News Releases
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and Cape Cod Children’s Museum partner for World Ocean Day celebration
The Cape Cod Children’s Museum (CCCM) is proud to announce that its Exploring Cape Cod Waters exhibit is now fully complete.
Read MoreSpring 2024: Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Elects New Trustees and Corporation Members
At Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s (WHOI’s) Spring Joint Meeting of the Board and Corporation today, Institution leaders elected three new Trustees and seven new Corporation Members.
Read MoreSea Surface Temperature Research Provides Clear Evidence of Human-Caused Climate Change
New oceanic research provides clear evidence of a human “fingerprint” on climate change and shows that specific signals from human activities have altered the seasonal cycle amplitude of sea surface temperatures.
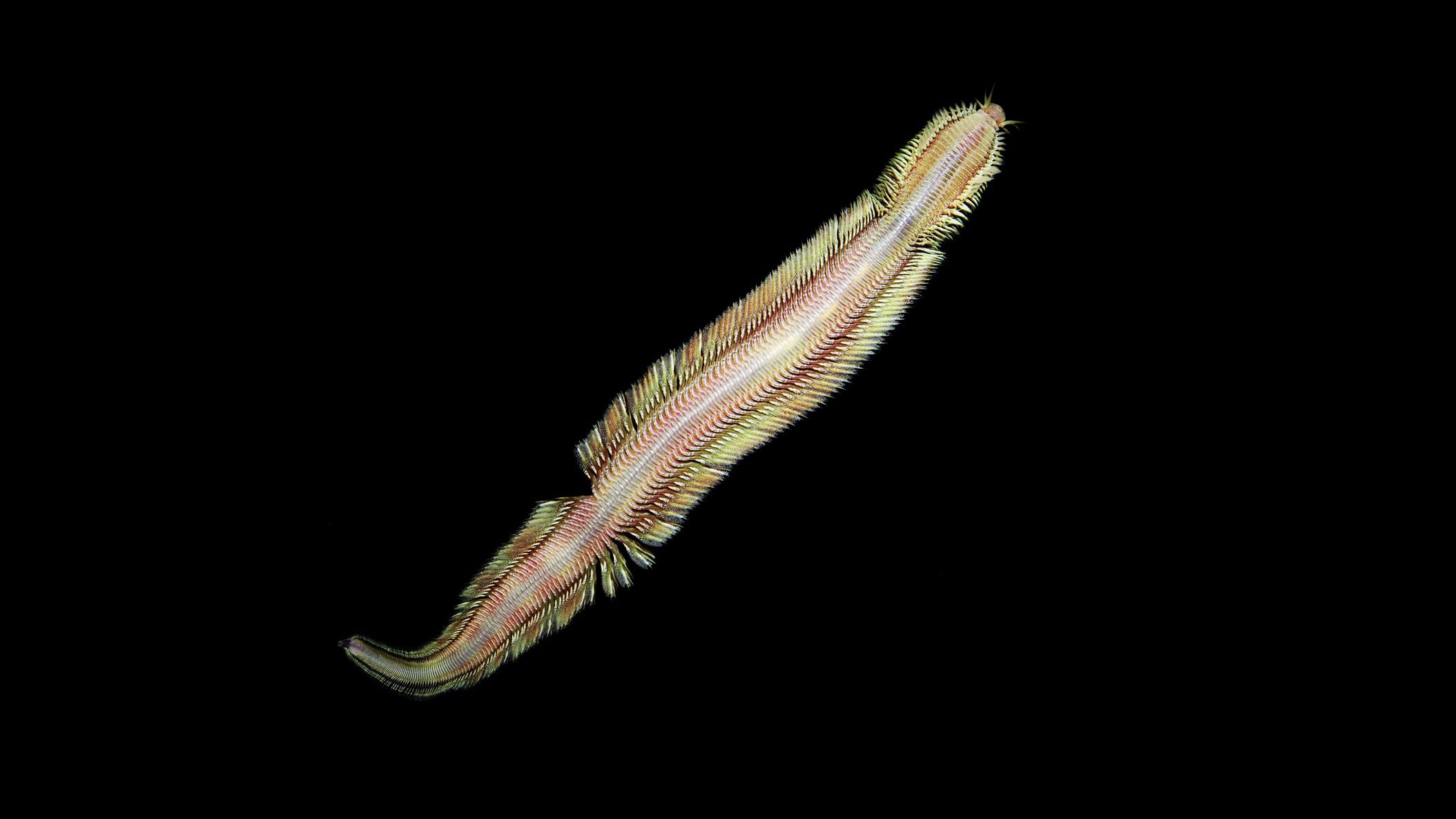
Read MoreNew Deep-Sea Worm Discovered at Methane Seep Off Costa Rica Named after Alvin Pilot Bruce Strickrott
The creature raises the number of new species found by scientists studying these seemingly inhospitable ecosystems to 48 Woods Hole, Mass. — Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), along with…
