News Releases
Scientists link the changing Azores High and the drying Iberian region to anthropogenic climate change
Projected changes in wintertime precipitation make agriculture in the Iberian region some of the most vulnerable in Europe, according to a new WHOI co-led study that links the changes to increased anthropogenic greenhouse gases.
Read MoreWHOI scientists receive 2022 Simons Early Career Investigator Awards
Two Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution scientists have received prestigious Simons Early Career Investigator in Marine Microbial Ecology and Evolution Awards. Maria Pachiadaki and Harriet Alexander are both assistant scientists at WHOI, focusing on different aspects of microbial ecology.
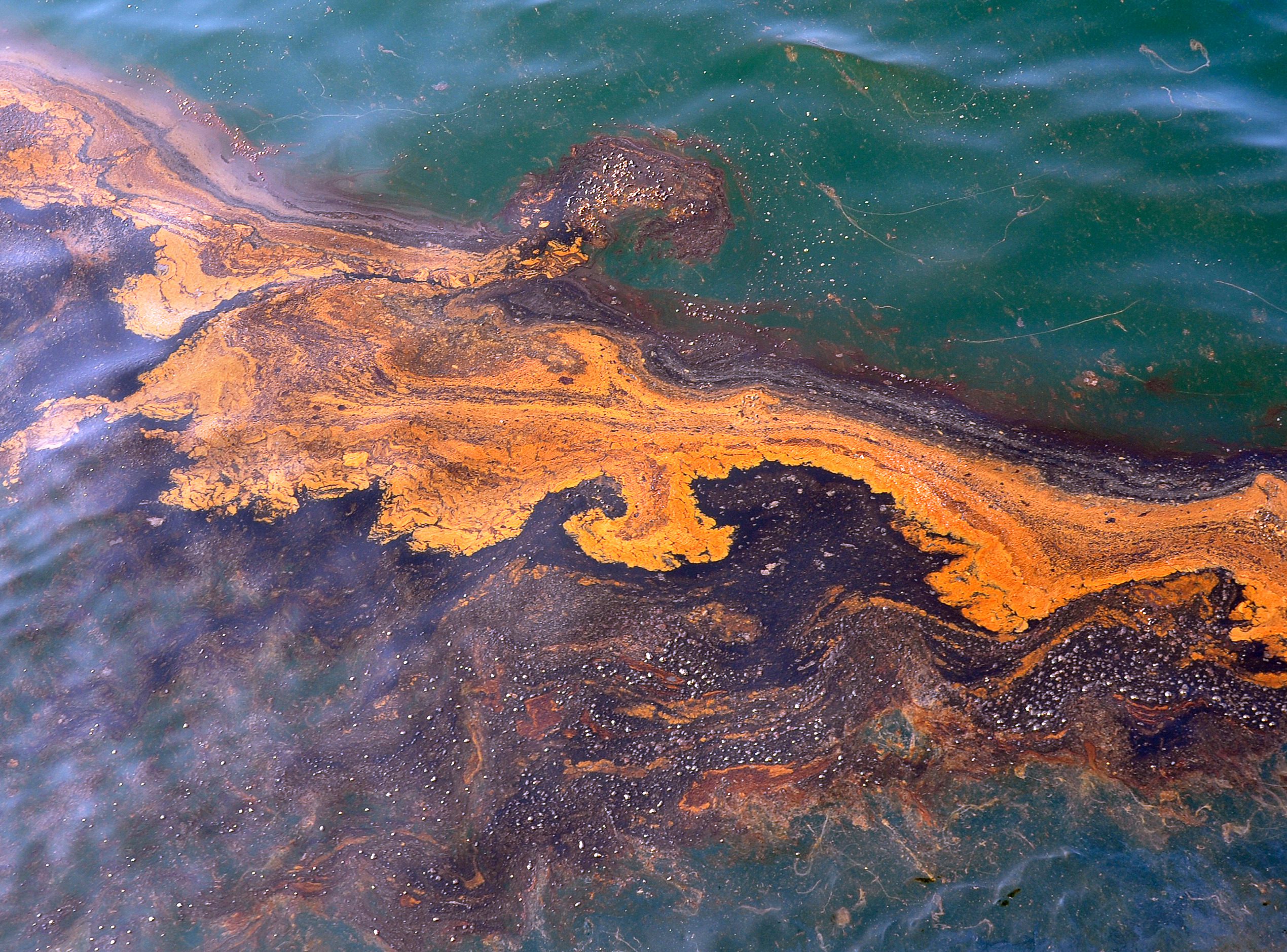
Read MoreDissolving oil in a sunlit sea
A team of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) researchers discovered that nearly 10 percent of the oil floating on the Gulf after the Deepwater Horizon disaster was dissolved into seawater by sunlight – a process called “photo-dissolution”. The findings were published today in the paper “Sunlight-driven dissolution is a major fate of oil at sea” in Science Advances.
