Researchers Issue Forecast for ‘Moderate’ New England Red Tide in 2013
March 25, 2013
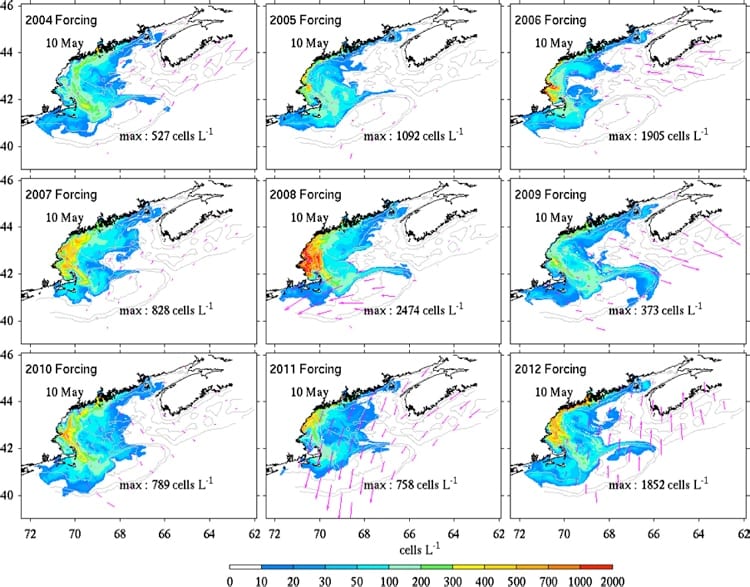
New England is expected to experience a “moderate” red tide this spring and summer, report NOAA-funded scientists studying the toxic algae that cause blooms in the Gulf of Maine. The “red tide” is caused by an alga Alexandrium fundyense, which produces a toxin that can cause paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP). Red tide typically occurs annually along some portions of the Gulf of Maine coast. This year’s outlook is similar to the 2012 red tide which was also classified as “moderate.”
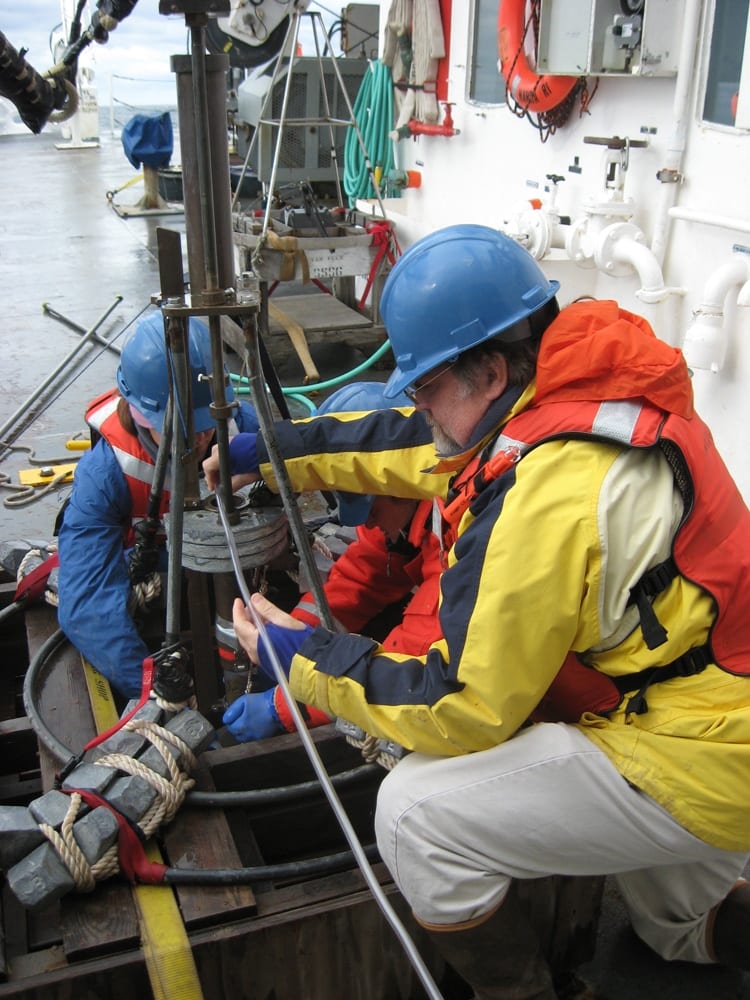
As with the past five forecasts for this region, the 2013 outlook is based on the quantities of the A. fundyense in its cyst (dormant) state detected in Gulf of Maine sediments last fall. These data are combined with a computer model to produce a range of bloom scenarios based on previous years’ conditions. This year, the team also used a forecast of toxicity impact developed from 34 years of historical data as part of the 2013 outlook. The 2013 bloom is expected to fall somewhere in the middle in terms of toxicity impact, justifying a “moderate” forecast done by the established method.
