News Releases
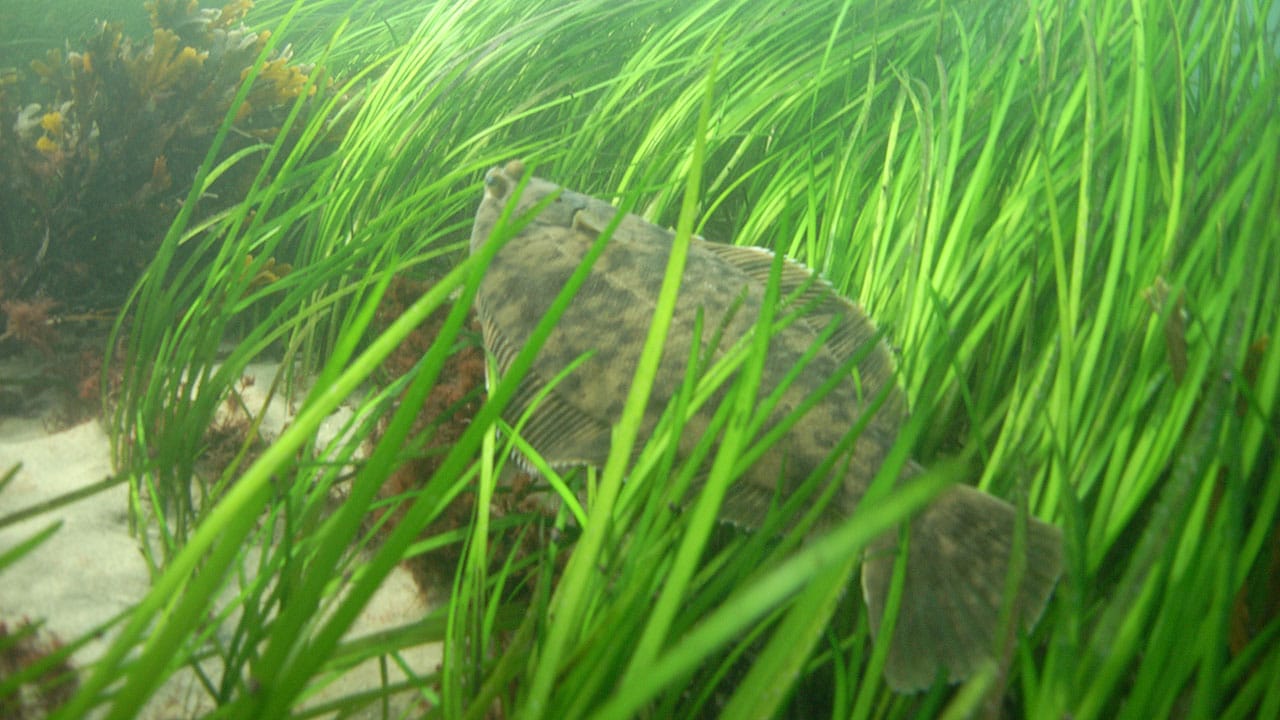
Flounder Now Tumor-free in Boston Harbor
In the late 1980s, more than three-quarters of the winter flounder caught in Boston Harbor – one of the most polluted harbors in America – showed signs of liver disease, many of them with cancerous tumors. But now, a scientist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has documented a dramatic rebound in flounder health spurred by decades of remediation efforts, including a $3.8 billion project to construct a sewage treatment plant and a 9.5-mile discharge tunnel with a 6,600-foot-long outfall diffuser. The findings appear in the Nov. 20, 2018 issue of the journal Diseases of Aquatic Organisms.
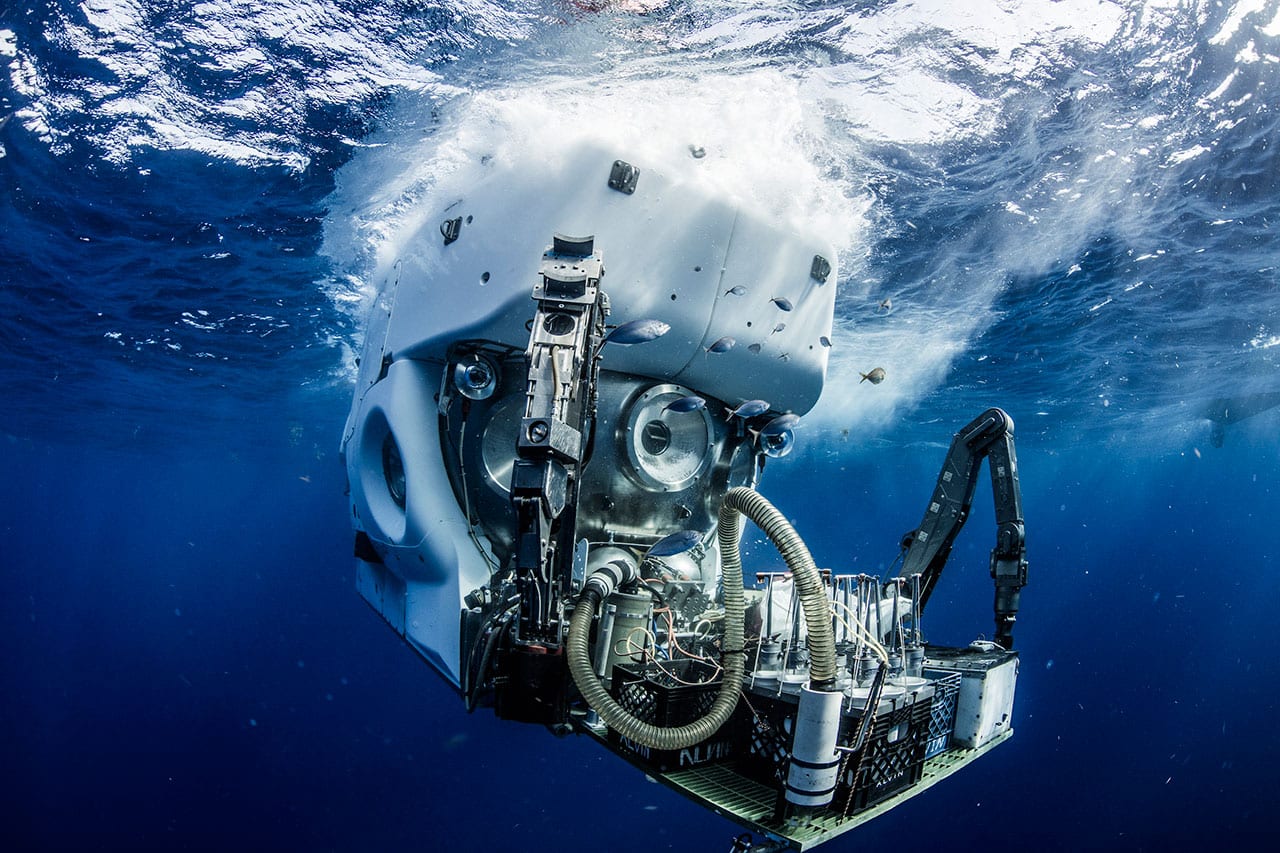
Read MoreAlvin Submersible Makes 5,000th Dive
Alvin, the country’s only deep-diving research submersible capable of carrying humans to the sea floor, reached another milestone in its long career on Nov. 26, 2018, when the sub made its 5,000th dive during an expedition to the Guaymas Basin in the Gulf of California.
