News Releases
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution leads multi-ship study of northwest Atlantic
Partners from National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, University of Rhode Island, to study Ocean Twilight Zone Woods Hole, Mass. (August 6, 2022) – Scientists from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI),…
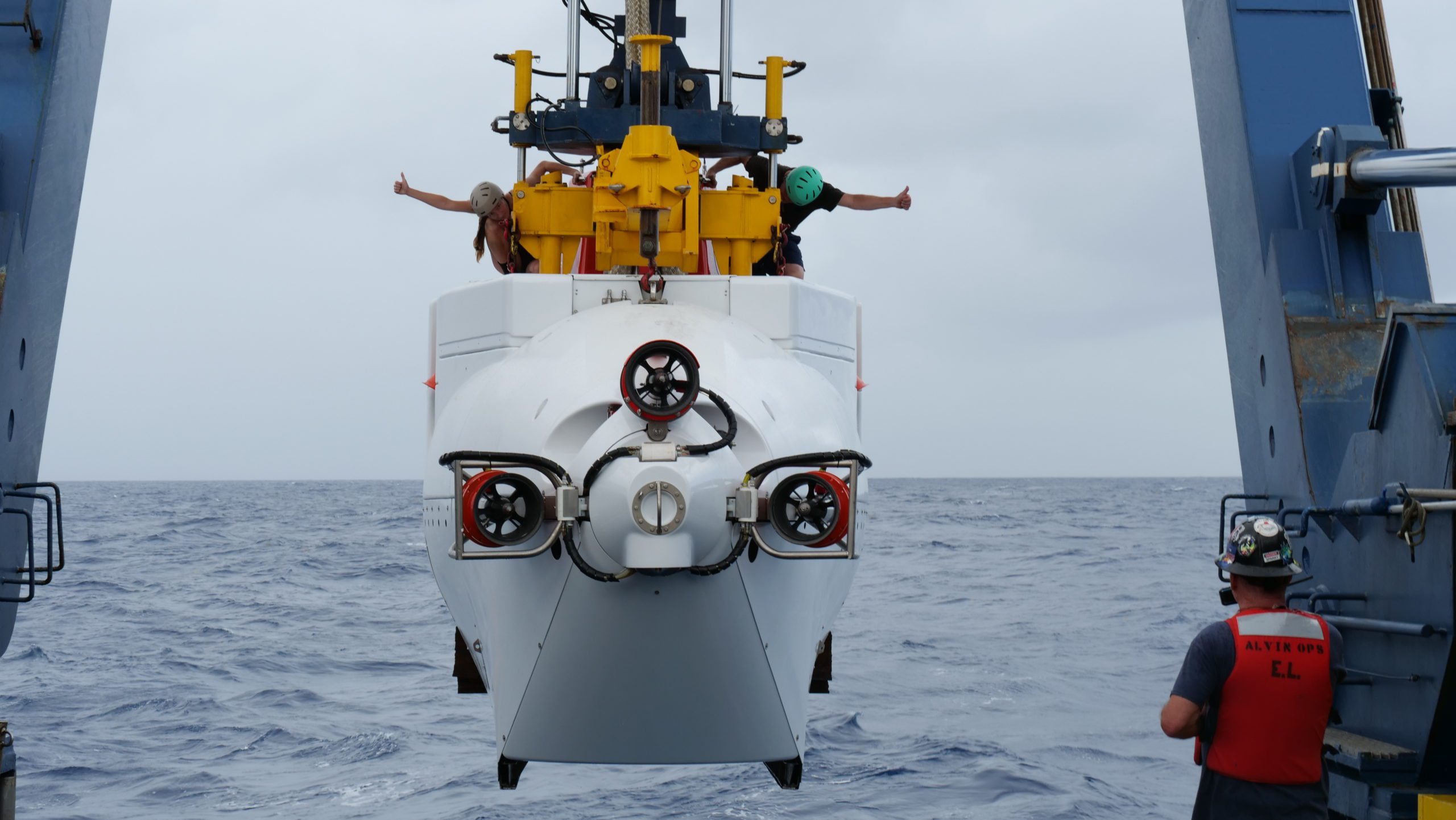
Read MoreHuman-occupied submersible Alvin makes historic dive
World’s most successful research submersible reaches 6,453 meters, its deepest dive ever Woods Hole, MA — Today, the human-occupied submersible Alvin made history when it successfully reached a depth of…
Read MoreHydrothermal field discovered at the East Pacific Rise 9°54’N
A new high-temperature, off-axis hydrothermal vent field on Pacific seafloor at 2550 meters depth was discovered in 2021 by a team that included researchers from Lehigh University; Scripps Institution of Oceanography (SIO); the University of Bergen Norway; and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
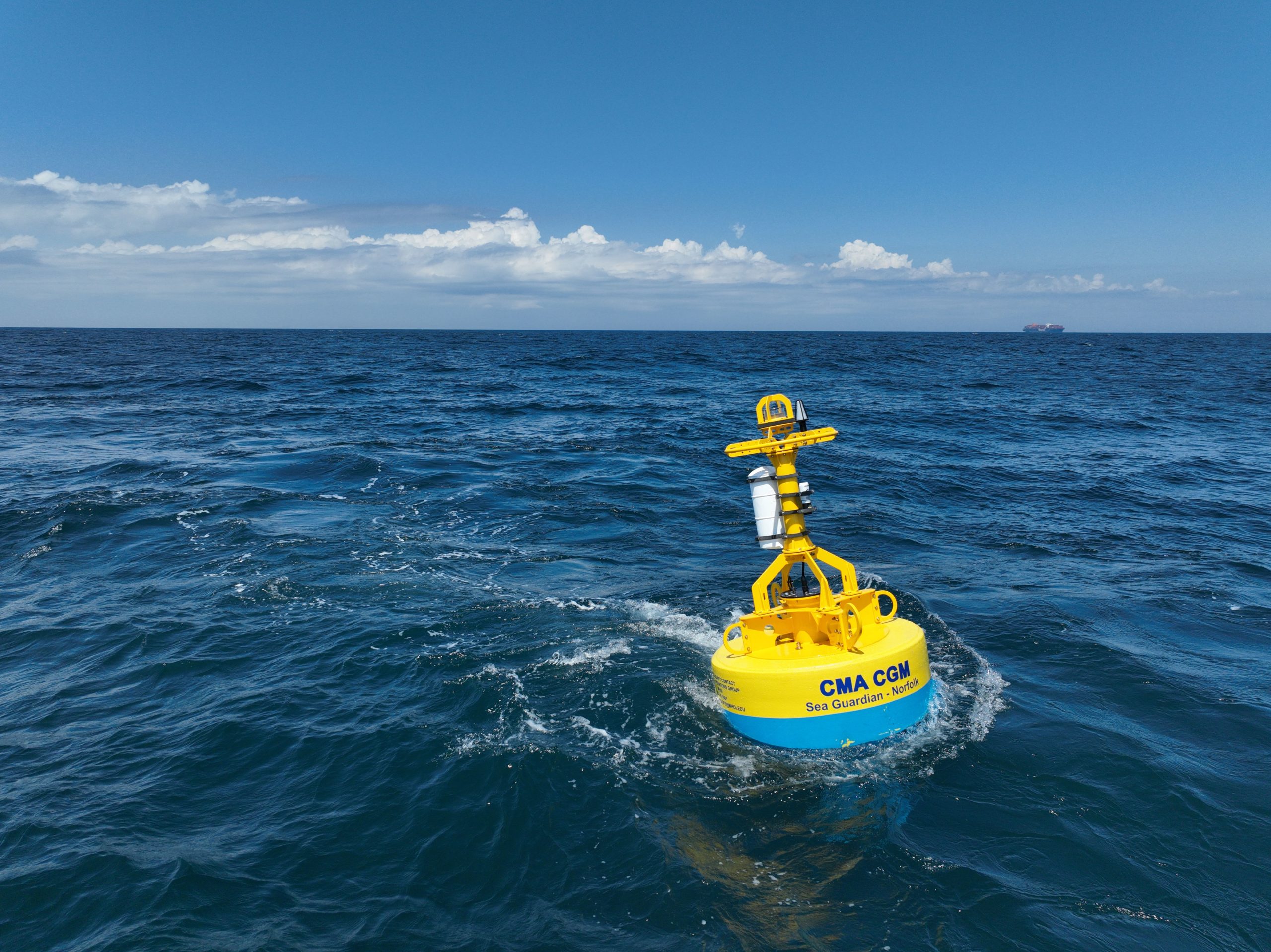
Read MoreWHOI and CMA CGM Group deploy acoustic monitoring buoy near Norfolk, Virginia
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and The CMA CGM Group, a global player in sea, land, air, and logistics solutions, have deployed an acoustic monitoring buoy 33 miles off the coast of Norfolk, Virginia. A second buoy is slated for deployment off the coast of Savannah, Georgia in the coming weeks.
Read MoreMid-depth waters off the United States East Coast are getting saltier
A new study led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) shows a significant increase in frequency of warm saltwater intrusions from the deep ocean to the continental shelf along the Middle Atlantic Bight, which extends from the Gulf of Maine to Cape Hatteras, North Carolina.
Read MoreScientists link the changing Azores High and the drying Iberian region to anthropogenic climate change
Projected changes in wintertime precipitation make agriculture in the Iberian region some of the most vulnerable in Europe, according to a new WHOI co-led study that links the changes to increased anthropogenic greenhouse gases.
