News Releases
Atlantic Ocean Circulation at Weakest Point in 1,600 years
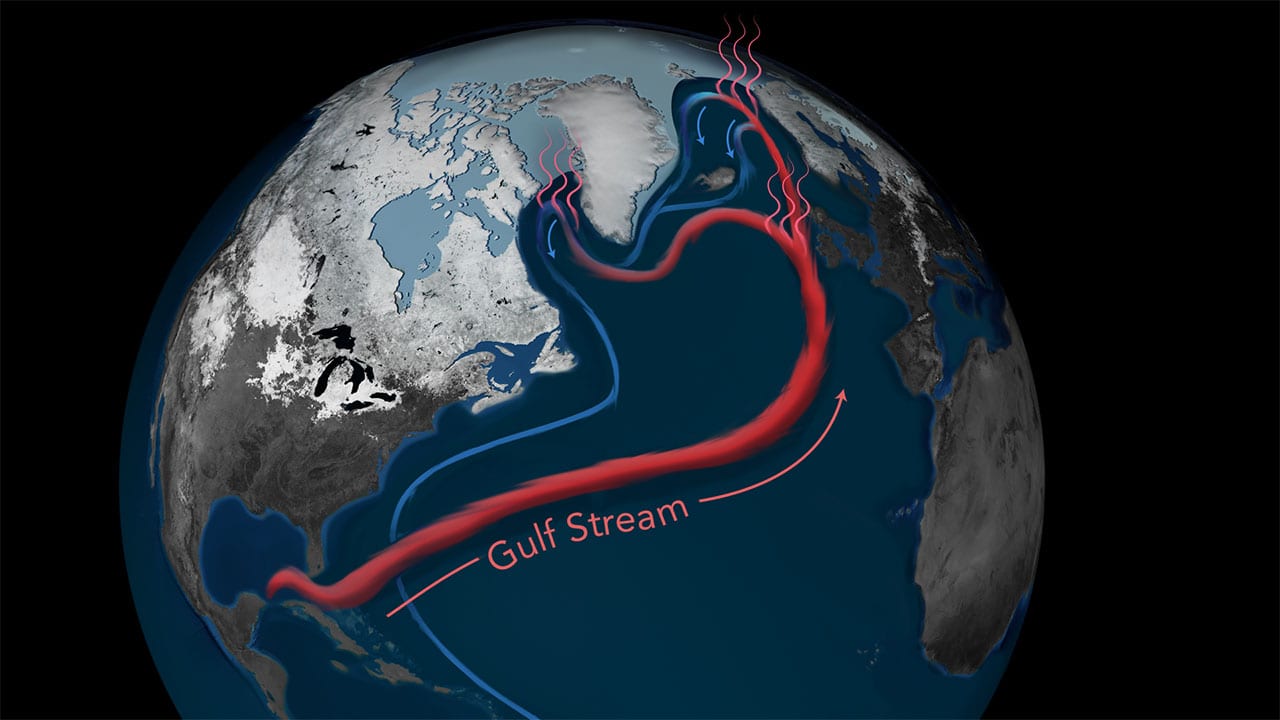
Atlantic Ocean Circulation at Weakest Point in More Than 1500 years New research led by University College London (UCL) and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) provides evidence that a key cog in the global ocean circulation system hasn’t been running at peak strength since the mid-1800s and is currently at its weakest point in the past 1,600 years. If the system continues to weaken, it could disrupt weather patterns from the United States and Europe to the African Sahel, and cause more rapid increase in sea level on the U.S. East Coast.
Read MoreWHOI Scientists Receive $11.6 Million to Measure Changes in Ocean Circulation
Ocean currents, in concert with the atmosphere, play a critical role in regulating Earth’s climate. Yet the complexities of how water is moved around the globe and how the strength…
Read MoreRate of Ocean Circulation Directly Linked to Abrupt Climate Change in North Atlantic Region
A new study strengthens evidence that the oceans and climate are linked in an intricate dance, and that rapid climate change may be related to how vigorously ocean currents transport heat from low to high latitudes.
Read MoreCritical Atlantic Ocean currents remained active during the last ice age, according to new study
The study shows that deep ocean water in the North Atlantic was much warmer during the last ice age than scientists once believed.
Read MoreOil residues can travel over 5,000 miles on ocean debris, study finds
Oil spill forensics reveal how plastic debris can carry petroleum pollution across entire ocean basins
Read MoreWHOI’s Michael Spall awarded AGU Harald Sverdrup Lecture recognizing outstanding contributions to ocean science
The Harald Sverdrup Lecture honors individuals who have made exceptional contributions to, and promoted collaboration within, atmospheric and oceanographic research.