Read MoreWHOI Arctic experts present at international climate conference overseas
Experts from WHOI and Woodwell Climate Research Center are on the ground at COP26 in Glasgow, Scotland, sharing critical perspective on the implications of a warming Arctic
Read MoreEnvironmental DNA is a reliable way to learn about migration from the twilight zone
Woods Hole, MA — The mid-ocean “twilight zone” holds the key to several tantalizing questions about the marine food web and carbon-sequestering capacity of the ocean. But studying this vast…
Read MoreWHOI selected for new NSF science & technology center
The new Center for Chemical Currencies of a Microbial Planet (C-CoMP) will focus on the chemical processes that underpin ocean ecosystems.
Read MorePapers Explore Massive Plankton Blooms with Very Different Ecosystem Impacts
Two papers explore the distribution and abundance of plankton and what conditions lead to big plankton blooms with vastly different potential impacts on the ecosystem.
Read MoreStudy reconstructs ancient storms to predict changes in a cyclone hotspot
Intense tropical cyclones are expected to become more frequent as climate change increases temperatures in the Pacific Ocean. But not every area will experience storms of the same magnitude
Read MoreNew multi-institutional grant will support a fleet of robotic floats
The National Science Foundation approved a $53 million grant to build a global network of chemical and biological sensors that will monitor ocean health.
Read MoreWHOI-NOAA partnership tackles critical gap in climate knowledge
Remote technologies, machine learning will improve simulations of polar ice melt and implications for the global climate Researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) were recently awarded a $500,000 grant…
Read MoreAntarctic Ice Sheet Loss Expected to Affect Future Climate Change
The research team reports that their new models with the added ice melt information reveal important interacting processes and demonstrate a need to accurately account for meltwater input from ice sheets in order to make confident climate predictions.
