News Releases
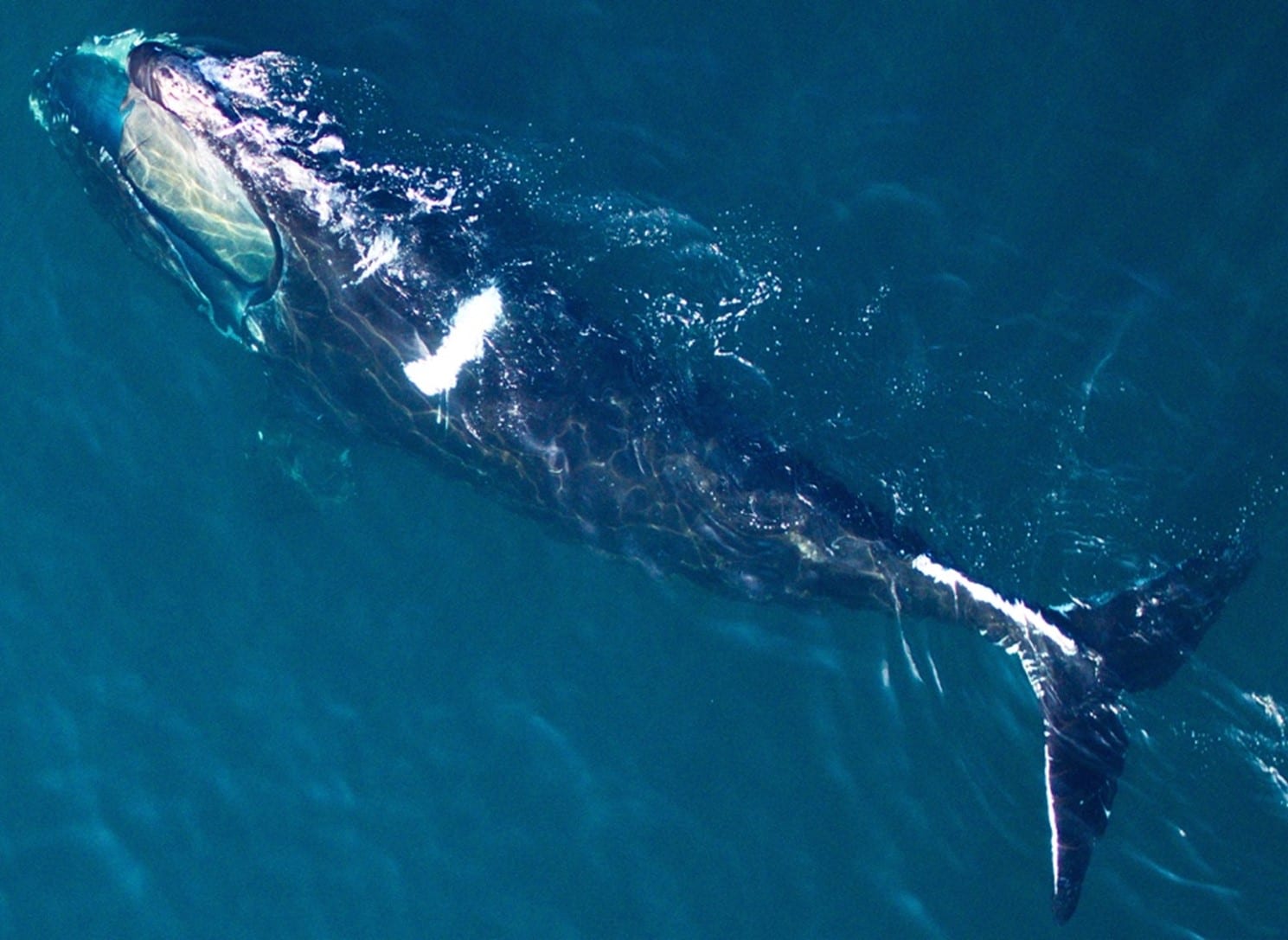
WHOI and NOAA Fisheries Release New North Atlantic Right Whale Health Assessment Review
North Atlantic right whales are critically endangered and declining. Climate change, vessel strikes, entanglements and noise engender poor health and reproductive failure, and are major threats to individuals and the species. Trauma reduction measures and applying new tools to assess and enhance their health, are critically important.
