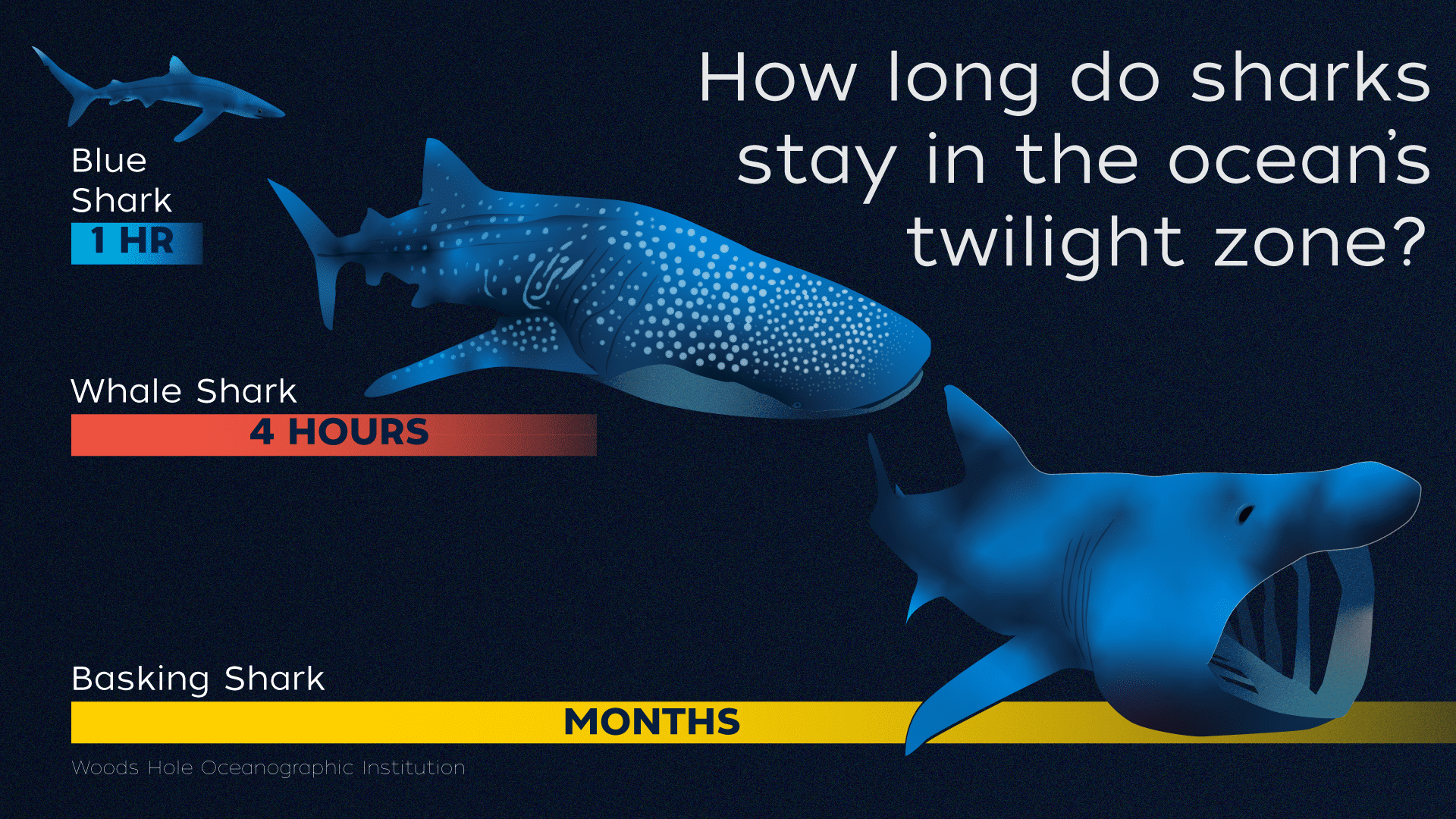Biology
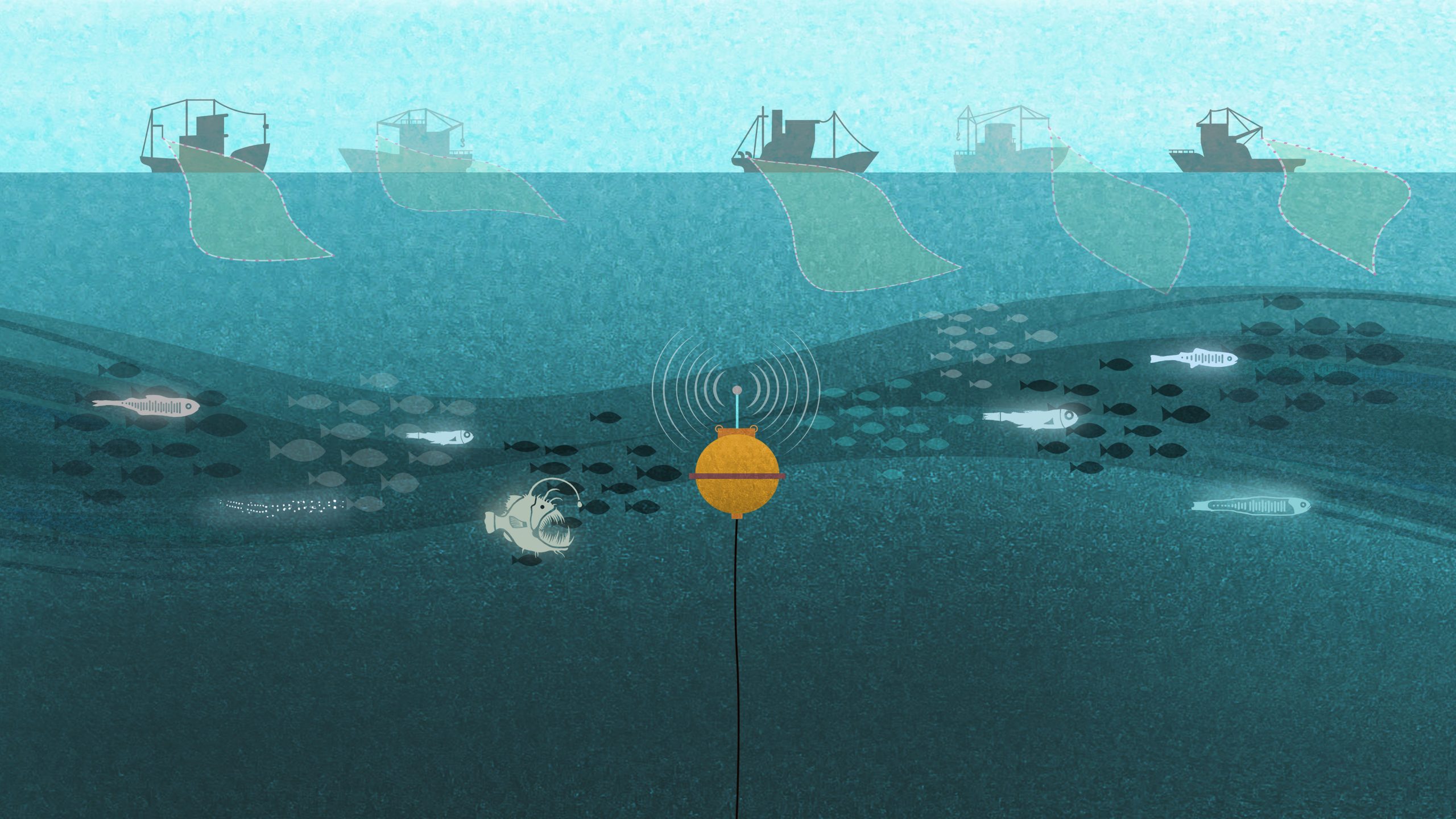
Measuring the great migration
A bioacoustic mooring will use sound to help estimate life migrating in the ocean’s twilight zone as part of a new long-term observation network in the Atlantic
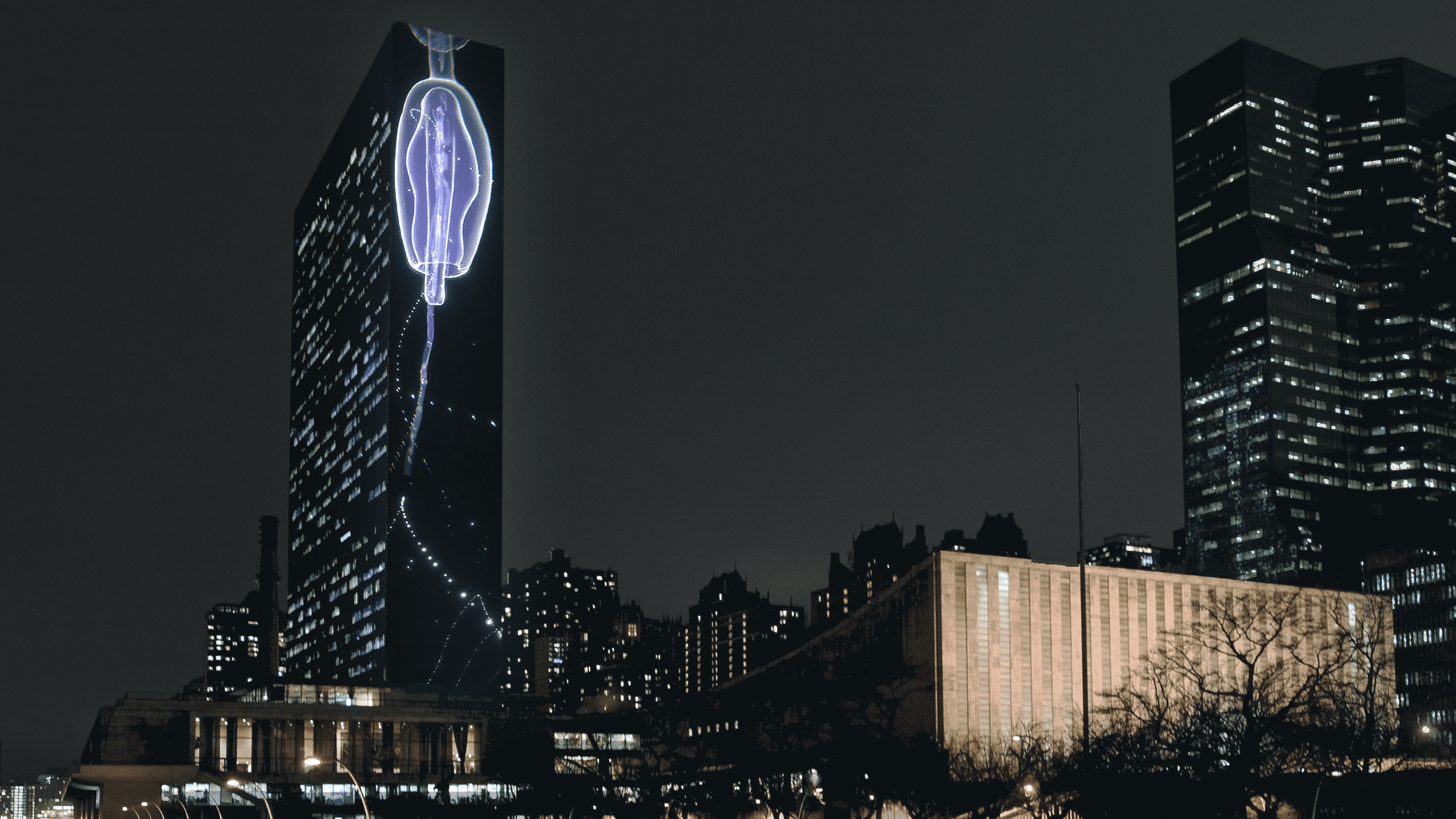
Read MoreWHOI collaborates to bring video installation to United Nation Headquarters
Vertical Migration by artist group SUPERFLEX will be projected onto the facade of the United Nations’ 505-foot tower in New York, on 21-24 September 2021, coinciding with the 76th General Assembly and Climate