News Releases
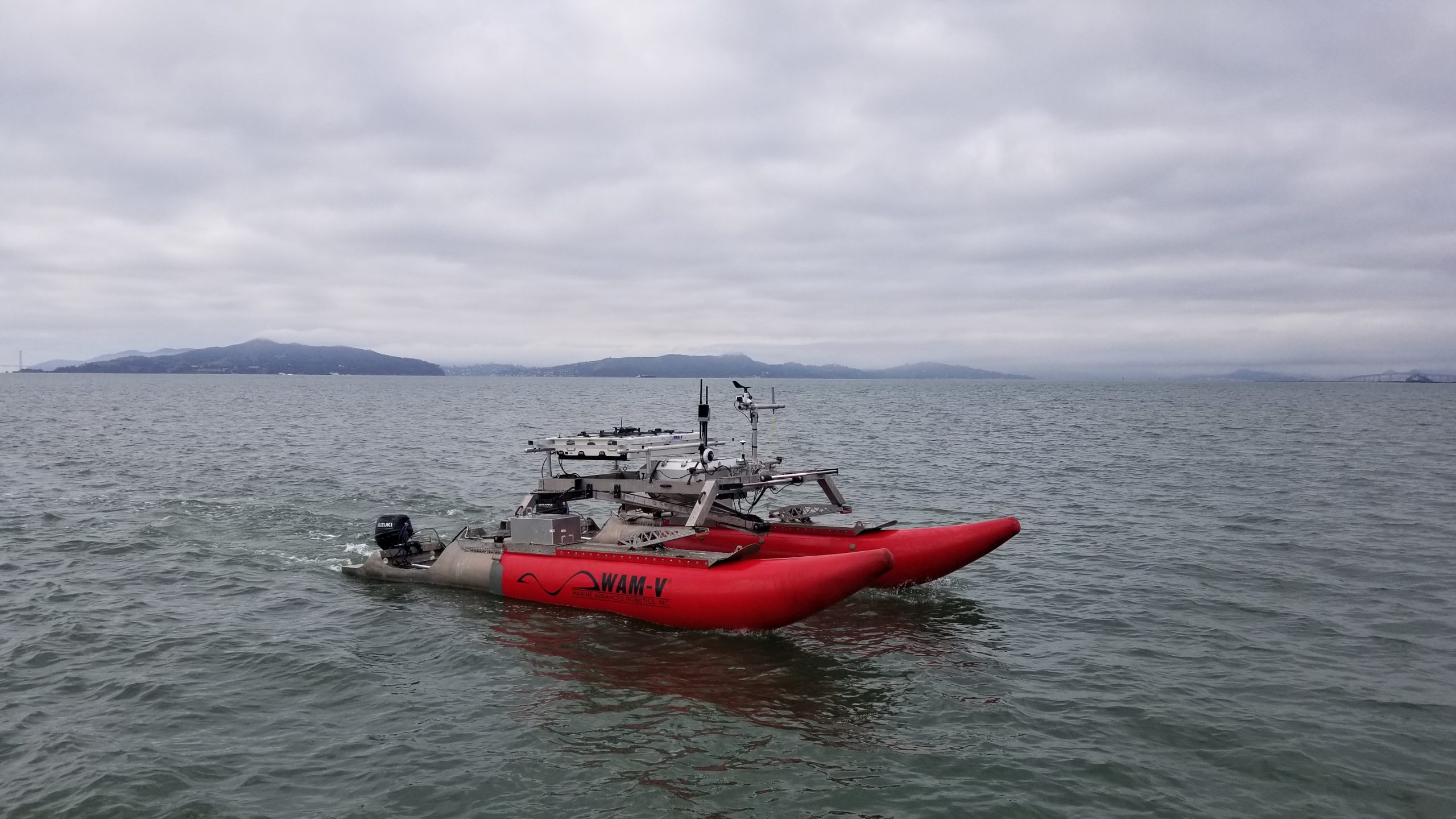
DOE Funding will Support WHOI Research to Support Sustainable Development of Offshore Wind
Woods Hole, MA — The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has received $750,000 in funding from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) to develop next‐generation autonomous robotic technology for environmental…