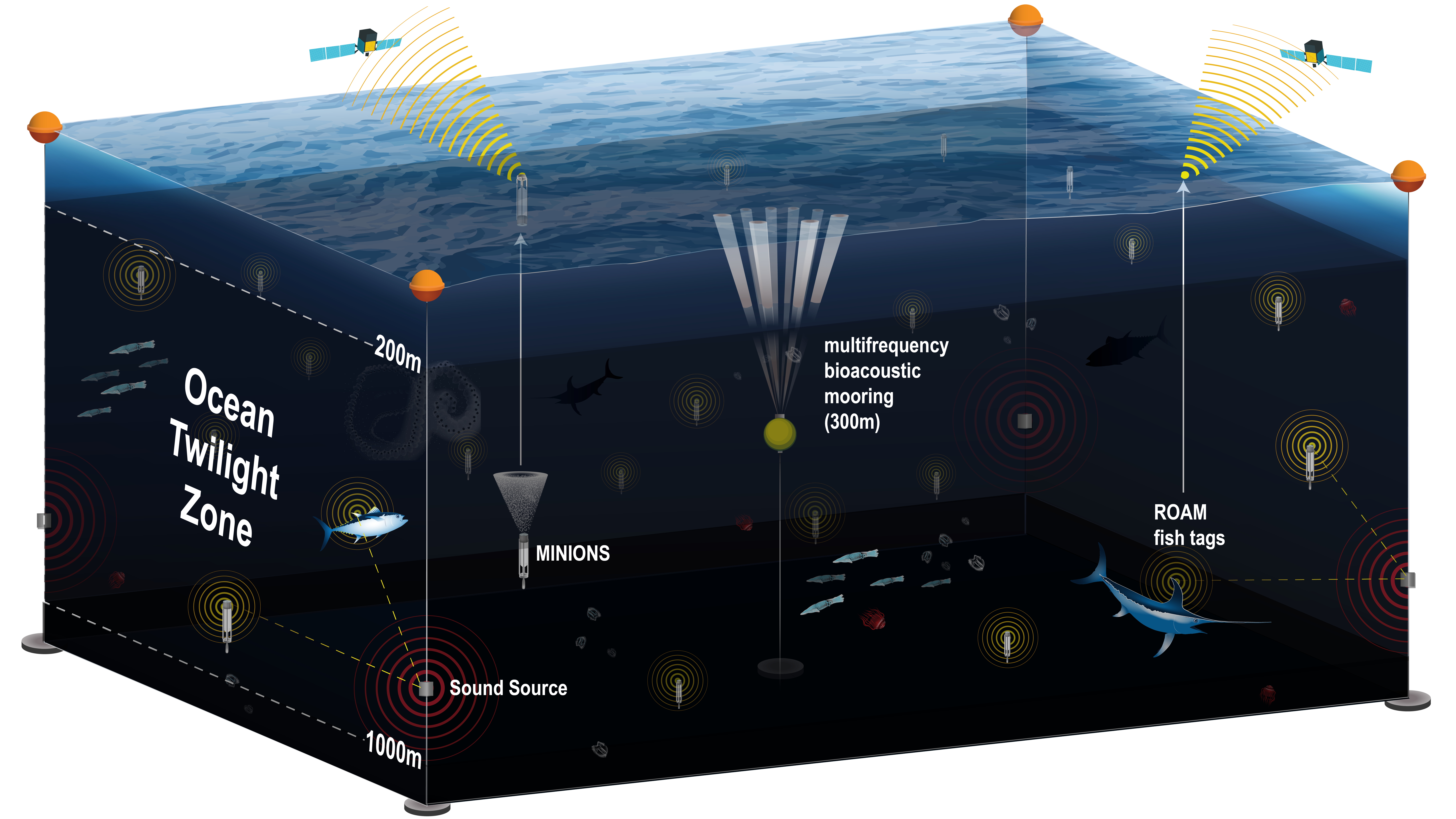
Read MoreNew observation network will provide unprecedented, long-term view of life in the ocean twilight zone
A new observation network under development by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will offer round-the-clock data about the ocean twilight zone – a dimly lit region roughly 200–1000 meters (650–3200 feet) below the surface, containing the largest amount of fish biomass on Earth.
Read MoreWHOI announces new CFO
Kathryn Link to join as WHOI’s new Chief Financial Officer, bringing with her over 25 experience in working with innovators from Harvard to the Broad Institute
Read MoreInstitute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers Honors WHOI Scientist
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) elected Dana Yoerger as a 2021 fellow for the development of autonomous underwater vehicles for deep-ocean exploration and science.
Read MoreCINAR Fellows in Quantitative Fisheries and Ecosystems Science Announced
The Cooperative Institute for the North Atlantic Region (CINAR), led by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, and the Northeast Fisheries Science Center are pleased to announce the appointment of five…