Week NYC. The projection seeks to draw global attention to the critical role of the ocean in global climate, a primary focus of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Ocean Twilight Zone Project.
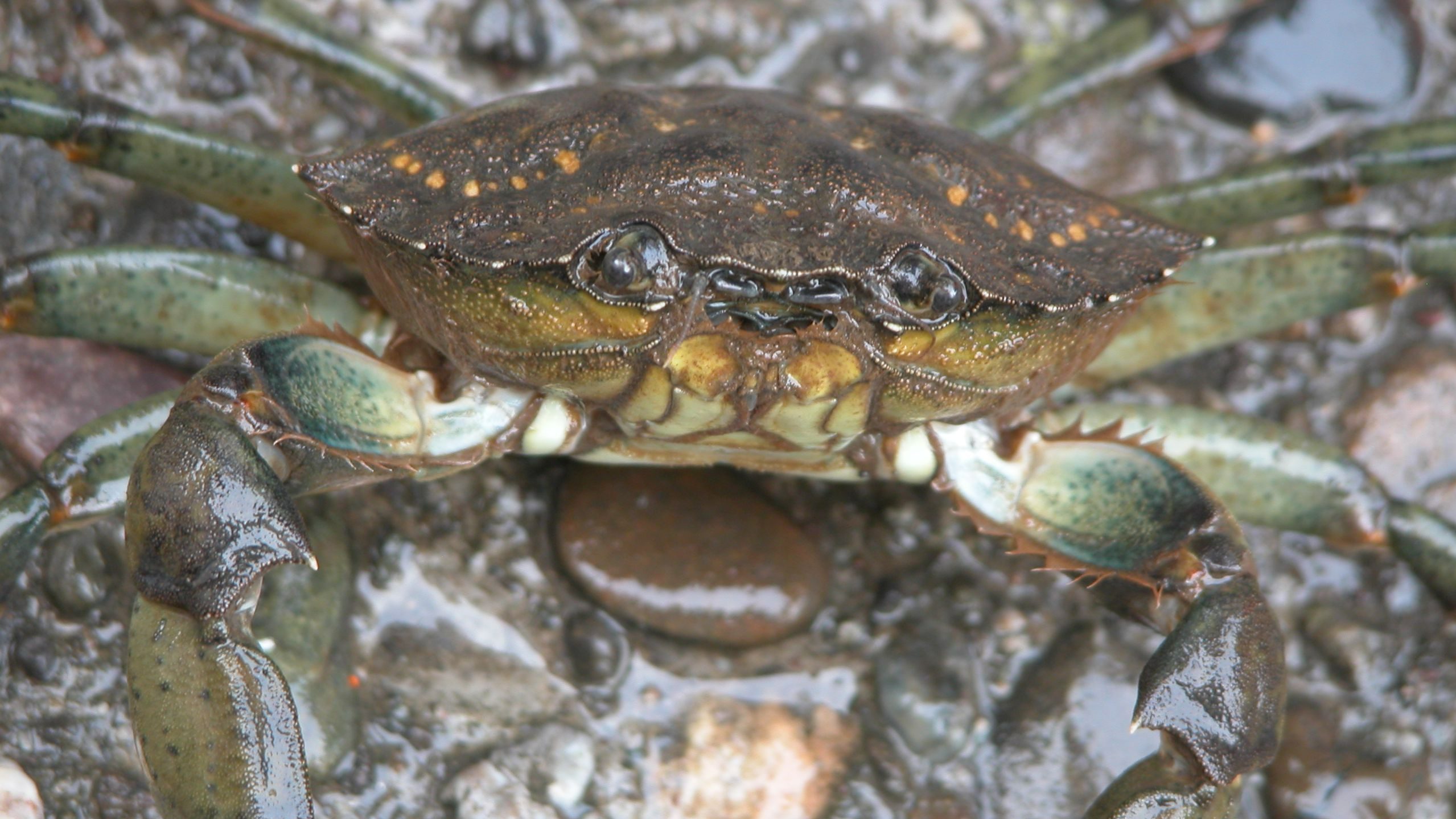
Read MoreFlipping the “genetic paradox of invasions”
A new study led by Carolyn Tepolt, an associate scientist of biology at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, is investigating the adaptive mechanisms of the green crab along the west coast of North America, where it has shown extensive dispersal in the last decade despite minimal genetic diversity.