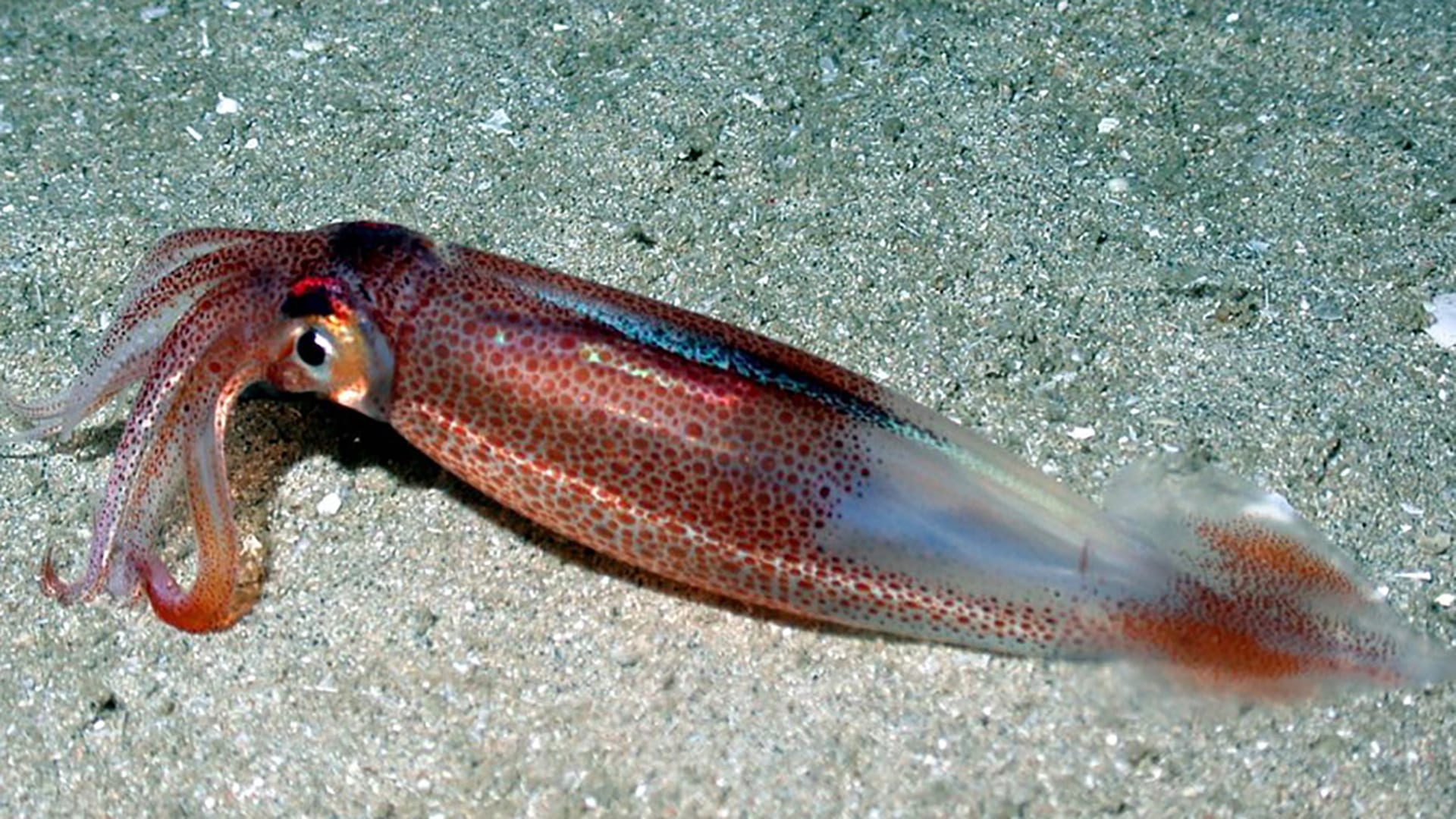
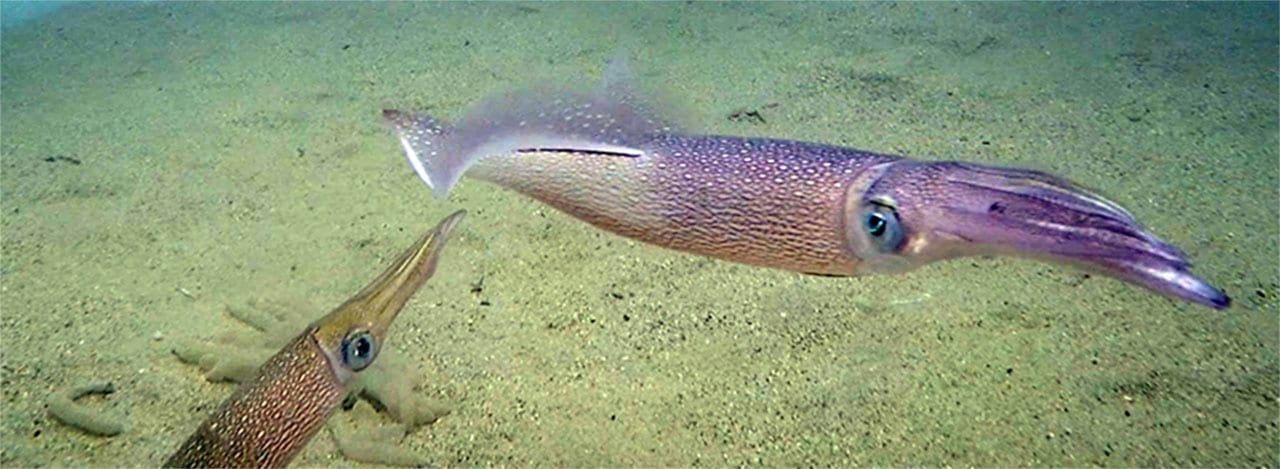
Read MoreStudy Finds that Offshore Pile Driving Noise Alters Feeding Behaviors of Longfin Squid
Squid less likely to capture killifish prey; more likely to miss attacks and abandoned pursuit of prey during pile driving noise.
