News Releases
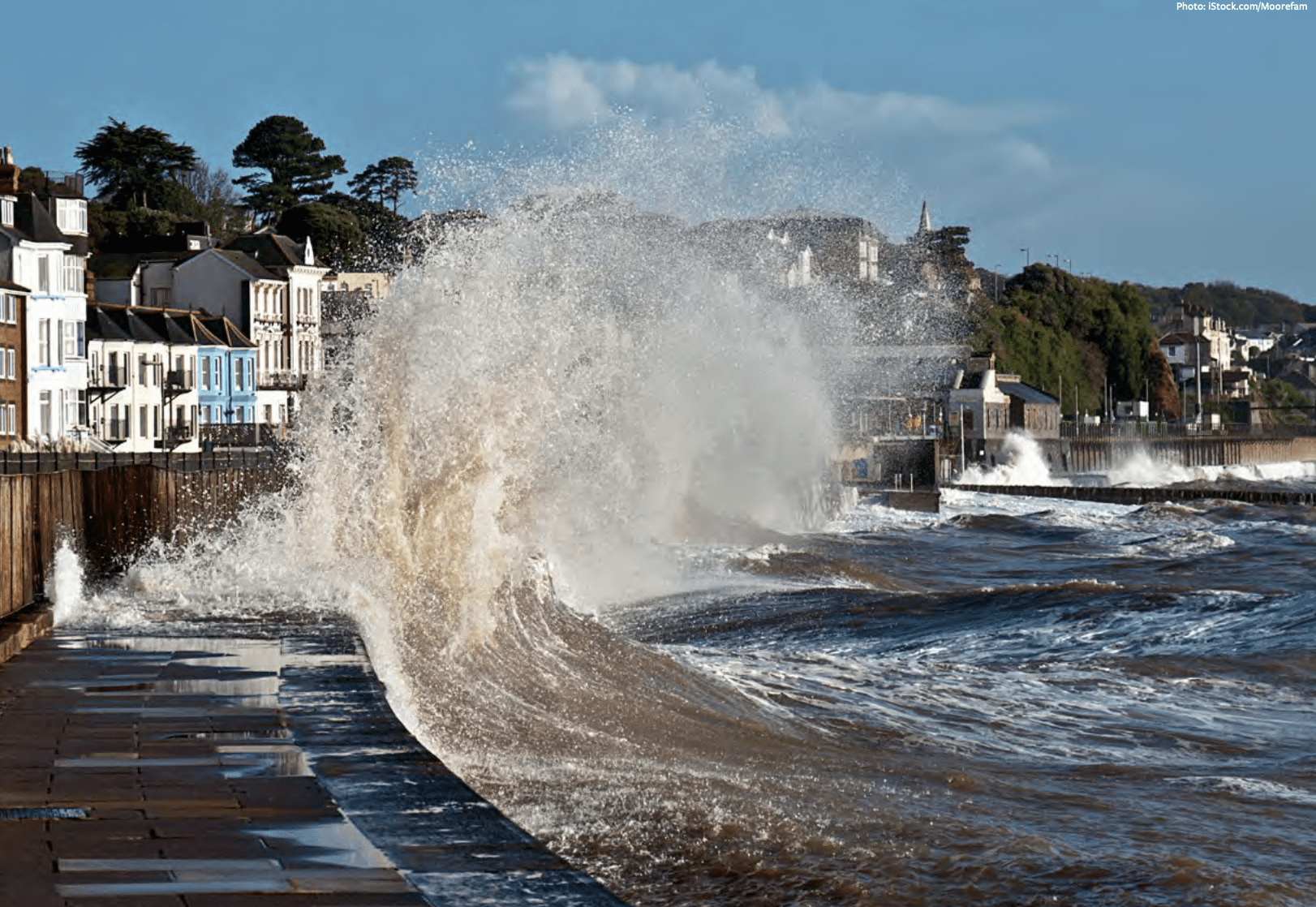
New study finds rate of U.S. coastal sea level rise doubled in the past century
The study finds that the rate of U.S. coastal sea-level rise has more than doubled in the past 125 years.
Read MoreNew report takes in-depth look at factors contributing to sea level rise
Sea levels in many areas across the global ocean are rising. Since the turn of the 20th century, the seas have risen between six and eight inches globally.
