News Releases
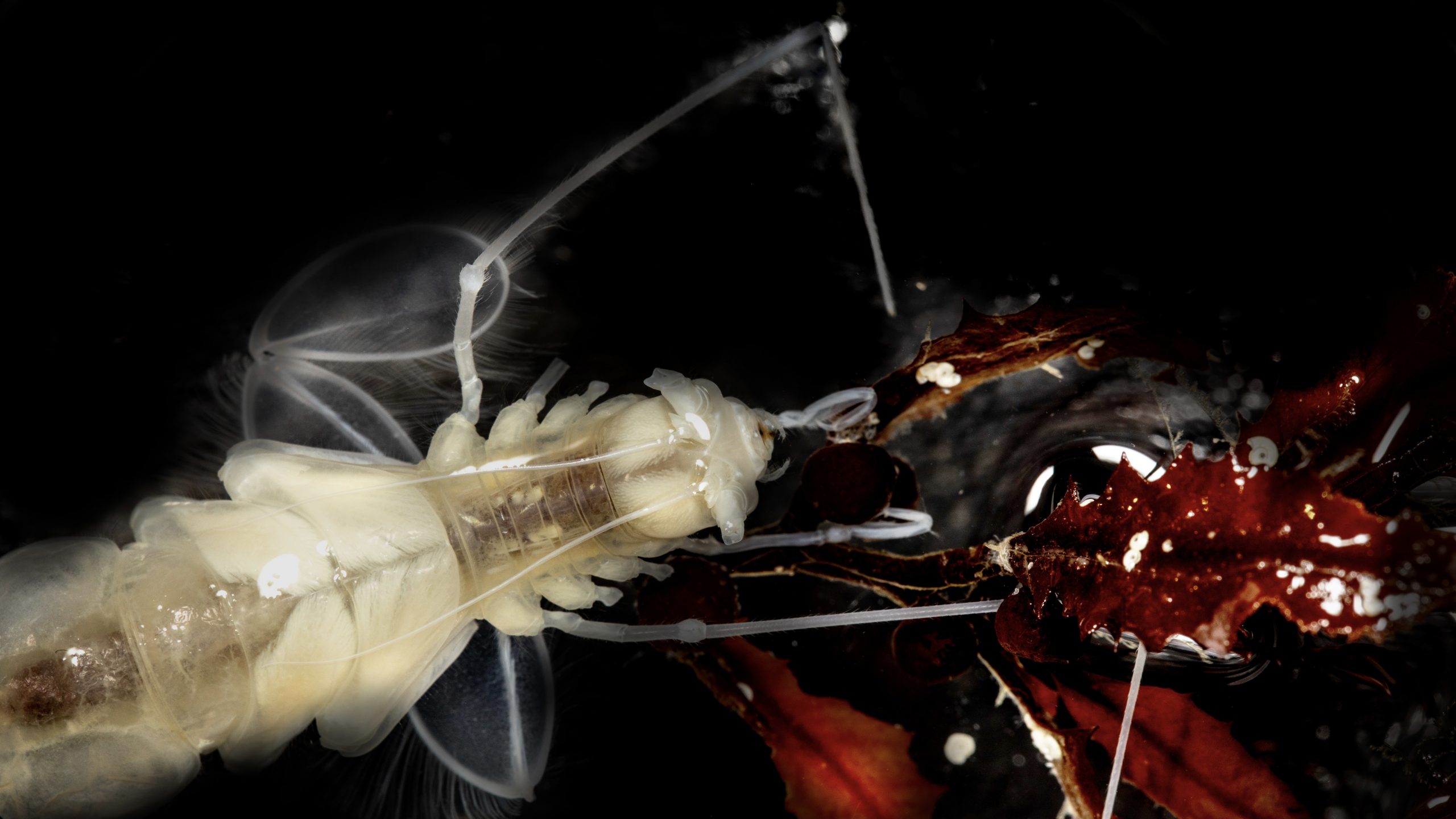
Swimming crustacean eats unlikely food source in the deep ocean
Increased capabilities in the human occupied submersible Alvin open a window on a rarely seen behavior.
Read MoreWHOI Sea Grant receives funding to support community-driven marine debris solutions
WHOI Sea Grant among recipients; funding will support innovative marine debris prevention and removal
Read MoreNew harmful algal blooms report
Updated national science strategy for harmful algal research and response builds on major accomplishments, findings.
Read MoreBlack Girls Dive Foundation Launches Program in Partnership with Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Three BGDF scholars will participate in the BGD IMPETUS-Internship at WHOI. This paid, 10-week summer program provides an opportunity for BGD Scholars to engage in cutting-edge research.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution and Cape Cod Children’s Museum partner for World Ocean Day celebration
The Cape Cod Children’s Museum (CCCM) is proud to announce that its Exploring Cape Cod Waters exhibit is now fully complete.