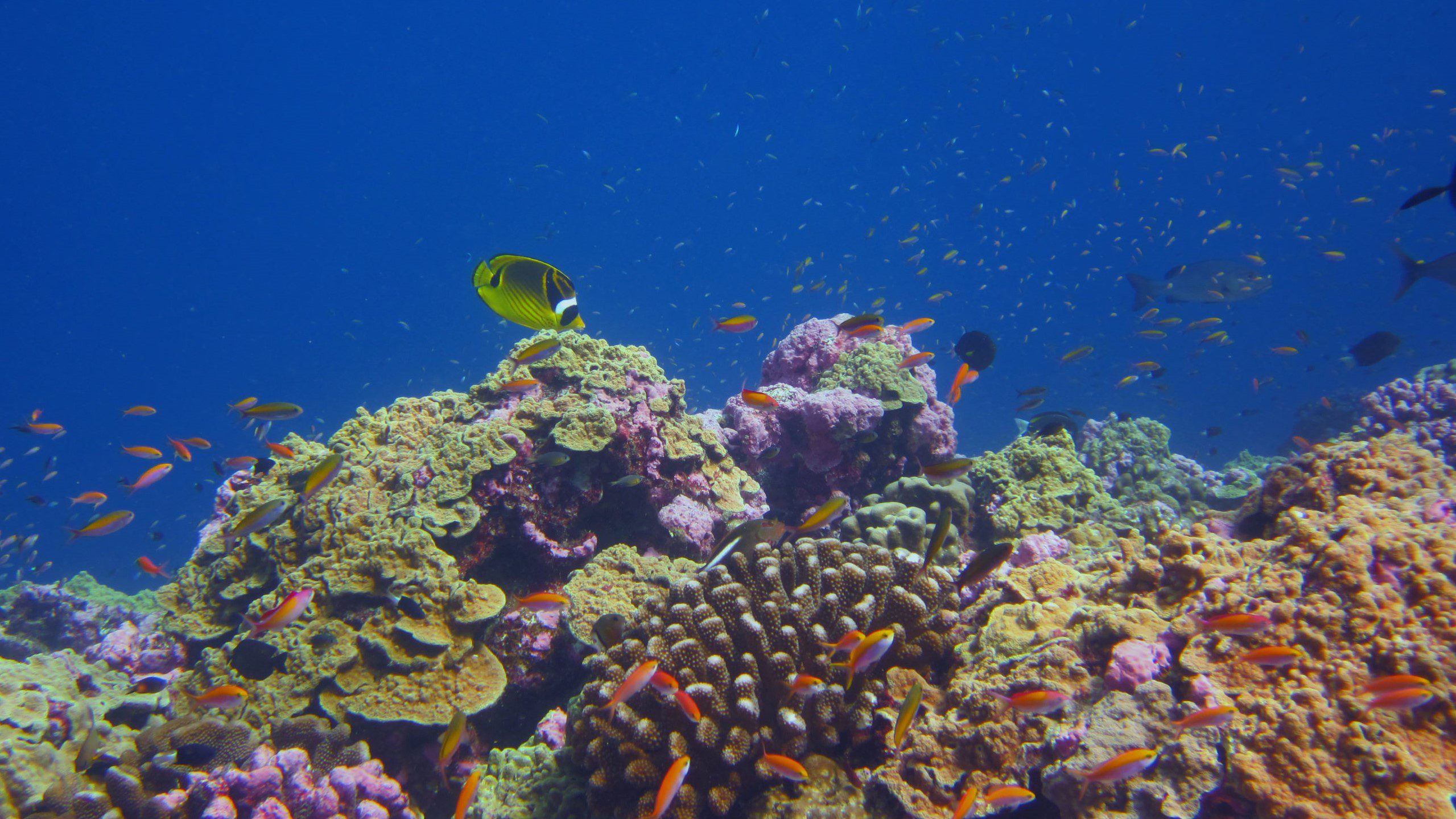
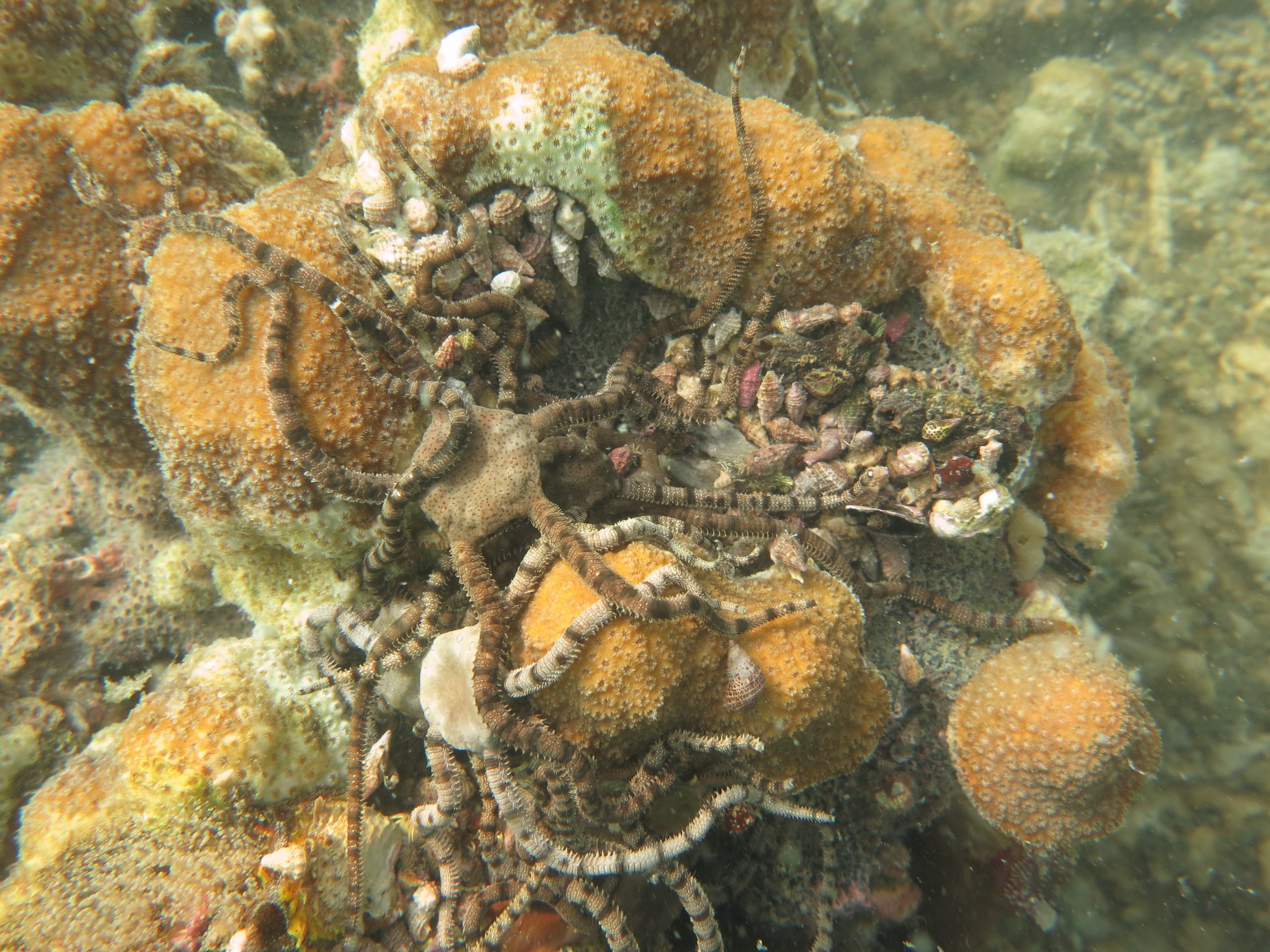
Read MoreSome coral reefs are keeping pace with ocean warming
Some coral communities are becoming more heat tolerant as ocean temperatures rise, offering hope for corals in a changing climate. After a series of marine heatwaves hit the Phoenix Islands Protected Area (PIPA) in the central Pacific Ocean, a new study finds the impact of heat stress on the coral communities lessened over time.