Read MoreNew federal funding to accelerate ocean-climate resilience
WHOI-led team receives funding to help small businesses prepare communities across the nation for climate change
Read MoreFall 2023: Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Elects New Trustee and Corporation Members
Woods Hole, MA – At Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Fall Joint Meeting of the Board and Corporation today, Institution leaders elected two new Trustees and seven new Corporation Members. “It…
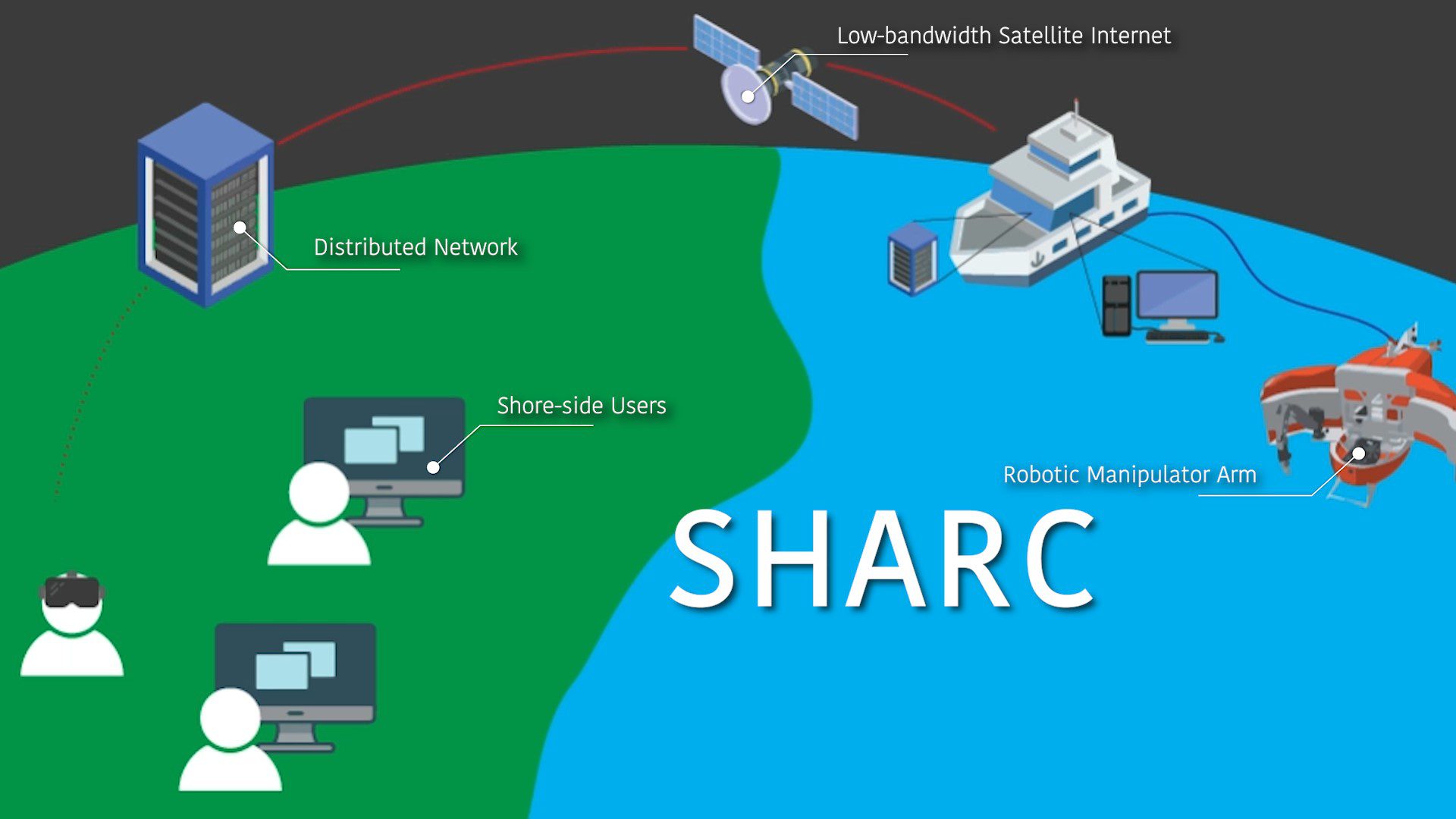