Read MoreOffshore Air-Sea Interaction Tower Expands Research Capabilities of the Martha’s Vineyard Coastal Observatory
Scientists at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and their colleagues will gain critical environmental information from the Air-Sea Interaction Tower (ASIT) being built off the south shore of Martha’s Vineyard. Construction of the tripod-shaped tower began in August and is expected to be completed in late September. The tower will be linked to the Institution’s Martha’s Vineyard Coastal Observatory (MVCO), which was built and installed several years ago off South Beach near the Katama Airfield.
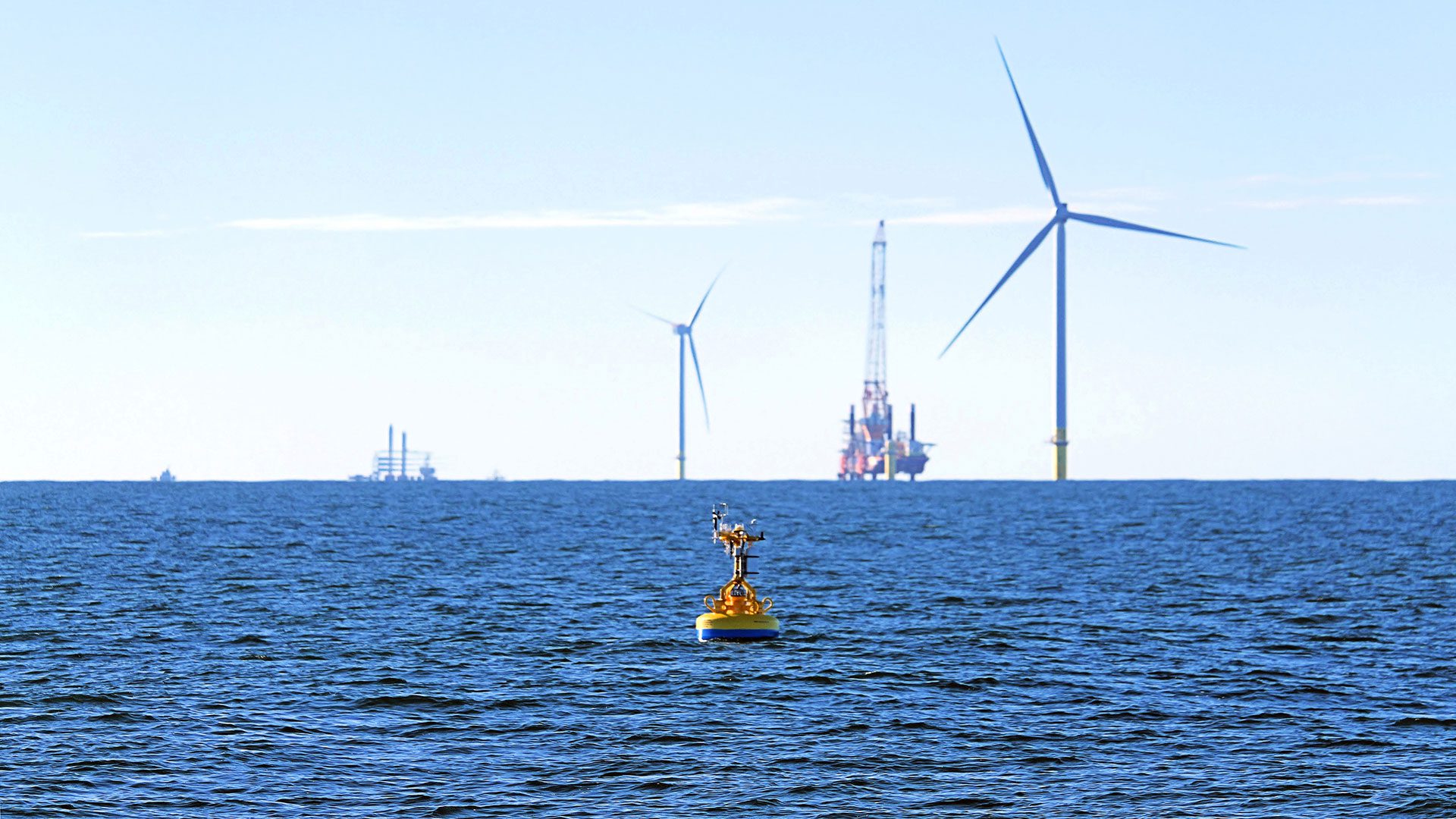
Read MoreCollaboration to monitor sea, weather, and wildlife
The U.S. DOE, WHOI, and partners to collect data near an East Coast offshore wind site
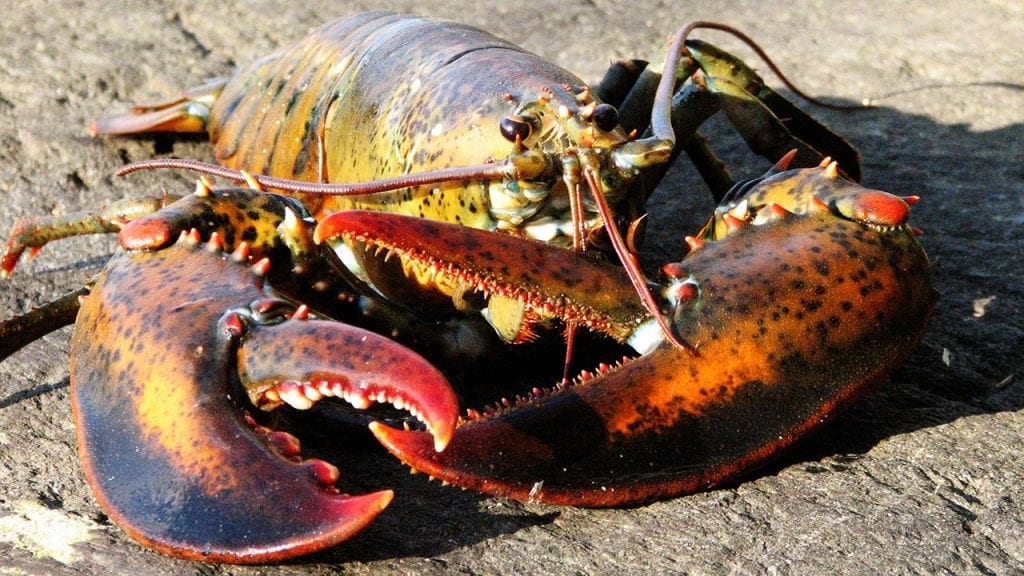
Read MoreStudy Shows that Lobsters Can Detect Sound
A new study demonstrates that lobsters can detect low-frequency sound and suggests that anthropogenic noise could affect lobsters. The study comes out at a time when the construction of more offshore wind farms, with their associated underwater pile driving noise, is being considered in New England.
Read MoreUnderwater pile driving noise causes alarm responses in squid
Exposure to underwater pile driving noise, which can be associated with the construction of docks, piers, and offshore wind farms, causes squid to exhibit strong alarm behaviors.
Read MoreFunders invests $250 million to supercharge ocean-based climate solutions
Coalition of philanthropic funders invests $250 million to supercharge ocean-based climate solutions Dubai, UAE — Many of the world’s leading philanthropic funders of ocean research and conservation have joined forces to…
Read MoreOcean Observatories Initiative‘s Pioneer Array Relocating to Southern Mid-Atlantic Bight
New location offers opportunities for new science observations with continued open access
Read MorePropeller Announces $100 Million Fund to Invest in Ocean-Climate Companies
Unique partnership with Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and veteran leadership team deploys vital capital to blue economy ‘narwhals’ at the nexus of ocean innovation, science and technology.