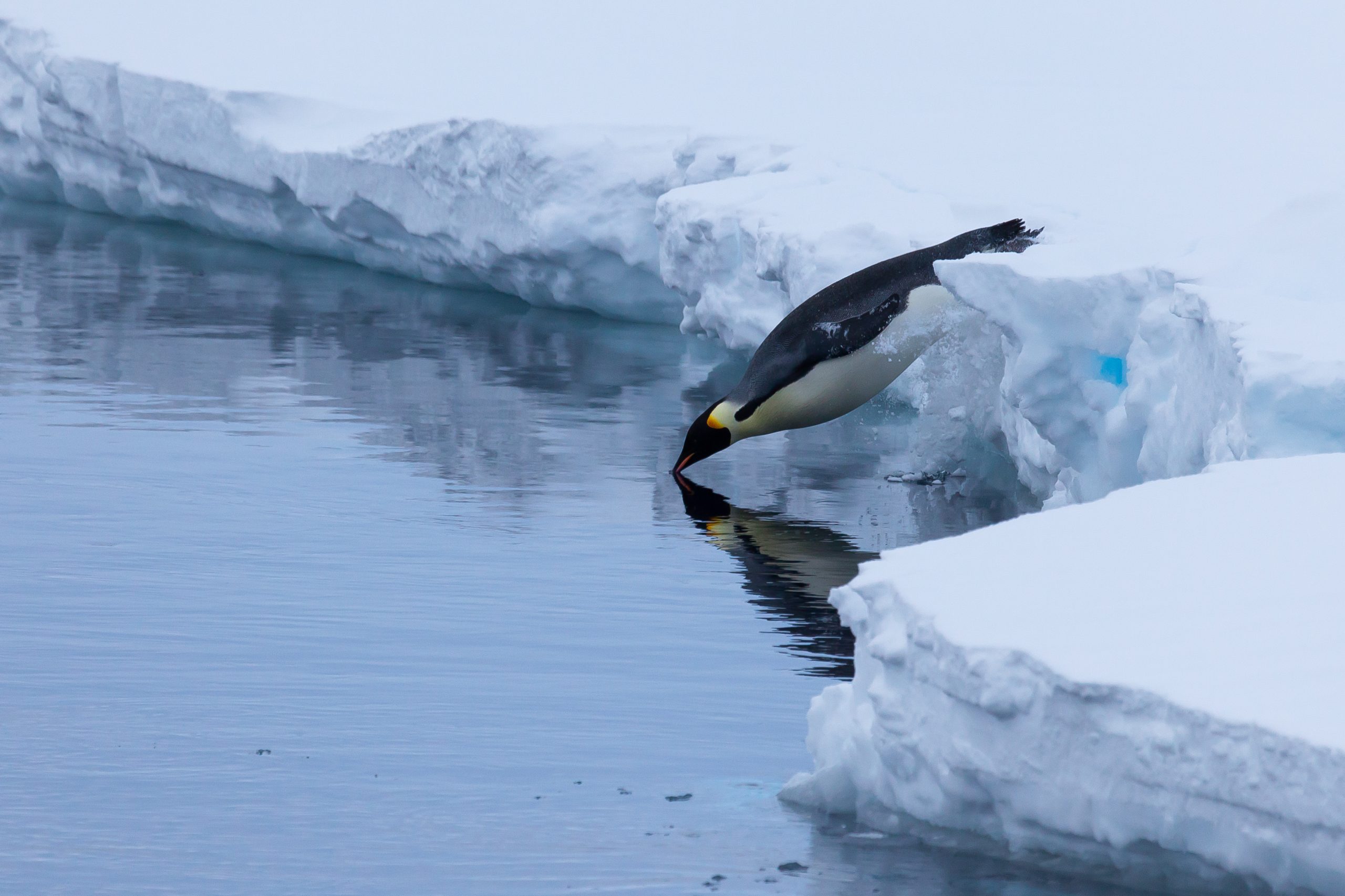
Read MoreFascinating facts about emperor penguins
We might chuckle at the sight of penguins waddling over ice, but these flightless birds would put Olympic swimmers to shame. Learn more about emperor penguins, the largest penguin in the world and permanent residents of Antarctica.
