News Releases
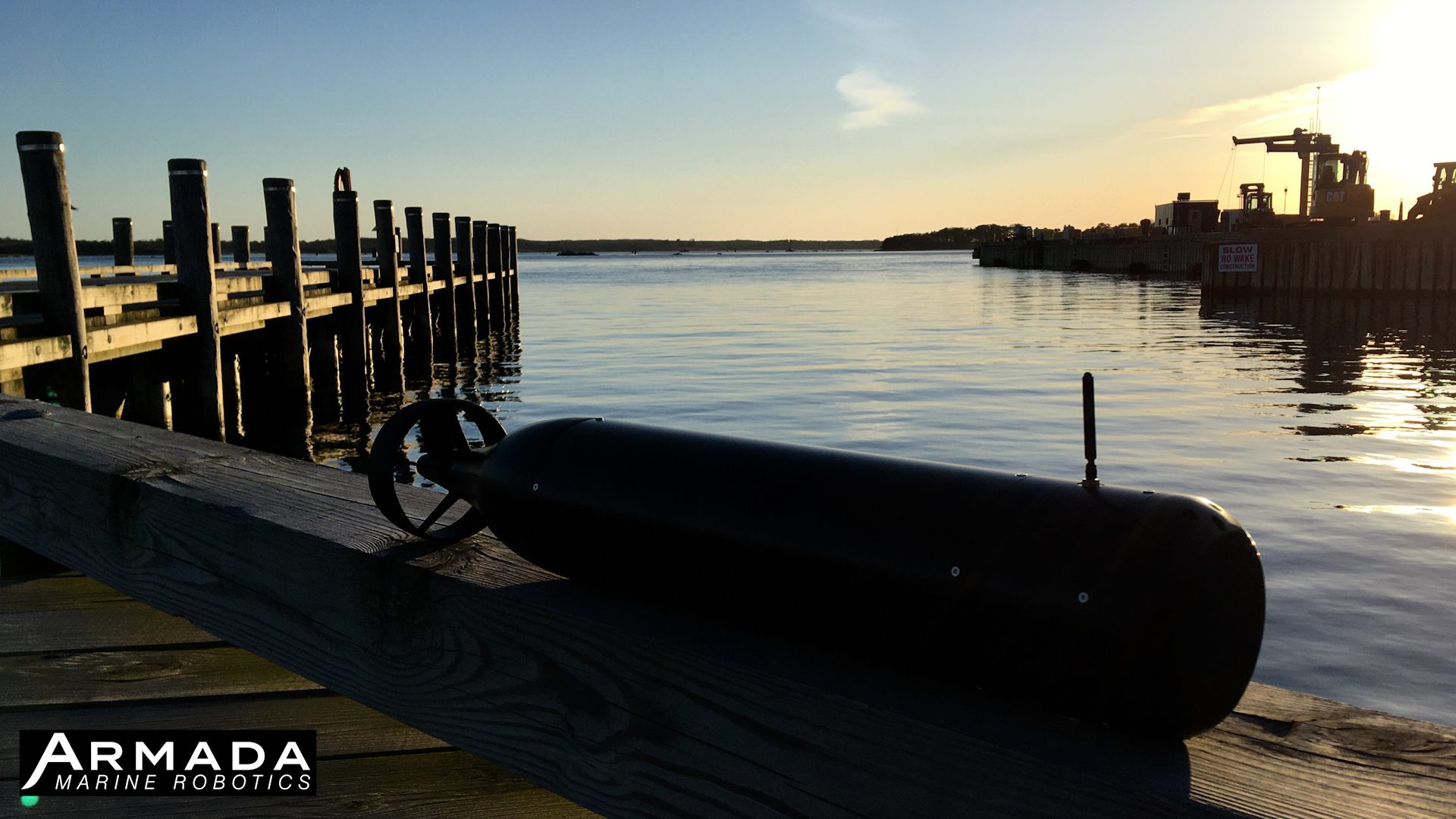
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Licenses Ocean Technology to ARMADA Marine Robotics
These agreements mark a significant milestone in WHOI’s efforts to foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and the commercialization of transformative ocean technologies.
Read MoreCan adding iron to the ocean help it absorb CO2?
A newly published article spells out the work needed to assess the potential of ocean iron fertilization as a low cost, scalable, and rapidly deployable method of mCDR.
Read MoreWHOI to Receive Funding For Ocean Margins Initiative in West Africa
New program at Schmidt Sciences will refine details of ocean carbon cycling and ecosystem resilience
Read MoreFor microscopic organisms, ocean currents act as ‘expressway’ to deeper depths, study finds
New research shows how tiny plant-like organisms hitch a ride on ocean currents to reach darker and deeper depths, where they impact carbon cycling and microbial dynamics in the subtropical oceans.