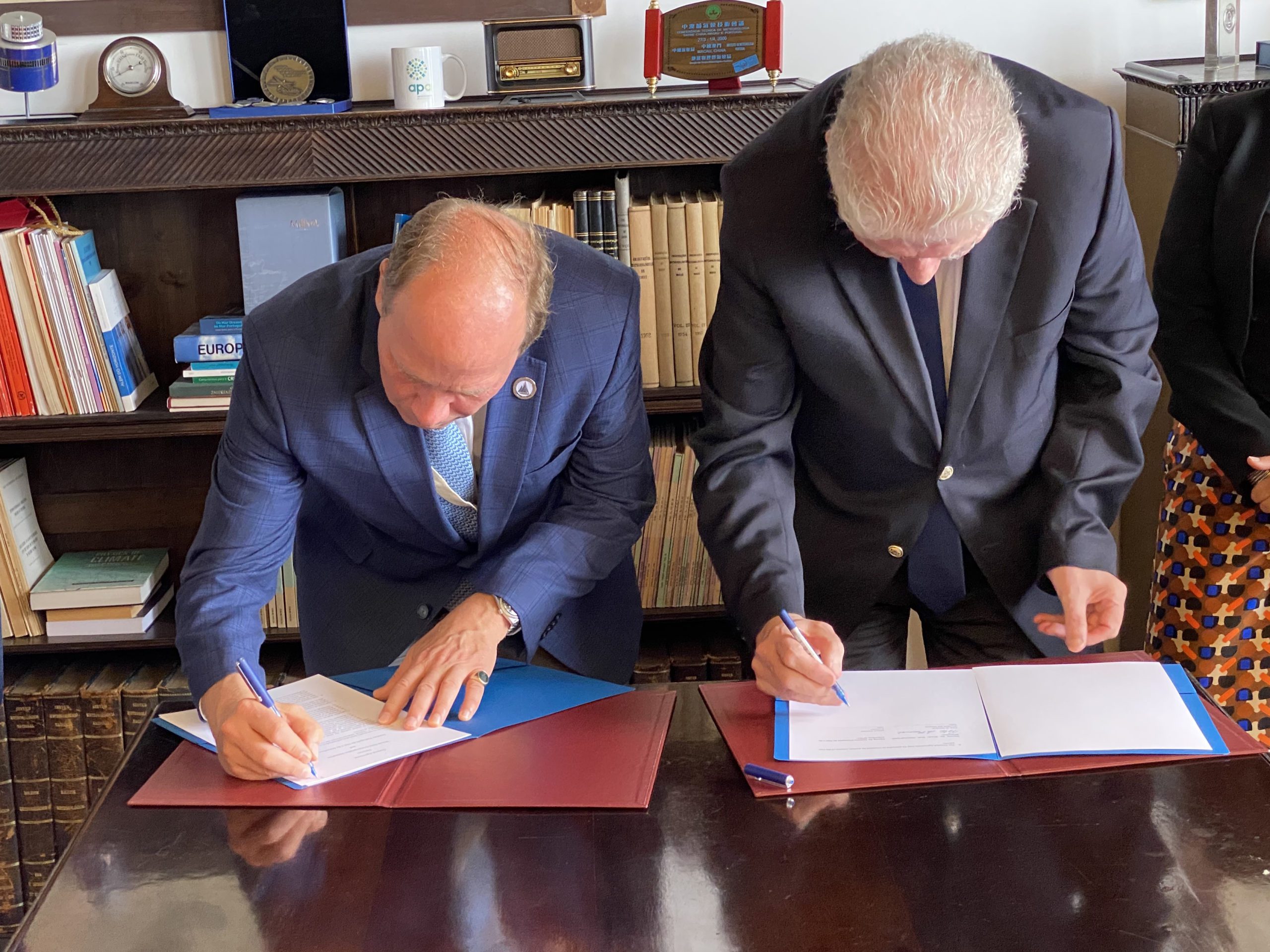
Read MoreWHOI signs a memorandum of understanding with Portuguese Ocean Institute
Today, the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) signed a memorandum of understanding with Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera (IPMA), the Portuguese national authority responsible for monitoring the country’s ocean, atmosphere, and land.
Read MoreInnovative, new “road map” for kelp crop improvement
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the University of Connecticut, and Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences have executed a license agreement for a kelp germplasm, or collection of microscopic cells called gametophytes, containing more than 1,200 samples all developed and isolated by WHOI and UConn-led teams. Bigelow Laboratory’s National Center for Marine Algae and Microbiota plans to maintain, market, and distribute the germplasm collection for broad use.
Read MoreClimate change could lead to a dramatic temperature-linked decrease in essential omega-3 fatty acids
The effects of global climate change already are resulting in the loss of sea ice, accelerated sea level rise, and longer and more intense heat waves, among other threats. Now, the first-ever survey of planktonic lipids in the global ocean predicts a temperature-linked decrease in the production of essential omega-3 fatty acids, an important subset of lipid molecules.