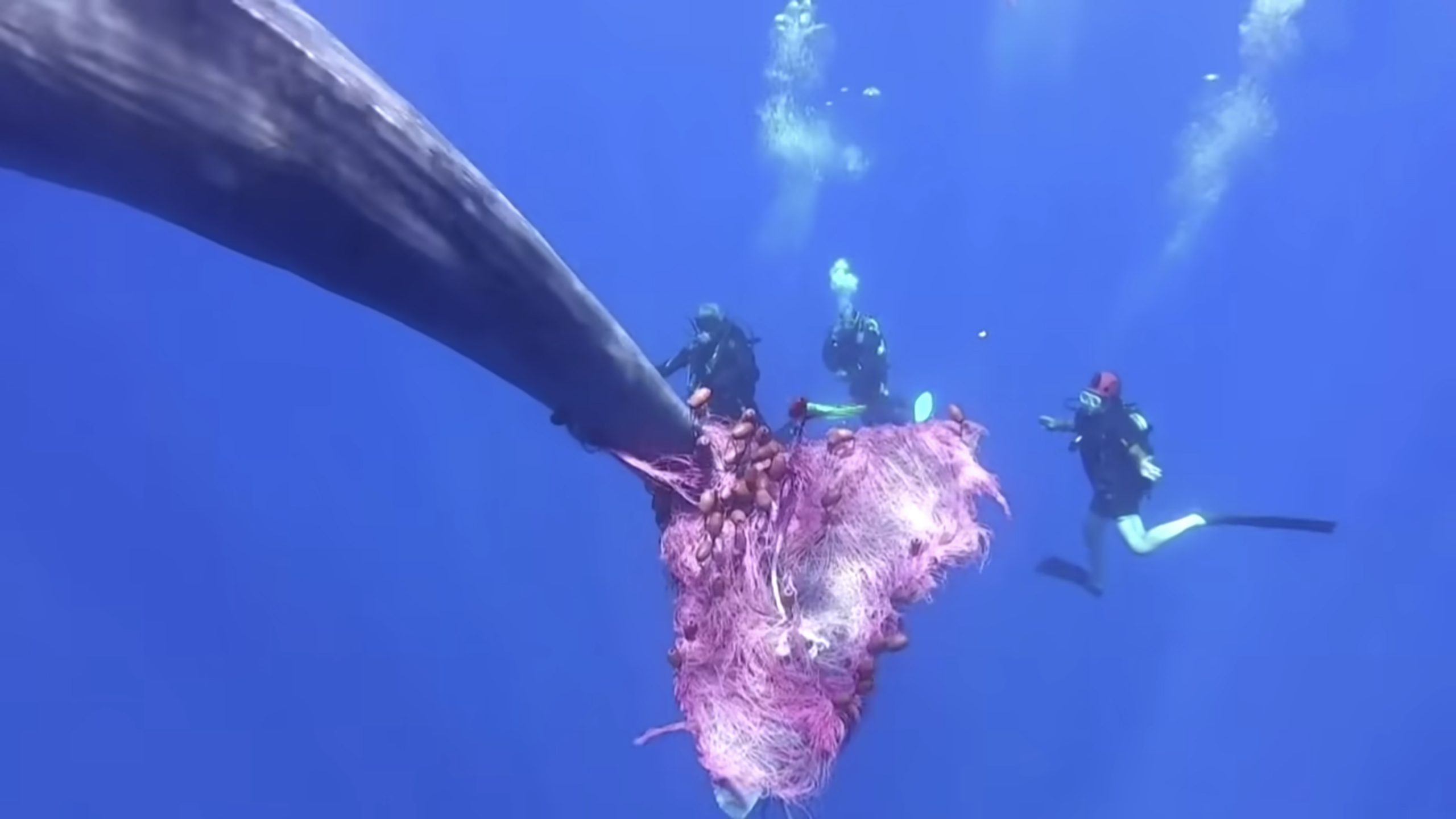
Read MoreKeeping an ear out for entangled whales
To help mitigate the impacts of illegal fishing off the Sicilian coast, a WHOI scientist and his collaborators are attaching acoustic tags to drift nets so sperm whales can be located and tracked for disentanglement crews.
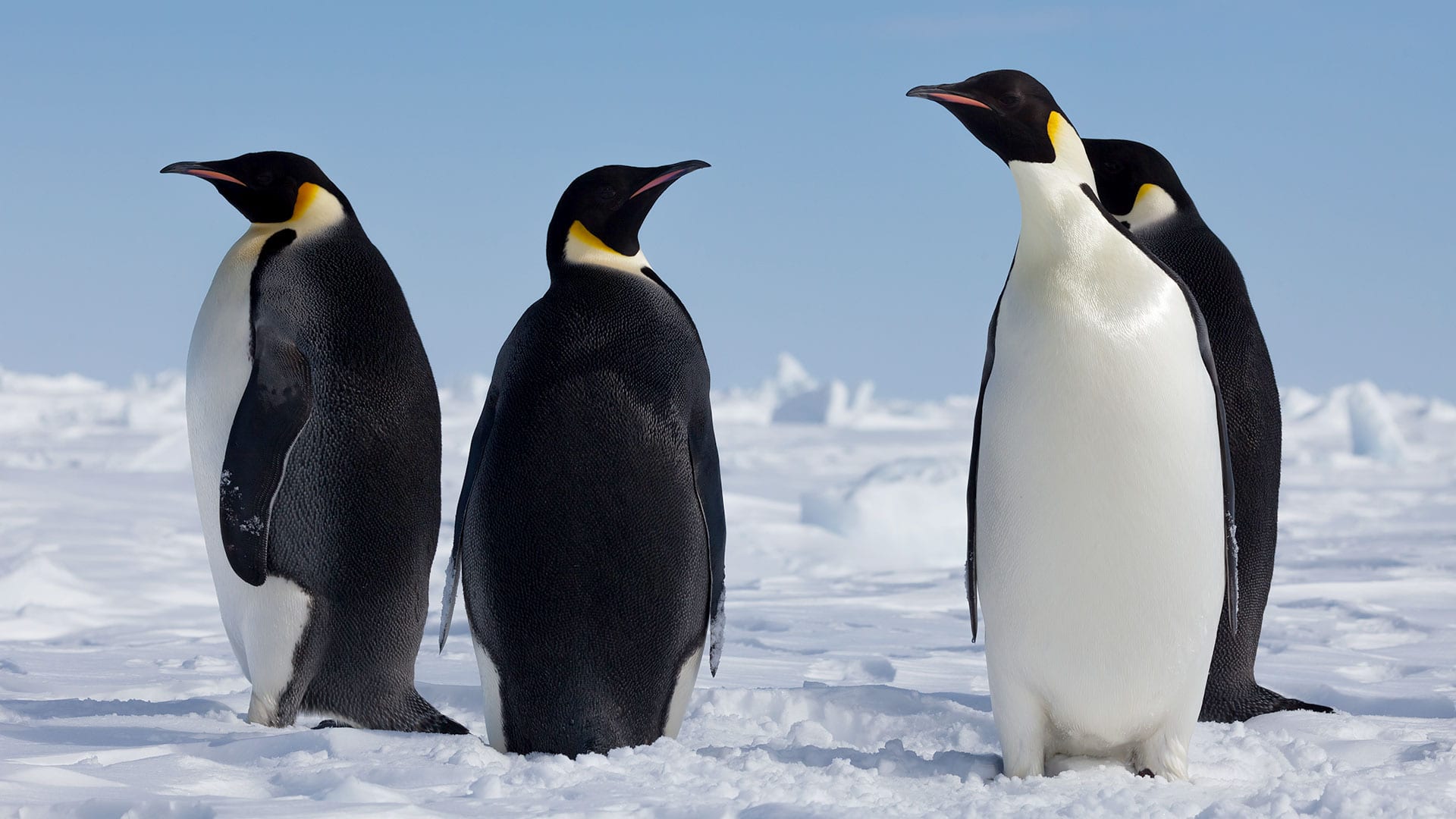
Read MoreEmperor Penguins
The emperor penguin is the largest living penguin species standing around 115 centimeters tall. Once they have found a partner, they work together to keep their young fed and safe.
Read MoreEmperor penguins, recommended as threatened species under Endangered Species Act
Today, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) announced a proposal to list the emperor penguin as a threatened species under the Endangered Species Act.