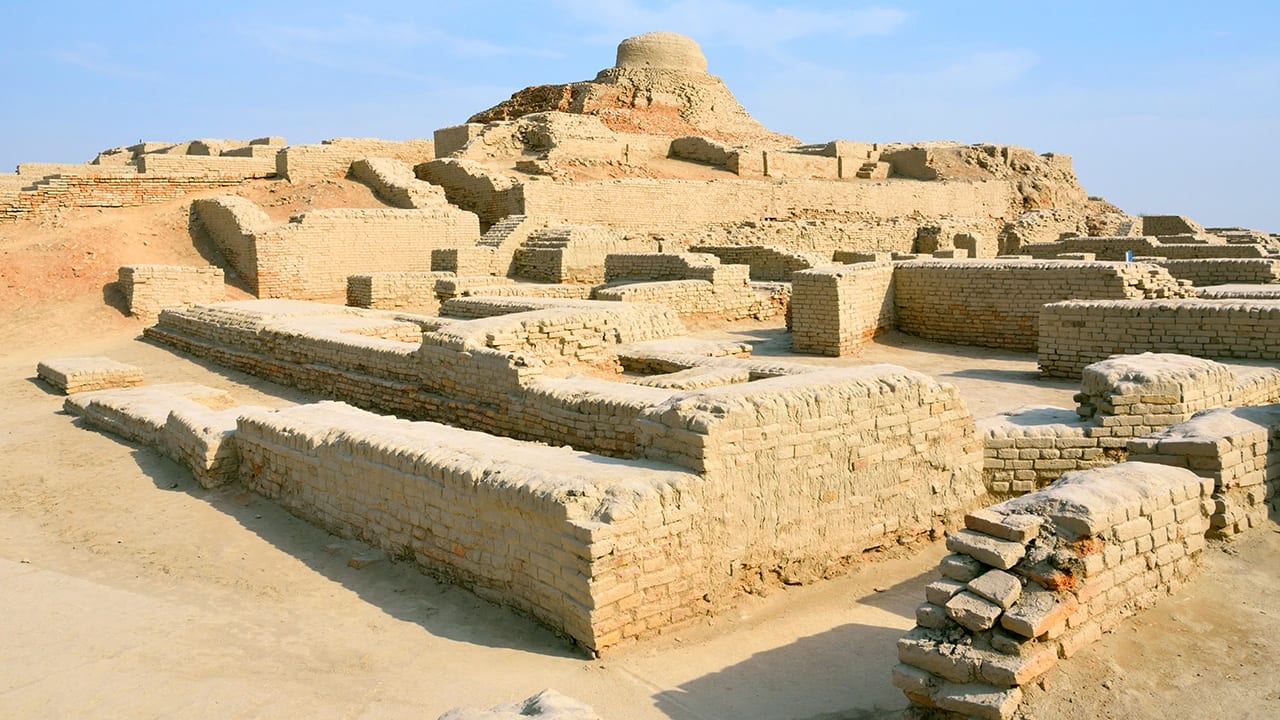
Read MoreClimate Change Likely Caused Migration, Demise of Ancient Indus Valley Civilization
More than 4,000 years ago, the Harappa culture thrived in the Indus River Valley of what is now modern Pakistan and northwestern India, where they built sophisticated cities, invented sewage systems that predated ancient Rome’s, and engaged in long-distance trade with settlements in Mesopotamia. Yet by 1800 BCE, this advanced culture had abandoned their cities, moving instead to smaller villages in the Himalayan foothills. A new study from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) found evidence that climate change likely drove the Harappans to resettle far away from the floodplains of the Indus.
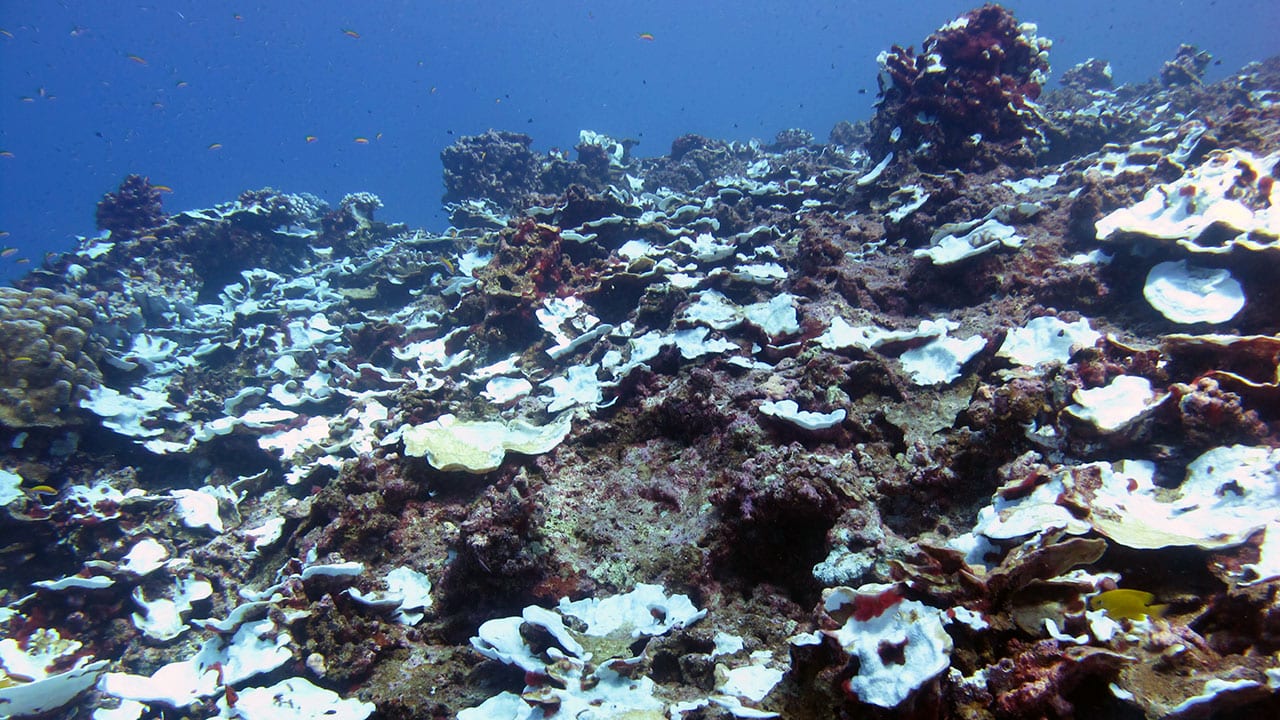
Read MoreStudy Tracks Severe Bleaching Events on a Pacific Coral Reef Over Past Century
As climate change causes ocean temperatures to rise, coral reefs worldwide are experiencing mass bleaching events and die-offs. For many, this is their first encounter with extreme heat. However for some reefs in the central Pacific, heatwaves caused by El Nino are a way of life. Exactly how these reefs deal with repeated episodes of extreme heat has been unclear. A new study from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), has uncovered the history of bleaching on a reef in the epicenter of El Nino, revealing how some corals have been able to return after facing extreme conditions. The study was published October 26, 2018, in the journal Communications Biology.
