a new sustainability metric for plastic products
Read MoreDan Lowenstein
MIT-WHOI Joint Program student
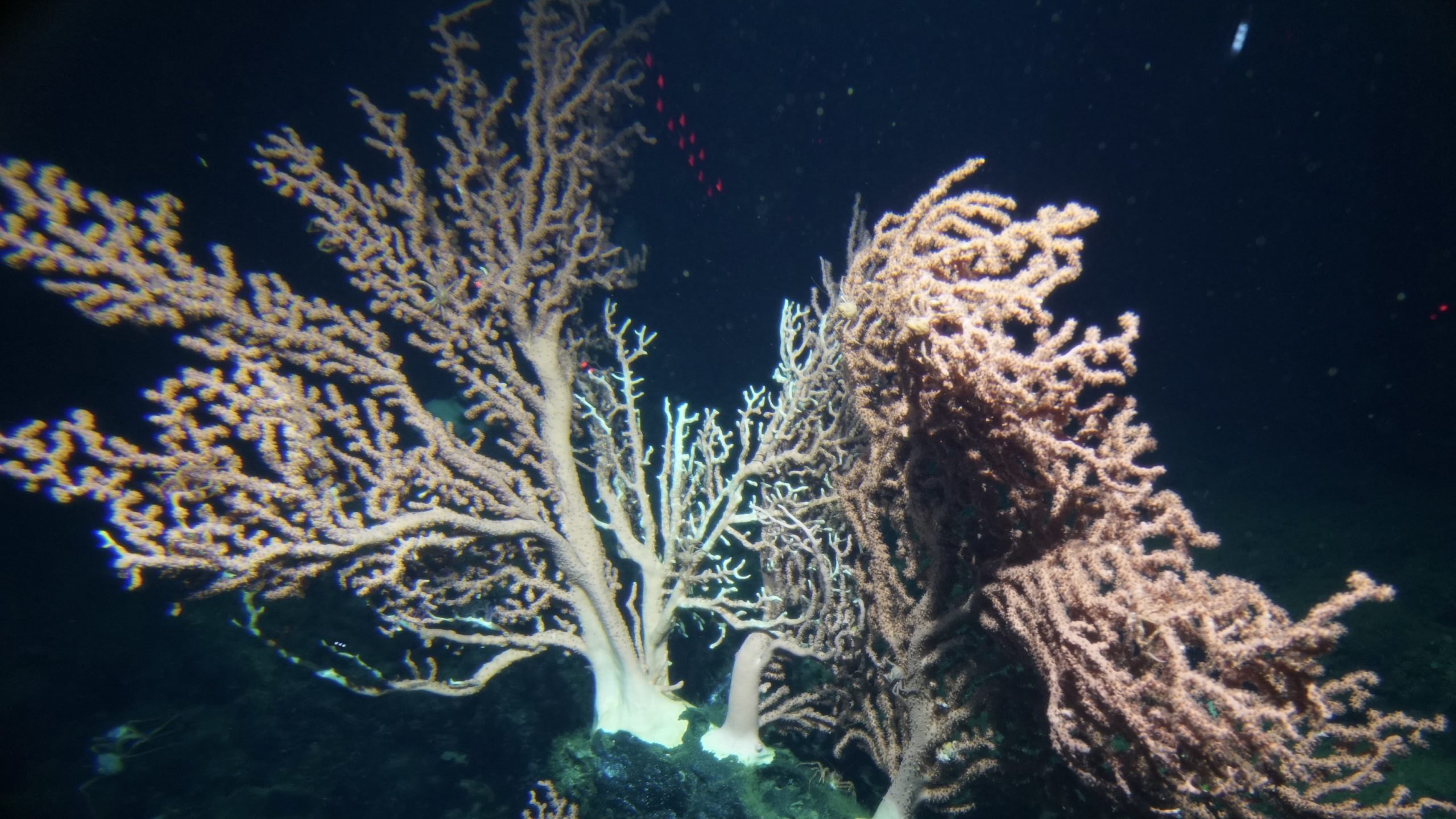
Read MoreNew Study: Deep Sea Sensor Reveals That Corals Produce Reactive Oxygen Species
A new sensor on the submersible Alvin discovered reactive oxygen species for the first time in deep-sea corals, broadening our understanding of fundamental coral physiology Woods Hole, MA — Just…
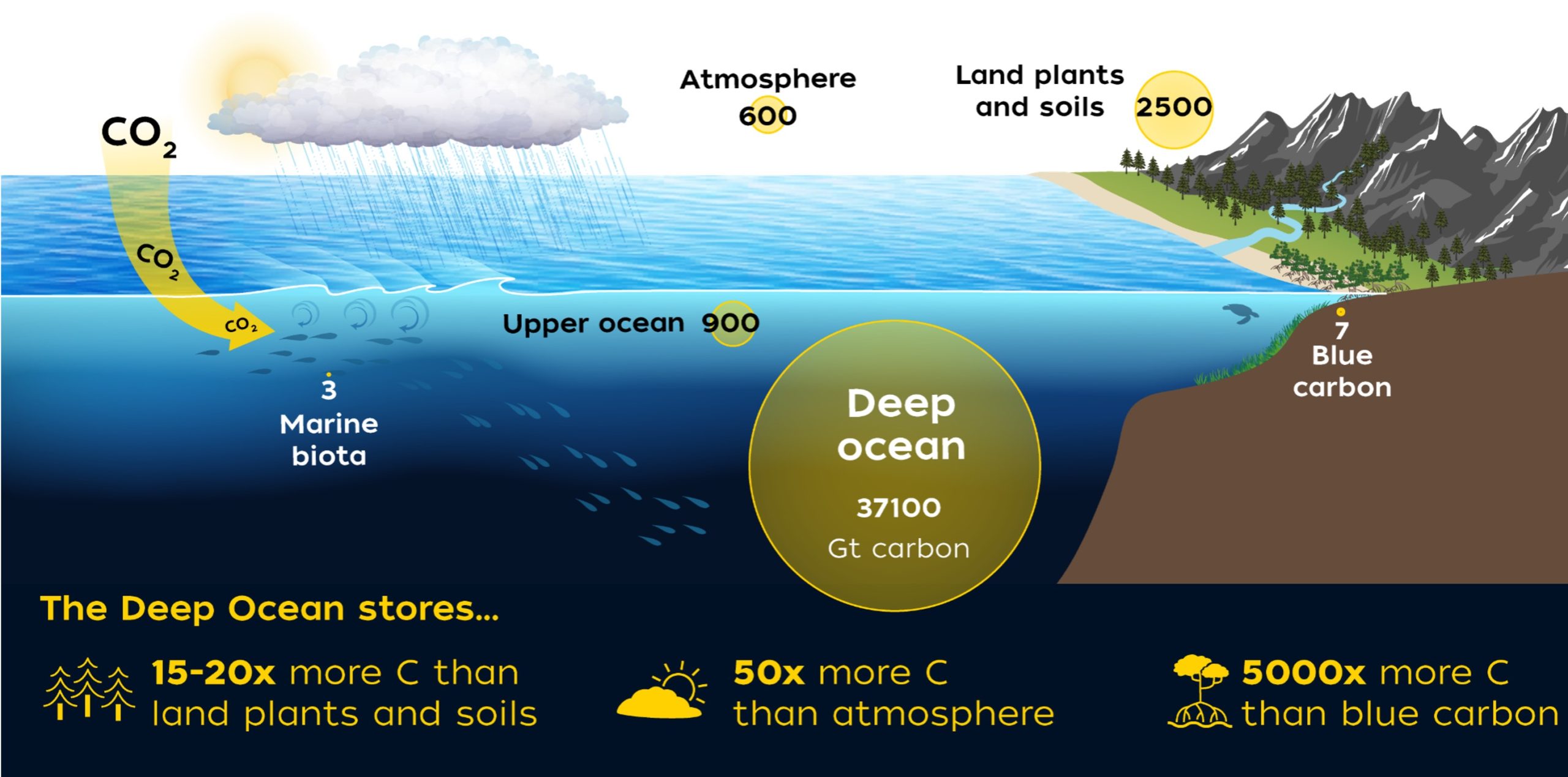
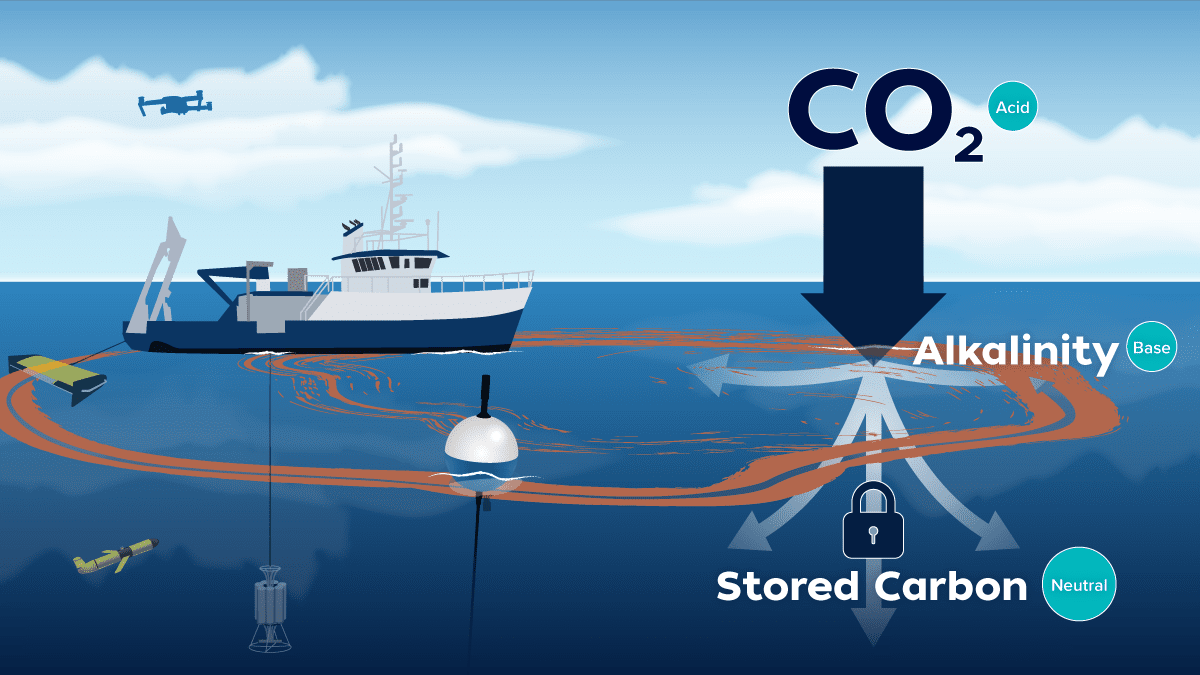
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution receives $8.5 million in Department of Energy funding for mCDR research
Woods Hole, Mass – The U.S. Department of Energy today announced Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is one of the ten organizations selected for funding to accelerate the development of…
Read MoreWHOI chemist given prestigious award
The award recognizes individuals who “materially increase the public’s knowledge of chemistry, chemical engineering, and related fields.”