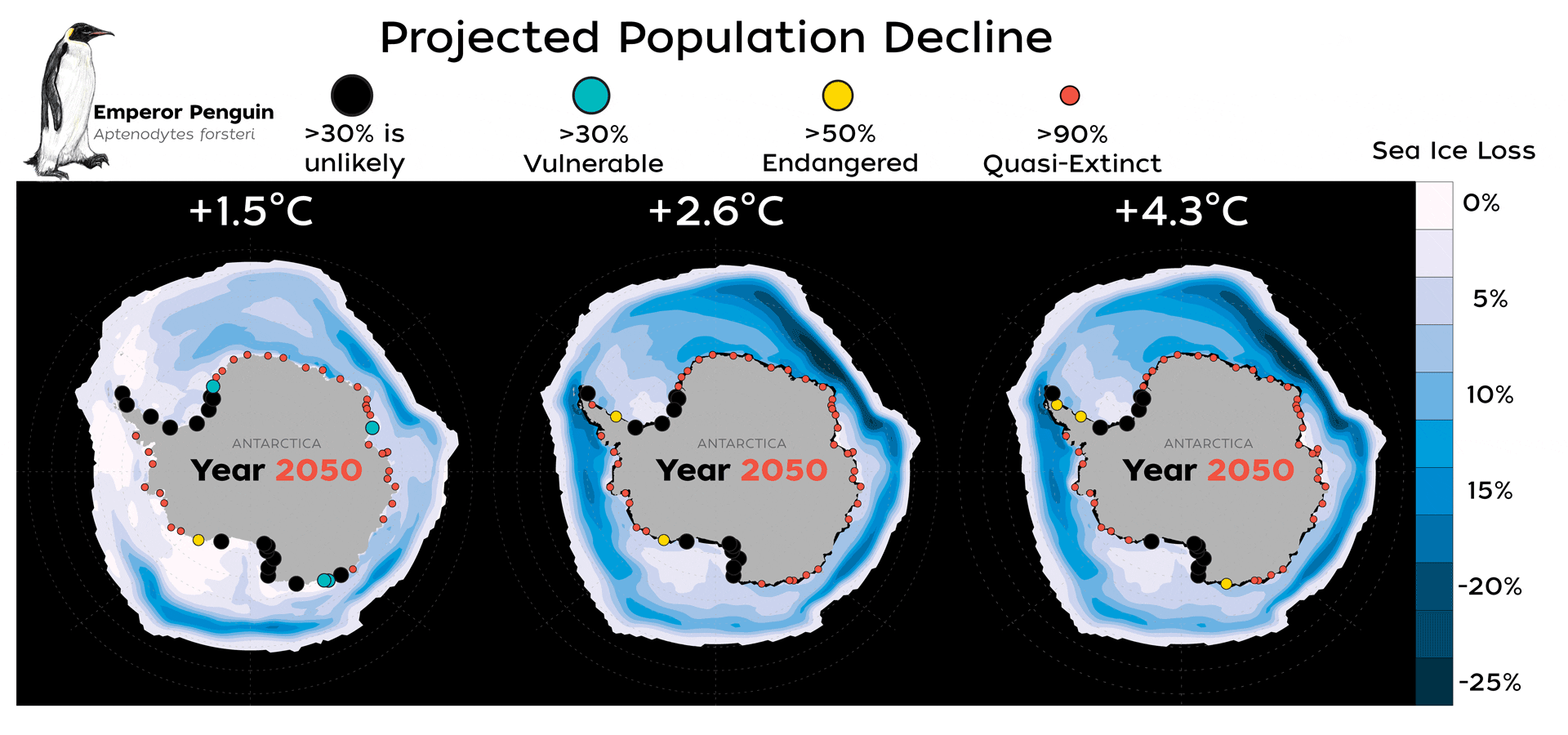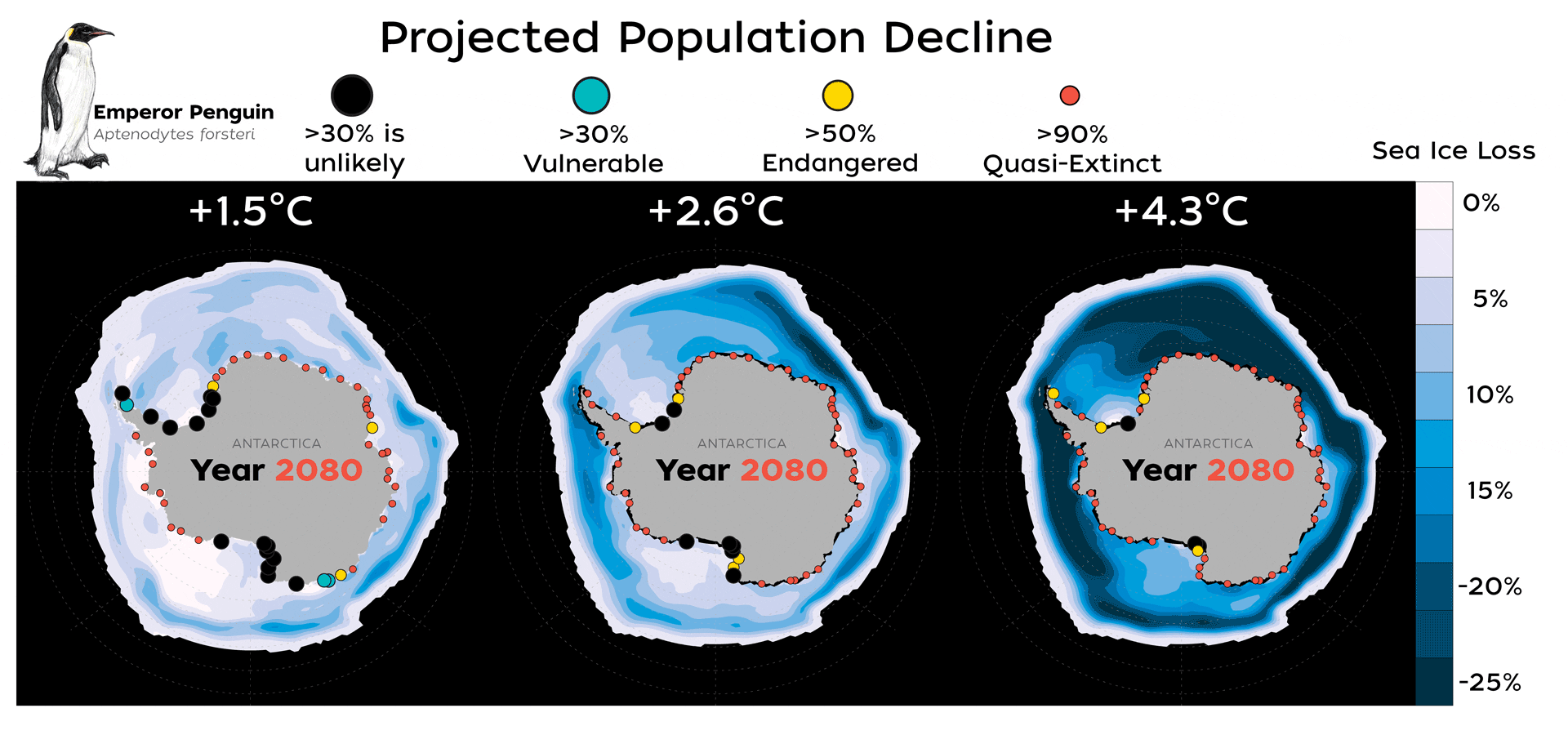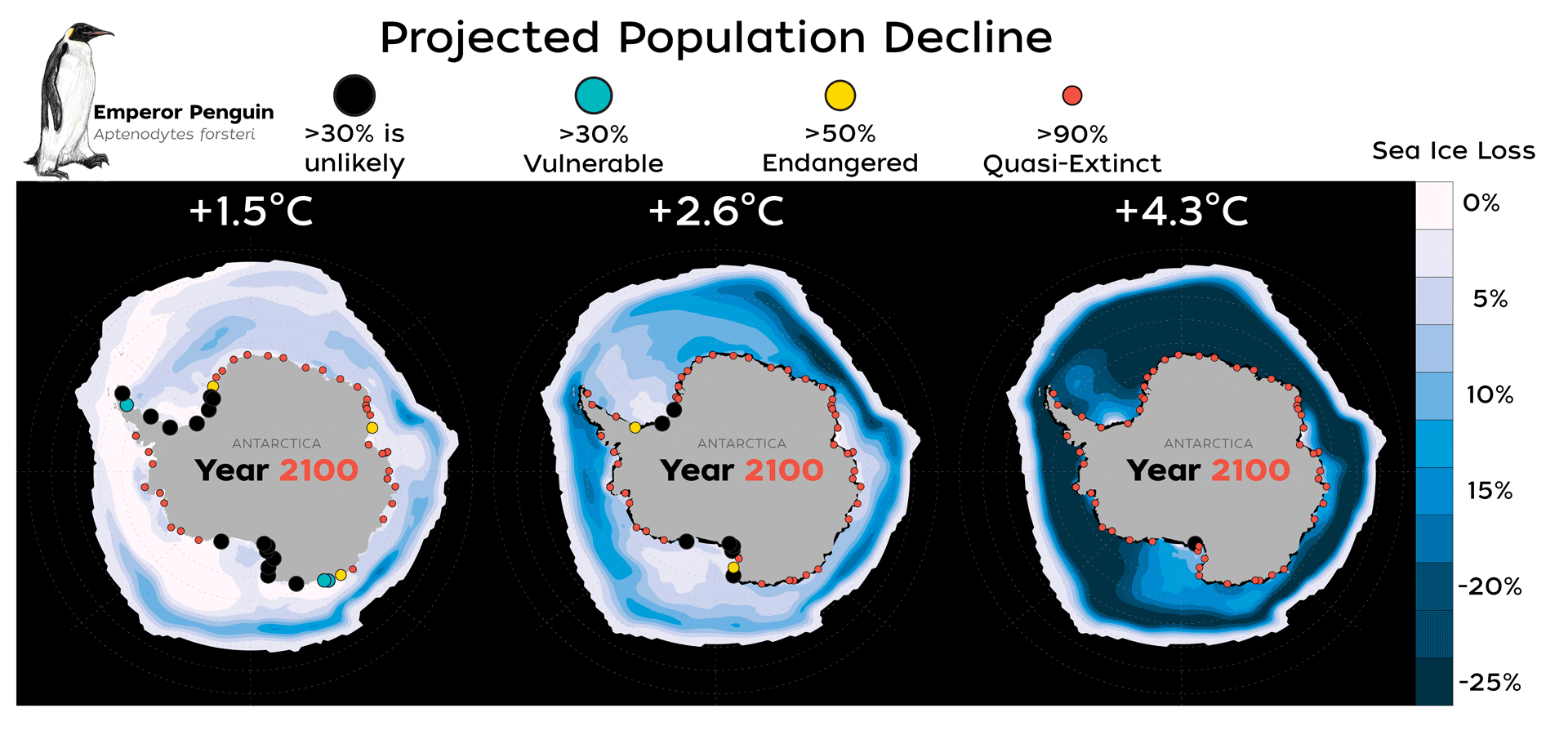
Read MoreNew Study Finds Emperor Penguins Increasingly Threatened by Climate Change
A new study published today in Global Change Biology provides valuable new data that highlights how species extinction risk is accelerating due to rapid climate change and an increase in extreme climate events, such as glacial calving and sea ice loss.
Read MoreMelting ice imperils 98% of Emperor penguin colonies by 2100
WASHINGTON (AP) — With climate change threatening the sea ice habitat of Emperor penguins, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service on Tuesday announced a proposal to list the species as…
Read MoreWhat Happens to Marine Life When There Isn’t Enough Oxygen?
In September of 2017, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution postdoctoral scholar Maggie Johnson was conducting an experiment with a colleague in Bocas del Toro off the Caribbean coast of Panama. After…
Read MoreA dragnet for toxic algae?
To keep a close eye on harmful algal blooms, shellfish farmers are relying on a WHOI-developed camera system that spies on toxic species below the surface and sends alerts when they’re present.
Read MoreWhat happens to marine life when oxygen is scarce?
A new study co-led by WHOI postdoctoral scholar Maggie Johnson looks closely at the changes occurring in both coral reef and microbial communities near Bocas del Toro during sudden hypoxic events, which occur when there is little to no oxygen in a given area of water.
Read MoreLife at Rock Bottom
This digital photo essay brings you the forms, figures, and facts of life more than a mile and half deep
Read MoreFalling in love with deep-sea parasites
At hydrothermal vents there are body-snatchers, intestinal hitchhikers, and chest-bursters, but something about them is still alluring to Lauren Dykman