Read MoreSea Grant Funds New Technology to Monitor for Harmful Algal Blooms
A new system using next generation robotic sensors to monitor coastal waters for disease-causing microalgae has been funded by the NOAA Sea Grant Program as part of a national strategic investment in aquaculture.
The PhytO-ARM (Phytoplankton Observing for Automated Real-time Management), under development by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) biologist Mike Brosnahan, will vastly improve our ability to detect harmful algal blooms (HABs) and the toxins they produce and provide aquaculturists, resource managers, and others detailed, real-time information about the bloom using a web-based, user-friendly dashboard.
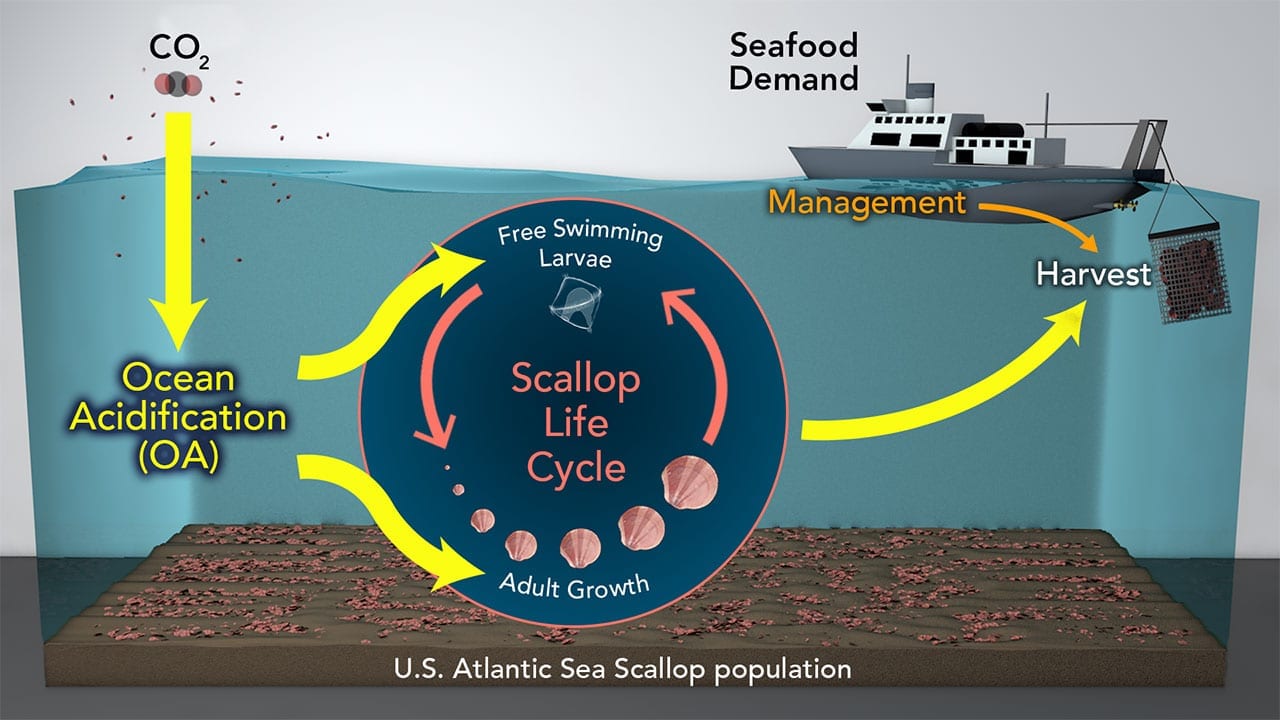
Read MoreOcean Acidification May Reduce Sea Scallop Fisheries
Each year, fishermen harvest more than $500 million worth of Atlantic sea scallops from the waters off the east coast of the United States. A new model created by scientists…
Read MoreNSF Awards Contract to Group Led by WHOI to Continue Operation of Ocean Observatories Initiative
The National Science Foundation (NSF) announced that it has awarded a coalition of academic and oceanographic research organizations a five-year, $220 million contract to operate and maintain the Ocean Observatories…
Read MoreStudy Links Natural Climate Oscillations in North Atlantic to Greenland Ice Sheet Melt
Scientists have known for years that warming global climate is melting the Greenland Ice Sheet, the second largest ice sheet in the world. A new study from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), however, shows that the rate of melting might be temporarily increased or decreased by two existing climate patterns: the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), and the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO).