Read MoreA new framework for oceanographic research
The Shared Autonomy for Remote Collaboration (SHARC) framework “enables remote participants to conduct shipboard operations and control robotic manipulators.
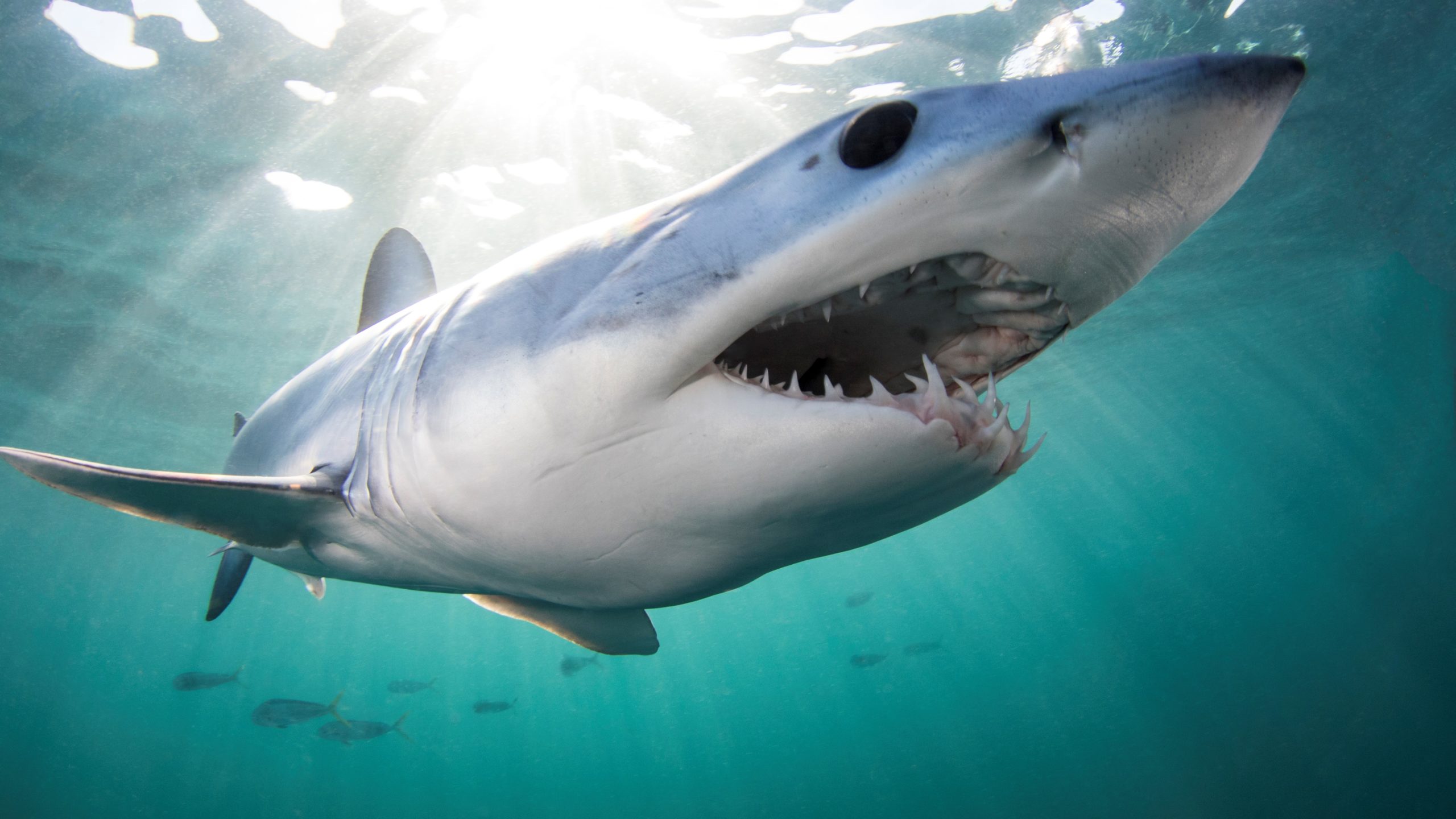
Read MoreTop Fish Predators Could Suffer Wide Loss of Suitable Habitat by 2100 Due to Climate Change
The impacts of climate change on habitats are already evident Woods Hole, MA — A study of 12 species of highly migratory fish predators—including sharks, tuna, and billfish such as…
Read MoreWHOI partners with Cape Cod Children’s Museum to create a new interactive, water exhibit