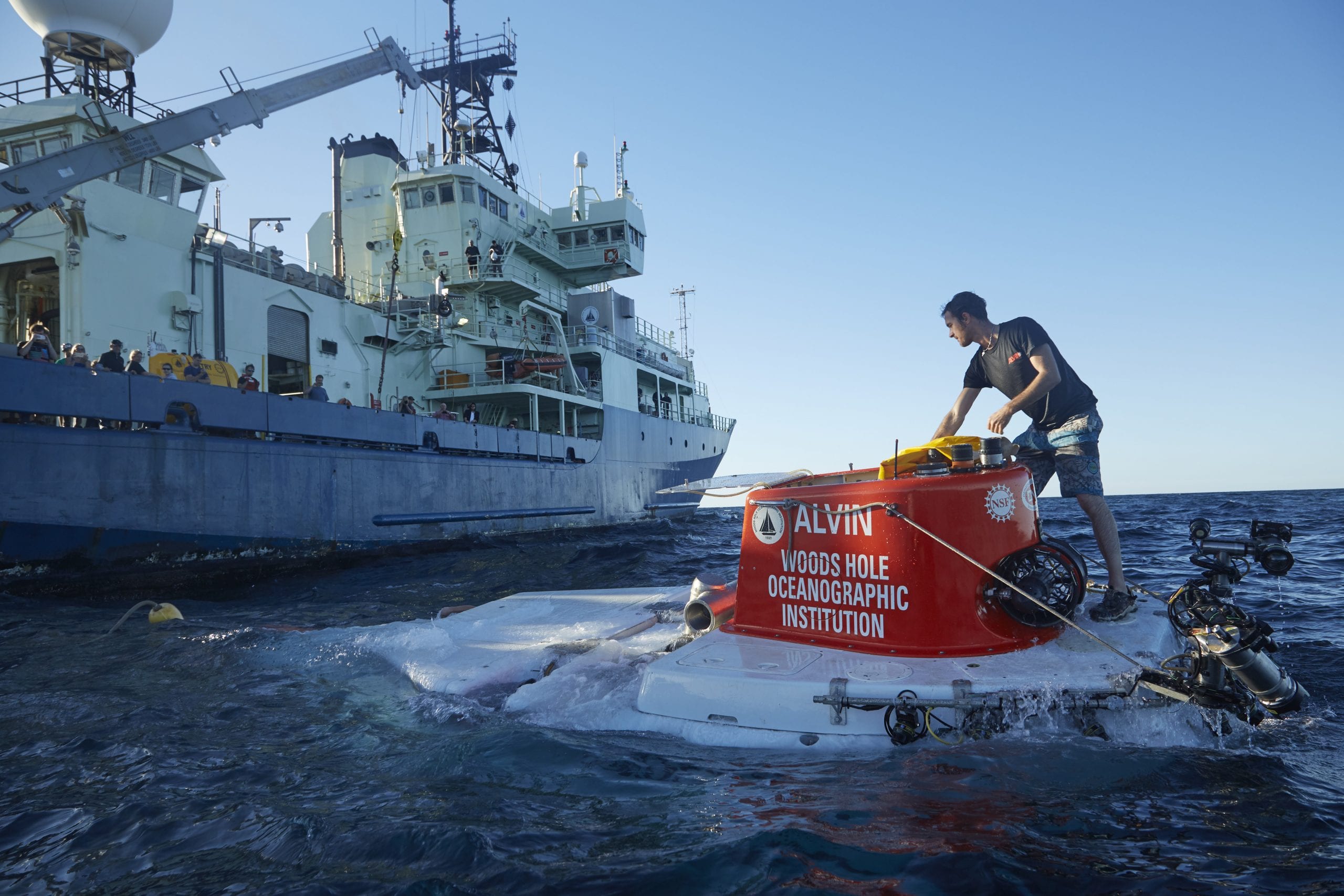
Read MoreWHOI reveals upgrades to iconic submersible Alvin
One of the world’s most prolific research submersibles will put 99% of the ocean floor within reach of science community when it relaunches in 2021
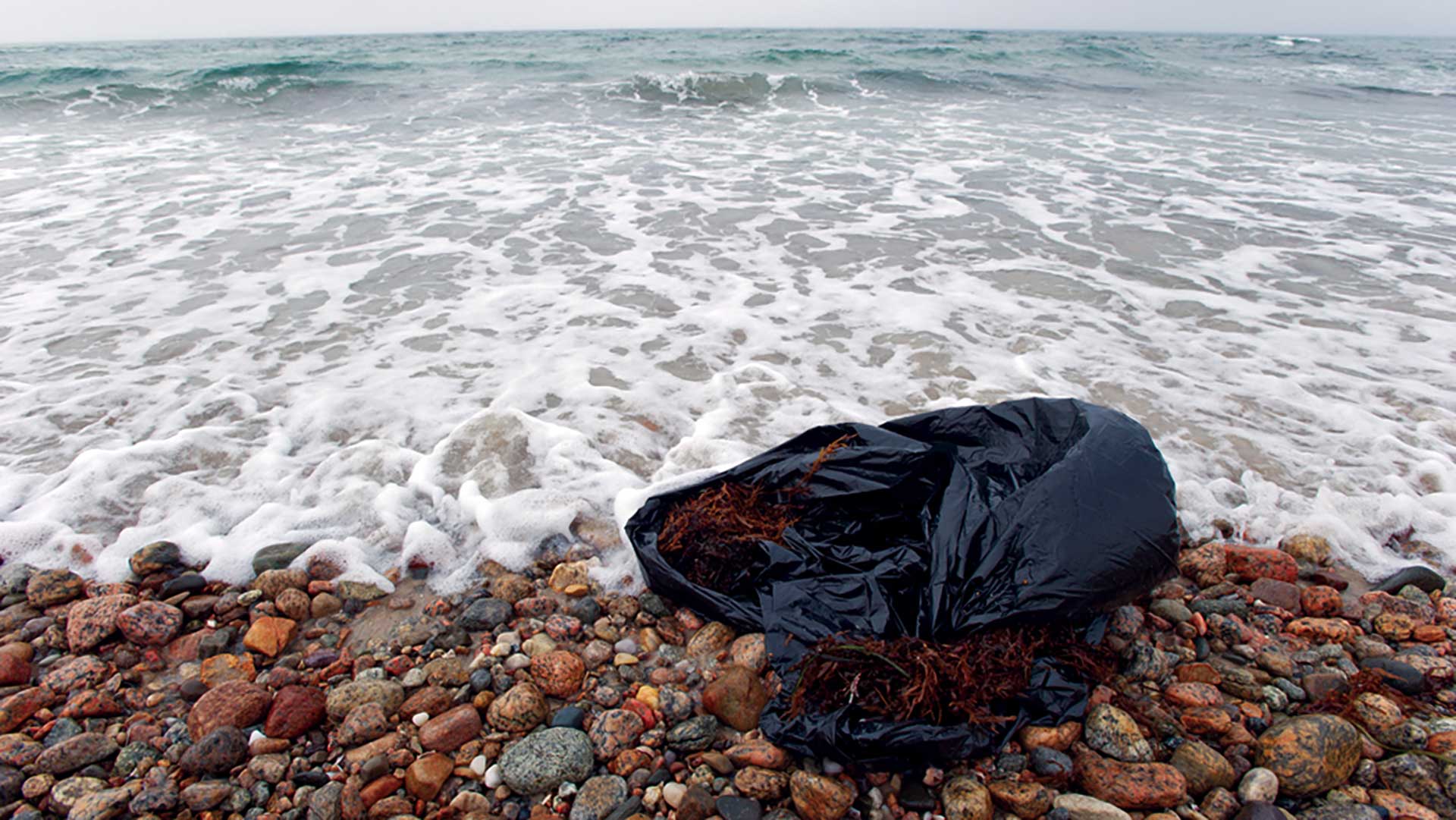
Read MoreNew study takes comprehensive look at marine pollution
Paper finds ocean pollution is a complex mix of chemicals and materials, primarily land-based in origin, with far-reaching consequences for environmental and human health, but there are options available for…
Read MoreScientists call for decade of concerted effort to improve understanding of the deep ocean
The deep ocean—vast expanses of water and seafloor more than 200 meters (660 feet) below the surface—are globally recognized as an important frontier of exploration and research. Despite the fact…
Read MoreWHOI President & Director Dr. Peter de Menocal Recognized as AAAS Fellow
Dr. Peter de Menocal, President and Director of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution of has been named a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS).