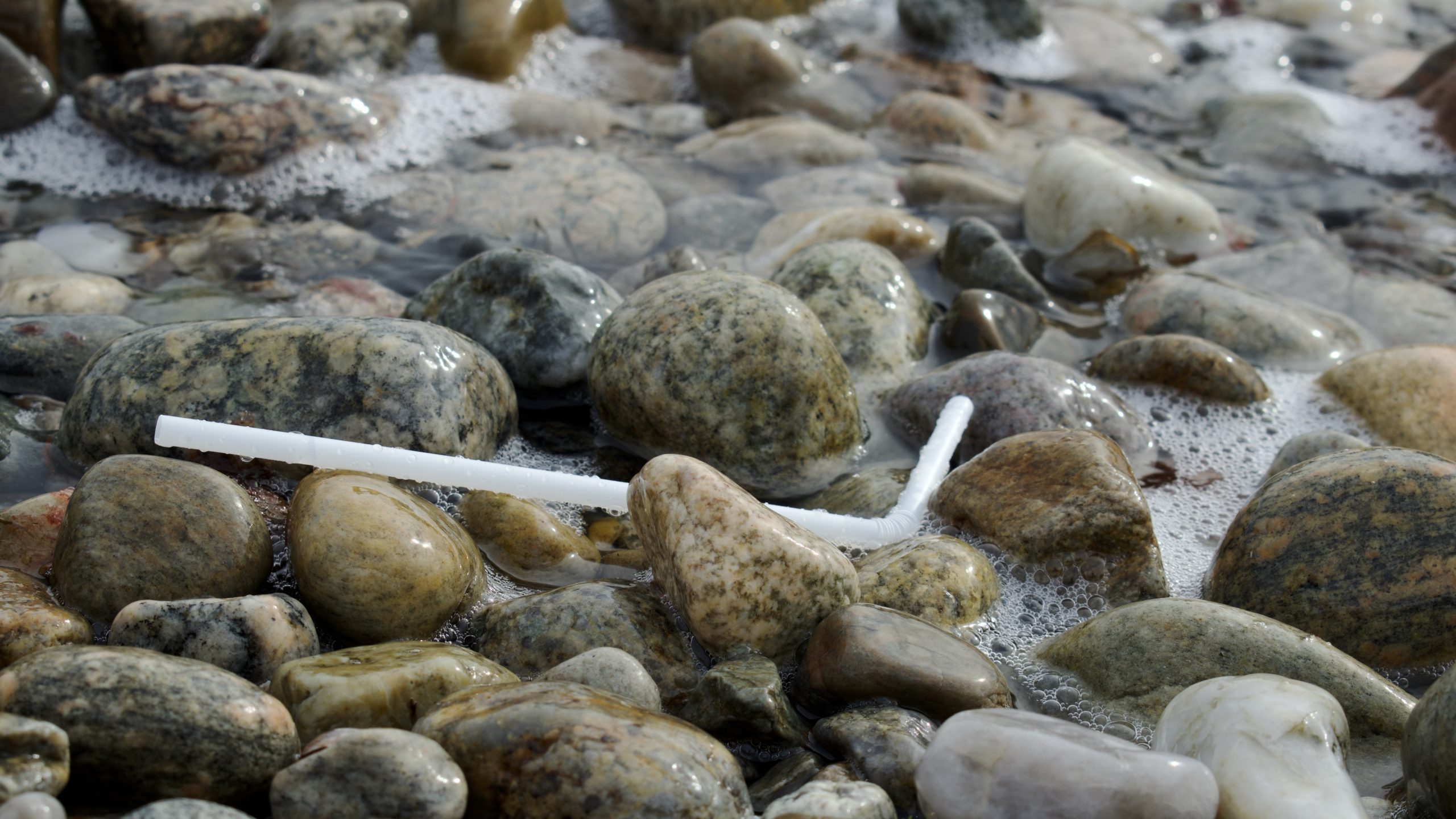
Read MoreSome Plastic Straws Degrade Quicker Than Others, New Study Shows
WHOI researchers determine lifetimes of drinking straws in the coastal ocean and develop a prototype bioplastic straw that degrades even faster than paper
Read MoreA new way of looking at plastics
WHOI researchers develop a new sustainability metric for plastic products
Read MoreFunders invests $250 million to supercharge ocean-based climate solutions
Coalition of philanthropic funders invests $250 million to supercharge ocean-based climate solutions Dubai, UAE — Many of the world’s leading philanthropic funders of ocean research and conservation have joined forces to…