“Exploring Cape Cod Waters – Become an Ocean Ambassador” now open
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution Elects New Trustee and Corporation Members
The Board of Trustees of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) today welcomed one new Board Member and eight new Corporation Members.
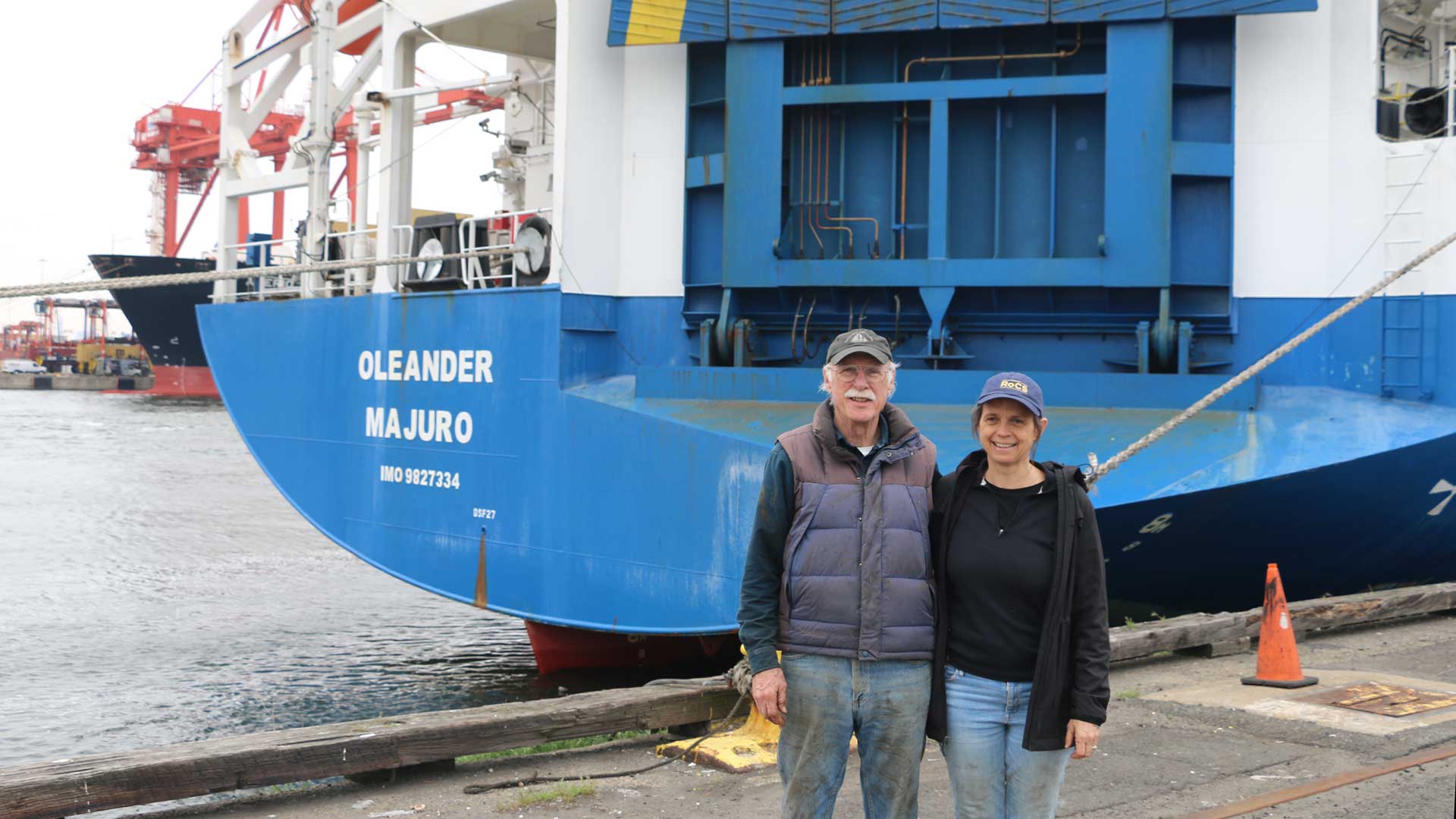
Read MoreOleander Project Transfers to WHOI Management
30-year effort to monitor the Gulf Stream and Northwest Atlantic circulation will continue providing crucial data and insights
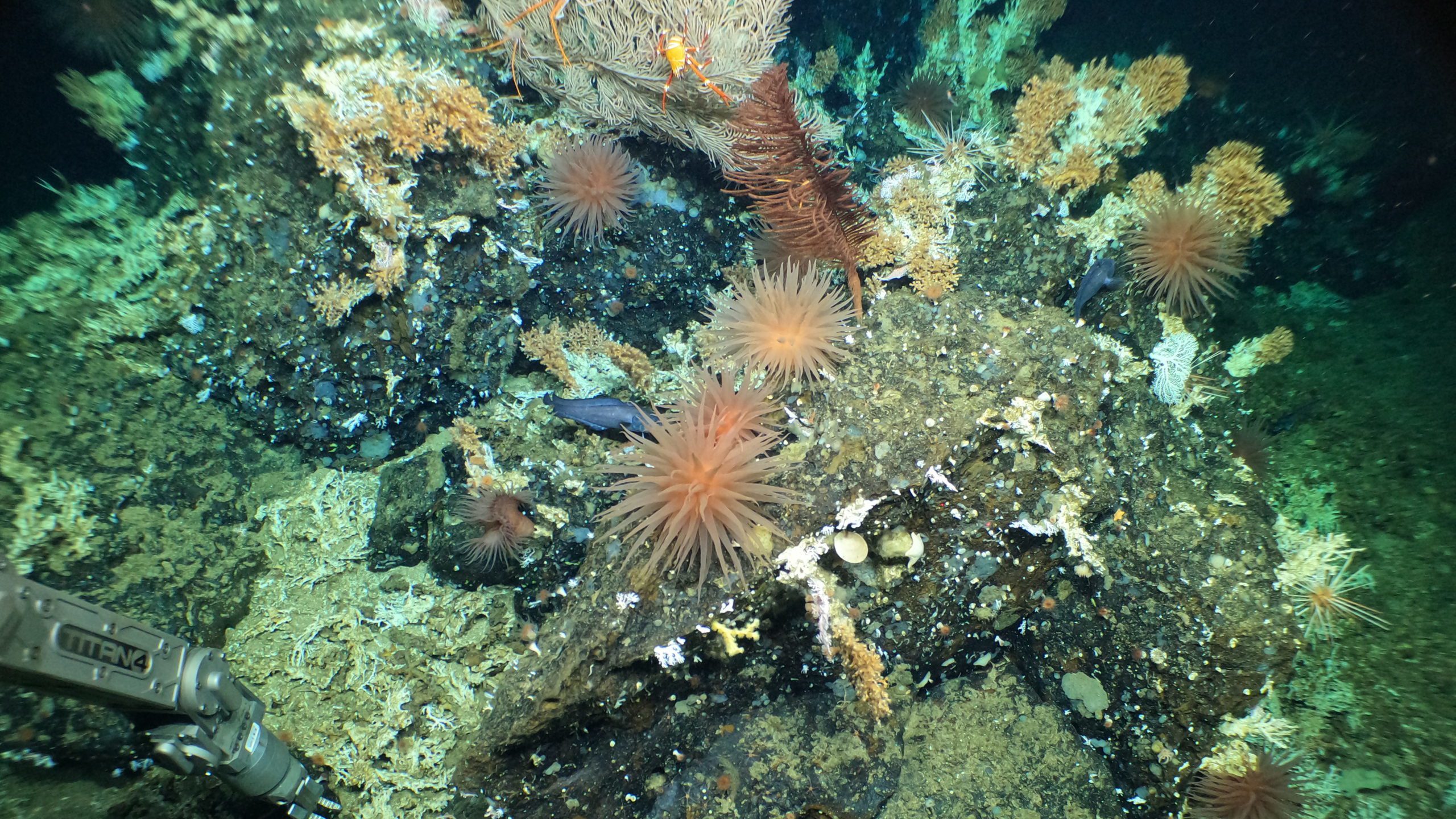
Read MoreScientists Aboard R/V Atlantis Discover Deep-Sea Coral Reefs in the Galápagos
Observations using the newly upgraded human-occupied vehicle Alvin are the first of a deep-water coral reef in the Galápagos Marine Reserve.
The reefs are located at depths between 400-600 m, atop previously unmapped seamounts.
CINAR Names Four New Fellows in Quantitative Fisheries and Ecosystems Science
The goal of the fellowship program is to engage early-career scientists in research that supports the training and education in the he assessment and management of living marine resources in the Northeast U.S.