Read MoreWoods Hole Center for Oceans and Human Health Receives Five-year Funding from NSF and NIEHS
The National Science Foundation (NSF) and National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), one of the National Institutes of Health, have announced that the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will…
Read MoreThree WHOI Scientists to be Honored by AGU
Three scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) are among those to be honored by the American Geophysical Union (AGU) with awards or special lectures at its upcoming fall…
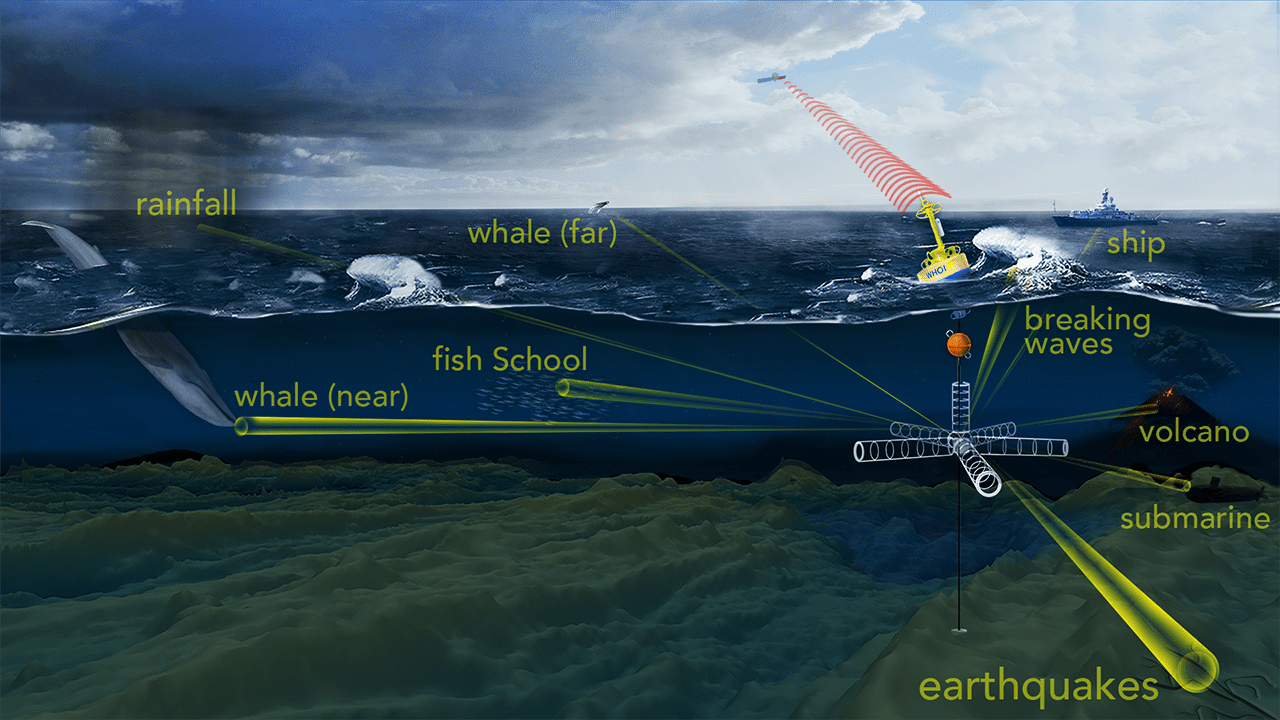
Read More$1 Million Grant to Build the WHOI-Keck Real Time 3-D Acoustic Telescope
A first-of-its-kind acoustic telescope is under development at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), funded by a $1 million grant from the W.M. Keck Foundation, that will permit researchers to…
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution Taps New Vice President for Advancement and Chief Marketing Officer