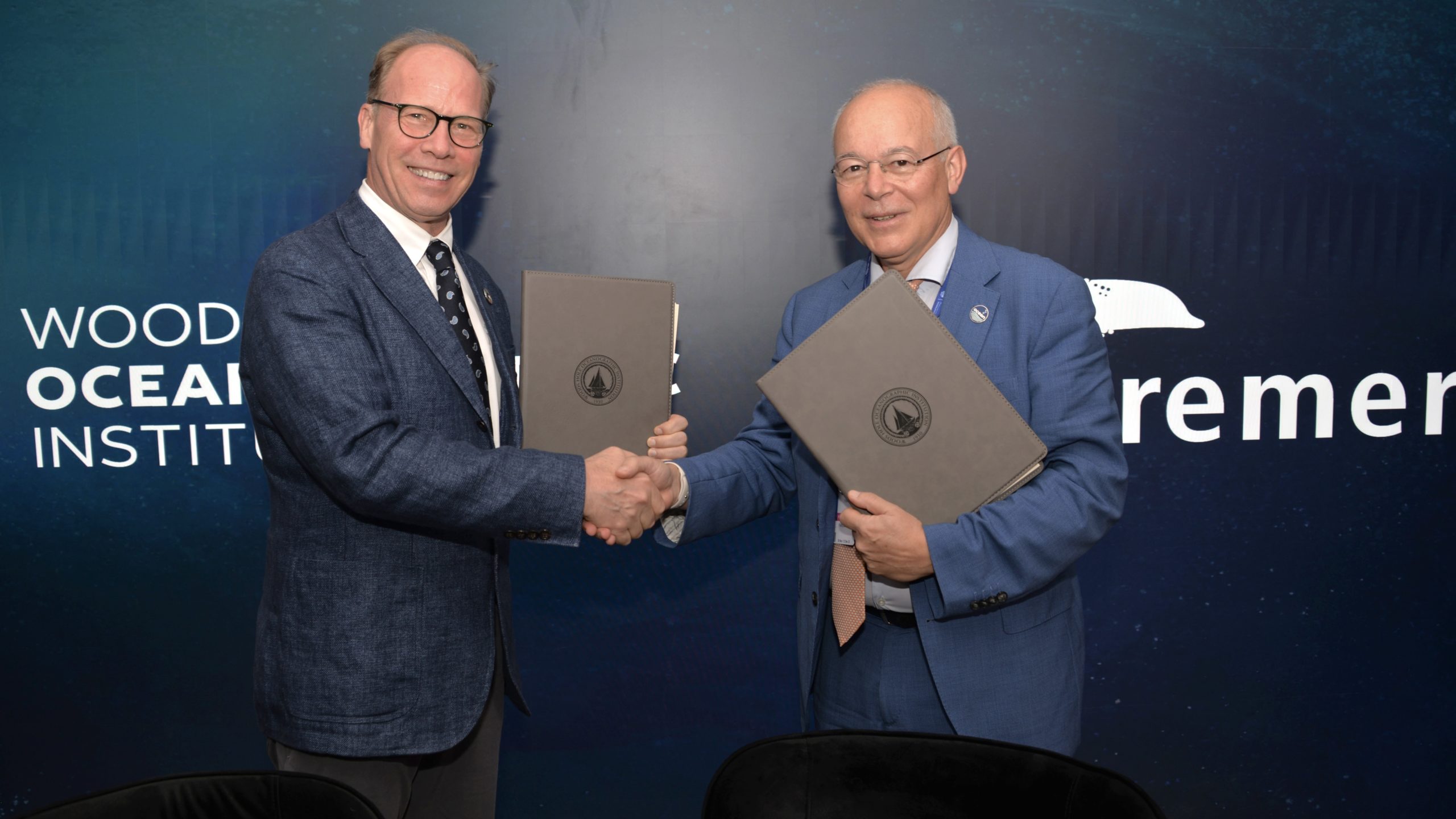
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution and IFREMER renew their partnership
Dubai, United Arab Emirates – Today, leaders at two of the world’s leading ocean science institutions signed a bilateral Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) extending their working partnership in the exploration,…
Read MoreNew Study Sheds Light on Why Some Animals Dive to The Dark, Deep Sea
Data from over 300 tags on large marine predators, along with shipboard sonar, point to the ecological importance of the ocean’s twilight zone
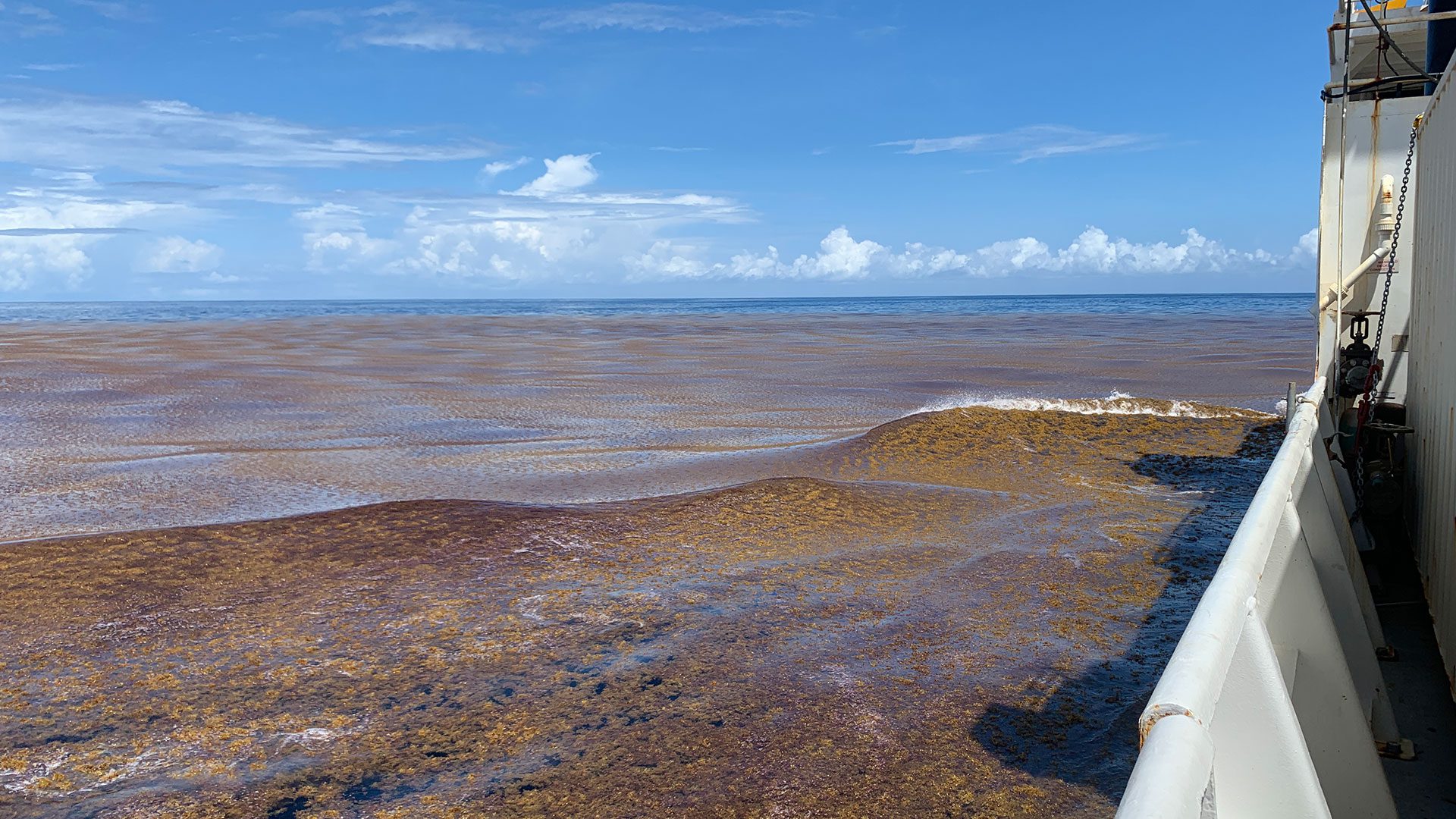