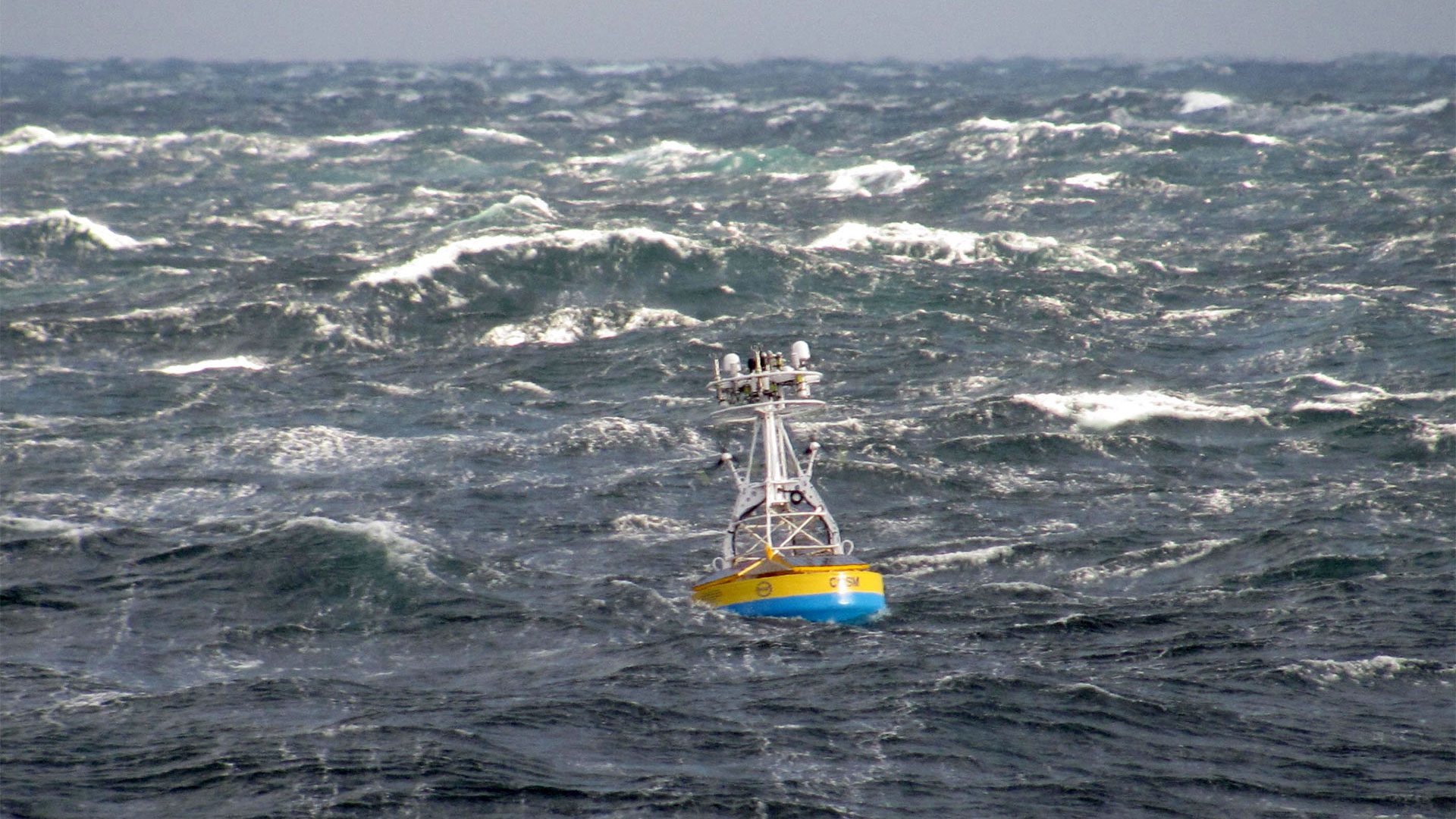
Read MoreOcean Observatories Initiative‘s Pioneer Array Relocating to Southern Mid-Atlantic Bight
New location offers opportunities for new science observations with continued open access
Read MoreStudy Examines the Impact of Coral Chemical Compounds on Reef Composition and Health
The study found that the organic chemical compounds produced through metabolism —known as metabolites or exudates—vary significantly by coral species and that the compounds impact the abundances and compositions of reef microorganisms differently.
Read More“Digital Reefs” awarded $5 million
The National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) $5 million to participate in NSF’s ground breaking Convergence Accelerator Program. The project, led by WHOI scientist Anne Cohen, builds the world’s first Coral Reef Digital Twin, a 4-dimensional virtual replica of a living coral reef powered by state-of-the art data and models.
Read More