Read MoreStudy reconstructs ancient storms to predict changes in a cyclone hotspot
Intense tropical cyclones are expected to become more frequent as climate change increases temperatures in the Pacific Ocean. But not every area will experience storms of the same magnitude
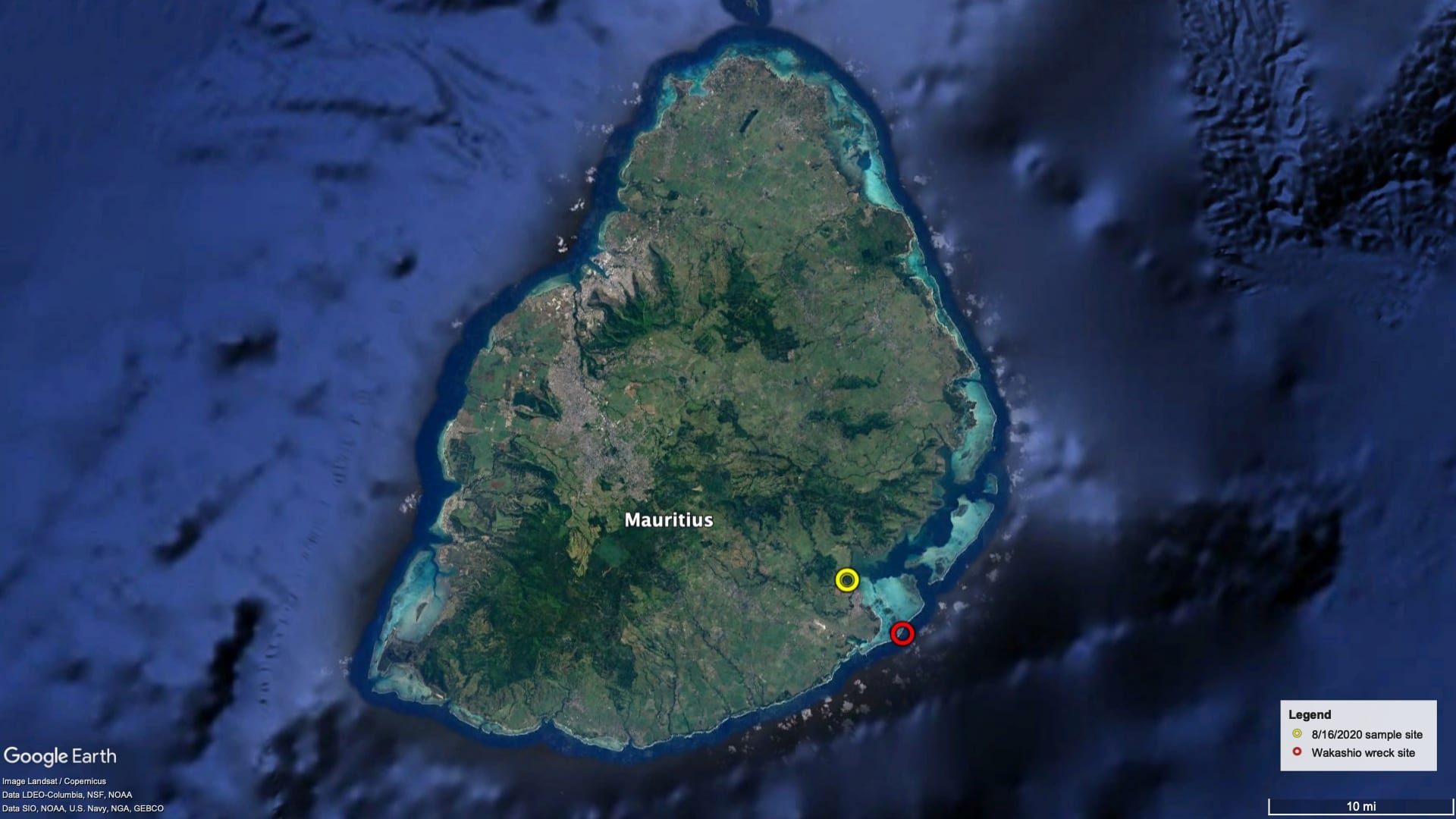
Read MoreFirst Detailed Oil Sample Analysis Completed from Mauritius Oil Spill
When the Japanese bulk carrier MV Wakashio struck a coral reef off the coast of Mauritius on July 25, 2020, and began leaking fuel oil two weeks later, local residents and the international community sprang into action to protect the pristine habitats that fringe the Indian Ocean nation.