Read MoreWHOI joins world leaders at UN Ocean Conference: June 27 – July 1, Lisbon, Portugal
Thousands of participants from around the world will converge in Lisbon beginning June 27 as part of the 2022 United Nations Ocean Conference. Among them will be representatives from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the world’s largest independent organization dedicated exclusively to ocean research, engineering, and education.
Read MoreWHOI-led projects receive UN endorsement as part of Decade of Ocean Science
Four projects led or co-led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists were named on World Ocean Day by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) to receive Endorsed Action status as part of the UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development 2021-2030.
Read MoreGeoscience technology company founded by MIT/WHOI Joint Program student awarded $3.8M from U.S. Department of Energy
Eden, a geoscience technology development company co-founded by Massachusetts Institute of Technology/Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Joint Program student Paris Smalls, will receive $3.8 million in federal funding from the U.S. Department of Energy Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E).
Read MoreYawkey Foundation and WHOI present Summer Speaker Series, “Dispatches from an Ocean Planet”
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, in partnership with the Yawkey Foundation, proudly presents “Dispatches from an Ocean Planet”, a summer series of film and literature. The series marks the return of WHOI in-person events after a two-year hiatus due to the pandemic. All events require pre-registration.
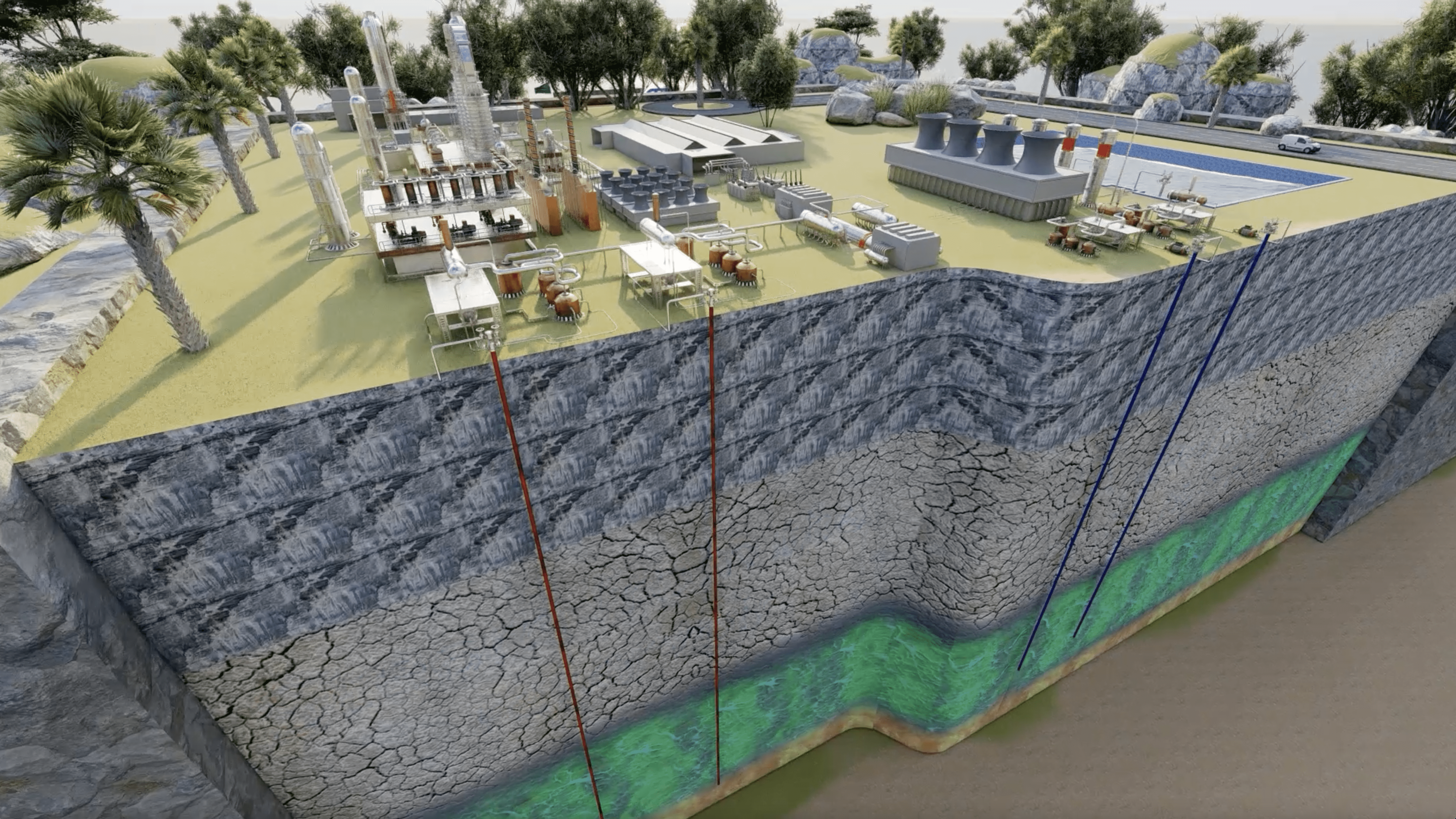
Read MoreArc volcanoes are wetter than previously thought, with scientific and economic implications
This increased amount of water has broad implications for understanding how Earth’s lower crust forms, how magma erupts through the crust, and how economically important mineral ore deposits form, according to a new paper led by authors from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
Read MoreWHOI campaign sheds light on new strategies and solutions for the coral reef crisis
In advance of World Ocean Day on June 8, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is launching its Give Reefs a Chance campaign, aimed at raising awareness of what WHOI scientists and engineers are doing to tackle the corals crisis, the importance of coral reefs, and what we can all do to give reefs a chance to survive.