Read MoreCamera’s Eye Sees Large Numbers of Young Scallops Off Delaware Bay
NOAA researchers and colleagues from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have reported what appears to be a banner year for young sea scallops off the Delmarva Peninsula in mid-Atlantic waters of the U.S. NOAA’s HabCamV4, a towed imaging and sensor platform, has photographed miles of sea bottom packed with as many as 350 sea scallops in less than 1 square meter (less than three square feet). Other colorful images captured by the HabCam showed swimming scallops, sea stars and crabs—both scallop predators—and many species of fish, squid and sponges.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution Will Lead Coastal and Global Observatories Effort
A Cooperative Agreement signed today by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Consortium for Ocean Leadership (OL) gives Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and its partners approval to begin…
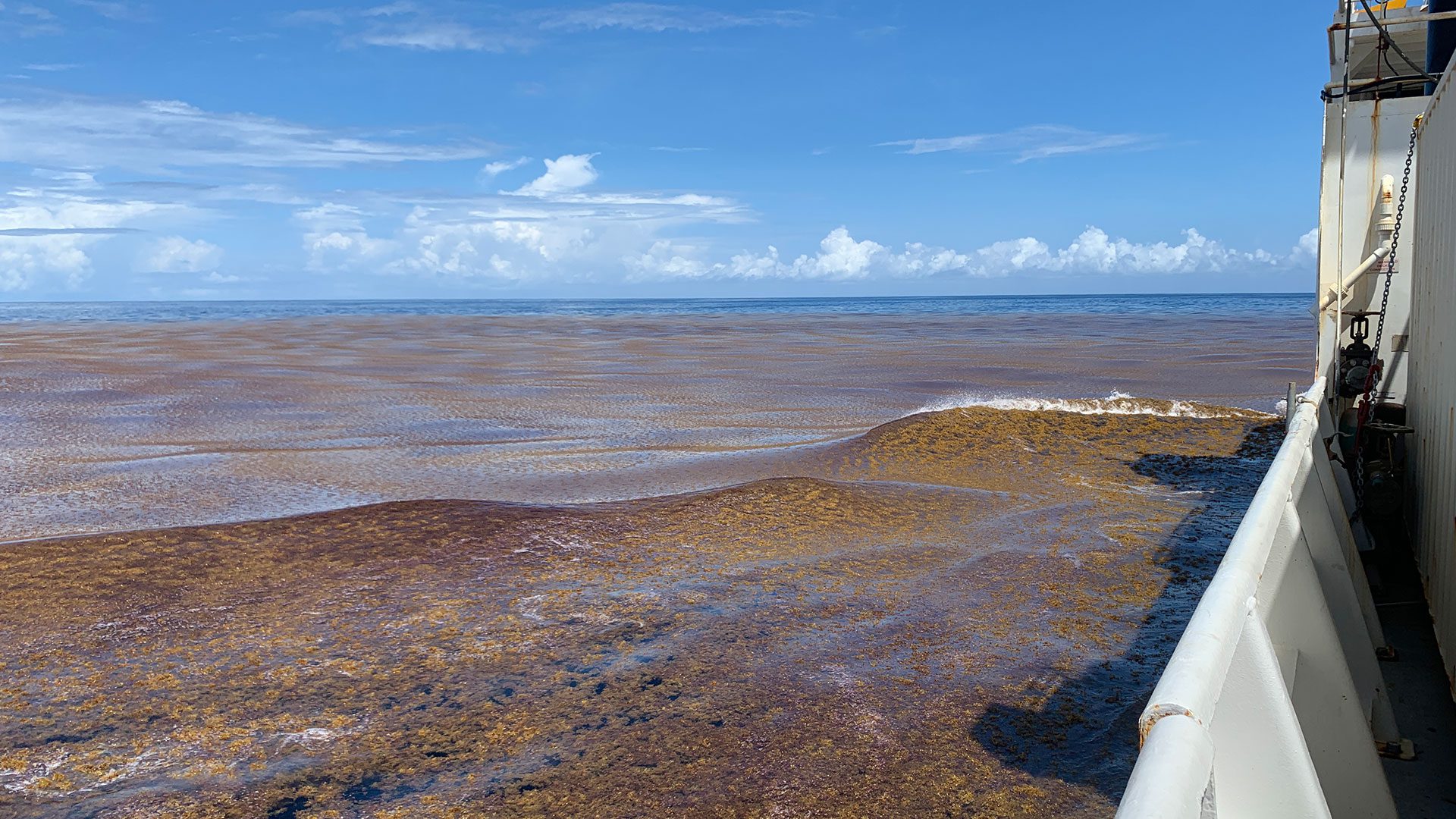
Read MoreNew study quantifies sargassum’s multi-million dollar impact to U.S. coastal economies
WHOI led the study’s economic modeling and analysis, examining impacts across three sectors central to coastal economies: tourism, recreation, and fisheries.
Read MoreThe Detection of a Massive Harmful Algal Bloom in the Arctic Prompts Real-Time Advisories to Western Alaskan Communities
The potent toxicity of the 2022 HAB event “posed an unprecedented risk to human and ecosystem health.”