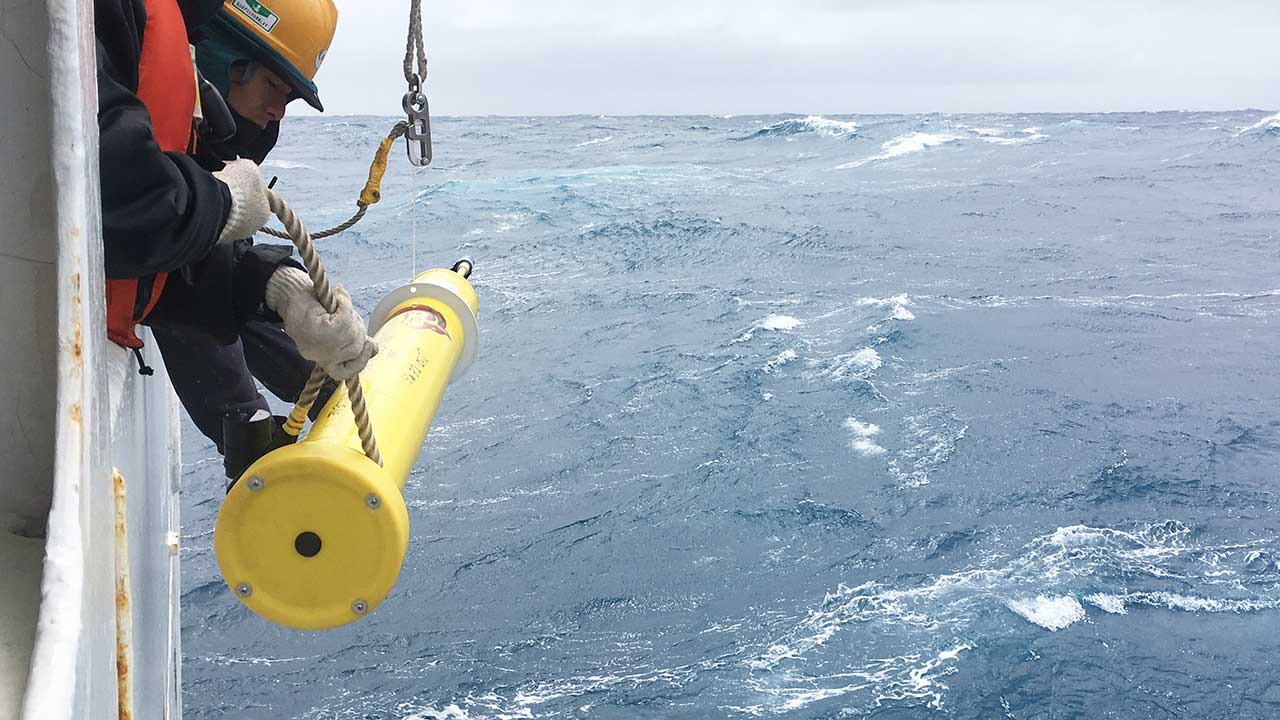
Read MoreNew multi-institutional grant will support a fleet of robotic floats
The National Science Foundation approved a $53 million grant to build a global network of chemical and biological sensors that will monitor ocean health.
