Study reveals how fishing gear can cause slow death of whales
May 21, 2013
Using a “patient monitoring” device attached to a whale entangled in fishing gear, scientists showed for the first time how fishing lines changed a whale’s diving and swimming behavior. The monitoring revealed how fishing gear hinders whales’ ability to eat and migrate, depletes their energy as they drag gear for months or years, and can result in a slow death.
The scientists in this entanglement response suction-cupped a cellphone-size device called a Dtag to a two-year-old female North Atlantic right whale called Eg 3911. The Dtag, developed at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), recorded Eg 3911’s movements before, during, and after at-sea disentanglement operations.
Immediately after Eg 3911 was disentangled from most of the fishing gear, she swam faster, dove twice as deep, and for longer periods. The study, by scientists at WHOI, the Georgia Department of Natural Resources, the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, and NOAA Fisheries, was published online May 21 in the journal Marine Mammal Science.
“The Dtag opened up a whole new world of Eg 3911’s life under water that otherwise we weren’t able to see,” said Julie van der Hoop, lead author of the study and a graduate student in the MIT/WHOI Joint Program in Oceanography.
North Atlantic right whales were nearly eradicated by whaling and remain endangered today, with a population of 450 to 500. About 75 percent bear scars of fishing lines that cut into their flesh.
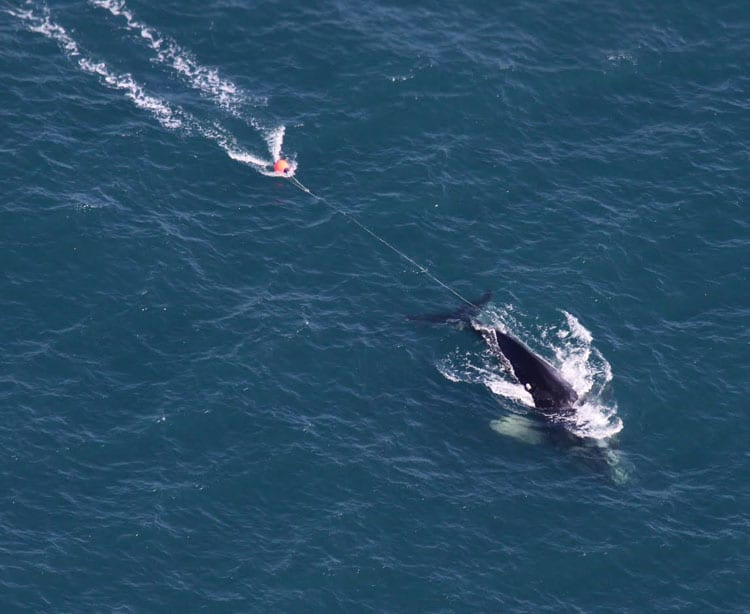
Born in 2009, Eg 3911 was first sighted entangled and emaciated by an aerial survey team on Christmas Day 2010, near Jacksonville, Florida. Fishing gear was entangled around her mouth, wrapped around both pectoral fins, and trailed about 100 feet behind her tail.
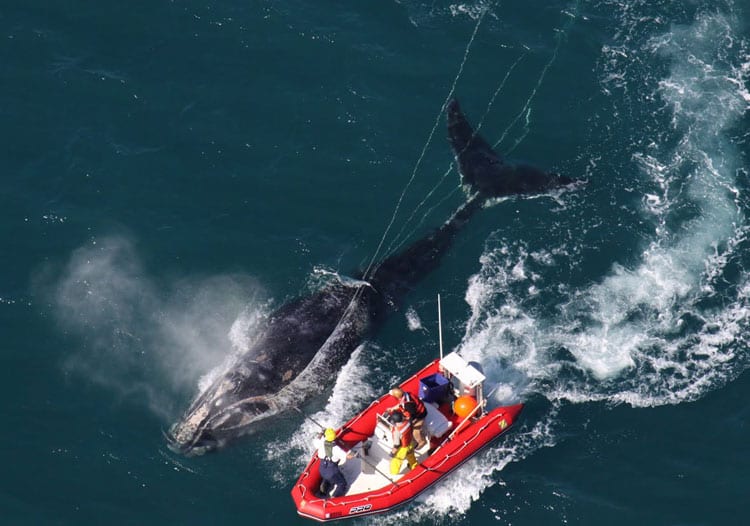
Teams aboard boats attempted to cut away the fishing gear on Dec. 29 and 30, 2010, but were not successful because the whale was evasive. A multiagency team tried again on Jan. 15, 2011. First, they applied a Dtag. Then they administered a carefully calculated sedative with a dart gun developed for large whale drug delivery by Paxarms NZ in collaboration with Dr. Michael Moore, director of the Marine Mammal Center at WHOI and a marine mammal veterinarian. The becalmed whale allowed the team to approach and remove nearly all the fishing gear.
The Dtag measured 152 dives that Eg 3911 took over six hours. There were no significant differences in depth or duration of dives after sedation, but “the whale altered its behavior immediately following disentanglement,” the scientists reported. “The near-complete disentanglement of Eg 3911 resulted in significant increases in dive duration and depth.”
“Together, the effects of added buoyancy, added drag, and reduced swimming speed due to towing accessory gear pose many threats to entangled whales,” the scientists wrote. Buoyant gear may overwhelm animals’ ability to descend to depths to forage on preferred prey. Increased drag can reduce swimming speeds, delaying whales’ timely arrival to feeding or breeding grounds. “Most significant, however, is the energy drain associated with added drag,” they said.
To calculate that drain, the scientists, in a separate experiment, towed three types of fishing gear from a skiff, using tensiometers to measure the drag forces acting on Eg 3911. They then calculated how much more energy whales would require to compensate for the drag. The results: Entangled whales have significantly higher energy demands, requiring 70 to 102 percent more power to swim at the same speed unentangled; or alternatively, they need to slow down their swimming speed by 16 to 20.5 percent.
The study provides the first data on the behavioral impacts of sedation and disentanglement and the energetic cost of entanglement in fishing gear due to drag.
On Feb. 1, 2011, an aerial survey observed Eg 3911 dead at sea.
“She didn’t make it,” van der Hoop said. The whale was towed ashore for a necropsy. “We showed up on the beach that night. I remember walking out there and seeing this huge whale, or what I thought was huge. She was only 10 meters long. She was only two years old. And all these people who had been involved in her life at some point, were there to learn from her what entanglement had caused.”
The necropsy showed that effects of the chronic entanglement were the cause of death.
“No fisherman wants to catch a whale, and I wish no fisherman a hungry day,” said Moore. “There needs to be a targeted assessment of how the fishery can still be profitable while deploying less gear so we can reduce the risk of marine mammals encountering fishing gear in the first place. At WHOI, we have hosted workshops talking with fisheries managers and fishermen about what might change so that they can continue to catch fish and stop catching whales.”
A dedicated network of scientists, veterinarians, and emergency responders support the Marine Mammal Health and Stranding Response Program (MMHSRP), which was formally established under the Marine Mammal Protection Act, is coordinated by NOAA Fisheries Service and coordinates the Atlantic Large Whale Entanglement Response Program. WHOI scientists have been long-standing contributors to the MMHSRP and routinely participate in rescues for marine mammals that are stranded, injured or entangled. Response efforts by the network for endangered species, such as North Atlantic right whales, are authorized by NOAA/NMFS Permit No. 932-1905-MA-009526 issued to the MMHSRP.
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, non-profit organization on Cape Cod, Mass., dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930 on a recommendation from the National Academy of Sciences, its primary mission is to understand the ocean and its interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate a basic understanding of the ocean’s role in the changing global environment.