Read MoreOcean Alkalinity Enhancement Project Looks at Pulling Carbon Dioxide from the Atmosphere
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution project is part of the broader carbon to sea initiative
Read MoreWHOI Marine Chemist Shares Hard Won Advice for Communicating in the Face of Environmental Disasters
Science Communications in a Crisis: An Insider’s Guide draws on decades of experience
Read MoreOxygen Dead Zones
Dead zones occur when the water lacks oxygen. Like us, marine animals require oxygen to breathe, and when oxygen levels drop too low they can suffocate.
Read MoreNatural Wax Holds Promise to Replace Petroleum in Cosmetics and Personal Care Products
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and Western Washington University Sign License Agreement for Upwell Cosmetics to Make and Market a Marine Microalga-Derived Wax
Read MoreToward a New Era of Reef Solutions
WHOI coral reef researchers propose a new technology-centered focus to study and conserve coral reefs
Read MoreWHOI helps lead groundbreaking study on the human and ocean health impacts of ocean plastics
For the first time, leading researchers from the fields of healthcare, ocean science, and social science have collaborated to quantify plastic’s considerable risks to all life on Earth. The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health report, released today, presents a comprehensive analysis showing plastics as a hazard at every stage of their life cycle.
Read MoreA Better Understanding of Gas Exchange Between the Atmosphere and Ocean Can Improve Global Climate Models
If scientists can improve the way models represent physical processes such as gas exchange, they can have more confidence in future simulations.
Read MoreExcess Nutrients Lead to Dramatic Ecosystem Changes in Cape Cod’s Waquoit Bay
The Bay Is a harbinger for estuaries worldwide, say researchers
Read More