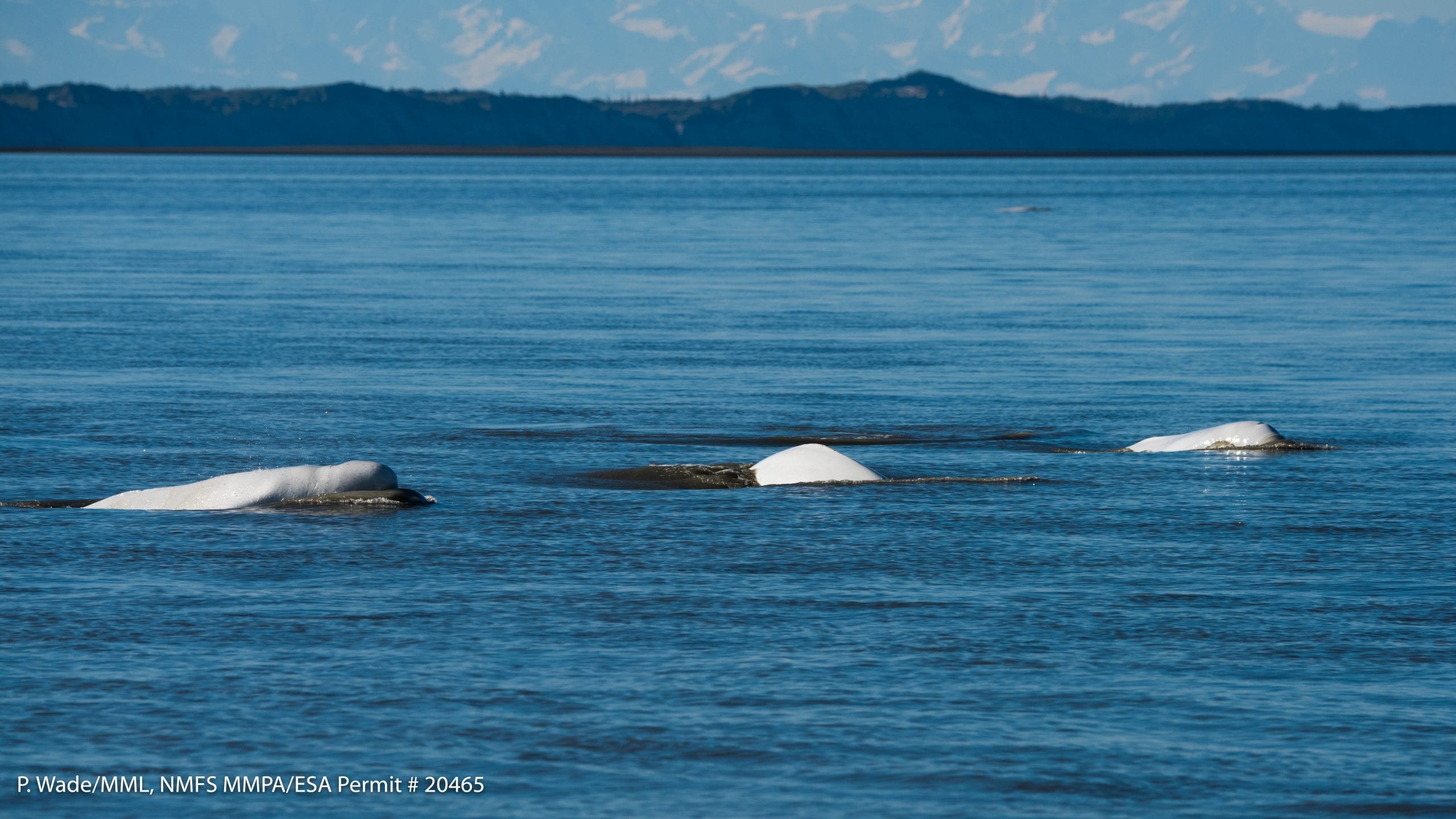
Read MoreStudy Sheds Light on Critically Endangered Beluga Whale Population
A team of scientists from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and NOAA Fisheries are collaborating to help stem the decline of a critically endangered population of beluga whales in the Cook Inlet, Alaska.
Read MoreTwo New Studies Substantially Advance Understanding of Currents that Help Regulate Climate
Two studies shed new light on a critical driver of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) and potential impacts of rising temperatures
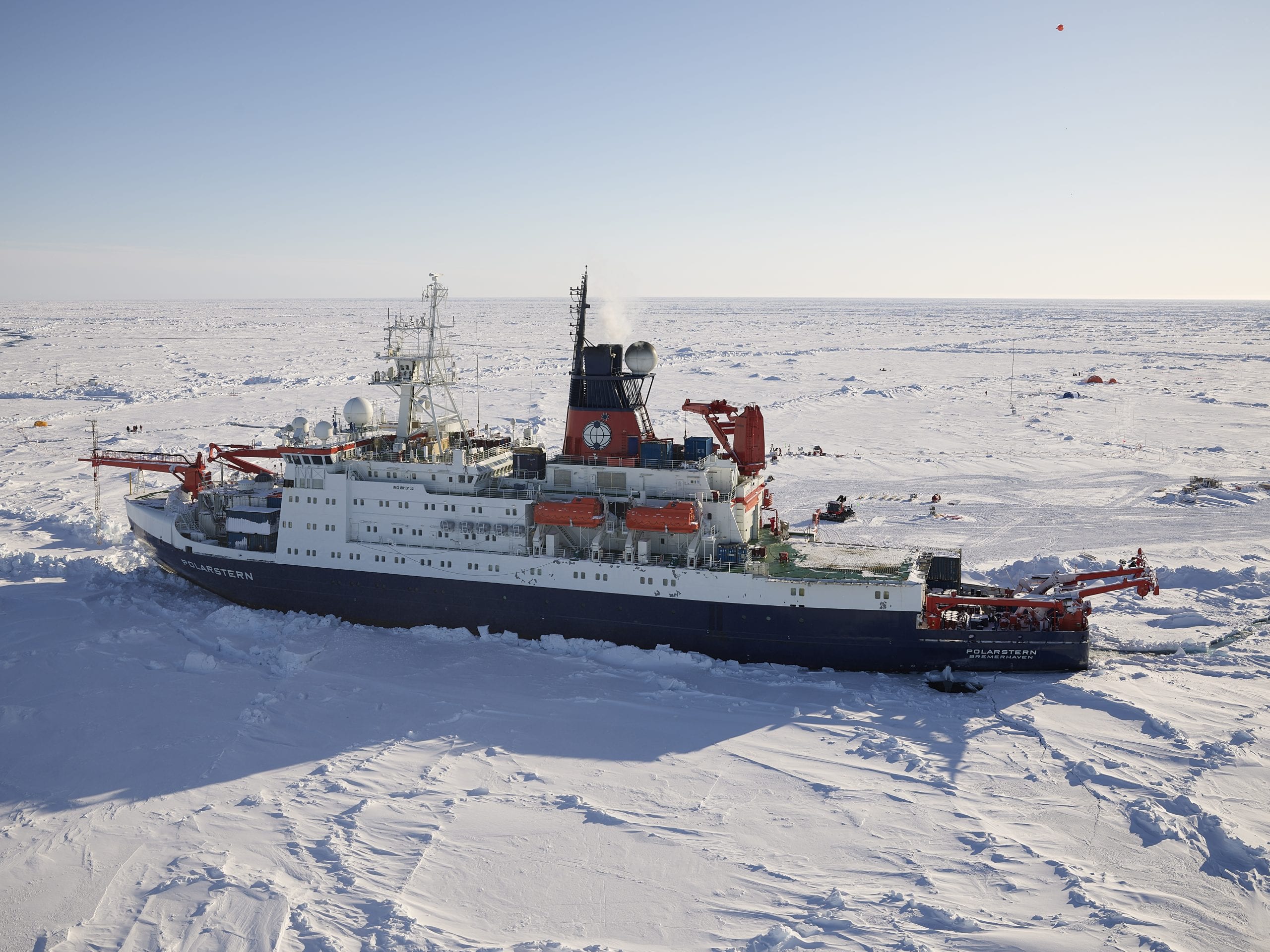
Read MoreEpic Arctic Mission Ends
An epic mission ended as the German icebreaker Polarstern returned home Oct. 12, 2020, after being frozen near the top of the world for nearly a year to study all aspects of the Arctic system.