Read MoreFecal samples from bowhead whales link ocean warming to rising algal toxins in Arctic waters
Filter-feeding whales sample the Arctic food web, tracking decades of change
Read MoreInnovative partnerships advancing ocean observations
WHOI’s Science RoCs aims to equip commercial vessels with sensors to measure physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the ocean along the world’s major shipping routes
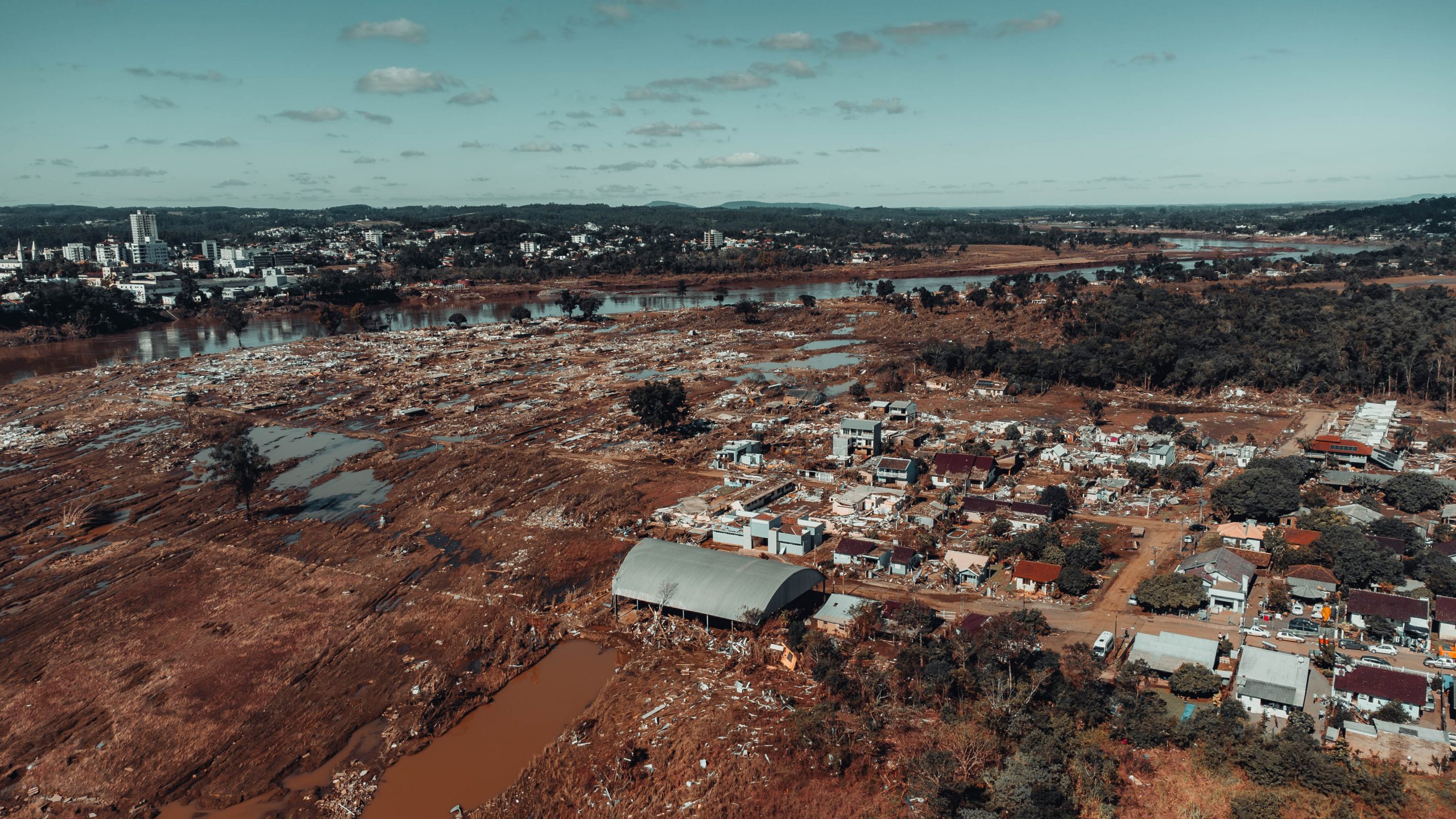
Read MoreWHOI oceanographers investigate southern Brazil’s catastrophic flooding
A new WHOI-led study uses satellite data to help uncover what caused devastating flooding and examine how it impacted some of the state’s most vulnerable residents.