Read MoreWHOI Will Host Public Forum on Sea Level Rise
sea level rise, Morss Colloquium, polar ice cap, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Read MoreRapid Sea Level Rise in the Arctic Ocean May Alter Views of Human Migration
Scientists have found new evidence that the Bering Strait near Alaska flooded into the Arctic Ocean about 11,000 years ago, about 1,000 years earlier than widely believed, closing off the…
Read MoreNew Coral Dating Technique Helps Resolve Changes in Sea Level Rise in the Past
Corals from Papua New Guinea and Barbados indicate that changes in sea level, one of the key indexes for global climate change, may have been more frequent in the past…
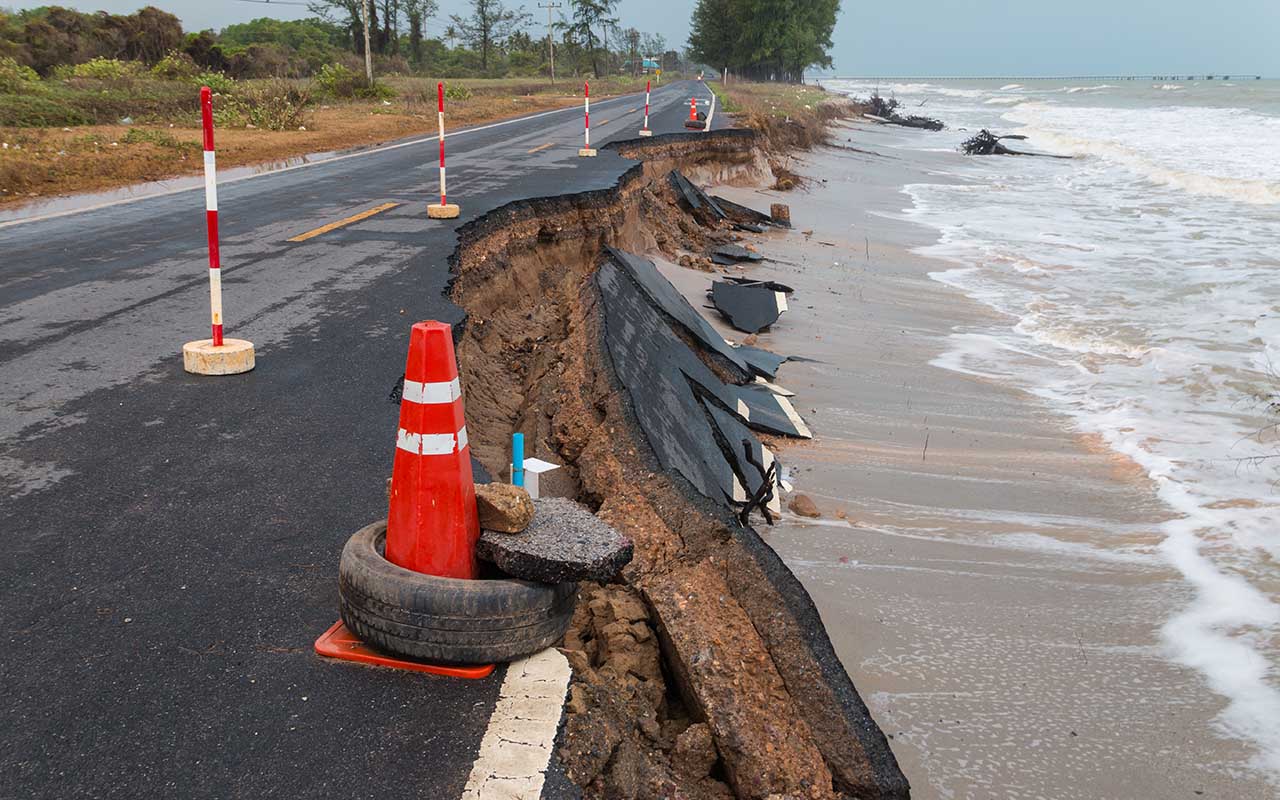
Read MoreStudy reveals rapid sea-level rise along U.S. Atlantic coast in 18th century
During the 18th century, sea levels along a stretch of the Atlantic coast of North America were rising almost as fast as they were during the 20th Century, reveals a new study.
Read MoreWeddell seals in the Antarctic strategically time their most extreme dives to maximize foraging
New research from WHOI and partners sheds light on a novel dive foraging strategy.