Read MoreVitamin B12 adaptability in Antarctic algae has implications for climate change
Woods Hole, Mass. — Vitamin B12 deficiency in people can cause a slew of health problems and even become fatal. Until now, the same deficiencies were thought to impact certain…
Read MoreStudy says ice age could help predict oceans’ response to global warming
Woods Hole, MA – A team of scientists led by a Tulane University oceanographer and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has found that deposits deep under the ocean floor…
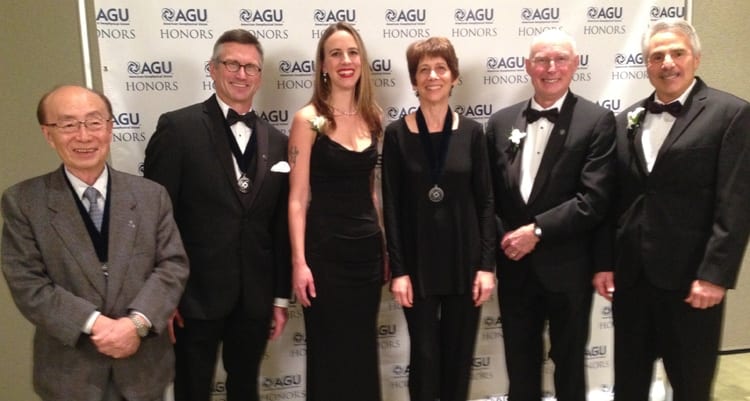
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Heather Benway Receives AGU Honor
Heather Benway, a senior research specialist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is the recipient of the 2023 Ocean Science Award from the American Geological Union (AGU).
Read MoreWHOI-led projects receive UN endorsement as part of Decade of Ocean Science
Four projects led or co-led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists were named on World Ocean Day by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) to receive Endorsed Action status as part of the UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development 2021-2030.
Read MoreWHOI’s Ken Buesseler named Geochemistry Fellow
Dr. Ken Buesseler has been selected as a Geochemistry Fellow by the Geochemical Society and the European Association of Geochemistry.
Read MoreBen Van Mooy awarded by Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography
WHOI senior scientist and Dept. Chair honored for phosphorus and lipid cycling research
Read MoreWHOI selected for new NSF science & technology center
The new Center for Chemical Currencies of a Microbial Planet (C-CoMP) will focus on the chemical processes that underpin ocean ecosystems.
Read MorePlate Tectonics Fuels a Vast Underground Ecosystem
The subsurface is among Earth’s largest biomes, but the extent to which microbial communities vary across tectonic plate boundaries or interact with subduction-scale geological processes remains unknown. In a recently published study, scientists compare bacterial community composition with deep-subsurface geochemistry from 21 hot springs across the Costa Rican convergent margin.
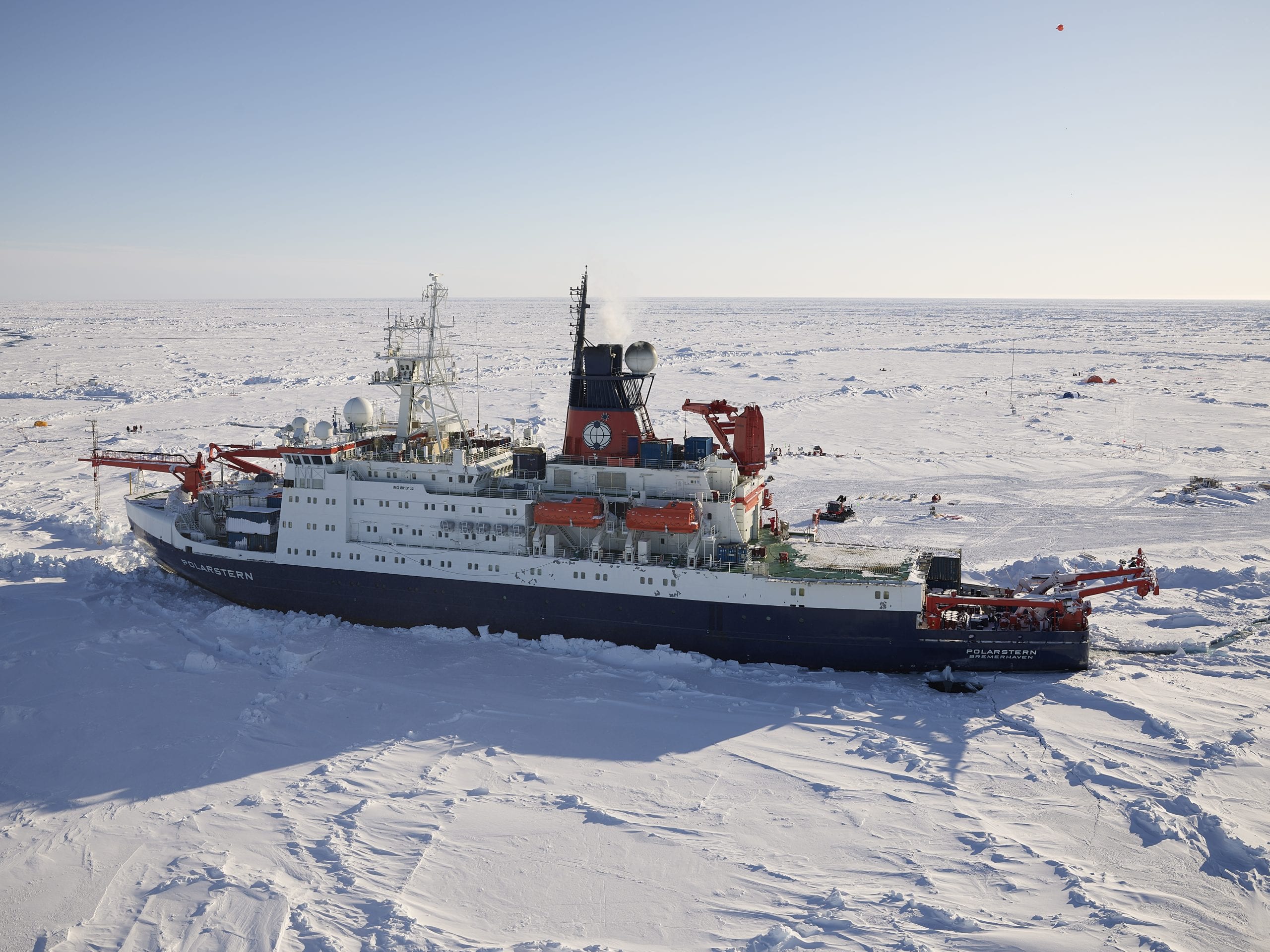
Read MoreEpic Arctic Mission Ends
An epic mission ended as the German icebreaker Polarstern returned home Oct. 12, 2020, after being frozen near the top of the world for nearly a year to study all aspects of the Arctic system.
Read MoreOSU Assumes Cyberinfrastructure Responsibility for OOI
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and Oregon State University (OSU) jointly announced that OSU will assume responsibilities for the systems management of the cyberinfrastructure that makes data transmission for the Ocean Observatories Initiative (OOI) possible through September of 2023.
Read MoreReport reveals ‘unseen’ human benefits from ocean twilight zone
A new report from researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) reveals for the first time the unseen—and somewhat surprising—benefits that people receive from the ocean’s twilight zone. Also known as the “mesopelagic,” this is the ocean layer just beyond the sunlit surface.
