News Releases
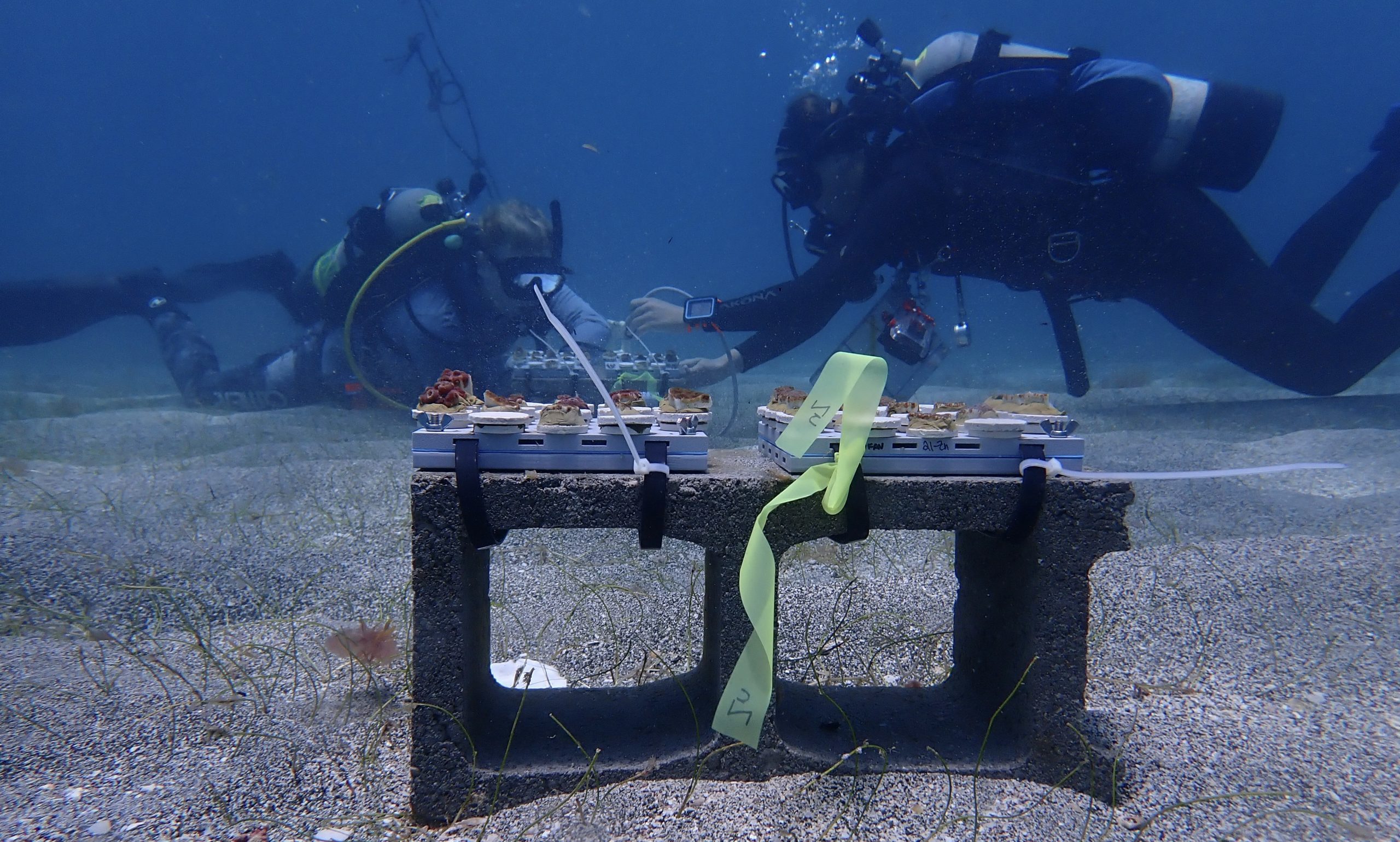
Could a multivitamin help save coral reefs? Preliminary data says yes
Scientists from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution partner with the University of the Virgin Islands to create a resilient artificial reef
Read MoreStudy: eDNA methods give a real-time look at coral reef health
Researchers from WHOI studied the microbes in coral reef water by examining eight reefs in the U.S. Virgin Islands over a period of seven years, which included periods of hurricane and coral disease disturbance.
Read MoreInnovative Techniques Provide New Means to Monitor Coral Reef Health
These new techniques, which look at microbes and dissolved metabolites of reefs, offer a new means to examine reef features and have broad conservation applications.