Read MoreOcean leaders renew focus on the sea ahead of UN summit
WHOI and partners pen Baku Declaration, emphasizing the need for ocean observatories to meet climate and biodiversity goals at COP29
Read MoreHuman Activity Is Causing Toxic Thallium to Enter the Baltic Sea, According to New Study
Human activities account for a substantial amount – anywhere from 20% to more than 60% – of toxic thallium that has entered the Baltic Sea over the past 80 years, according to new research by scientists affiliated with WHOI and other institutions.
Read MoreWHOI Sea Grant commits $1.7 million to coastal research
The funding will support five major projects from watershed contaminant monitoring to data collection for sustainable fisheries and more
Read MorePaleoclimate data show land will warm more than sea
Understanding differences in land vs. sea temperatures may improve climate models, says WHOI study
Read MoreArctic Hydrothermal Vent Site Could Help in Search for Extraterrestrial Life
When scientists discovered a hydrothermal vent site in the Arctic Ocean’s Aurora hydrothermal system in 2014, they did not immediately realize just how exciting their discovery was.
Read MoreWHOI to Launch New Center for Ocean and Climate Research
Today WHOI announced the establishment of the Francis E. Fowler IV Center for Ocean and Climate to seek new knowledge and solutions at the intersection of oceanography and climate science. A generous gift from Francis E. Fowler, IV established the center and will enable it to immediately commence operations.