Read MoreOcean Bacteria Get ‘Pumped Up’
In a new study published April 27 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and their colleague from Rutgers University discovered a surprising new short-circuit to the biological pump. They found that sinking particles of stressed and dying phytoplankton release chemicals that have a jolting, steroid-like effect on marine bacteria feeding on the particles. The chemicals juice up the bacteria’s metabolism causing them to more rapidly convert organic carbon in the particles back into CO2 before they can sink to the deep ocean.
Read More
Study Finds Deep Ocean is Source of Dissolved Iron in Central Pacific
A new study led by scientists at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) points to the deep ocean as a major source of dissolved iron in the central Pacific Ocean. This finding highlights the vital role ocean mixing plays in determining whether deep sources of iron reach the surface-dwelling life that need it to survive.
Read MoreThree WHOI Scientists Named 2014 American Geophysical Union Fellows
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists Rockwell Geyer, Susumu Honjo, and Delia Oppo have been elected 2014 fellows of the American Geophysical Union (AGU).
Read MoreDoney receives A.G. Huntsman Award for Excellence in Marine Science
WHOI Senior Scientist Scott Doney has been awarded the 2013 A.G. Huntsman Award for Excellence in Marine Science. He will receive the award later this year at the Bedford Institute…
Read MoreNewly discovered ocean plume could be major source of iron
Scientists have discovered a vast plume of iron and other micronutrients more than 1,000 km long billowing from hydrothermal vents in the South Atlantic Ocean. The finding, published online Aug.…
Read MoreNew Study Reveals How Sensitive U.S. East Coast Regions May Be to Ocean Acidification
A continental-scale chemical survey in the waters of the eastern U.S. and Gulf of Mexico is helping researchers determine how distinct bodies of water will resist changes in acidity. The…
Read MoreScientists Discover New Trigger for Immense North Atlantic Ocean Spring Plankton Bloom
On this July 4th week, U.S. beachgoers are thronging their way to seaside resorts and parks to celebrate with holiday fireworks. But across the horizon and miles out to sea…
Read MoreBacterial Communication Could Affect Earth’s Climate
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists have discovered that bacterial communication could have a significant impact on the planetÃÂs climate.
Read MoreIdentical Virus, Host Populations Can Prevail for Centuries, WHOI Researcher Reports
A Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientist, analyzing ancient plankton DNA signatures in sediments of the Black Sea, has found for the first time that the same genetic populations of a virus and its algal host can persist and coexist for centuries. The findings have implications for the ecological significance of viruses in shaping algae ecosystems in the ocean, and perhaps fresh water as well.
Read More