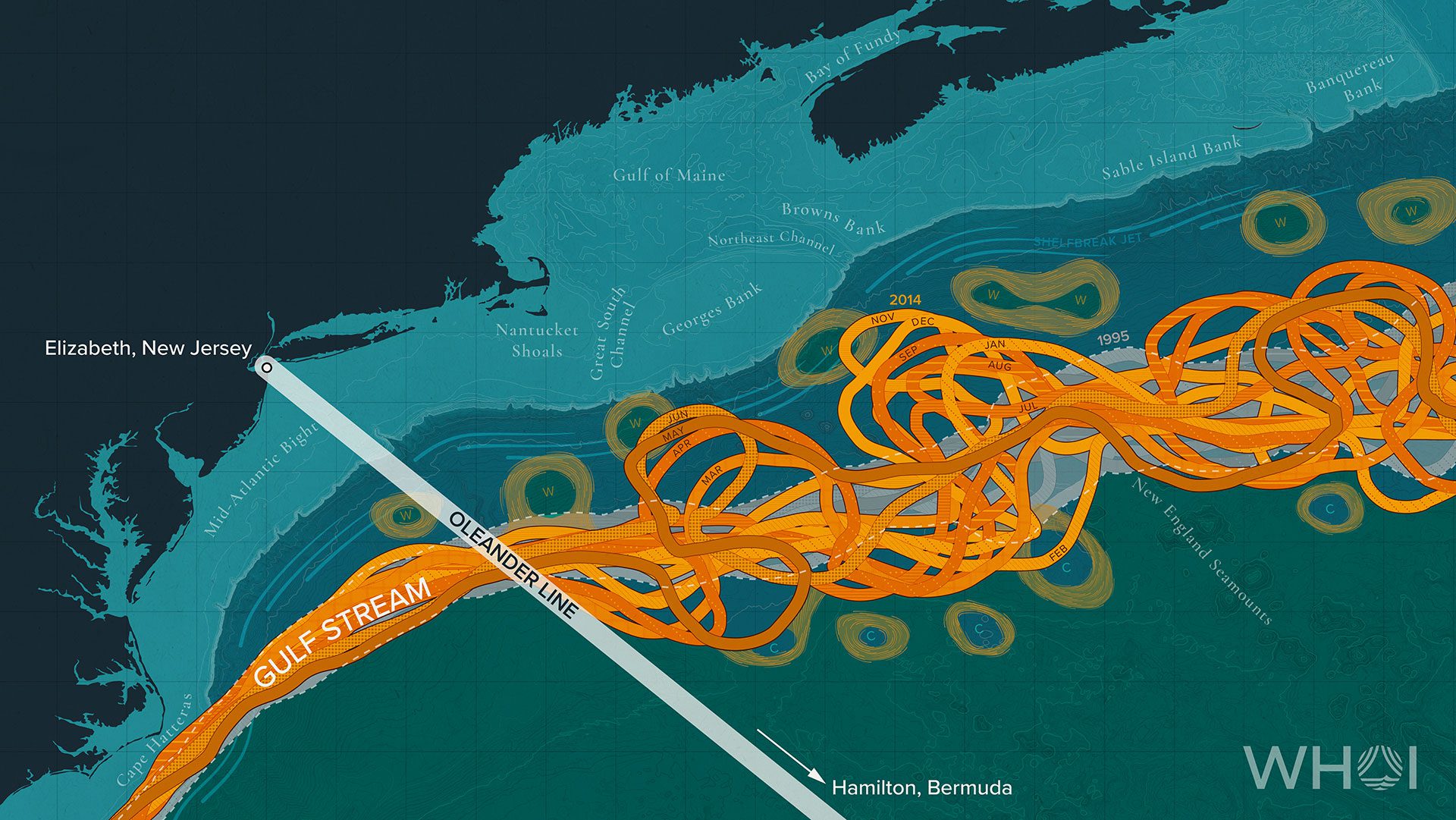
Read MoreNew study finds that critical ocean current has not declined in the last 60 years
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) helps to regulate the Earth’s climate and weather
Read MoreDeep ocean clues to a million-year-old Ice Age puzzle revealed in new study
A new WHOI-led study challenges theories regarding the origins of a significant transition through the Earth’s ice ages.