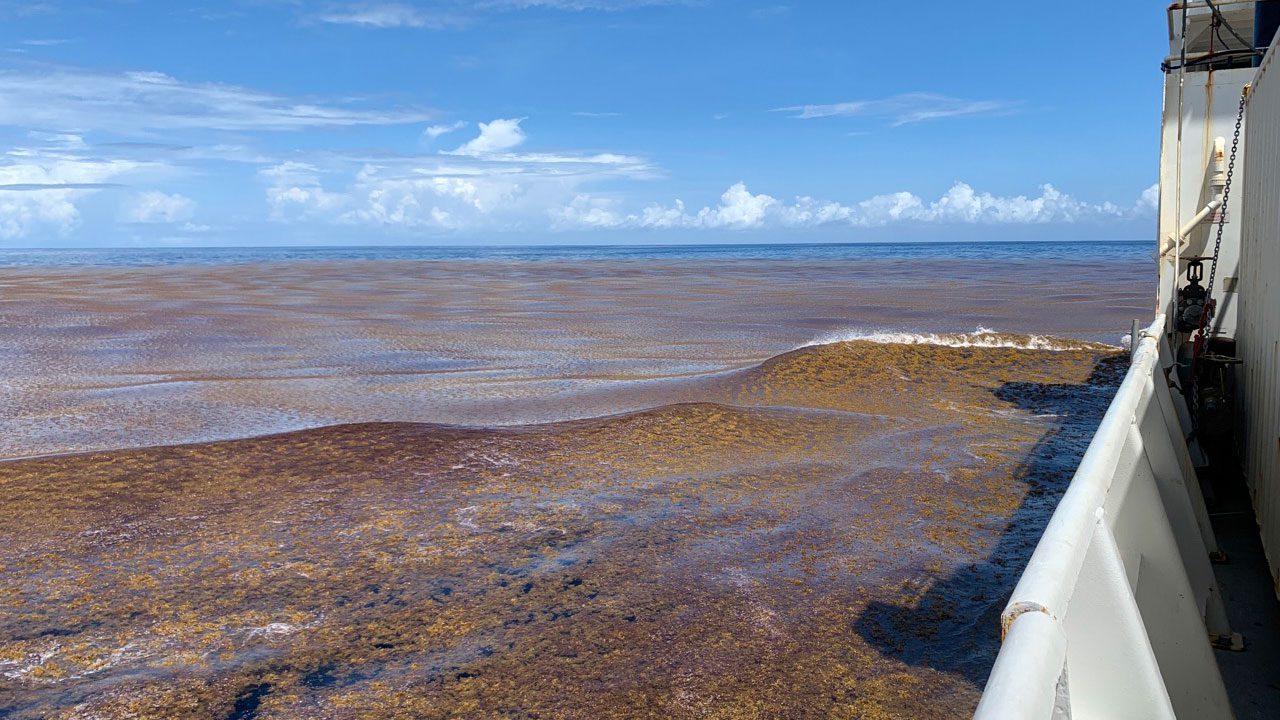
Read MoreStudy Clearly Identifies Nutrients as a Driver of the Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt
Findings could lead to locating nutrient sources and providing management options
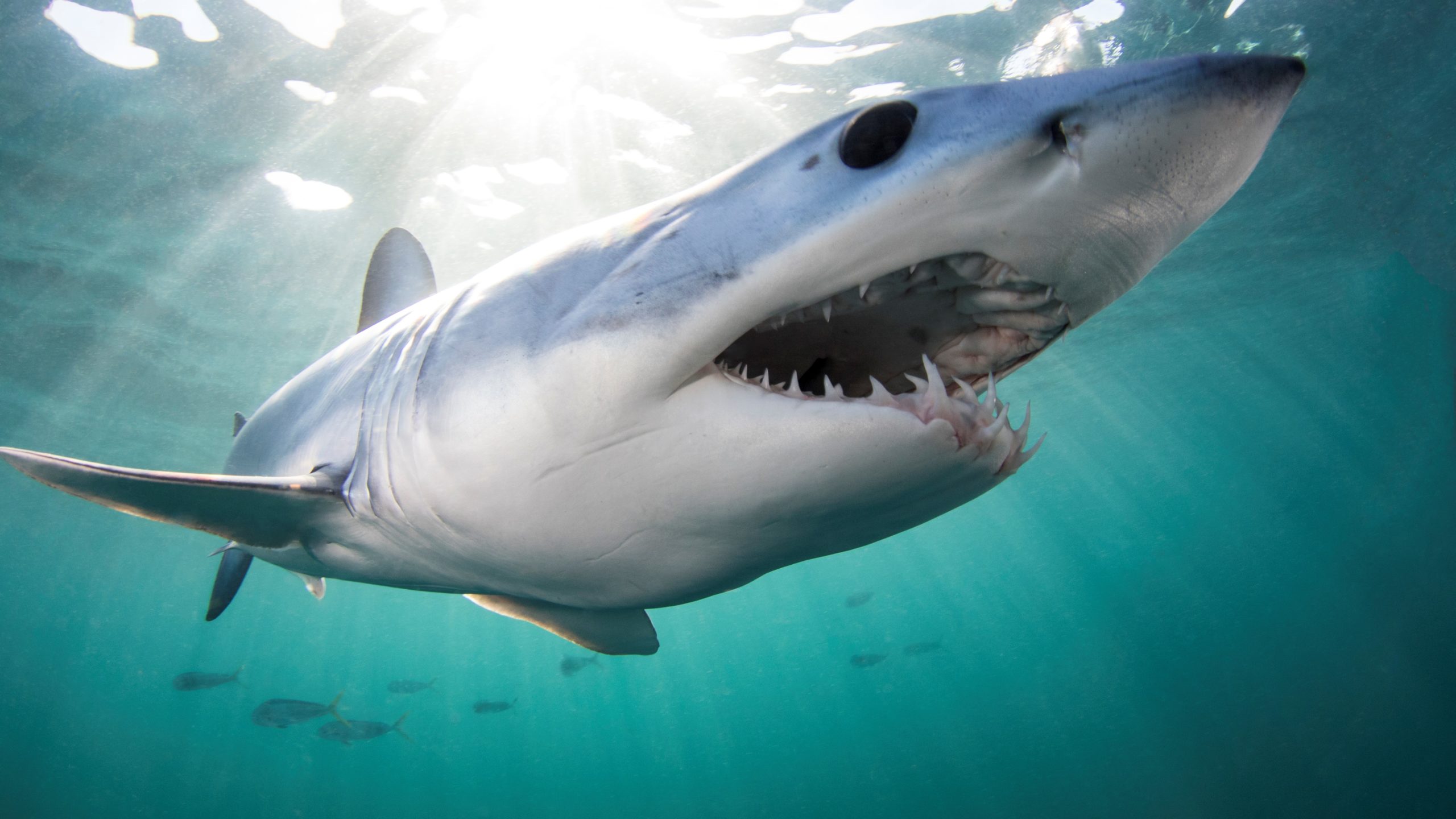
Read MoreTop Fish Predators Could Suffer Wide Loss of Suitable Habitat by 2100 Due to Climate Change
The impacts of climate change on habitats are already evident Woods Hole, MA — A study of 12 species of highly migratory fish predators—including sharks, tuna, and billfish such as…
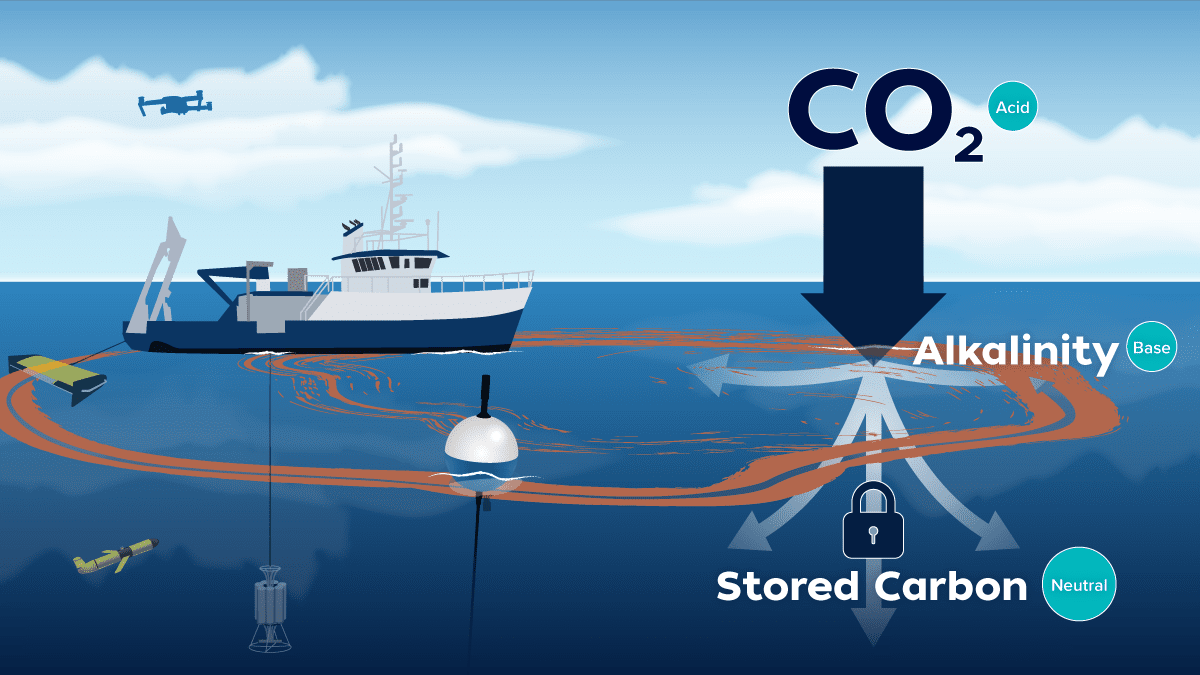
Read MoreOcean Alkalinity Enhancement Project Looks at Pulling Carbon Dioxide from the Atmosphere