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has selected Samuel C. Harp, an international brand marketing expert, as the Institution’s first Vice President for Advancement and Chief Marketing Officer. Harp has…
Read MoreWHOI Chosen as Location of New NSF-funded Ocean Bottom Seismograph Instrument Center
The National Science Foundation (NSF) has announced that the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will operate a new center to provide seafloor seismographs and technical support to the U.S. academic…
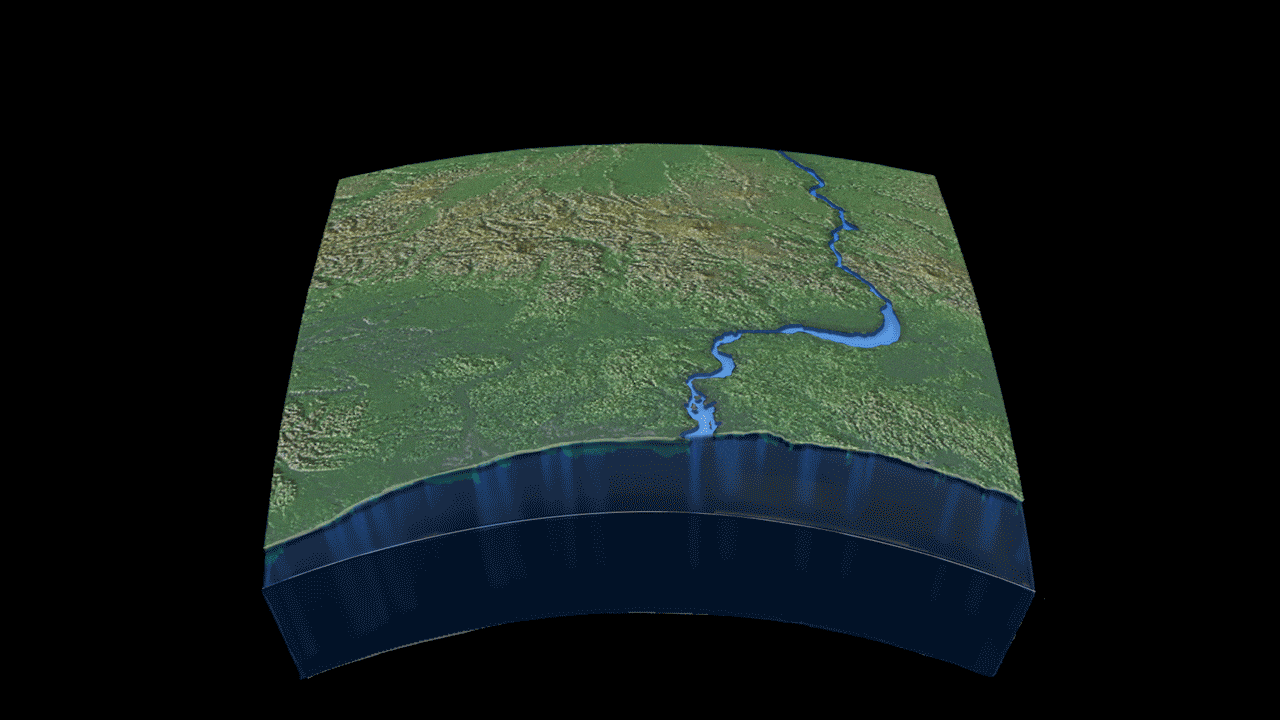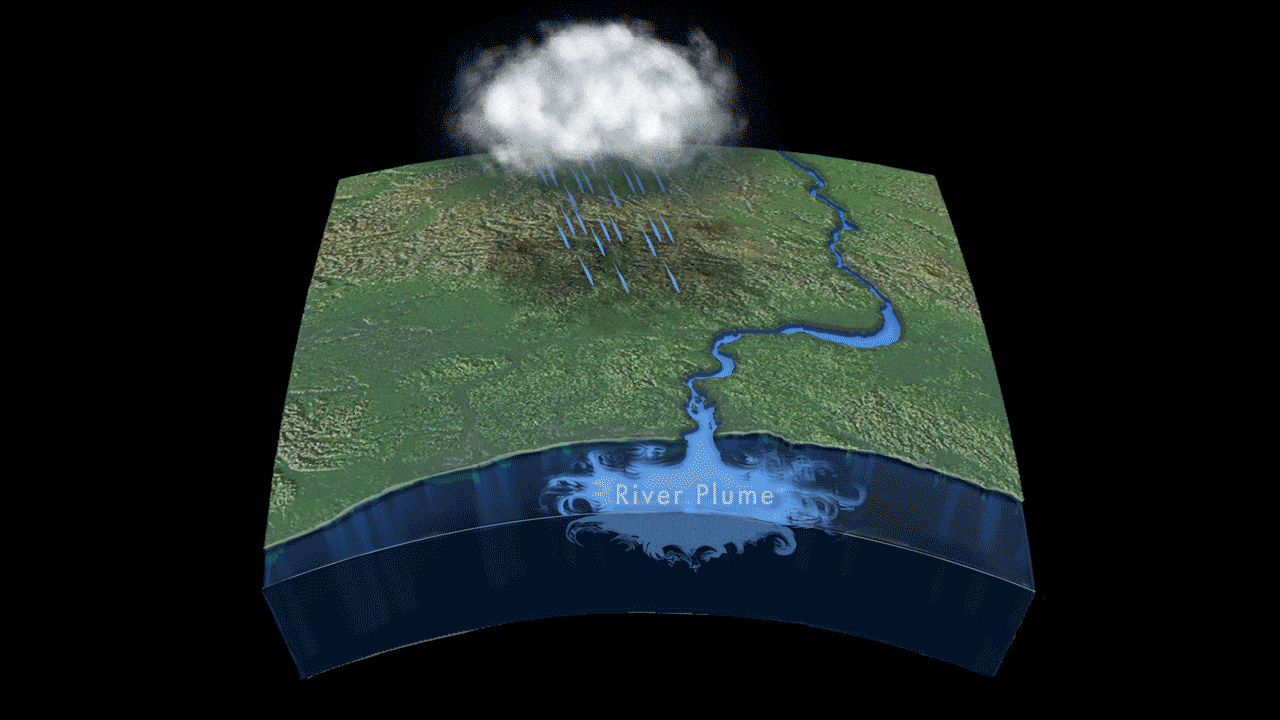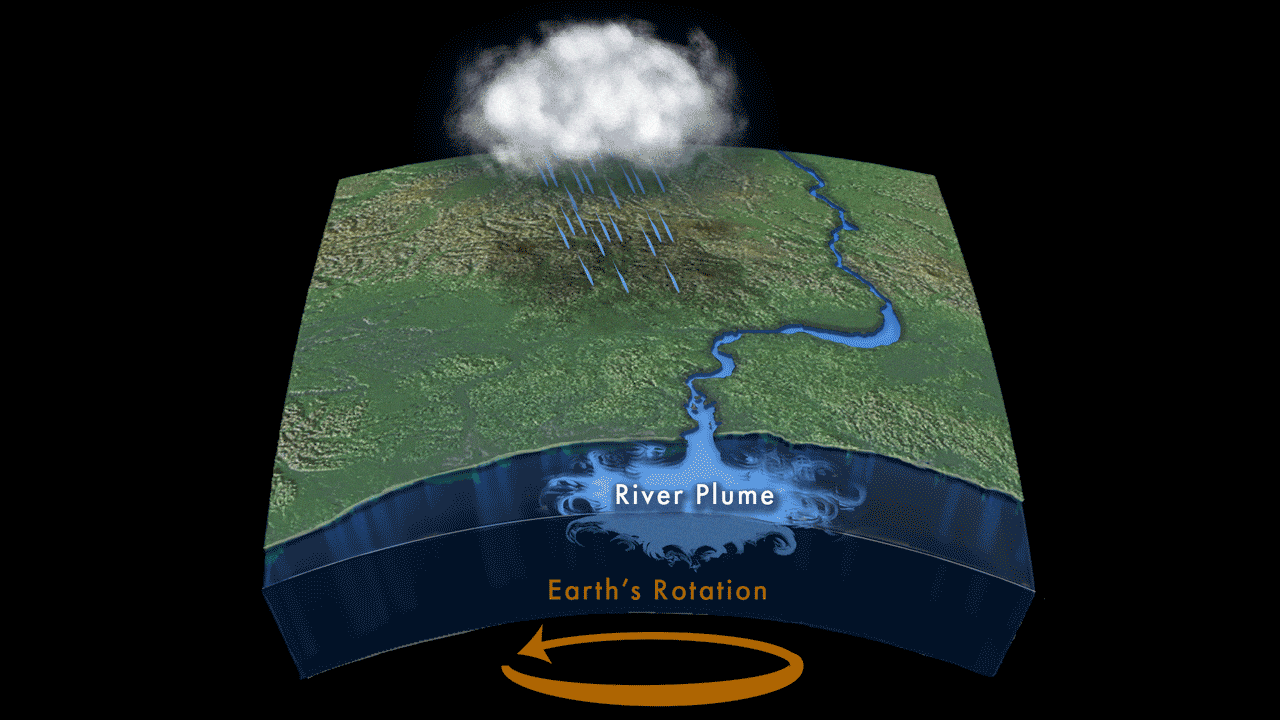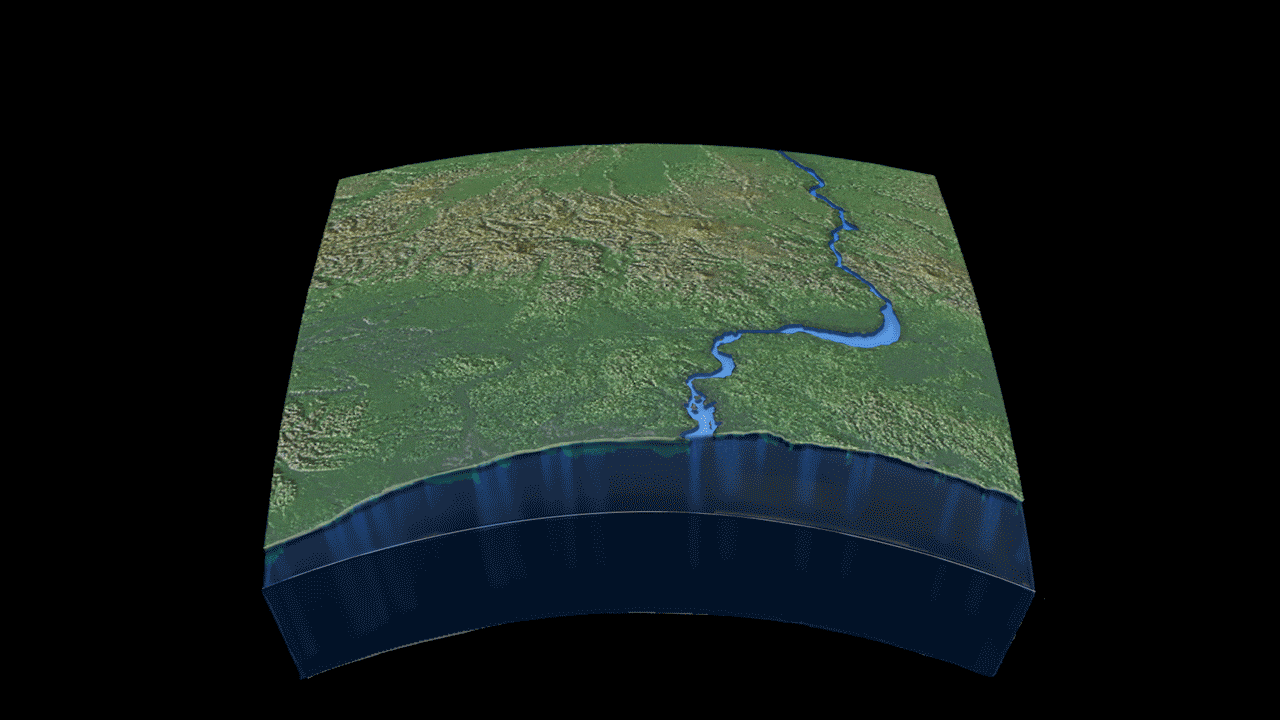
Read MoreStudy Finds Link Between River Outflow and Coastal Sea Level
Sea levels in coastal areas can be affected by a number of factors: tides, winds, waves, and even barometric pressure all play a role in the ebb and flow of the ocean. For the first time, however, a new study led by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has shown that river outflow could play a role in sea level change as well.