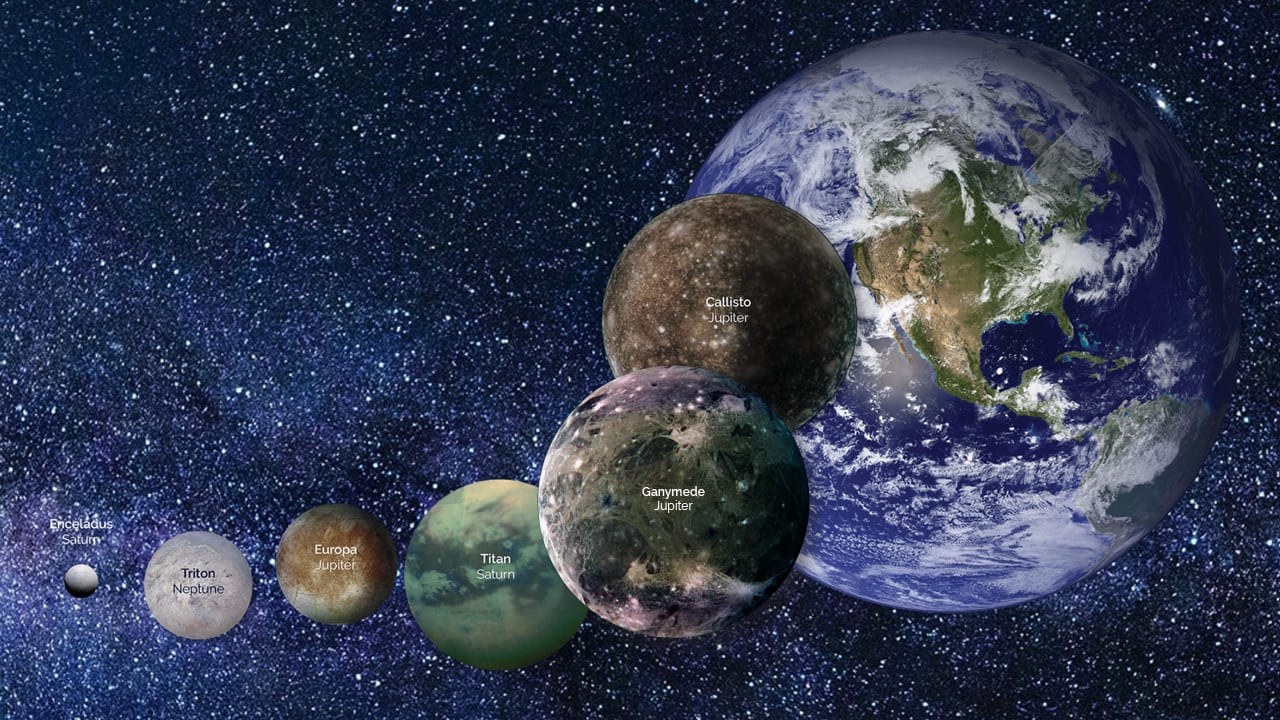
Read MoreWarm water could persist within icy ocean worlds
A new study investigates how the influence of low gravity, as found on ocean worlds in our solar system, impacts flow of water and heat below their seafloors.
Read MoreEvidence of Climate Change in the North Atlantic can be Seen in the Deep Ocean, Study Finds
Woods Hole, Mass. –Evidence of climate change in the North Atlantic during the last 1,000 years can be seen in the deep ocean, according to a newly published paper led…
Read MoreA Better Understanding of Gas Exchange Between the Atmosphere and Ocean Can Improve Global Climate Models
If scientists can improve the way models represent physical processes such as gas exchange, they can have more confidence in future simulations.
Read MoreModeling our climate future; WHOI to lead ocean current research
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) senior scientist of physical oceanography, Dr. Young-Oh Kwon, and WHOI adjunct scientist, Dr. Claude Frankignoul, have received a new research grant from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Modeling, Analysis, Predictions and Projections (MAPP) Program, funding their research project focusing on western boundary ocean currents and their correspondence with the atmosphere in relation to modern day climate.
Read MoreReview Evaluates the Evidence for an Intensifying Indian Ocean Water Cycle
Report Calls for Better Integration of Observations, Models, and Paleo Proxies The Indian Ocean has been warming much more than other ocean basins over the last 50-60 years. While temperature…
Read MoreStudies investigate marine heatwaves, shifting ocean currents
North America experienced a series of dangerous heatwaves during the summer of 2020, breaking records from coast to coast. In the ocean, extreme warming conditions are also becoming more frequent and intense.
Read MoreNASA Makes Dual Investment in Ocean Worlds Research at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Agency funds five-year effort to understand the potential for life in outer solar system and establishes a new Network for Ocean Worlds The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) will…
Read MoreStudy Finds No Direct Link Between North Atlantic Ocean Currents, Sea Level Along New England Coast
A new study by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) clarifies what influence major currents in the North Atlantic have on sea level along the northeastern United States. The study, published June 13 in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, examined both the strength of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)—a conveyor belt of currents that move warmer waters north and cooler waters south in the Atlantic—and historical records of sea level in coastal New England.