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution project is part of the broader carbon to sea initiative
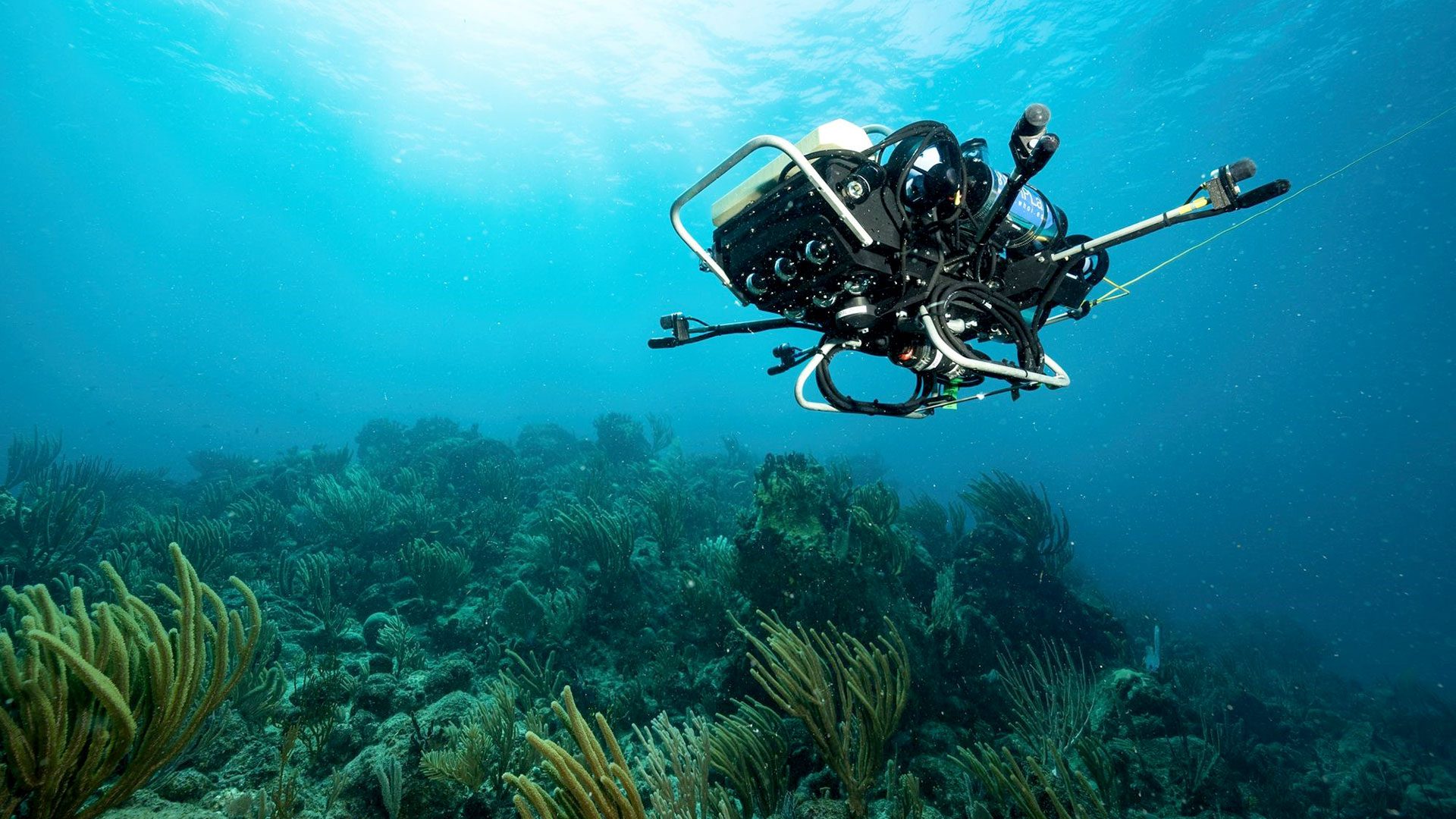
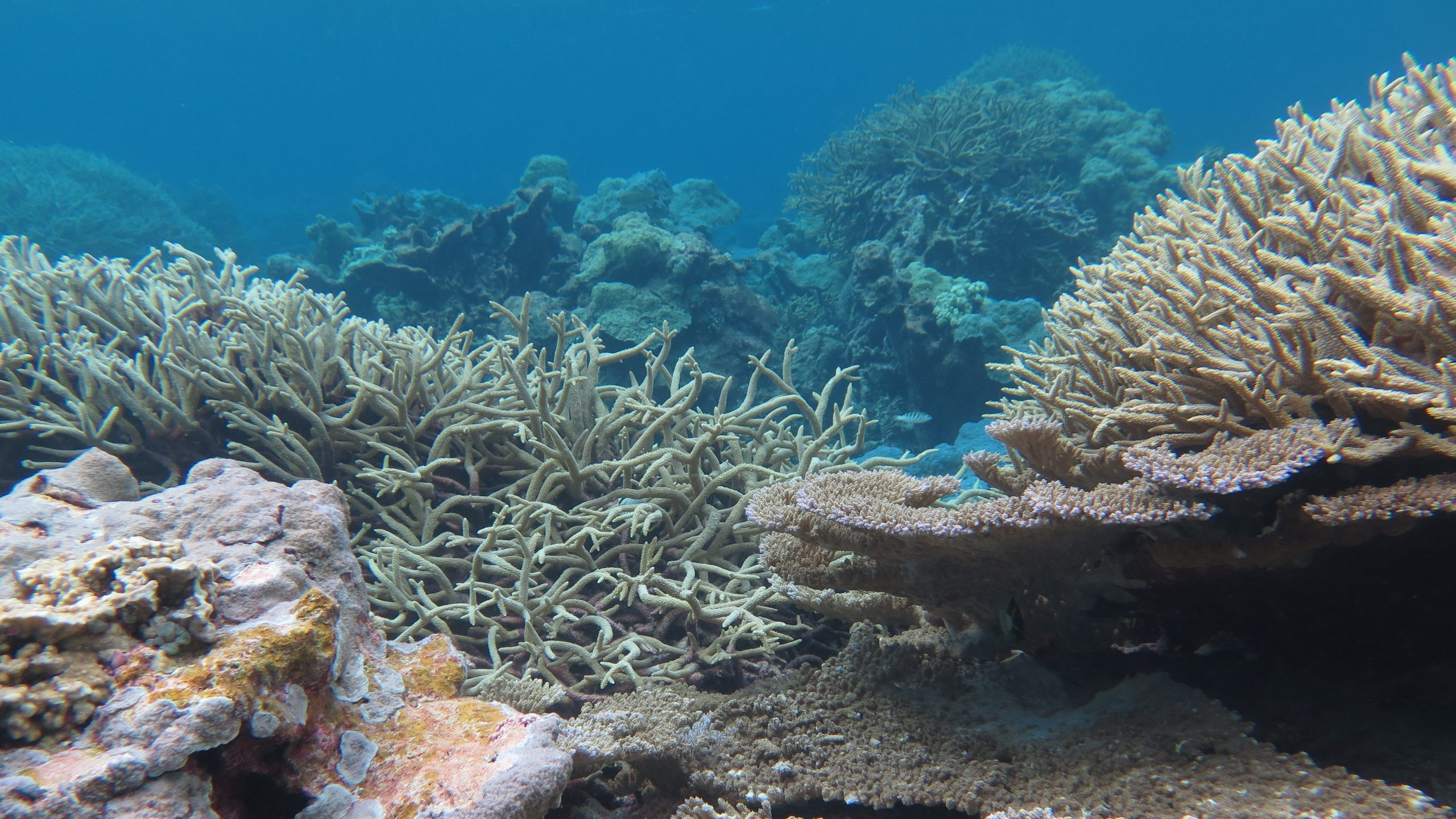
Read MoreToward a New Era of Reef Solutions
WHOI coral reef researchers propose a new technology-centered focus to study and conserve coral reefs
Read MoreThe Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt
Opportunistic sampling shows geographic scope of distribution, offer some of the first sampling opportunities
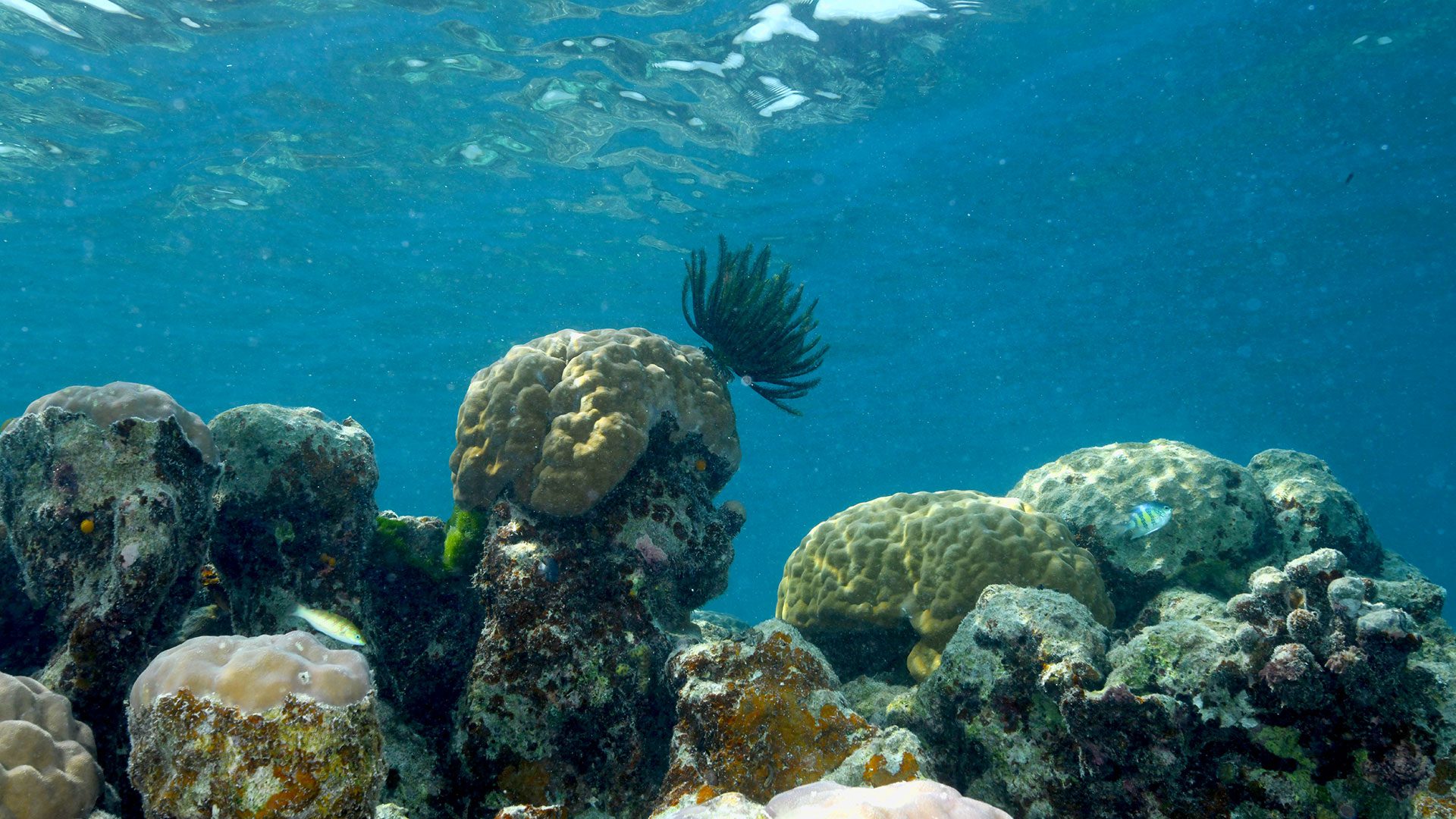
Read MorePalau’s Rock Islands Harbor Heat-resistant Corals