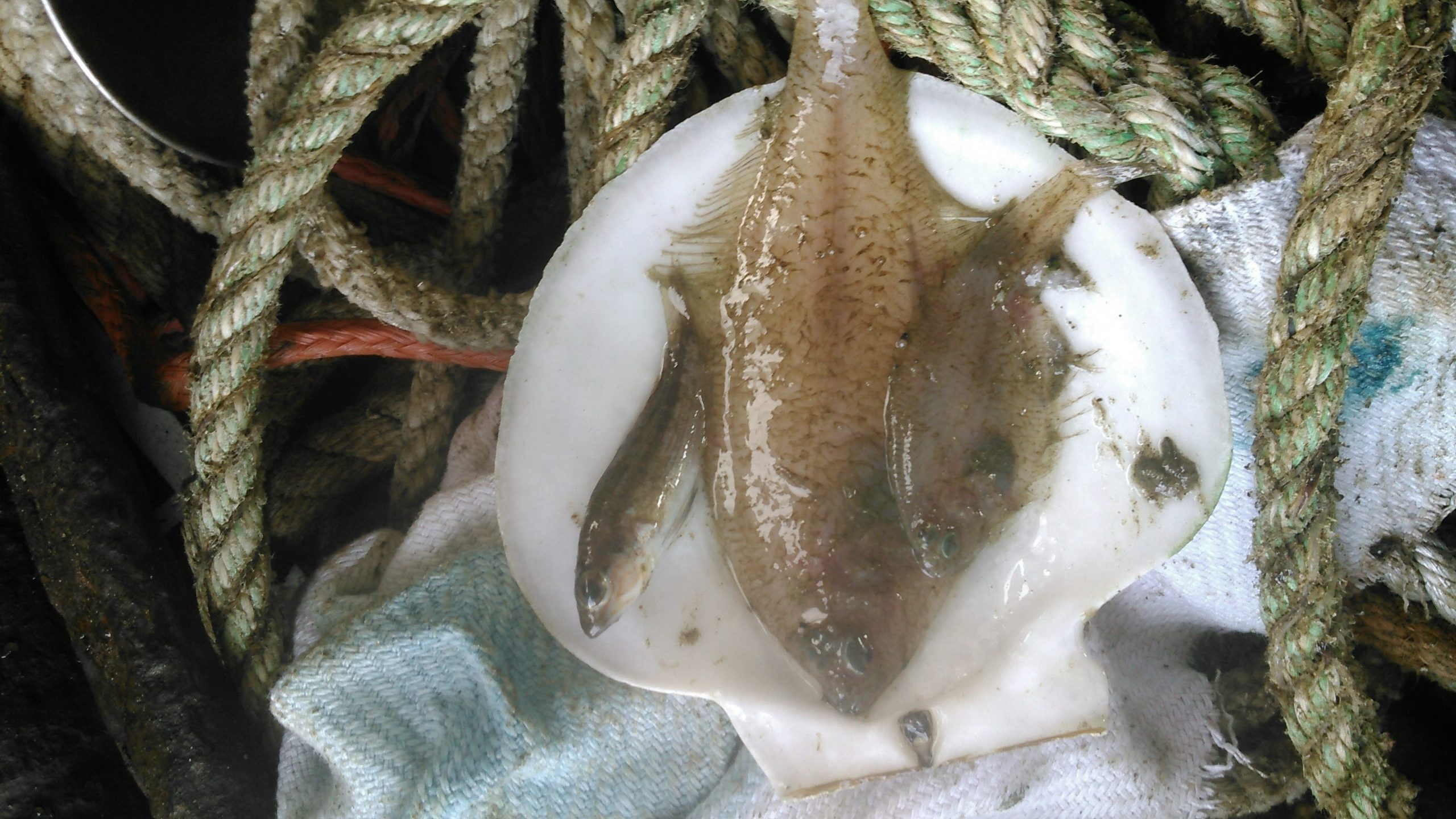
Read MoreTropical fish…up north? How ocean physics play a role in altering water temperature and salinity
A study led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution scientists is explaining why warm and salty water along with warm water fish species, such as the deep-sea dwelling Gulf Stream flounder and Black Sea bass, were found far inshore in New England in the middle of winter 2017. How did this happen? Researchers say it is due to an intrusion of offshore water from the open ocean onto the Northeast U.S. Shelf, caused by eddies (a circular current of water) and wind.
