Oceanus Online Archive
Worlds Apart, But United by the Oceans
Jian Lin came of age in an era of both geological and political seismic shifts in China, experiencing the deadliest earthquake in the 20th century in Tangshen in 1976 and the Cultural Revolution in the 1970s. Then he immigrated to America and came full circle in 2005 to become the first U.S. scientist to co-lead a Chinese deep-sea research cruise.
Read MoreMass Strandings Keep New Marine Mammal Facility Busy
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s new Marine Research Facility (MRF) opened its doors just in time for a terribly busy winter season. An unprecedented number of fatal dolphin and whale strandings…
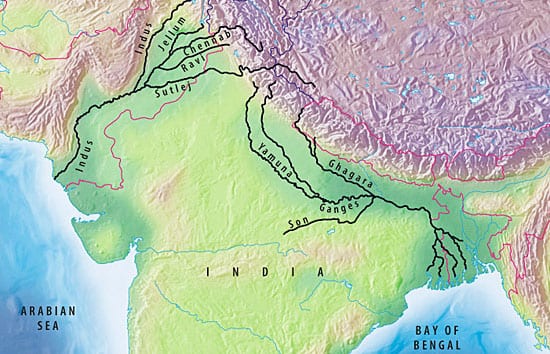
Read MoreChanging the Course of Rivers and History
Punjab means “five rivers.” The region in northern Pakistan is named for the great rivers that branch through the landscape, creating an ancient cradle of civilization and a modern agricultural…
Read MoreLurking Benignly on the Seafloor, the ‘Yeti’ Crab is Discovered
Biologist Cindy Van Dover routinely finds new, unusual creatures when she dives to unexplored areas of the ocean in the deep-sea submersible Alvin. So she was not particularly fazed when…
Read MoreAbout Oceanus Magazine
Oceanus explores the oceans in depth, highlighting the research and researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in news, features, and interviews.
Read MoreABE—The Autonomous Benthic Explorer
The pioneering deep-submergence vehicle, now 10 years old, continues to demonstrate its versatility on each new cruise.
Read MoreThe Oceans Have Their Own Weather Systems
From June to September 2005, oceanographer Dennis McGillicuddy and a team of more than 20 scientists from WHOI and five other marine science labs tracked an eddy named A4. It was the oceanic equivalent of a hurricane?a huge mass of water, spinning like a whirlpool, moving through the ocean for months, stretching across tens to hundreds of kilometers, stirring up a vortex of water and material from the depths to the surface. But unlike destructive hurricanes, eddies are productive.
Read MoreLive From the Tropics, It’s an Ocean Network
With a click of his computer mouse, Scott Gallager was swimming with the fishes off the west coast of Panama. Virtual reality? Well, the fish, corals, and currents are real;…
Read MoreThe Hunt for 18° Water
In 1959, oceanographer Valentine Worthington gave a name and an identity to a long-observed but poorly understood phenomenon of the North Atlantic. Valentine described how the interior of the Sargasso Sea contained distinct parcels of water with remarkably constant salinity, density, and temperature?roughly 18? Celsius. Decades later, his successors from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and eight other institutions have launched a far-reaching program to examine the formation and evolution of Worthington?s famous water and how it might influence North Atlantic climate.
Read MoreCaught in the Middle of the Marine Mammal Protection Act
In the past few years, several research projects have been halted because of conflicting interpretations of the Marine Mammal Protection Act. Energy, shipping, and naval interests claim the MMPA hampers their ability to work in the sea. Environmentalists and animal rights want the act strictly enforced. In between are scientists.
Read MoreOne of the Greatest Volcanic Shows on Earth
About 50,000 years ago, a huge meteorite smacked into our planet, gouging a hole more than a mile wide and 790 feet deep in India. Of the roughly 150 known…
Read MoreWhat Brings the Food that Brings the Whales?