Read MoreInnovation Takes Off at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the world’s largest independent institution specifically focused on ocean science, engineering, and education, today announced the establishment of the George and Wendy David Center for Ocean Innovation, the latest in a series of new initiatives aimed at cementing WHOI’s position as a national leader in ocean innovation and laying the foundation for a future of scientific discoveries, breakthrough technologies, and unparalleled advances on land and at sea.
Read MoreWHOI scientists receive 2022 Simons Early Career Investigator Awards
Two Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution scientists have received prestigious Simons Early Career Investigator in Marine Microbial Ecology and Evolution Awards. Maria Pachiadaki and Harriet Alexander are both assistant scientists at WHOI, focusing on different aspects of microbial ecology.
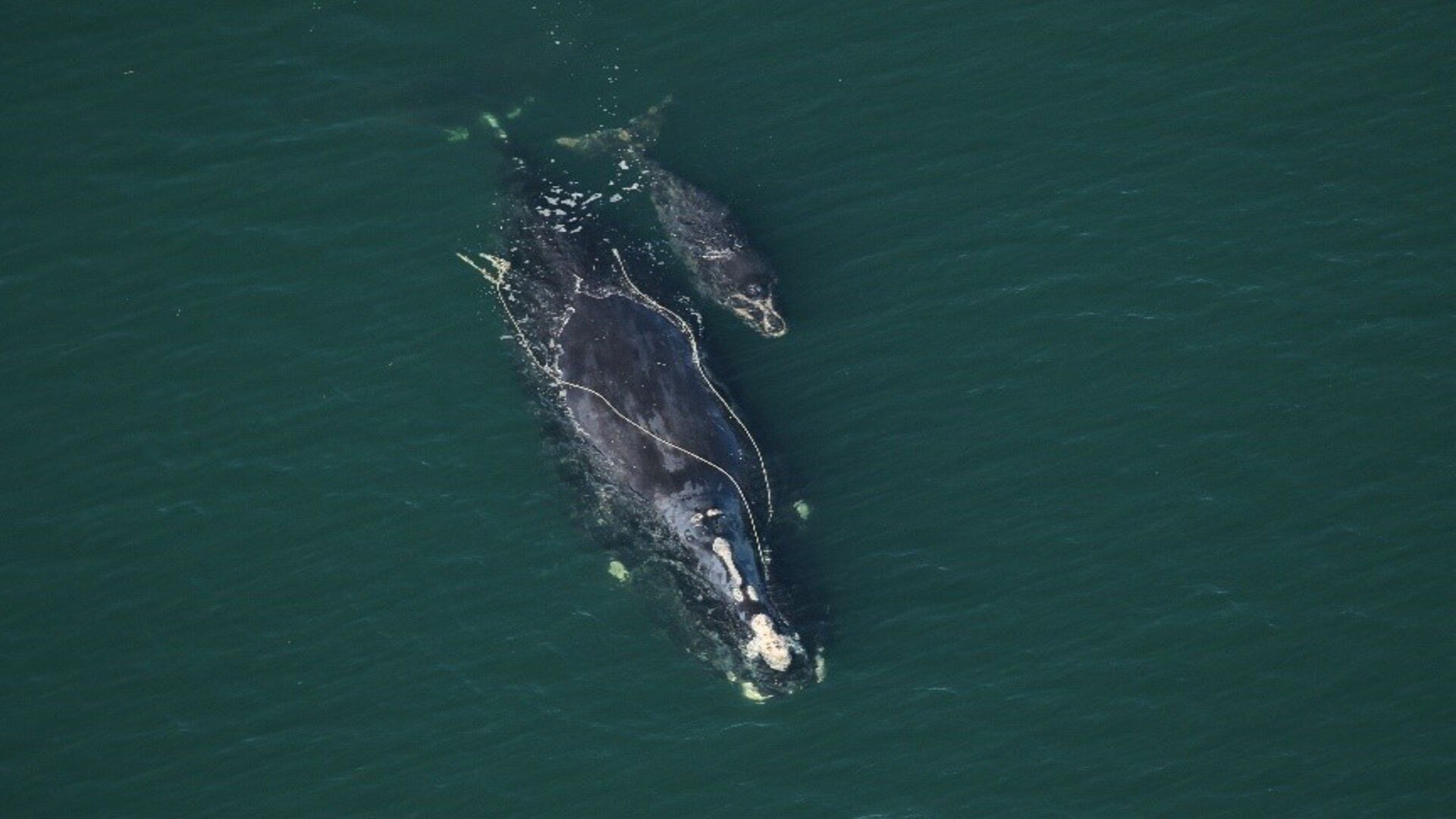
Read MoreSmaller female North Atlantic right whales, fewer calves
The declining body size of North Atlantic right whales may have critical consequences for the future of the species. New research, co-authored by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s senior scientist Michael Moore, shows that smaller females produce fewer calves.