Read MoreNorth Atlantic Ocean productivity has dropped 10 percent during industrial era
Scientists at MIT, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), and elsewhere have found evidence that phytoplankton’s productivity is declining steadily in the North Atlantic, one of the world’s most productive marine basins.
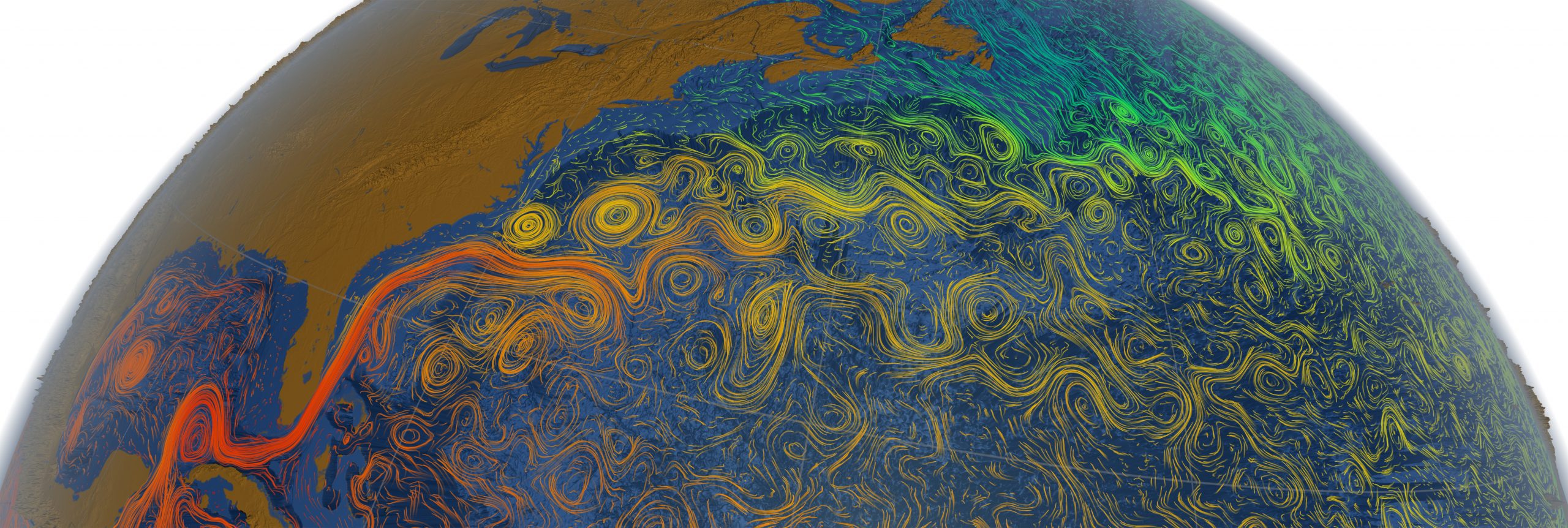
Read MoreWaters West of Europe Drive Ocean Overturning, Key for Regulating Climate
In the Atlantic MOC, warm, salty, shallow waters are carried northward from the tropics by currents and wind, and then converted into colder, fresher, deep waters that return southward through the Iceland and Irminger basins. In a departure from the prevailing scientific view, the study shows that most of the conversion from warm to cold water – or ‘overturning’ and its month-to-month variability – is occurring in regions between Greenland and Scotland, rather than in the Labrador Sea off Canada, as many past modeling studies have suggested.
Read MoreThe long memory of the Pacific Ocean
Researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and Harvard University have found that the deep Pacific Ocean lags a few centuries behind in terms of temperature and is still adjusting to the entry into the Little Ice Age. Whereas most of the ocean is responding to modern warming, the deep Pacific may be cooling.
Read MoreNSF Awards Contract to Group Led by WHOI to Continue Operation of Ocean Observatories Initiative
The National Science Foundation (NSF) announced that it has awarded a coalition of academic and oceanographic research organizations a five-year, $220 million contract to operate and maintain the Ocean Observatories…
Read MoreJim Ledwell Selected as a Fellow of The Oceanography Society
Jim Ledwell, Emeritus Research Scholar at the Wood Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), has been named a 2017 Fellow of The Oceanography Society (TOS). The society noted his many achievements, in…
Read More