“This region is very fortunate to have a long time series of cyst abundance data, toxicity records in shellfish, and long-term measurements of ocean conditions from ships and moored instrumented buoys to develop these two complementary approaches to the seasonal forecast,” said Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) biologist Don Anderson.
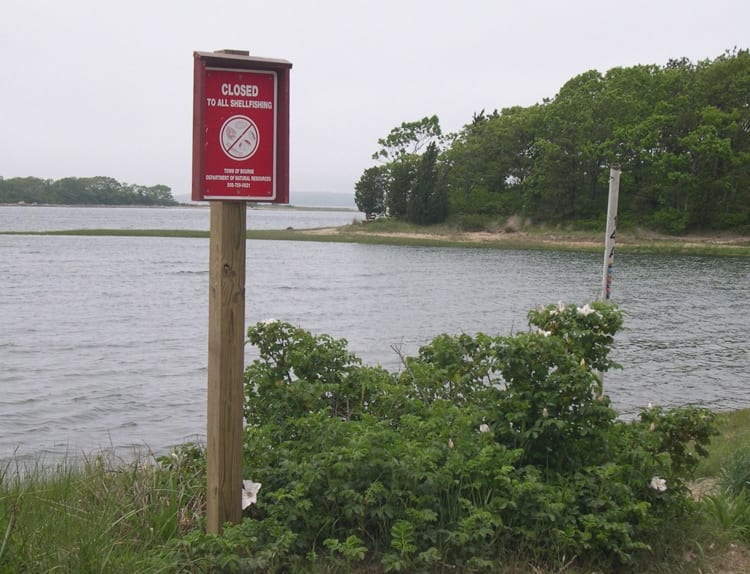
The forecast team emphasizes the need to consult state and local management agencies for updated harvesting closure information. In order to protect public health, shellfish beds are closed when toxicities rise above a quarantine level, often during the peak harvesting season. Due to effective monitoring by state agencies, there have been no illnesses from legally harvested shellfish in recent years, despite some severe blooms during that time period. There have been, however, several severe poisonings of individuals who ignored closure signs.
“Red tide is a chronic problem throughout the Gulf of Maine, affecting commercial and recreational harvesting interests,” said Chris Nash, shellfish program manager for the New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services. “State agencies are responsible for monitoring toxicity levels in shellfish harvest areas and implementing harvest closures when needed. As a state manager, regional-scale, seasonal outlooks help us plan and use limited monitoring resources effectively. Ultimately our goals are to protect public health and give consumers confidence in the quality of the seafood products they purchase from markets and restaurants, and these forecasts are useful in realizing those goals.”
Project researchers regularly share their field observations and models with more than 150 coastal resource and fisheries managers in six states as well as federal agencies such as NOAA, the FDA and the EPA. Real-time forecasts are updated on a weekly basis and additional information will be provided on the “Current Status” page of the Northeast PSP website. The National Weather Service is also providing extended hydrological and meteorological outlooks to accompany the bloom forecasts.
“NOAA-funded research has led to the development of seasonal forecasts which aid in monitoring and planning for red tides,” said Quay Dortch, program coodinator for NOAA’s Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms (ECOHAB) Program. “These forecasts will be an important part of the Operational HAB Forecasting System NOAA is developing to reduce the impacts of harmful algae.”
The forecasting project is a collaboration of investigators from NOAA’s National Ocean Service, National Weather Service and National Marine Fisheries Service, WHOI, NCSU, University of Maine, the FDA, Maine Department of Marine Resources, New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services, Massachusetts Division of Marine Fisheries, and the North Atlantic Clam Association. Funding is provided through the NOAA program Prevention, Control and Mitigation of Harmful Algal Blooms (PCMHAB), led by Dennis McGillicuddy (WHOI). Long-term support for Alexandrium studies in the Gulf of Maine is provided by the NOAA NOS NCCOS Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research (CSCOR) and NIEHS and the NSF through the Woods Hole Center for Oceans and Human Health.
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, non-profit organization on Cape Cod, Mass., dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930 on a recommendation from the National Academy of Sciences, its primary mission is to understand the oceans and their interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate a basic understanding of the oceans’ role in the changing global environment. For more information, please visit www.whoi.edu.