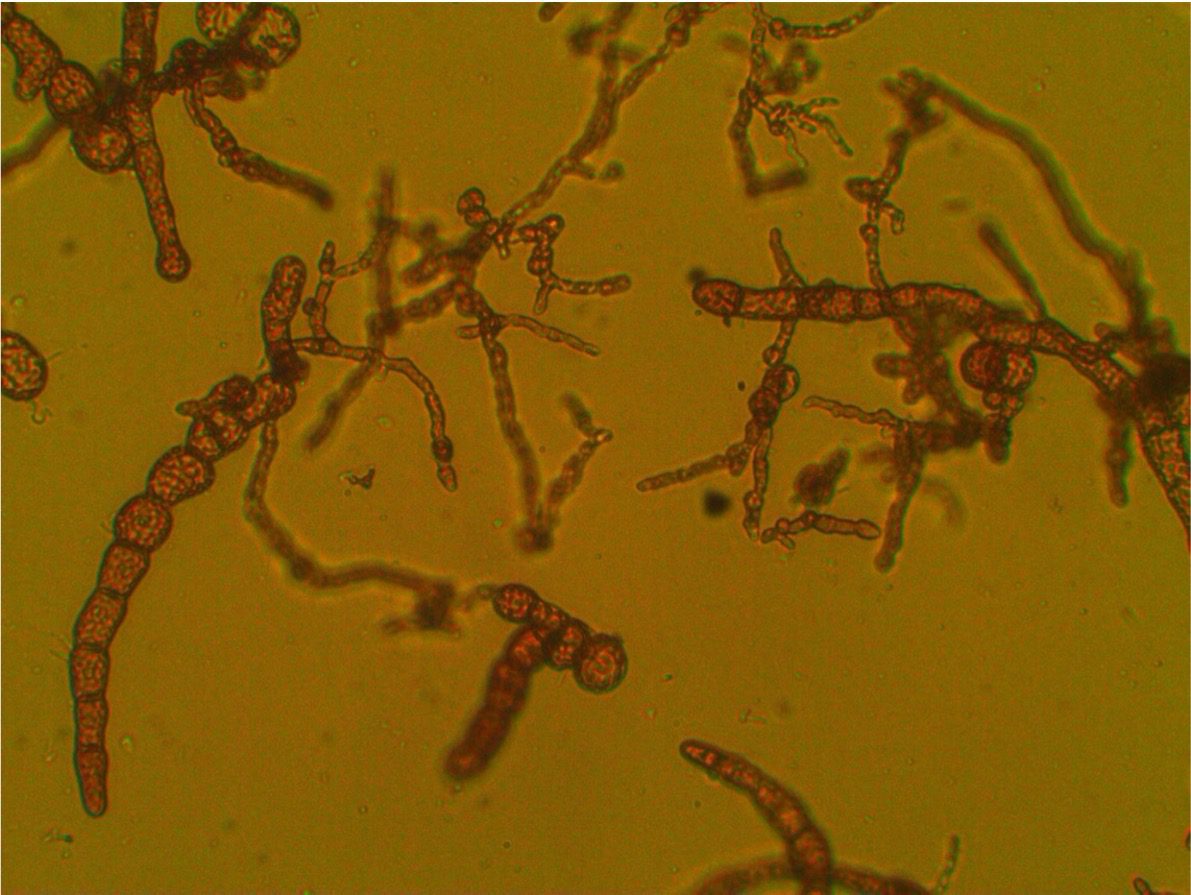
Read MoreFluid Flow Stimulates Chemosynthesis in a Greek Salad of Hydrothermal Microbes
A new study uses an innovative approach to examine the bay’s shallow-water hydrothermal system and the production of microbes there in situ and near natural conditions as a model to assess the importance of hydrothermal fluid circulation on chemosynthesis.