Read MoreFollowing the Fresh Water
A research team led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) found the fingerprint of a massive flood of fresh water in the western Arctic, thought to be the cause of an ancient cold snap that began around 13,000 years ago.
Read MoreHearing Tests on Wild Whales
Scientists published the first hearing tests on a wild population of healthy marine mammals. The tests on beluga whales in Bristol Bay, AK, revealed that the whales have sensitive auditory systems and showed less age-related hearing loss than is expected.
Read MoreGeologic History of Ayeyawady River Delta Mapped for the First Time
The Ayeyawady River delta in Myanmar is home to millions of people, and is a hub of agricultural activity. Unlike other large rivers across the world, however, the Ayeyawady has been relatively untouched by large infrastructure and dam projects for the past 50 years, and its geologic evolution has never previously been studied.
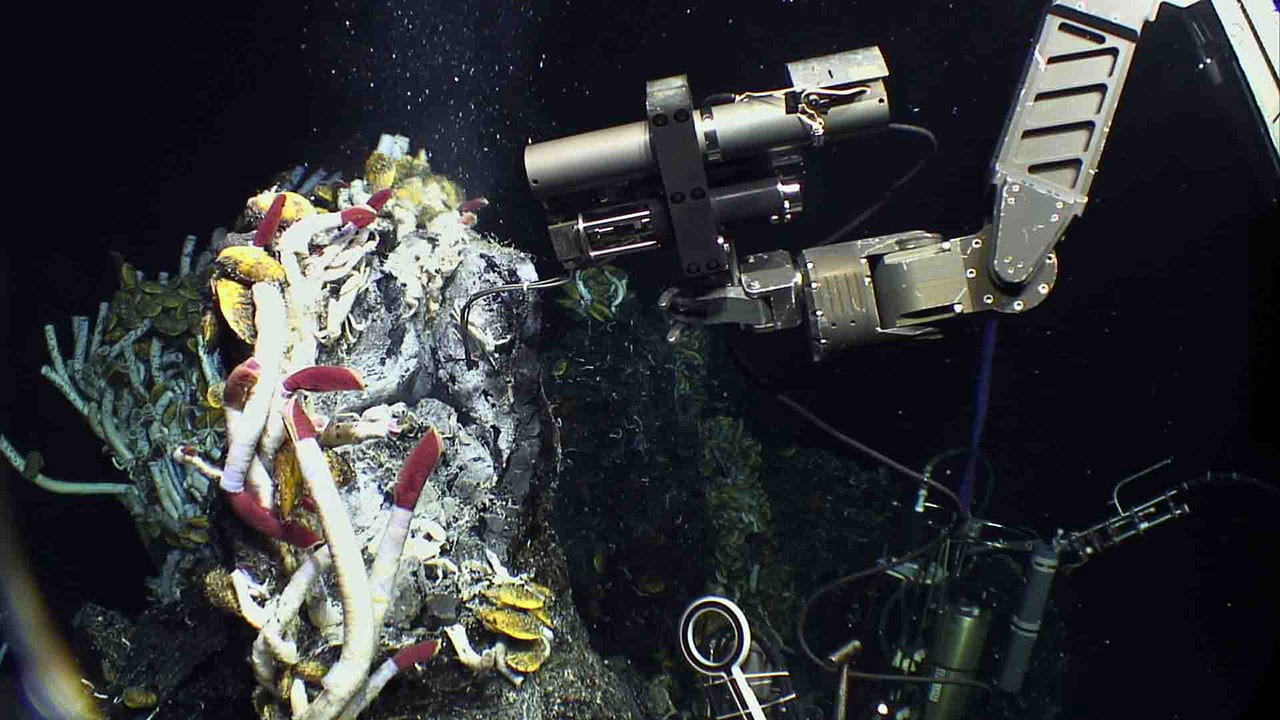
Read MoreFueling a Deep-Sea Ecosystem
Miles beneath the ocean surface in the dark abyss, vast communities of subseafloor microbes at deep-sea hot springs are converting chemicals into energy that allows deep-sea life to survive, and even thrive, in a world without sunlight. Until now, however, measuring the productivity of subseafloor microbe communities (or how fast they oxidize chemicals and the amount of carbon they produce) has been nearly impossible.