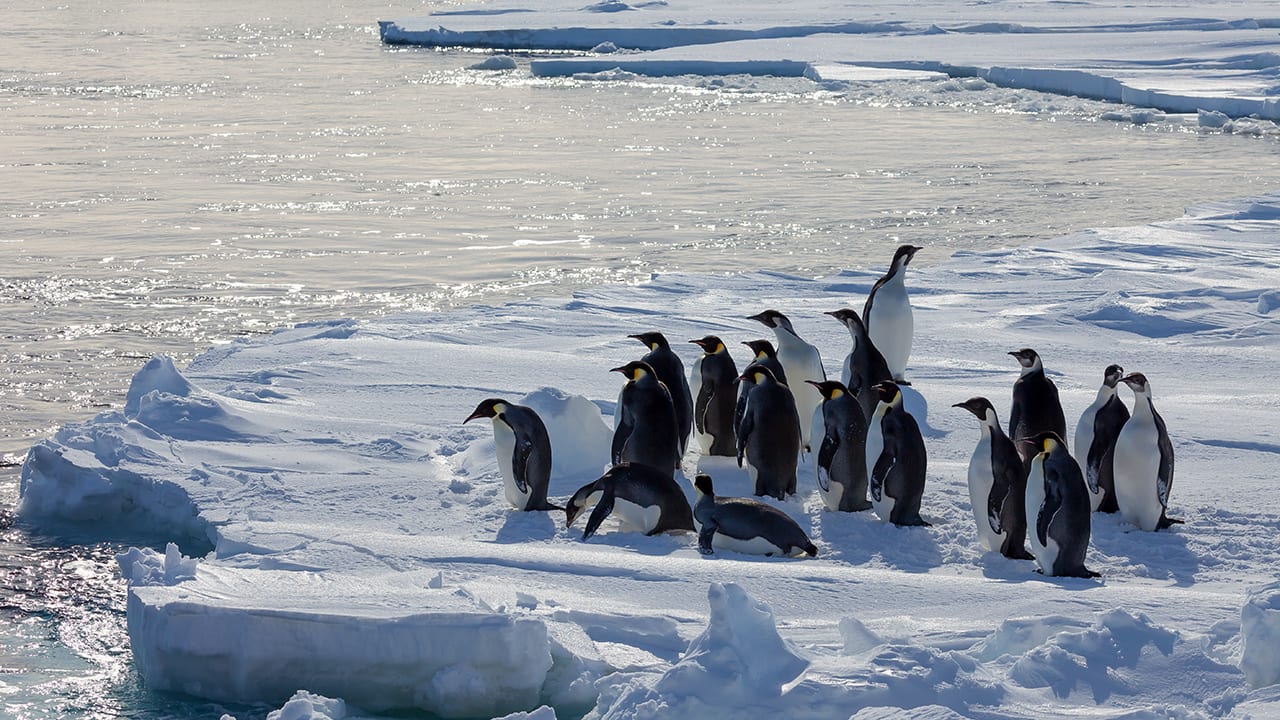
Read MoreFinding New Homes Won’t Help Emperor Penguins Cope with Climate Change
Unlike other species that migrate successfully to escape the wrath of climate change, a new study shows that dispersal may help sustain global Emperor penguin populations for a limited time, but, as sea ice conditions continue to deteriorate, the 54 colonies that exist today will face devastating declines by the end of this century.
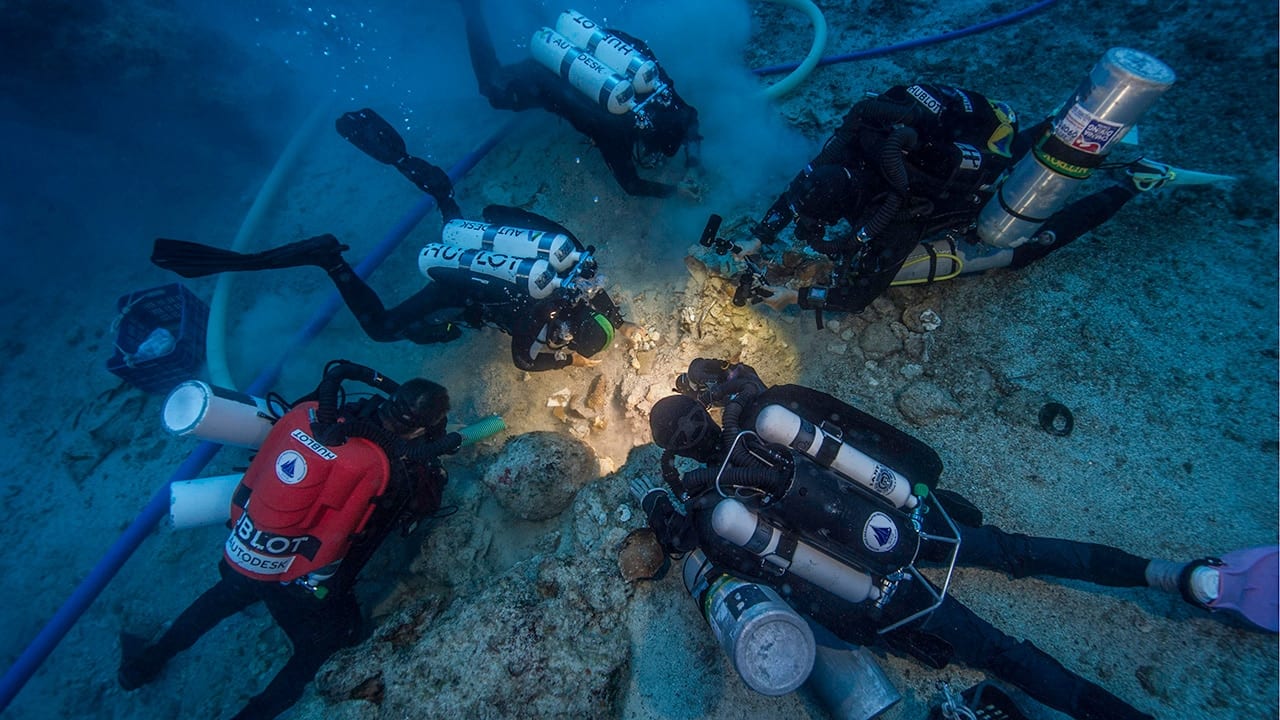
Read MoreAncient Skeleton Discovered on Antikythera Shipwreck
An international research team discovered a human skeleton during its ongoing excavation of the famous Antikythera Shipwreck (circa 65 B.C.) this month. The shipwreck, which holds the remains of a Greek trading or cargo ship, is located off the Greek island of Antikythera in the Aegean Sea. The first skeleton recovered from the wreck site during the era of DNA analysis, this find could provide insight into the lives of people who lived 2100 years ago.
Read MoreWhere Iron and Water Mix
A new study by researchers from University of Washington (UW), Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), and the University of Southern California, demonstrates that chemical-laden plumes erupted from vents at one section of Mid Ocean Ridge in the SE Pacific can be traced all the way across the Pacific for more than 4000 kilometers. Further, the study shows how the iron transported by this process is ultimately brought to the surface oceans of Antarctica where it is serves as a key life-sustaining micro-nutrient supporting up to 30 percent of all the organic carbon uptake in that ocean.
Read MoreGulf of Maine Red Tide Bloom Expected to Be Similar to Past Three Years
New England’s spring and summer red tides will be similar in extent to those of the past three years, according to the 2015 Gulf of Maine red tide seasonal forecast. The forecast is the eighth seasonal Gulf of Maine red tide forecast funded by NOAA and issued by scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and North Carolina State University.