Read MoreSharks and the ocean’s twilight zone: Some female great white sharks can deep dive for hours
Much of the shark focus around the Cape is on great whites roaming close to the shoreline as they prowl for seals, but researchers are finding out that several sharks…
Read MoreShark Week 2021: Sharks and the Ocean’s Twilight Zone
How large marine predators use the twilight zone to thrive, and survive Woods Hole, MA (July 11, 2021) — Sharks are some of the largest fish in the ocean, known…
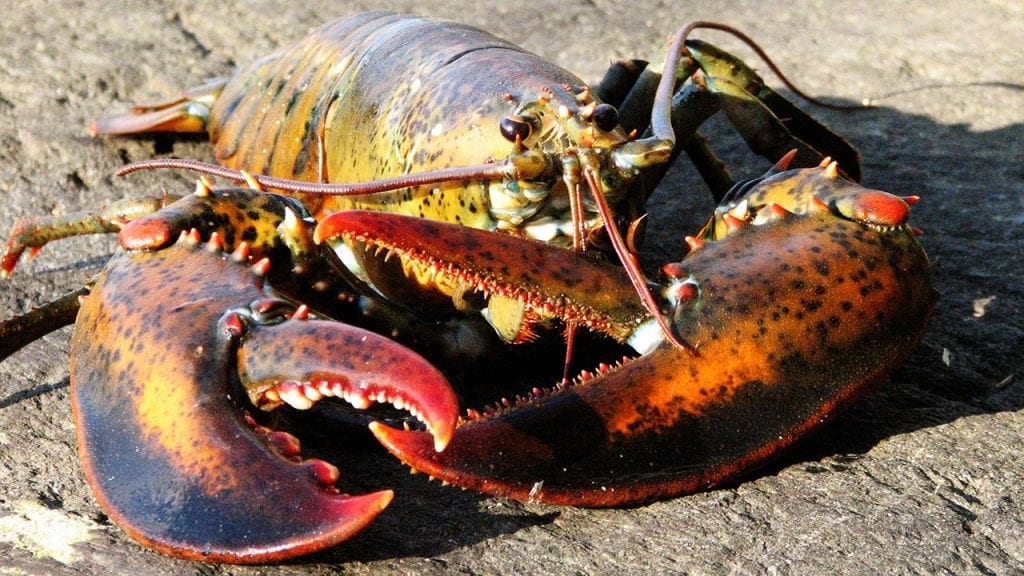
Read MoreStudy Shows that Lobsters Can Detect Sound
A new study demonstrates that lobsters can detect low-frequency sound and suggests that anthropogenic noise could affect lobsters. The study comes out at a time when the construction of more offshore wind farms, with their associated underwater pile driving noise, is being considered in New England.
Read More‘What we know now is how much we don’t know’: Enter the strange world of the ocean twilight zone
A difficult area to study and often overlooked by science, new technology is aiding its exploration, forcing researchers to re-evaluate just how much life is down there. Researchers now believe…
Read MoreMaine’s having a lobster boom. A bust may be coming.
The waters off Maine’s coast are warming, and no one knows what that’s going to mean for the state’s half-billion-dollar-a-year lobster industry—the largest single-species fishery in North America. Some fear that continued warming could cause the lobster population to collapse. To understand what’s happening to the ecosystem of the Gulf of Maine, says Glen Gawarkiewicz, an oceanographer at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, in Massachusetts, you have to look beyond it—see how it’s affected by the atmosphere, ocean currents, and rivers that flow into it.