Read MoreStudy Examines the Impact of Coral Chemical Compounds on Reef Composition and Health
The study found that the organic chemical compounds produced through metabolism —known as metabolites or exudates—vary significantly by coral species and that the compounds impact the abundances and compositions of reef microorganisms differently.
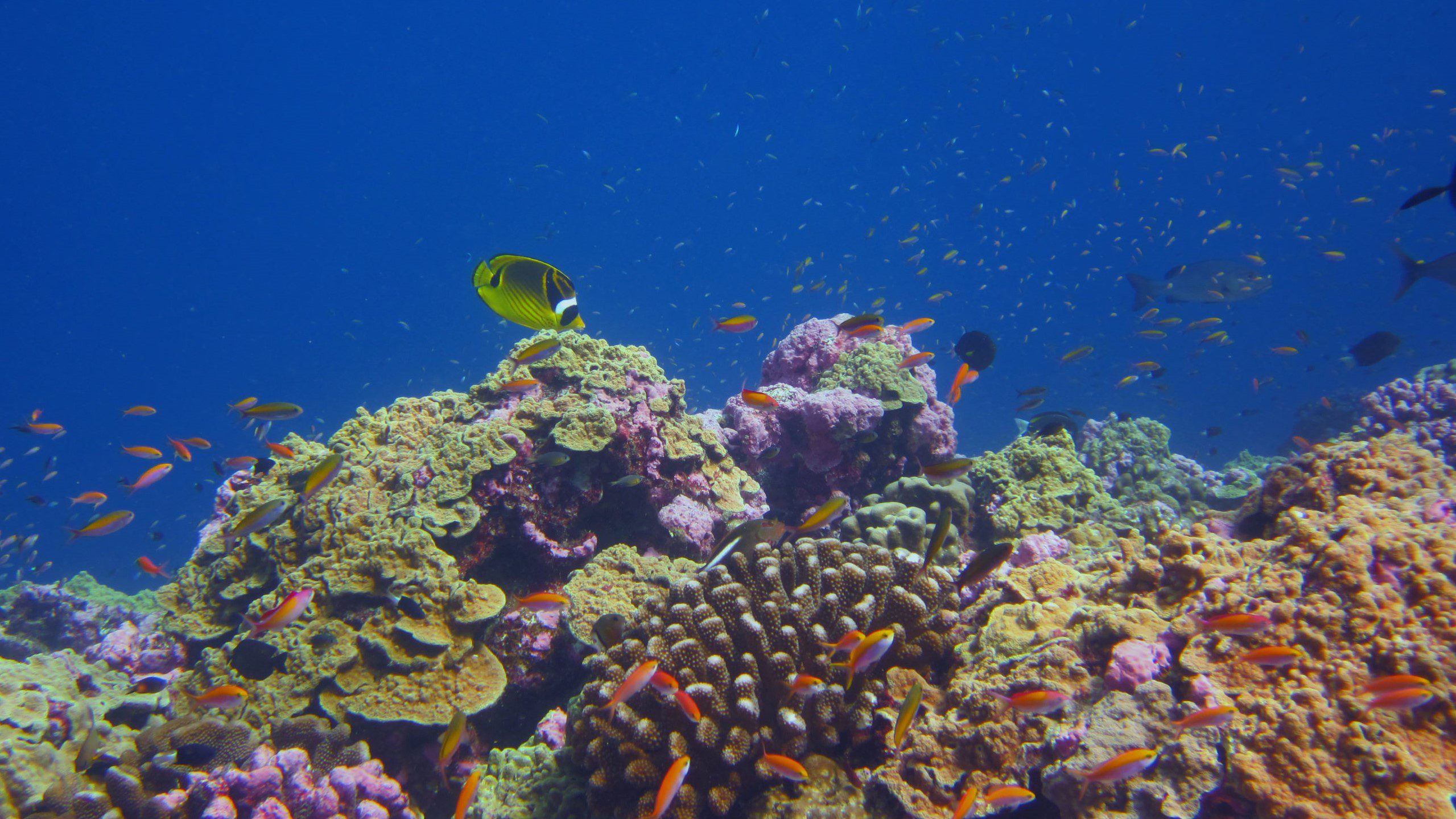
Read MoreSome coral reefs are keeping pace with ocean warming
Some coral communities are becoming more heat tolerant as ocean temperatures rise, offering hope for corals in a changing climate. After a series of marine heatwaves hit the Phoenix Islands Protected Area (PIPA) in the central Pacific Ocean, a new study finds the impact of heat stress on the coral communities lessened over time.