Watching the gray, pitching ocean from the beach in Barrow, Alaska, Carin Ashjian, a biologist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), wonders if the seas are too rough for the…
Read MoreNew Sonar Method Offers Window into Squid Nurseries
Squid fishing has increased substantially in the past decade, with no way to assess the continuing viability of the stock?until now.
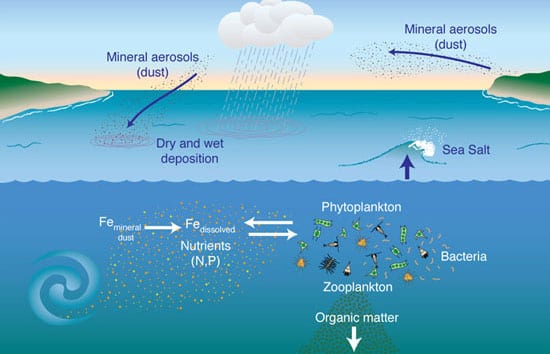
Read MoreDust Busters for the Oceans
Like most living things, microscopic marine plants need iron and other minerals to live and grow. On land, soil provides a ubiquitous source of minerals, but how do essential nutrients…
Read MoreAnalyzing Ancient Sediments at Warp Speed
Like a toy out of a science fiction story, the X-ray fluorescence core scanner reveals intimate details of the composition of ancient mud and sediment–which can contain a variety of clues about past climate and environmental conditions on Earth–without breaking the surface. In a matter of hours, the XRF simultaneously captures digital photographs and X-ray images of every millimeter of a core sample, while detecting the presence of any of 80 chemical elements.
Read MoreSmall Island. Big Ocean.
This week, more than 200 WHOI scientists and graduate students will brave the balmy trade winds, drooping palm trees, and misdirected laser pointers to present research in Honolulu. Reporters Hugh…
Read MoreAn Ocean Warmer Than a Hot Tub
Scientists have found evidence that tropical Atlantic Ocean temperatures may have once reached 107°F (42°C)—about 25°F (14°C) higher than today. The surprisingly high ocean temperatures occurred millions of years ago…
Read MoreGraduate Student Discovers an Unusual New Species
Sheri Simmons gets into the rugged wilderness as often as she can, backpacking in Newfoundland, the Sierras, the Adirondacks, and Alaska—where she once encountered a grizzly bear on a trail.…
Read MoreFloat 312, Where Are You?
The ocean is so enormous, even a fleet of 2,338 ocean-monitoring instruments can sail into it and go largely unnoticed. That’s what floats 312 and 393 were doing until something…
Read MoreUnder-ice Floats Offer a ‘Breakthrough’
The Arctic Ocean, home to fierce winds, punishing temperatures, and thick sea ice, is no place for wimpy people?or machines. So when WHOI physical oceanographers Peter Winsor and Breck Owens set out to explore the largely unknown currents beneath the polar sea ice, they had to design an instrument with true grit. (Fifth in a five-part series.)
Read MoreA Sentry at the Atlantic Gateway
Here’s an easy recipe to change Earth’s climate: Just add more fresh water to the North Atlantic Ocean. In this oceanic part of the world lies a critical—and sensitive—component of…
Read MoreThe Flywheel of the Arctic Climate Engine
A key component of the Arctic climate clockworks is the Beaufort Gyre?a bowl of cold, icy, relatively fresh waters north of Alaska that is swept by prevailing winds into a circular swirl larger than the Gulf of Mexico.
Read MoreFlying Blind in the Ice Factory
Al Plueddemann wants to push the envelope and fly a robotic vehicle into the wild blue under the polar ice cap. North of Alaska lies a key region for understanding…
Read MoreIs Global Warming Changing the Arctic?
In the Arctic, the air, sea ice, and underlying ocean all interact in a delicately balanced system. Four ambitious Arctic projects are pulling back the icy veil that shrouds our understanding of the Arctic Ocean?s role in our climate system. (First of a five-part series.)
Read More