Read MoreStudy Finds No Direct Link Between North Atlantic Ocean Currents, Sea Level Along New England Coast
A new study by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) clarifies what influence major currents in the North Atlantic have on sea level along the northeastern United States. The study, published June 13 in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, examined both the strength of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)—a conveyor belt of currents that move warmer waters north and cooler waters south in the Atlantic—and historical records of sea level in coastal New England.
Read MoreWHOI Names Rick Murray Deputy Director & Vice President for Research
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) announces that Dr. Richard W. Murray has accepted the position of the Deputy Director & Vice President for Research of the institution. He will assume…
Read MoreWHOI, Falmouth Win Second Seaport Economic Council Grant
Members of the Massachusetts Seaport Economic Council (SEC) gave the green-light to a $1 million grant proposal from the Town of Falmouth and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI). The SEC, chaired by Lieutenant Governor Karyn Polito, promotes economic growth in the maritime sector through competitive grants to municipalities and their partners.
Read MoreWhy Is Sea Level Rising Faster in Some Places Along the U.S. East Coast Than Others?
Sea levels are rising globally from ocean warming and melting of land ice, but the seas aren’t rising at the same rate everywhere. Sea levels have risen significantly higher in some U.S. East Coast regions compared to others. A new study led by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) reveals why.
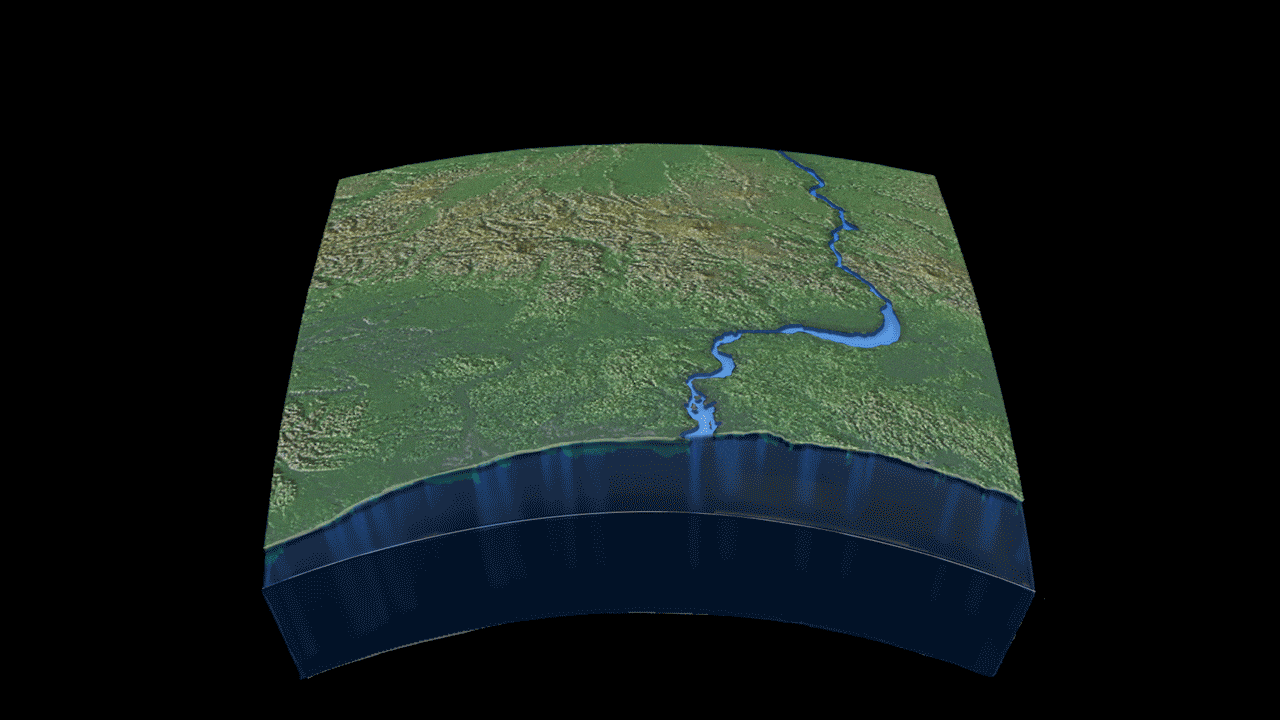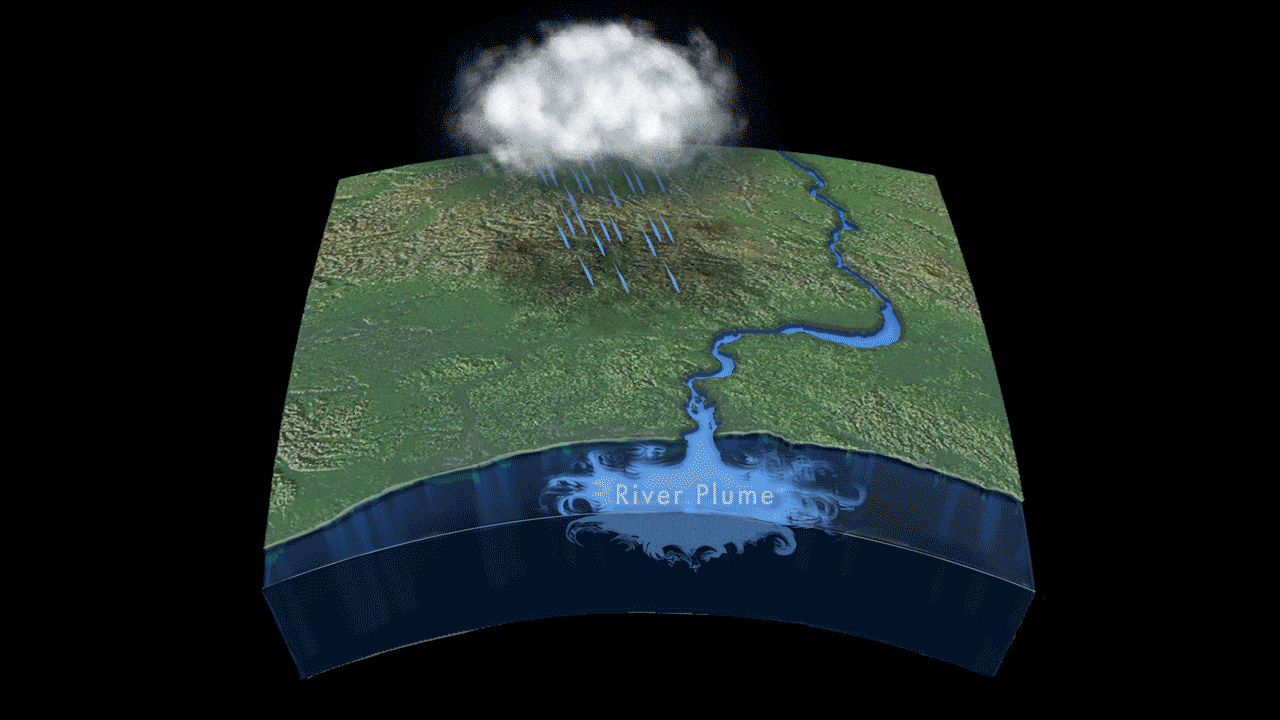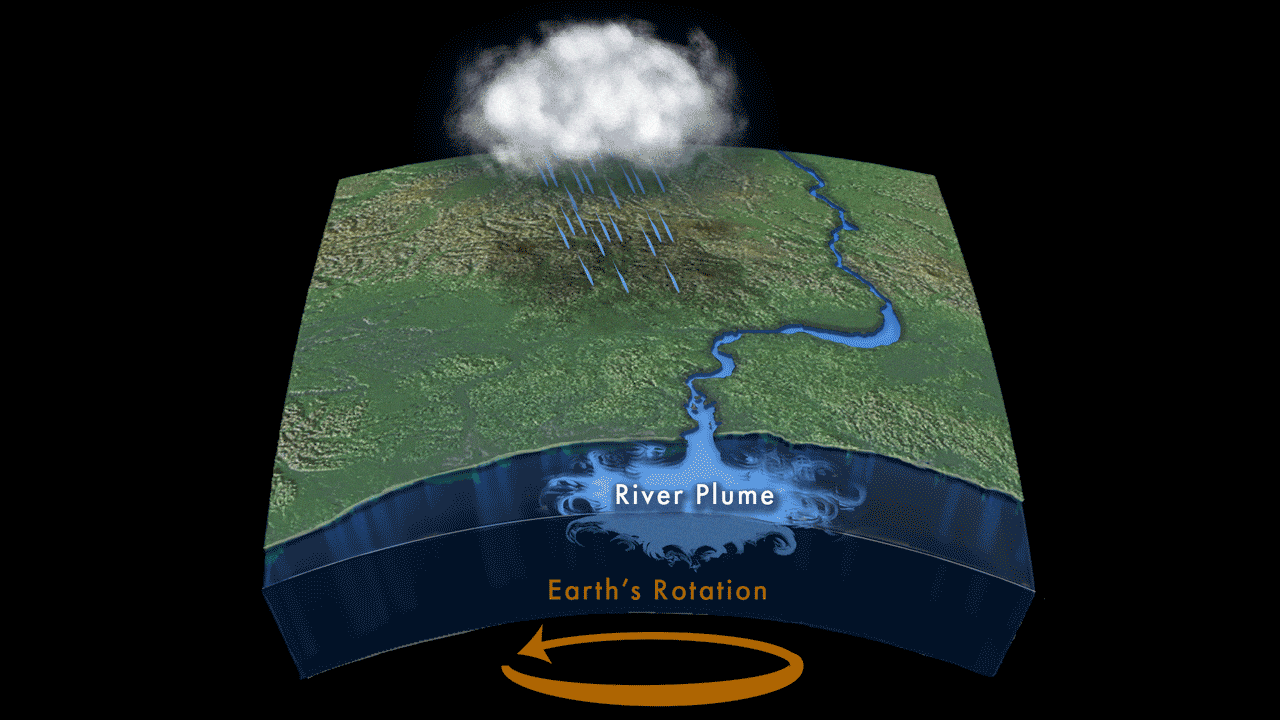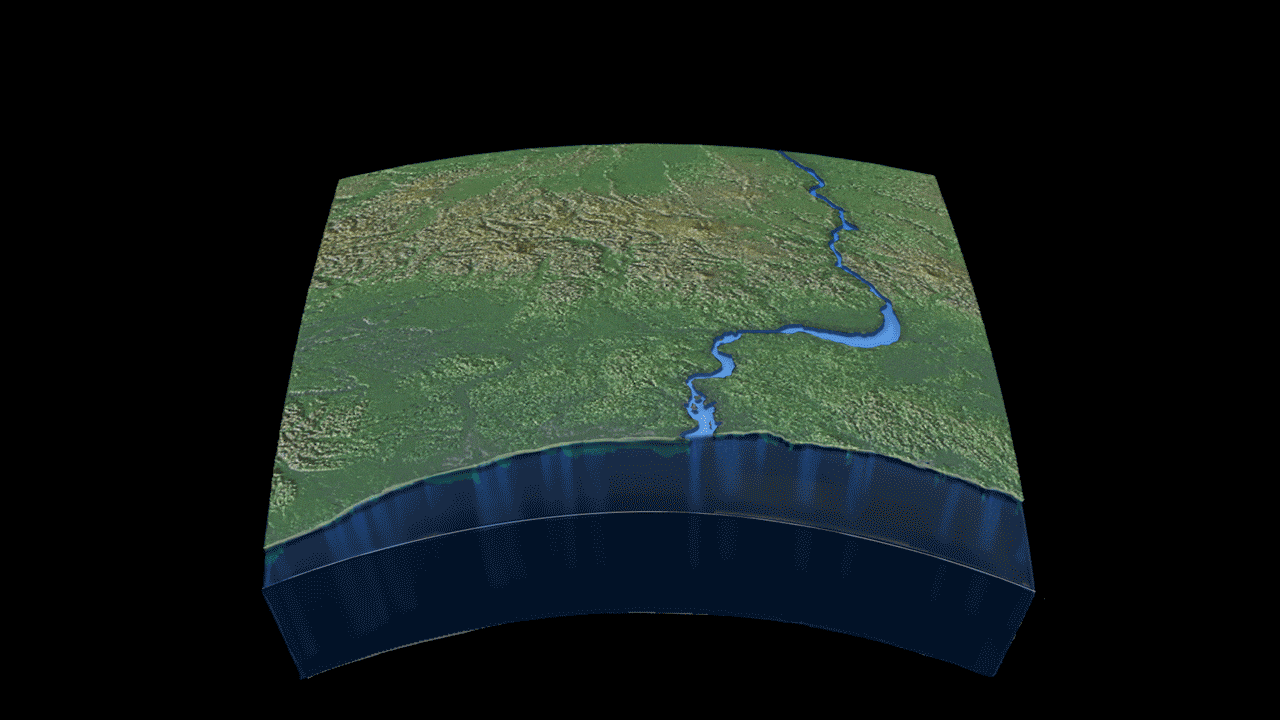
Read MoreStudy Finds Link Between River Outflow and Coastal Sea Level
Sea levels in coastal areas can be affected by a number of factors: tides, winds, waves, and even barometric pressure all play a role in the ebb and flow of the ocean. For the first time, however, a new study led by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has shown that river outflow could play a role in sea level change as well.
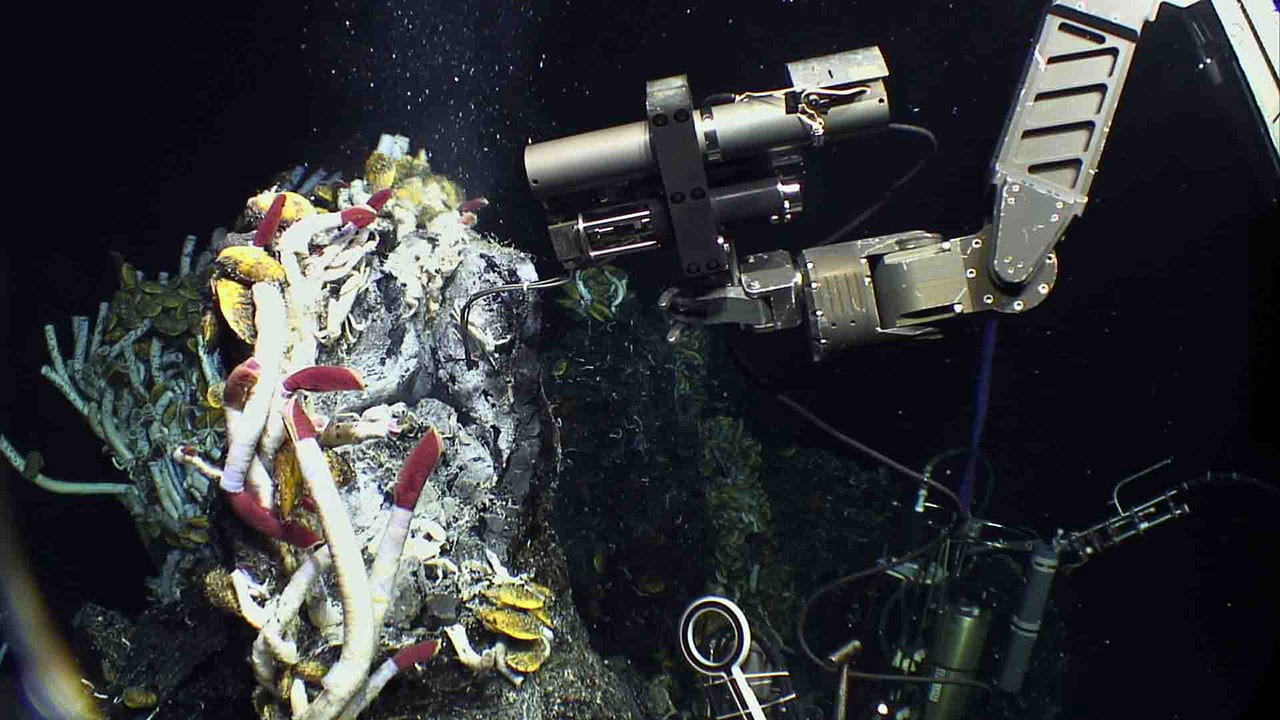
Read MoreFueling a Deep-Sea Ecosystem
Miles beneath the ocean surface in the dark abyss, vast communities of subseafloor microbes at deep-sea hot springs are converting chemicals into energy that allows deep-sea life to survive, and even thrive, in a world without sunlight. Until now, however, measuring the productivity of subseafloor microbe communities (or how fast they oxidize chemicals and the amount of carbon they produce) has been nearly impossible.
Read MoreGalapagos Expedition Reveals Unknown Seamounts, New Species
During a three-week expedition in August, an international team led by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), in partnership with the Charles Darwin Foundation for the Galápagos Islands and in close collaboration with the Galápagos National Park Directorate, conducted the first scientific expedition to map and characterize the seamounts on the Galápagos platform and the diverse marine life that these underwater mountains support.