Read MoreWHOI-NOAA partnership tackles critical gap in climate knowledge
Remote technologies, machine learning will improve simulations of polar ice melt and implications for the global climate Researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) were recently awarded a $500,000 grant…
Read MoreWHOI receives NOAA awards to study, predict harmful algal blooms
Projects will help enhance monitoring and determine socioeconomic impacts of blooms nationwide Researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) were recently named in a list of 17 new research projects…
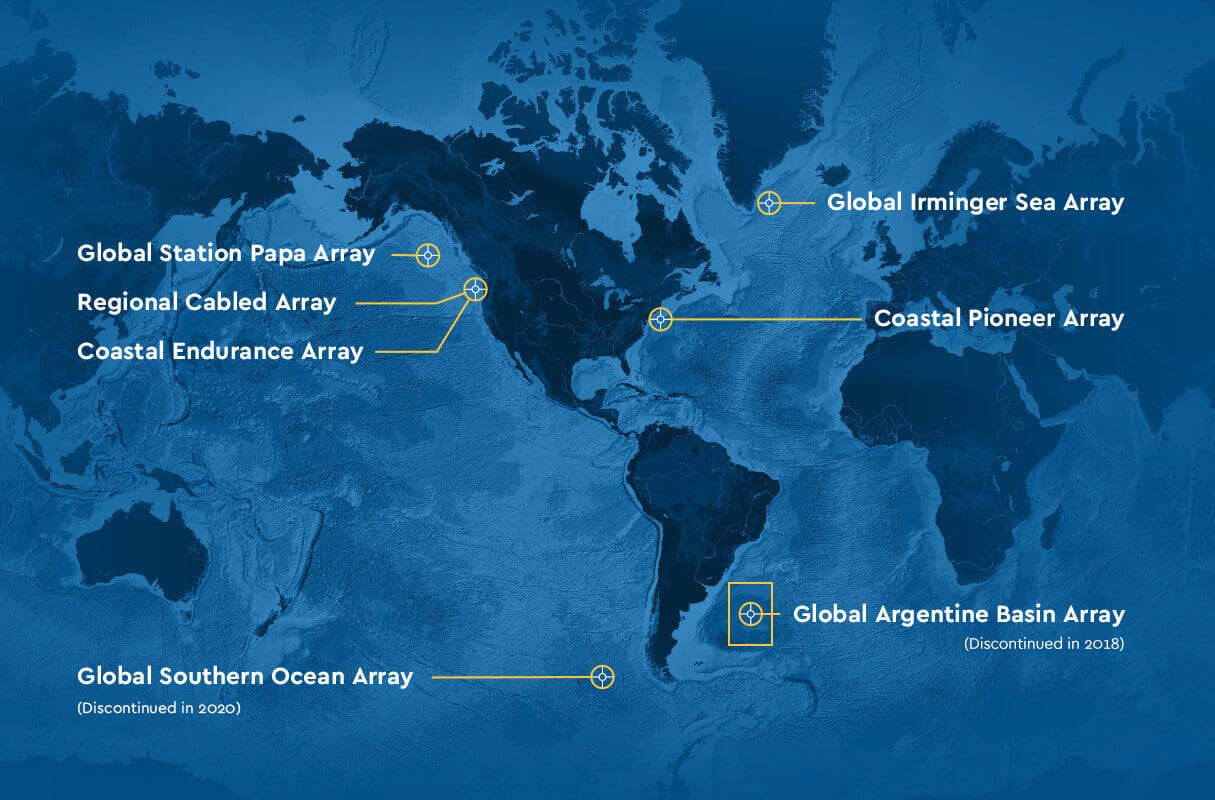
Read MoreOSU Assumes Cyberinfrastructure Responsibility for OOI
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and Oregon State University (OSU) jointly announced that OSU will assume responsibilities for the systems management of the cyberinfrastructure that makes data transmission for the Ocean Observatories Initiative (OOI) possible through September of 2023.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution Elects New Corporation Members
The Board of Trustees of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) elected today six new corporation members at its Fall Joint Meeting of the Board and Corporation.