The forecast is part of a larger NOAA effort to deliver ecological forecasts that support human health and well-being, coastal economies, and coastal and marine stewardship.
Red tide, a type of harmful algal bloom (HAB) caused by the alga Alexandrium fundyense, produces a toxin that can lead to paralytic shellfish poisoning, which can result in serious or even fatal illness in humans who eat contaminated shellfish. In 2005, an unusually large red tide event caused $23 million in lost shellfish sales in Massachusetts and Maine.
Read MoreWhitehead to Receive AGU’s 2014 Maurice Ewing Medal
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) Scientist Emeritus Dr. John (Jack) Whitehead has been selected to receive the 2014 Maurice Ewing Medal from the America Geophysical Union (AGU). The Maurice Ewing…
Read MoreAlexander von Humboldt Foundation Honors Two WHOI Scientists
The Alexander von Humboldt Foundation in Bonn, Germany, has recognized two Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists with honors: Chris German received a Humboldt Research Award and Caroline Ummenhofer was chosen for a Humboldt Research Fellowship.
Read MoreWHOI Part of the Stantec Team Selected to Lead Major Marine Arctic Ecosystem Study
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), as a part of the Stantec Team, has been selected by an interagency scientific review panel to lead a long-term scientific study of the Arctic marine ecosystem along the Beaufort Sea shelf from Barrow, Alaska, to the Mackenzie River delta in Canadian waters.
Read MoreWHOI Scientists Receive $1 Million Grant from MacArthur Foundation
Rapid climate change and an increasing range of climate impacts are already being felt along our coasts, and new research suggests that U.S. Northeast coastal waters may be more vulnerable…
Read MoreThree WHOI Scientists Named 2014 American Geophysical Union Fellows
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists Rockwell Geyer, Susumu Honjo, and Delia Oppo have been elected 2014 fellows of the American Geophysical Union (AGU).
Read More