Read MoreNew Details on Discovery of San Jose Shipwreck
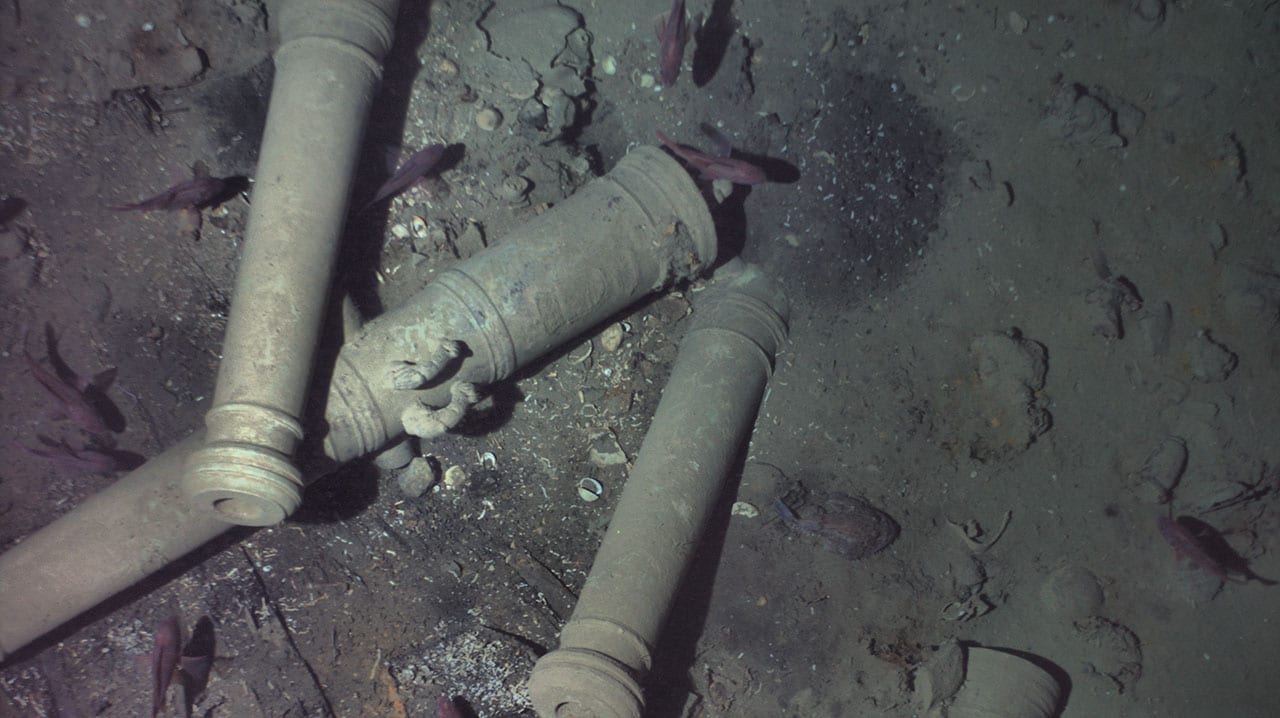
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) recently obtained authorization by Maritime Archaeology Consultants, Switzerland AG (MAC), and the Colombian government to release new details from the successful search for the three-century old San José 62-gun, three-masted Spanish galleon ship that sank with a cargo believed to be worth billions of dollars. The ship, which is often called the ‘holy grail of shipwrecks,’ went down with a treasure of gold, silver, and emeralds in 1708 during a battle with British ships in the War of Spanish Succession.
Read MoreAre Emperor Penguins Eating Enough?
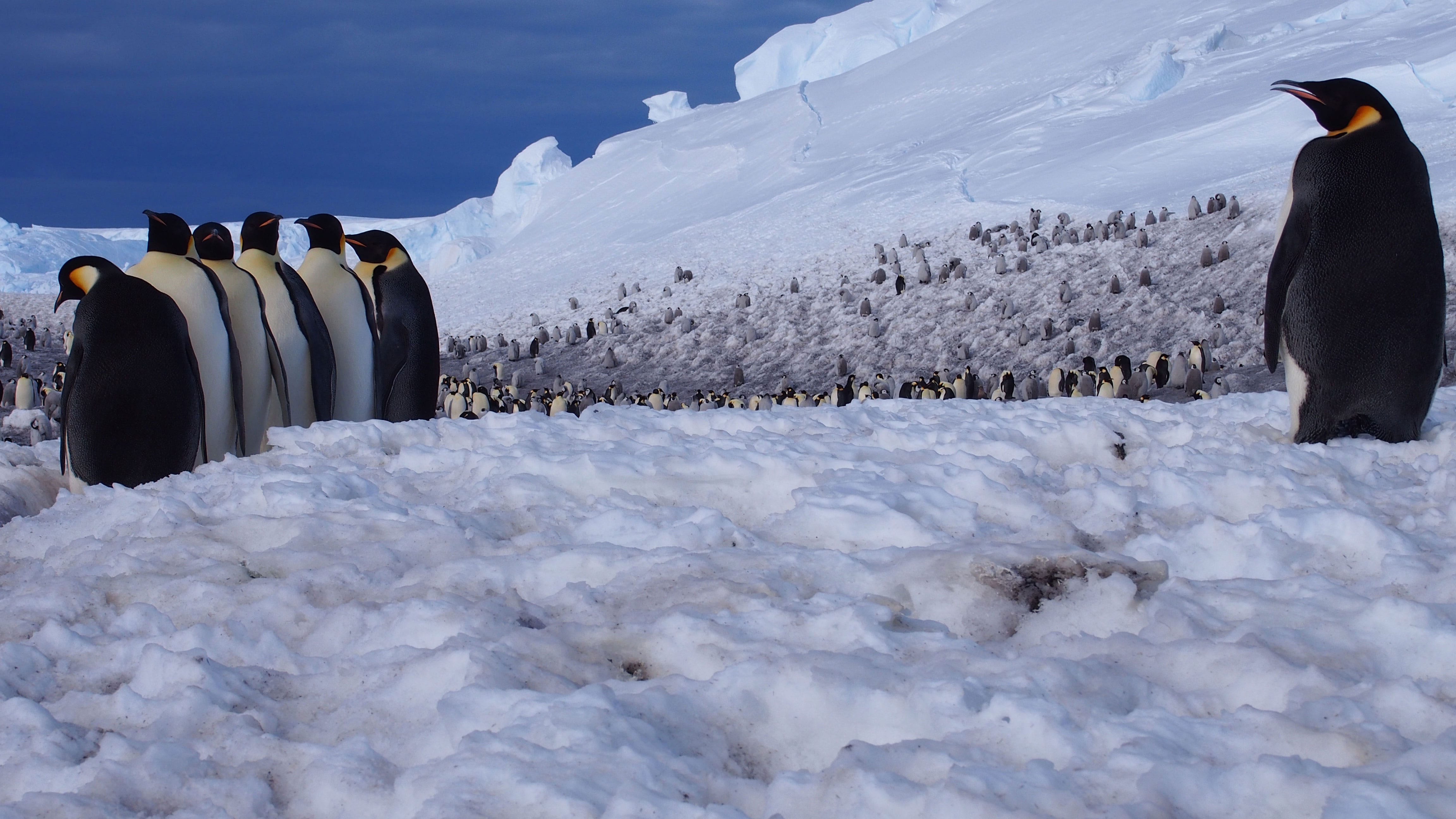
For Emperor penguins waddling around a warming Antarctic, diminishing sea ice means less fish to eat. How the diets of these tuxedoed birds will hold up in the face of…
Read MoreHow Do Marine Mammals Avoid the Bends?
Deep-diving whales and other marine mammals can get the bends – the same painful and potentially life-threatening decompression sickness that strikes scuba divers who surface too quickly. A new study offers a hypothesis of how marine mammals generally avoid getting the bends and how they can succumb under stressful conditions.