Read MoreAntarctic Ice Sheet Loss Expected to Affect Future Climate Change
The research team reports that their new models with the added ice melt information reveal important interacting processes and demonstrate a need to accurately account for meltwater input from ice sheets in order to make confident climate predictions.
Read MoreStudies investigate marine heatwaves, shifting ocean currents
North America experienced a series of dangerous heatwaves during the summer of 2020, breaking records from coast to coast. In the ocean, extreme warming conditions are also becoming more frequent and intense.
Read MoreThe $500 billion question: what’s the value of studying the ocean’s biological carbon pump?
A new study puts an economic value on the benefit of research to improve knowledge of the biological carbon pump and reduce the uncertainty of ocean carbon sequestration estimates.
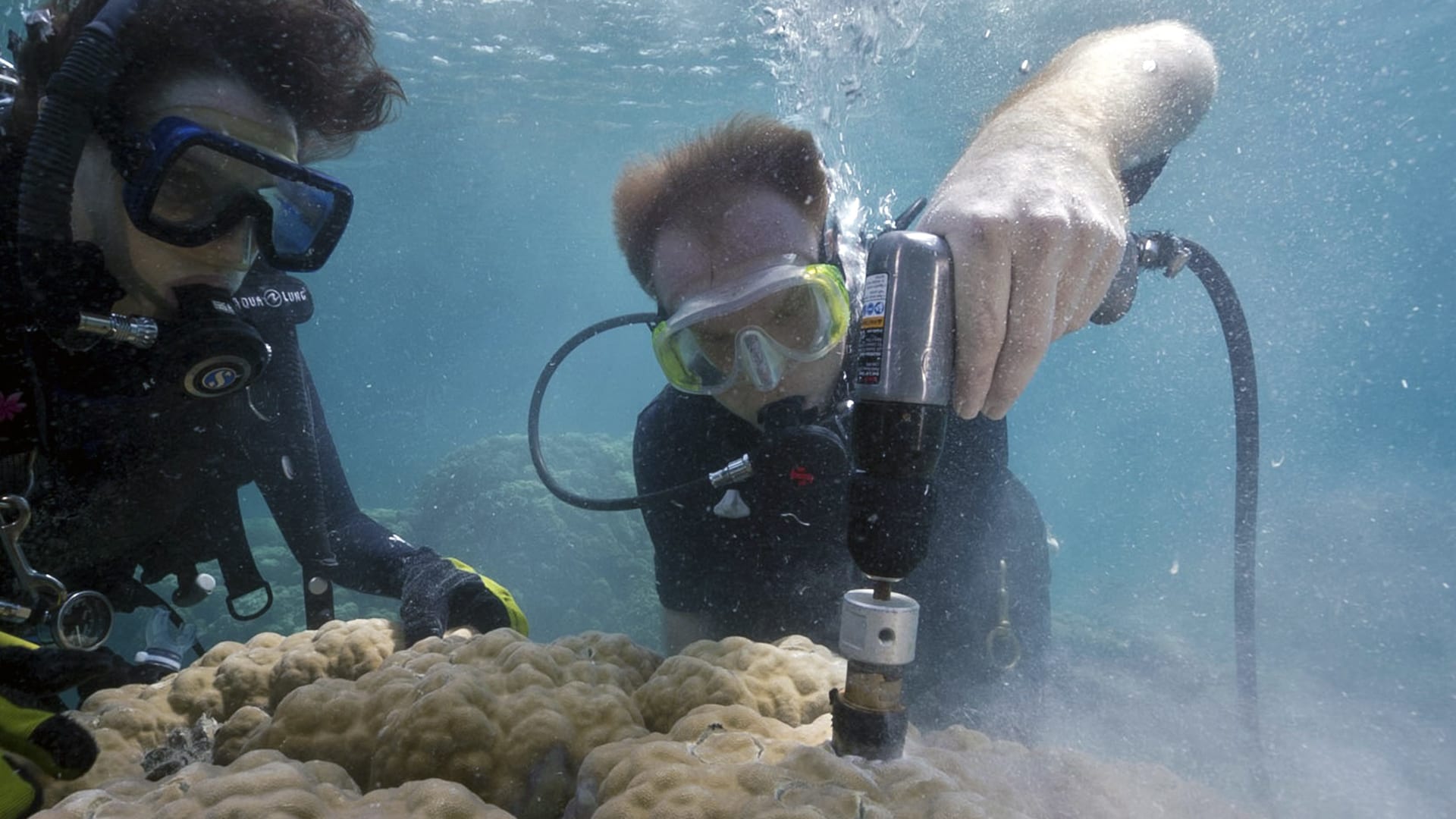
Read MoreOcean acidification causing coral ‘osteoporosis’ on iconic reefs
Scientists have long suspected that ocean acidification is affecting corals’ ability to build their skeletons, but it has been challenging to isolate its effect from that of simultaneous warming ocean…
Read MoreWHOI Announces D’Works Marine Technology Initiative for Massachusetts Startups and Entrepreneurs
Massachusetts has long been known as a center of invention and technical innovation and, more recently, has gained attention for its vibrant marine robotics startup community. Now startup companies, entrepreneurs,…
Read More