Scientists studying reefs in Palau have identified subgroups of a coral species that exhibit remarkable tolerance to the extreme heat associated with marine heatwaves
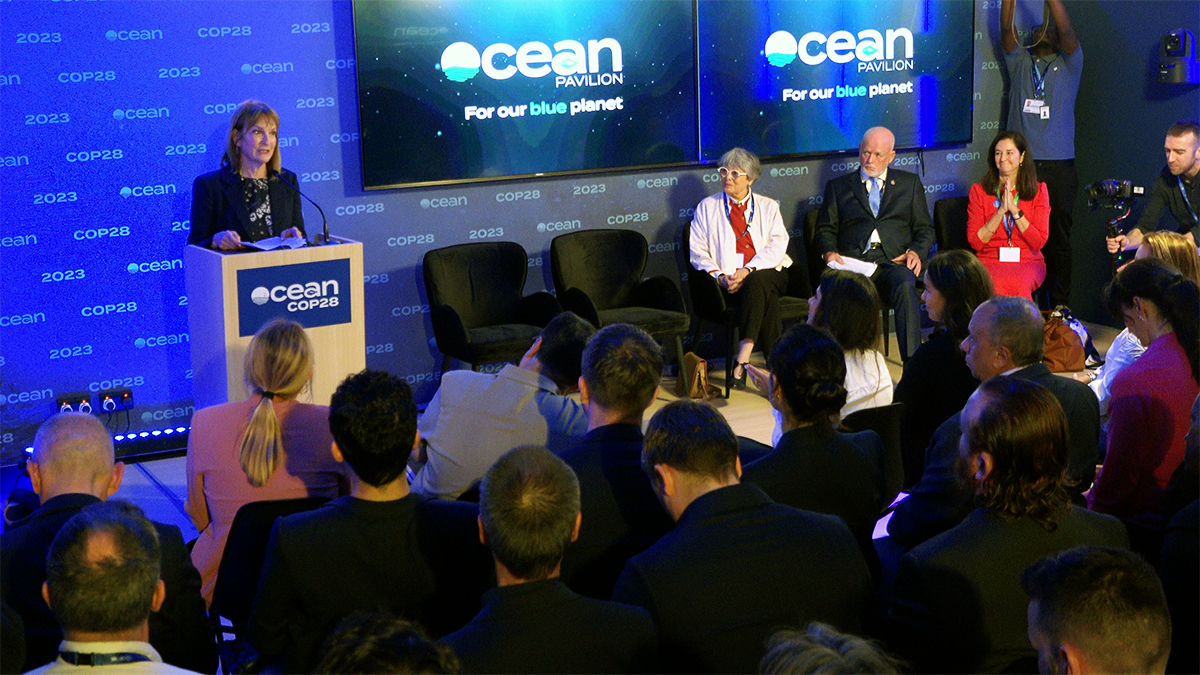
Read MoreThe Ocean Pavilion announces schedule of events for COP27
The Ocean Pavilion, the first time the ocean has been a singular focus of a pavilion inside the central “Blue Zone,” will host approximately 60 sessions over the two-week period, Nov. 6-18.
Read MoreWHOI-led projects receive UN endorsement as part of Decade of Ocean Science
Four projects led or co-led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists were named on World Ocean Day by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) to