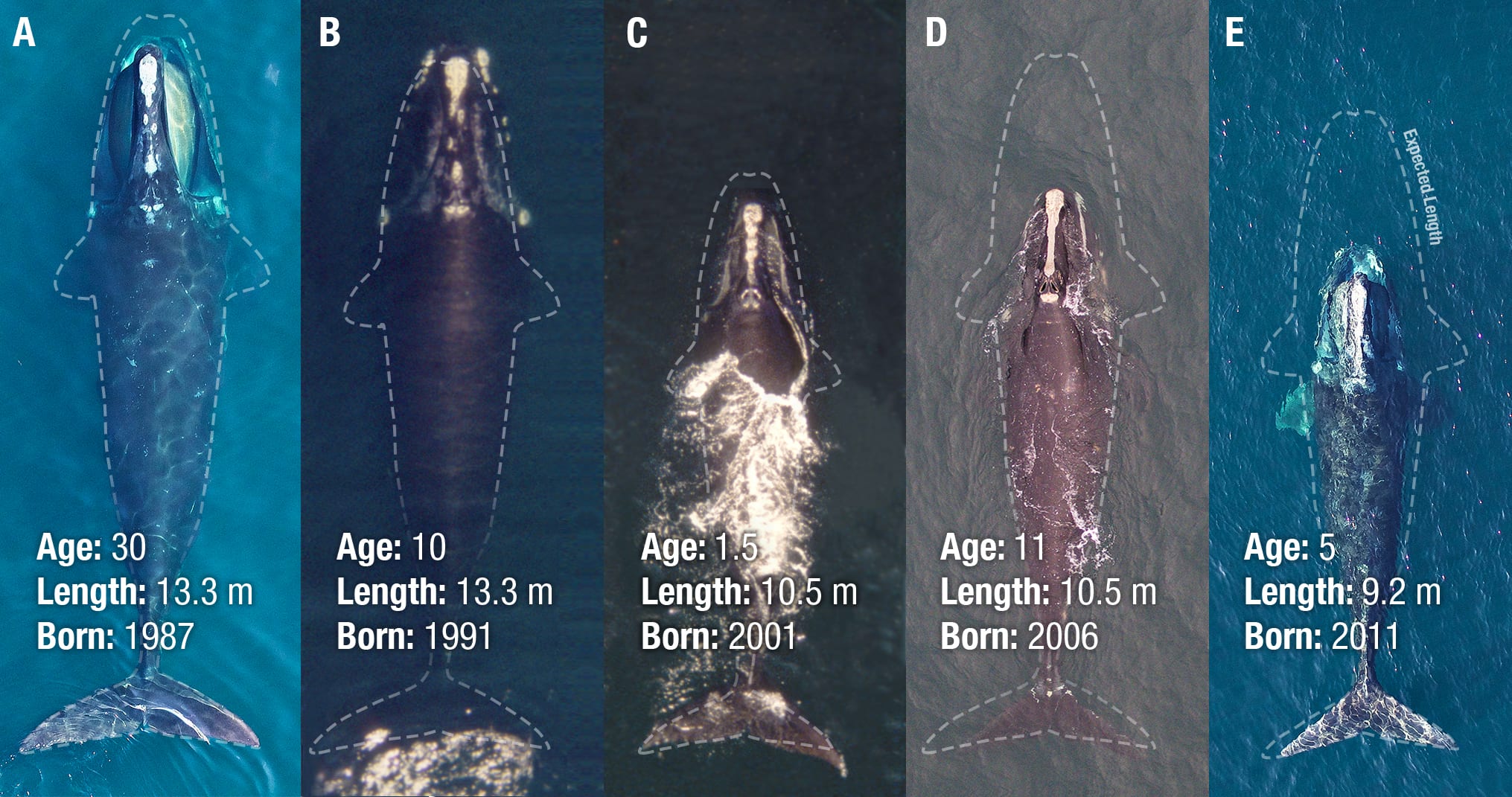
Read MoreCritically Endangered North Atlantic Right Whales Getting Smaller, New Research Finds
A report out this week in Current Biology reveal that critically endangered North Atlantic right whales are up to three feet shorter than 40 years ago. This startling conclusion reinforces what scientists have suspected: even when entanglements do not lead directly to the death of North Atlantic right whales, they can have lasting effects on the imperiled population that may now number less than 400 animals. Further, females that are entangled while nursing produce smaller calves.
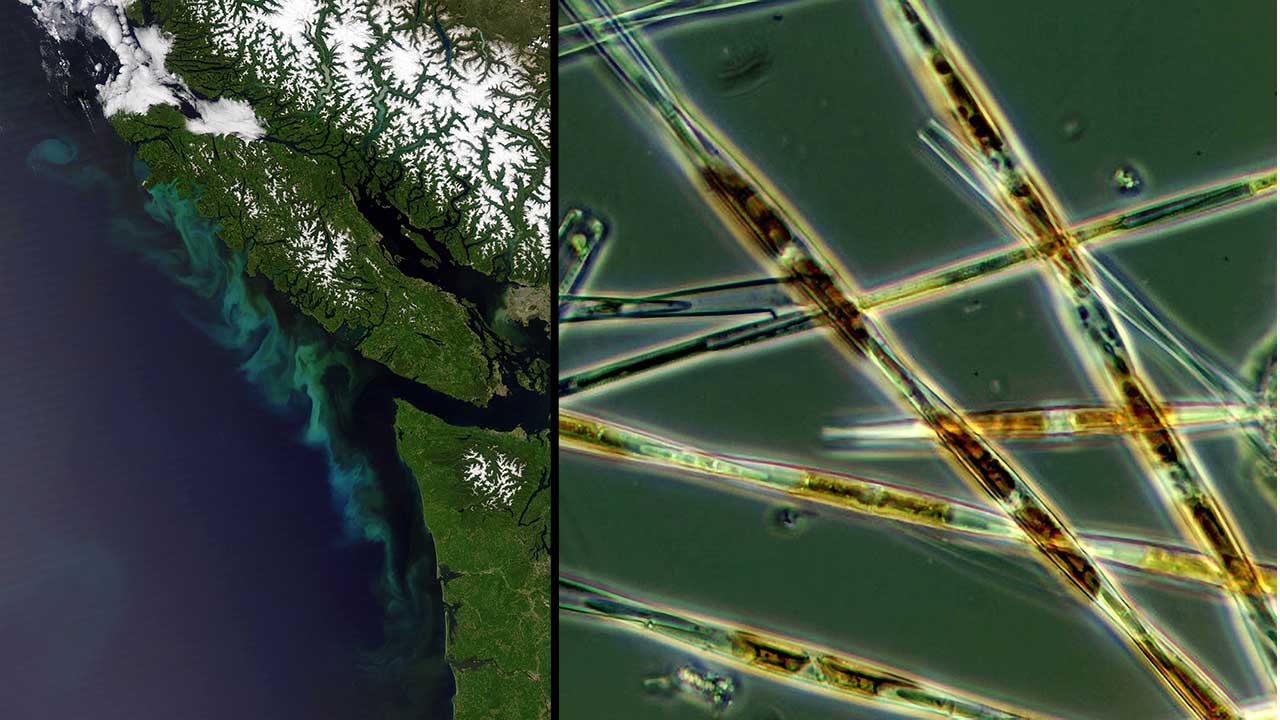
Read MoreFirst Global Statistical Analysis of Harmful Algal Blooms
International study finds no worldwide trend in blooms, but significant increases in some regions and of certain species, pointing to the need for better monitoring and data collection—especially in light…
Read MoreOn the Verge of Extinction, These Whales Are Also Shrinking
Most of the 360 or so North Atlantic right whales alive today bear scars from entanglements in fishing gear and collisions with speeding ships and, according to new study, they…
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution Wants Everyone to “Keep it Weird”
Campaign raises awareness of the ocean twilight zone by celebrating the “weird” in all of us Woods Hole, Mass. (May 27, 2021) — Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) wants to…
Read More