Read MoreSunlight Reduces Effectiveness of Dispersants Used in Oil Spills
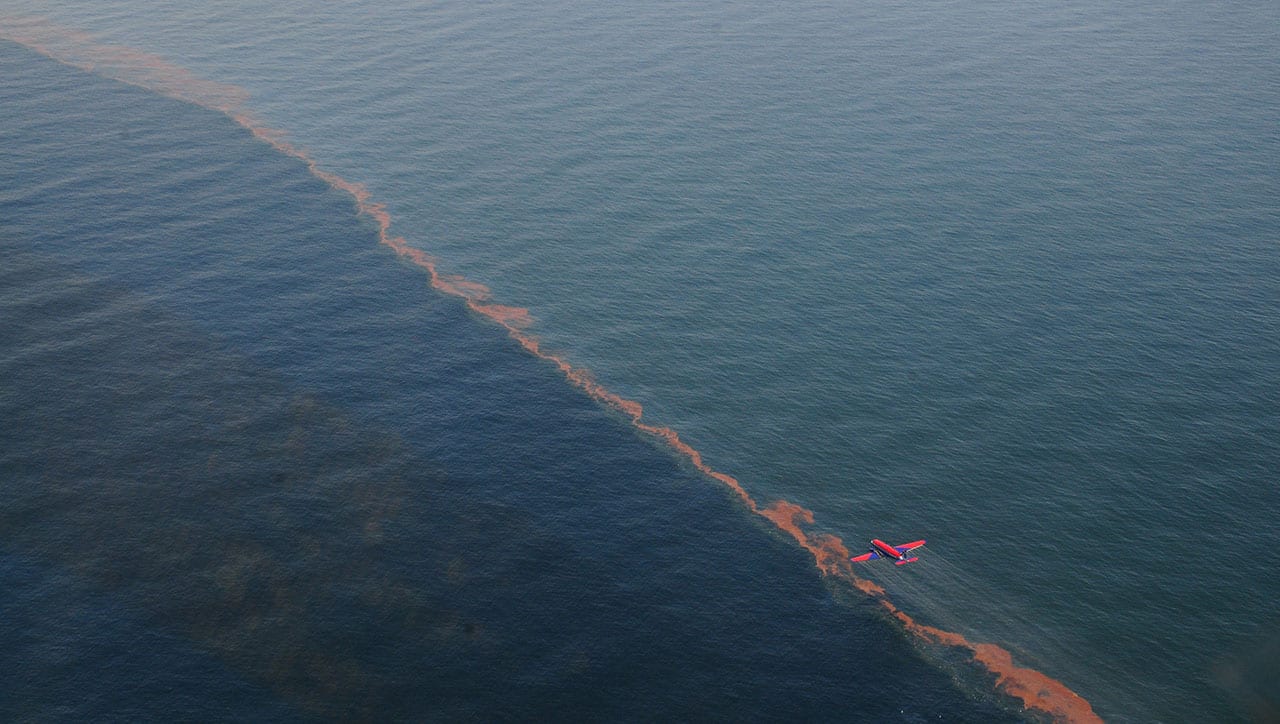
A research team led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) found that sunlight chemically alters crude oil floating on the sea surface within hours or days. In a follow-up study the team reported that sunlight changes oil into different compounds that dispersants cannot easily break up. The results of these two studies could affect how responders decide when, where, and how to use dispersants.
Read MoreMountain Erosion May Add Carbon Dioxide to Atmosphere
Scientists have long known that steep mountain ranges can draw carbon dioxide (CO2) out of the atmosphere as erosion exposes new rock, it also starts a chemical reaction between minerals on hill slopes and CO2 in the air, weathering the rock and using CO2 to produce carbonate minerals like calcite.
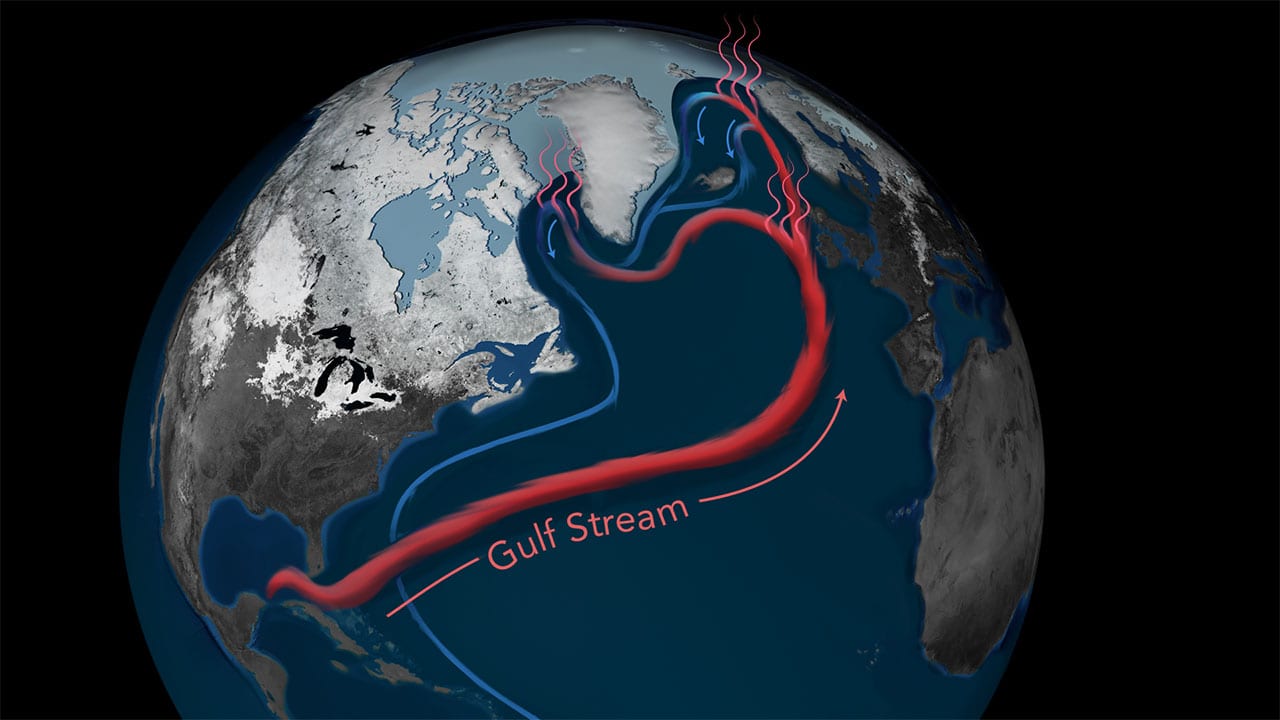
Read MoreAtlantic Ocean Circulation at Weakest Point in 1,600 years
Atlantic Ocean Circulation at Weakest Point in More Than 1500 years New research led by University College London (UCL) and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) provides evidence that a key cog in the global ocean circulation system hasn’t been running at peak strength since the mid-1800s and is currently at its weakest point in the past 1,600 years. If the system continues to weaken, it could disrupt weather patterns from the United States and Europe to the African Sahel, and cause more rapid increase in sea level on the U.S. East Coast.
Read More