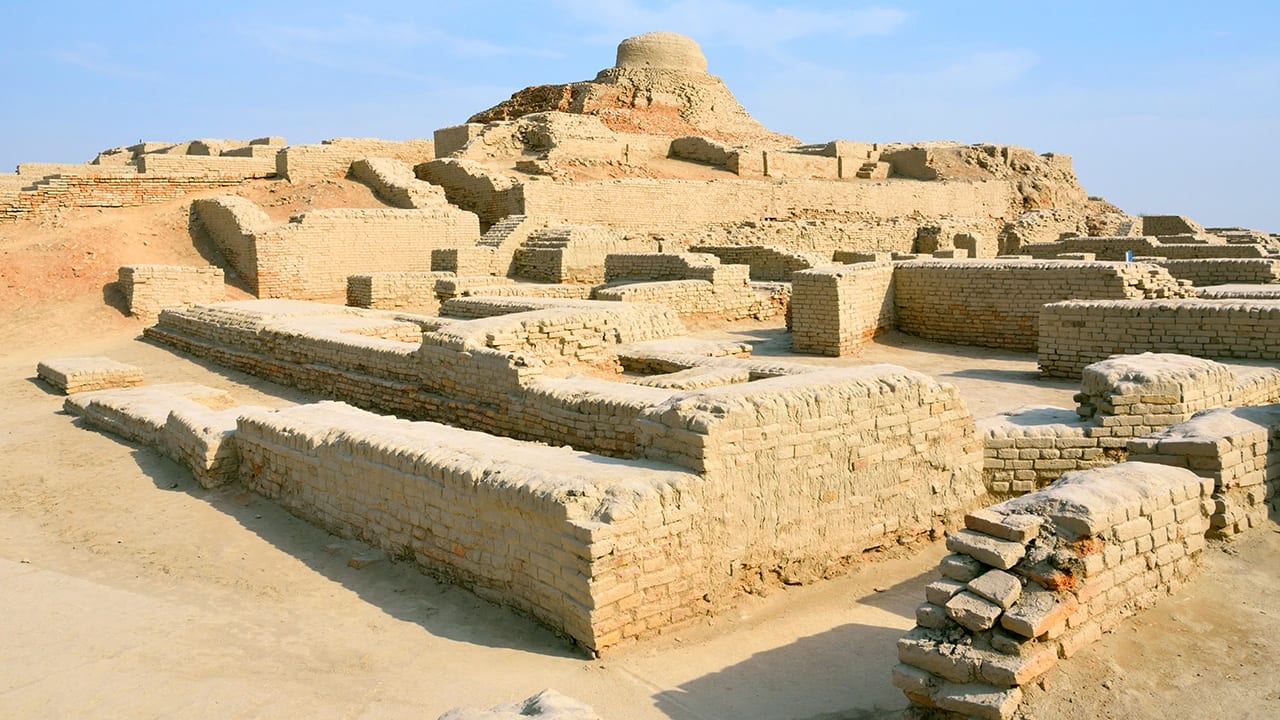
Read MoreClimate Change Likely Caused Migration, Demise of Ancient Indus Valley Civilization
More than 4,000 years ago, the Harappa culture thrived in the Indus River Valley of what is now modern Pakistan and northwestern India, where they built sophisticated cities, invented sewage systems that predated ancient Rome’s, and engaged in long-distance trade with settlements in Mesopotamia. Yet by 1800 BCE, this advanced culture had abandoned their cities, moving instead to smaller villages in the Himalayan foothills. A new study from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) found evidence that climate change likely drove the Harappans to resettle far away from the floodplains of the Indus.