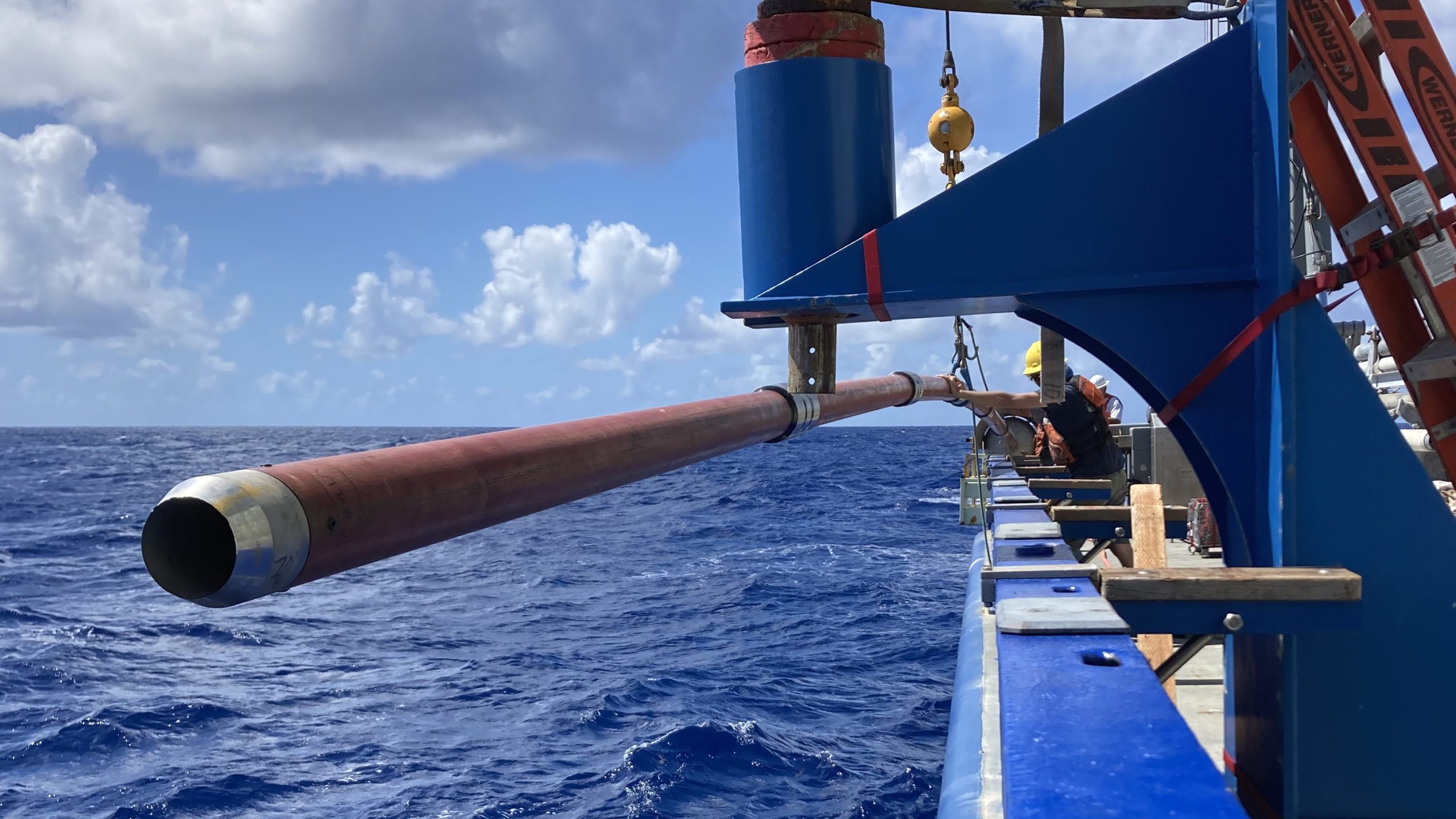
Read MoreDeepest sediment core collected in the Atlantic Ocean
A team of scientists, engineers, and ship’s crew on the research vessel Neil Armstrong operated by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) recently collected a 38-foot-long cylindrical sediment sample from the deepest part of the Puerto Rico Trench, nearly 5 miles below the surface.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s “Ocean Encounters” nominated for Webby Award
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s virtual education series, Ocean Encounters, has been nominated for a People’s Voice Webby Award in the Virtual and Remote – Series, Health and Science category, and was also named an honoree in the Virtual and Remote: Best Series category.