receive Endorsed Action status as part of the UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development 2021-2030.
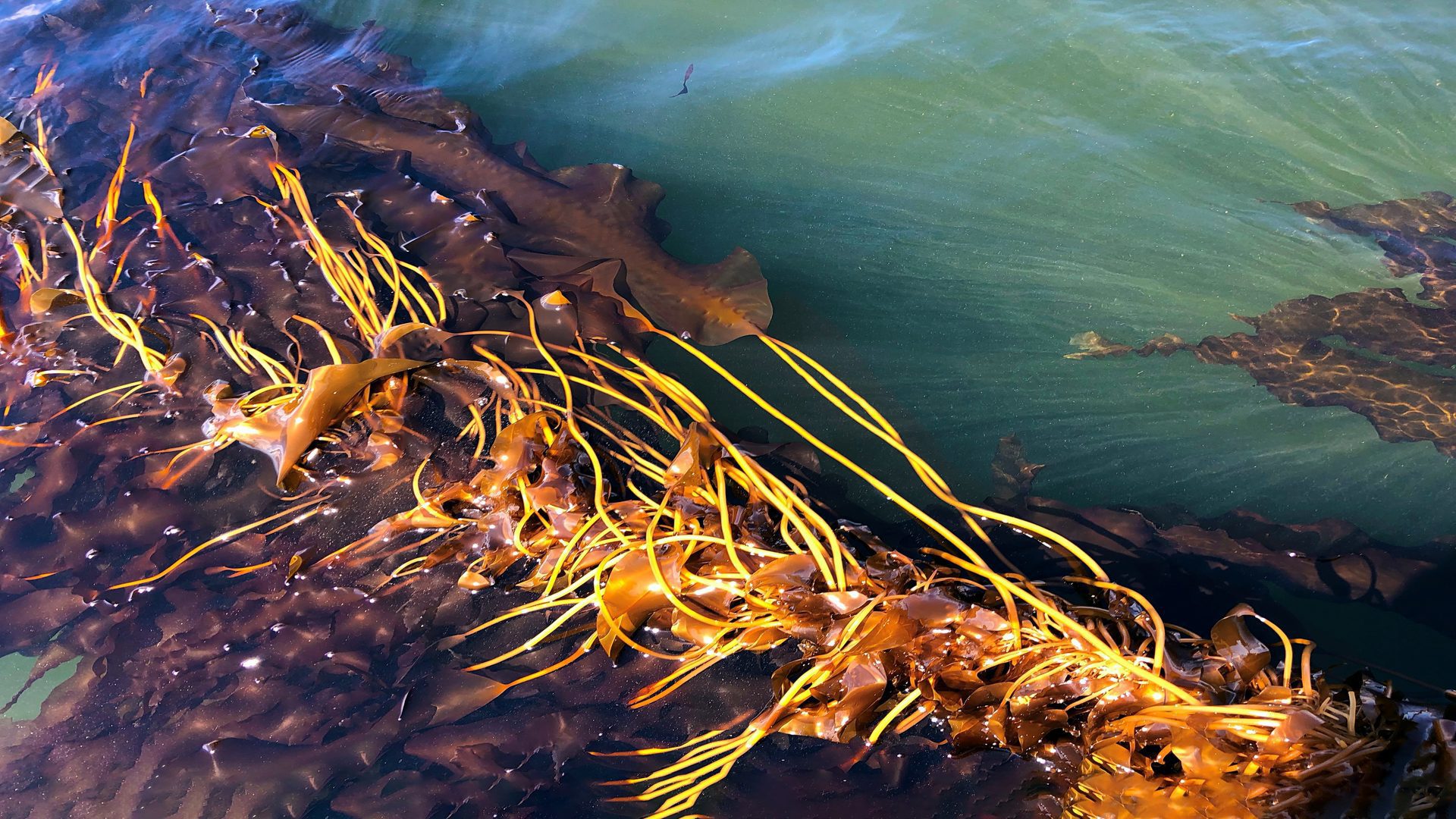
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution and collaborators launch world’s largest kelp map
To further investigate and track kelp growth and survival over time, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, The Nature Conservancy, University of California Los Angeles, and the University of California Santa Barbara have launched the world’s largest map of kelp forest canopies extending from Baja California, Mexico to the Oregon-Washington border.