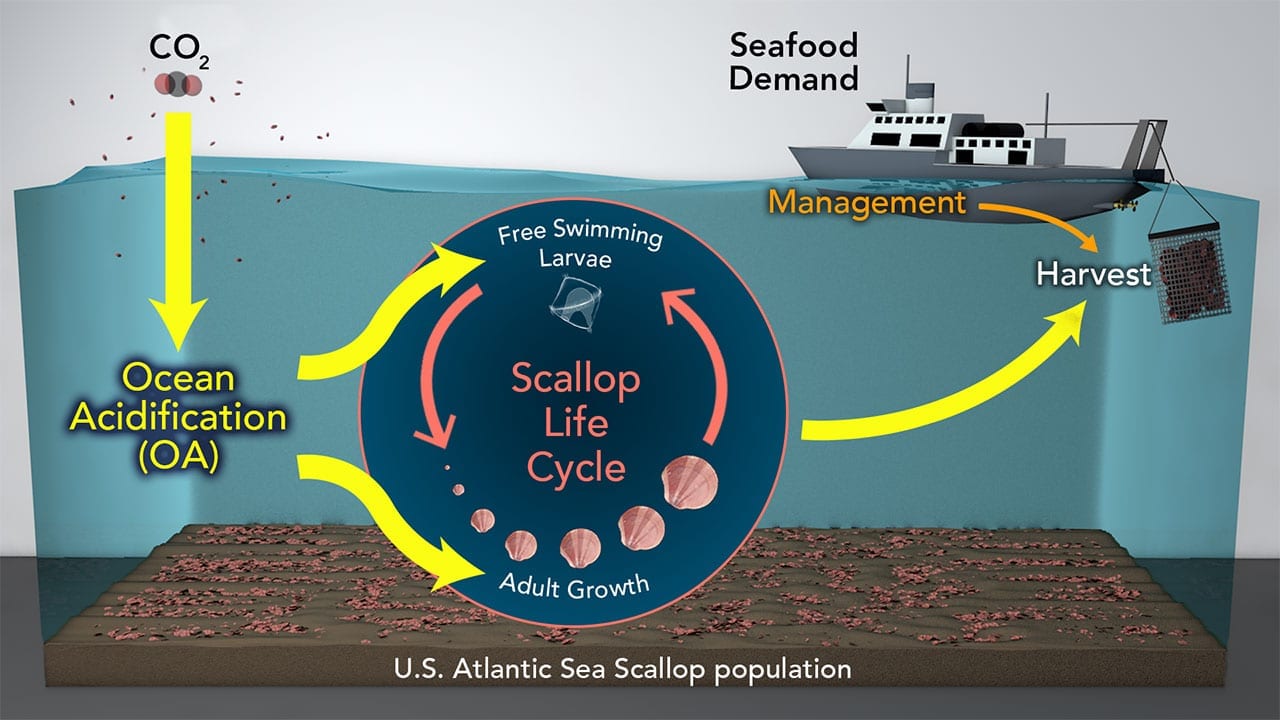
Read MoreOcean Acidification May Reduce Sea Scallop Fisheries
Each year, fishermen harvest more than $500 million worth of Atlantic sea scallops from the waters off the east coast of the United States. A new model created by scientists…
Read MoreGeologic History of Ayeyawady River Delta Mapped for the First Time
The Ayeyawady River delta in Myanmar is home to millions of people, and is a hub of agricultural activity. Unlike other large rivers across the world, however, the Ayeyawady has been relatively untouched by large infrastructure and dam projects for the past 50 years, and its geologic evolution has never previously been studied.
Read MoreWHOI Spins Off Local Technology Start-up
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is selling its controlling interest in EOM Offshore, a mooring systems company based on technology developed by engineers at WHOI. The company was founded as a start-up in 2010 to commercialize highly stretchable, fatigue-resistant hoses to transmit power and data to and from undersea sensors.
Read MoreCorals Die as Global Warming Collides with Local Weather in the South China Sea
New research highlights the devastation caused when global-scale ocean warming interacts with short-lived weather anomalies, and adds urgency to the question of how reefs will fare through the end of this century.
Read MoreResearchers Report Potential for a “Moderate” New England “Red Tide” in 2012
New England is expected to experience a “moderate” regional “red tide” this spring and summer, report NOAA-funded scientists working in the Gulf of Maine to study the toxic algae that causes the bloom. The algae in the water pose no direct threat to human beings, however the toxins they produce can accumulate in filter-feeding organisms such as mussels and clams— which can cause paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) in humans who consume them.
Read MoreMysterious Flotsam in Gulf of Mexico Came from Deepwater Horizon Rig, Study Finds
Shortly after the Deepwater Horizon disaster, mysterious honeycomb material was found floating in the Gulf of Mexico and along coastal beaches. Using state-of-the-art chemical forensics and a bit of old-fashioned…
Read MoreResearchers Report Potential for a Moderate New England ‘Red Tide’ in 2011
Scientists from the NOAA-funded Gulf of Maine Toxicity (GOMTOX) project issued an outlook for a moderate regional bloom of a toxic alga that can cause ‘red tides’ in the spring…
Read MoreResearchers Issue Outlook for a Significant New England ‘Red Tide’ in 2010
Today, scientists from the NOAA-funded Gulf of Maine Toxicity (GOMTOX) project issued an outlook for a significant regional bloom of a toxic alga that can cause ‘red tides’ in the…
Read MoreResearchers Report Potential for “Moderately Large” Red Tide Outbreak in the Gulf of Maine Region for 2009
The potential for an outbreak of the phenomenon commonly called “red tide” is expected to be “moderately large” this spring and summer, according to researchers with the Woods Hole Oceanographic…
Read More