Read MoreRiver Buries Permafrost Carbon at Sea
As temperatures rise, some of the carbon dioxide stored in Arctic permafrost meets an unexpected fate—burial at sea. As many as 2.2 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) per year are swept along by a single river system into Arctic Ocean sediment, according to a new study led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) researchers and published today in Nature. This process locks away the greenhouse gas and helps stabilize the earth’s CO2 levels over time, and it may help scientists better predict how natural carbon cycles will interplay with the surge of CO2 emissions due to human activities.
“The erosion of permafrost carbon is very significant,” says WHOI Associate Scientist Valier Galy, a co-author of the study. “Over thousands of years, this process is sequestering CO2 away from the atmosphere in a way that amounts to fairly large carbon stocks. If we can understand how this process works, we can predict how it will respond as the climate changes.”
Permafrost—the permanently frozen ground found in the Arctic and Antarctic and in some alpine regions—is known to hold billions of tons of organic material, including vast stores of CO2. Amid concerns about rising Arctic temperatures and their impact on permafrost, many researchers have directed their efforts to studying the permafrost carbon cycle—the processes through which the carbon circulates between the atmosphere, the soil and surface (the biosphere), and the sea. Yet how this cycle works and how it responds to the warming, changing climate remains poorly understood.
Galy and his colleagues from Durham University, the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, the NERC Radiocarbon Facility, Stockholm University, and the Universite Paris-Sud set out to characterize the carbon cycle in one particular piece of the Arctic landscape—northern Canada’s Mackenzie River, the largest river flowing into the Arctic Ocean from North America and that ocean’s greatest source of sediment. The researchers hypothesized that the Mackenzie’s muddy water might erode thawing permafrost along its path and wash that biosphere-derived material and the CO2 within it into the ocean, preventing the release of that CO2 into the atmosphere.
Read MoreResearch Enables Fishermen to Harvest Lucrative Shellfish on Georges Bank
Combined research efforts by scientists involved in the Gulf of Maine Toxicity (GOMTOX) project, funded by NOAA’s Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms (ECOHAB) program, and administered by the…
Read MoreResearchers Issue Forecast for ‘Moderate’ New England Red Tide in 2013
New England is expected to experience a “moderate” red tide this spring and summer, report NOAA-funded scientists studying the toxic algae that cause blooms in the Gulf of Maine. The…
Read MoreHuman Impact Felt on Black Sea Long Before Industrial Era
When WHOI geologist Liviu Giosan first reconstructed the history of how the Danube River built its delta, he was presented with a puzzle. In the delta’s early stages of development,…
Read More