Read MoreWHOI & Pangaea Logistics Solutions to advance ocean science data acquisition through Science RoCS program
WHOI and Pangaea Logistics Solutions (Pangaea), a U.S. based, international maritime and logistics transportation company, today announced the launch of a new science program aboard Pangaea’s fleet of ships. Science RoCS (Science Research on Commercial Ships) is an innovative program pairing scientists with commercial vessels to regularly monitor the vast and open ocean, particularly along repeat routes in hard-to-reach areas where critical gaps in monitoring exist.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution and collaborators launch world’s largest kelp map
To further investigate and track kelp growth and survival over time, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, The Nature Conservancy, University of California Los Angeles, and the University of California Santa Barbara have launched the world’s largest map of kelp forest canopies extending from Baja California, Mexico to the Oregon-Washington border.
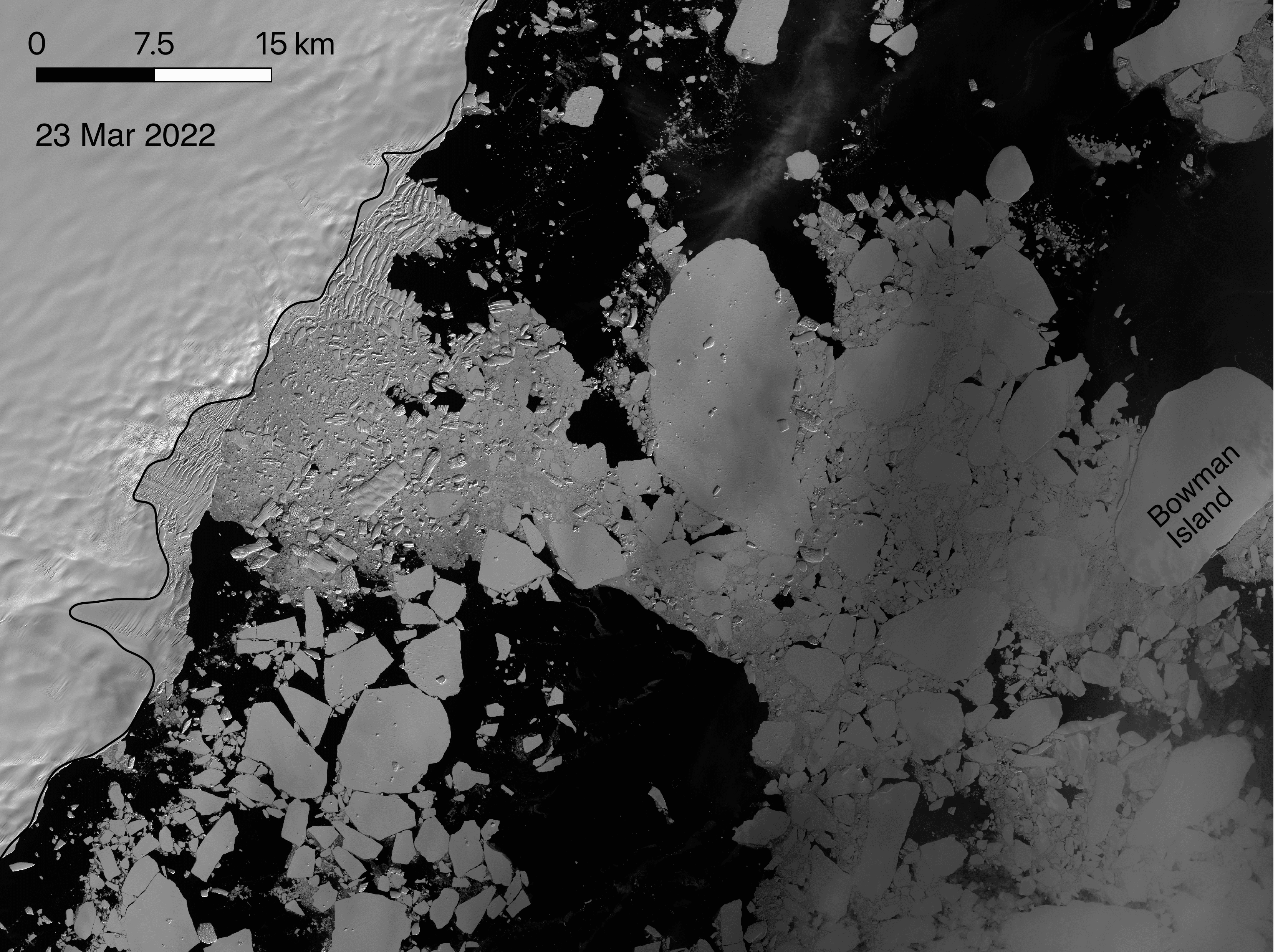
Read MoreScientists report complete collapse of East Antarctica’s Conger Ice Shelf
Satellite data has confirmed that an ice shelf about the size of Manhattan has completely collapsed in East Antarctica within days of record high temperatures. The Conger ice shelf, which had an approximate surface area of 1,200 sq km, collapsed around 15 March, scientists confirmed today.
Read More