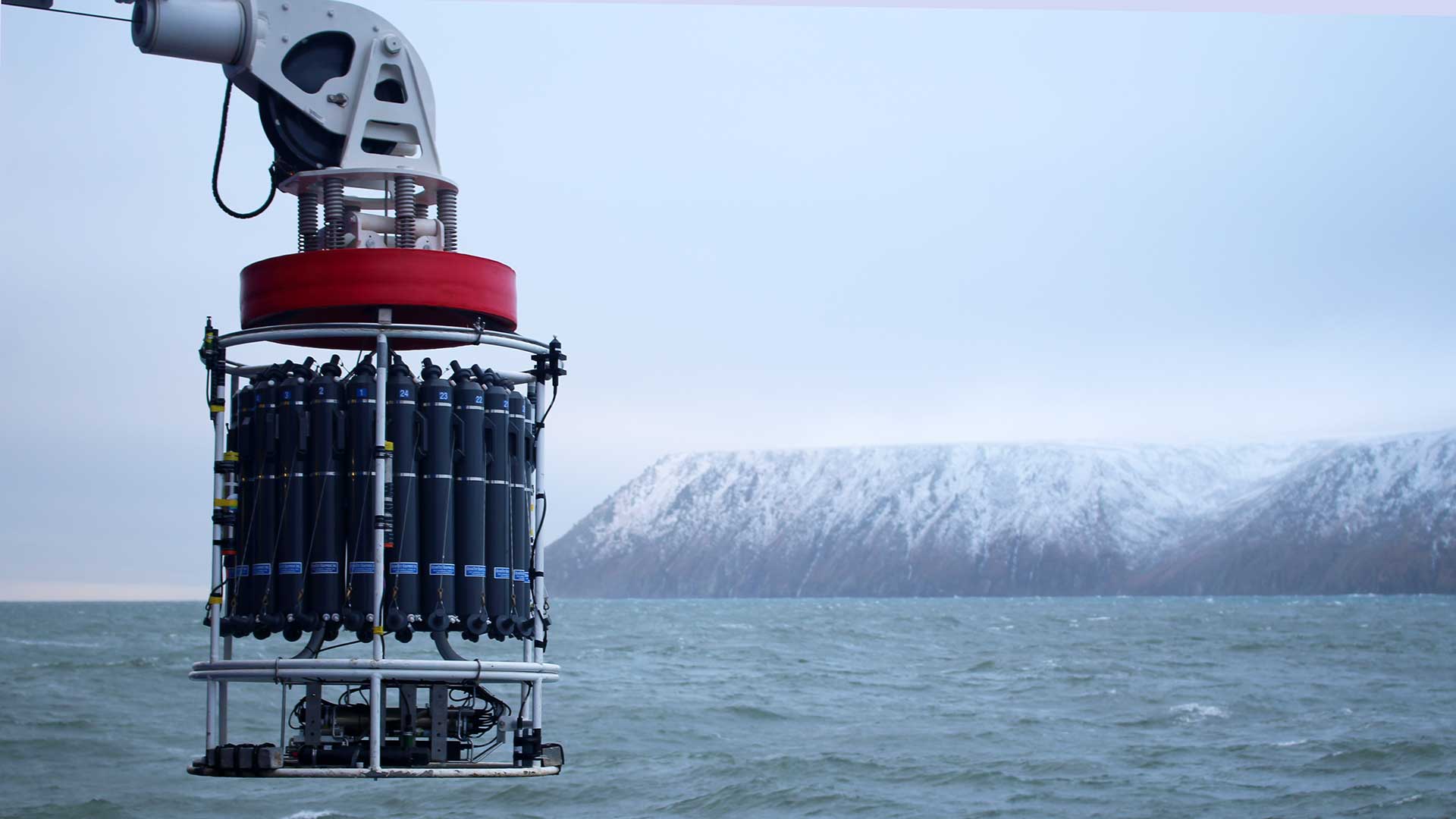
Read MoreNew ocean floats to boost global network essential for weather, climate research
WHOI and partners join together to launch approximately 100 new Argo floats across the Atlantic Ocean to collect data that supports ocean, weather and climate research and prediction
Read MoreDOE Funding will Support WHOI Research to Support Sustainable Development of Offshore Wind
Woods Hole, MA — The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has received $750,000 in funding from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) to develop next‐generation autonomous robotic technology for environmental…
Read MoreWHOI multidisciplinary team selected for prestigious National Science Foundation Program
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has been selected by the U.S National Science Foundation (NSF) for phase one of a two-part Convergence Accelerator Program, a $21 million investment to advance use-inspired solutions addressing national-scale societal challenges. WHOI is one of sixteen teams across the US chosen to participate in Track E: The Networked Blue Economy, which aims to create a smart, integrated, connected, and open ecosystem for ocean innovation, exploration, and sustainable utilization.
Read MoreStudy Finds Growing Potential for Toxic Algal Blooms in the Alaskan Arctic
A warming Arctic presents potential new threats to humans and marine wildlife in the fast-changing region Changes in the northern Alaskan Arctic ocean environment have reached a point at…
Read MoreWHOI advancing a seaweed solution to develop new kelp strains
A leader in ocean science, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is embarking on a study of how new seaweed strains could further enhance the burgeoning seaweed industry and offer solutions to some of the world’s pressing challenges. This research is funded in part by World Wildlife Fund (WWF) with support from the Bezos Earth Fund.
Read More