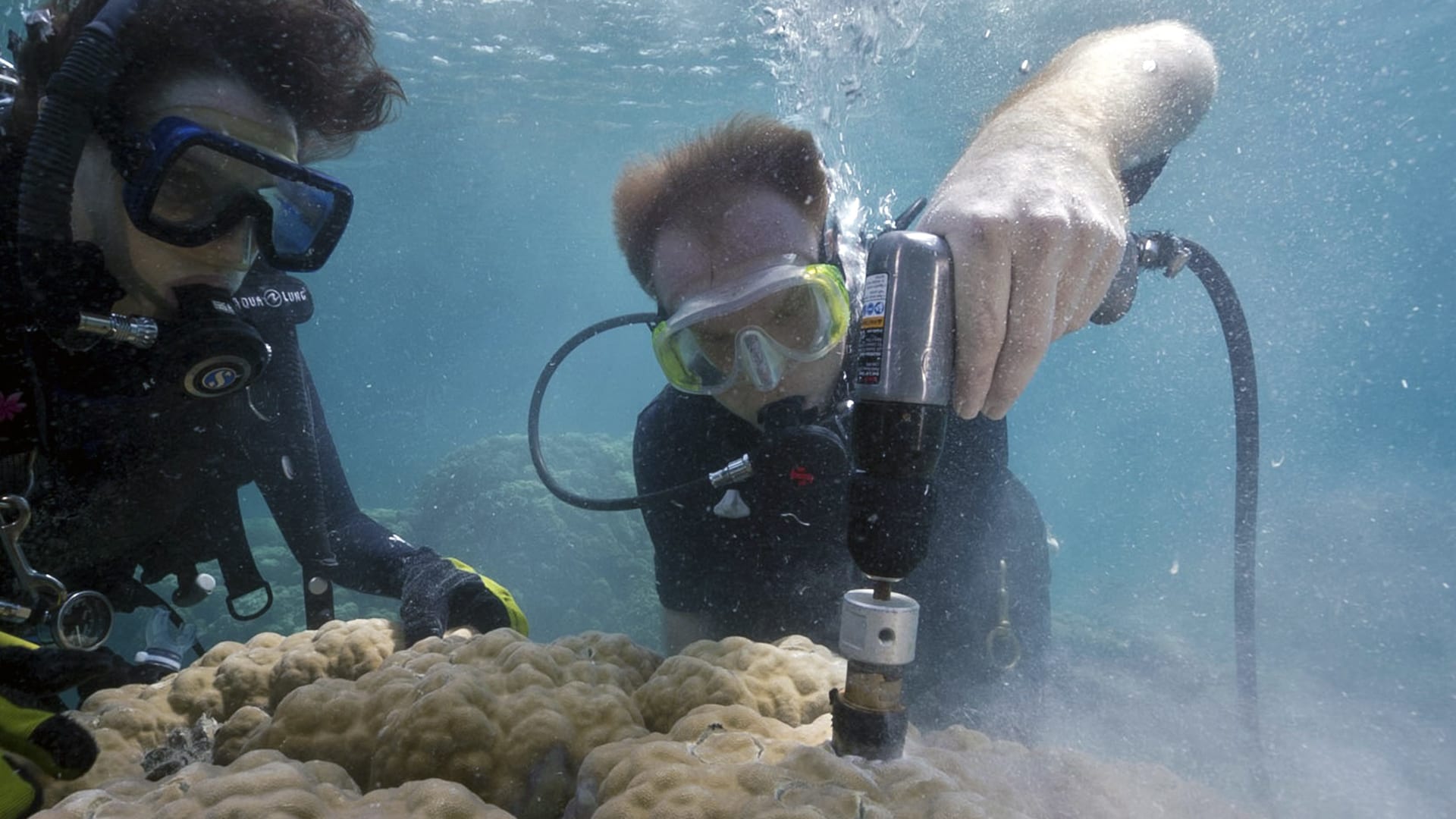
Read MoreNorthern Star Coral Study Could Help Protect Tropical Corals
Worldwide, coral reefs are in crisis. Researchers at WHOI and Roger Williams University are finding that studying the recovery of this local New England species from a laboratory induced stressor could help better understand how to protect endangered tropical corals around the world.
Read MoreOcean acidification causing coral ‘osteoporosis’ on iconic reefs
Scientists have long suspected that ocean acidification is affecting corals’ ability to build their skeletons, but it has been challenging to isolate its effect from that of simultaneous warming ocean…
Read MoreScientists Pinpoint How Ocean Acidification Weakens Coral Skeletons
The rising acidity of the oceans threatens coral reefs by making it harder for corals to build their skeletons. A new study identifies the details of how ocean acidification affects coral skeletons, allowing scientists to predict more precisely where corals will be more vulnerable.
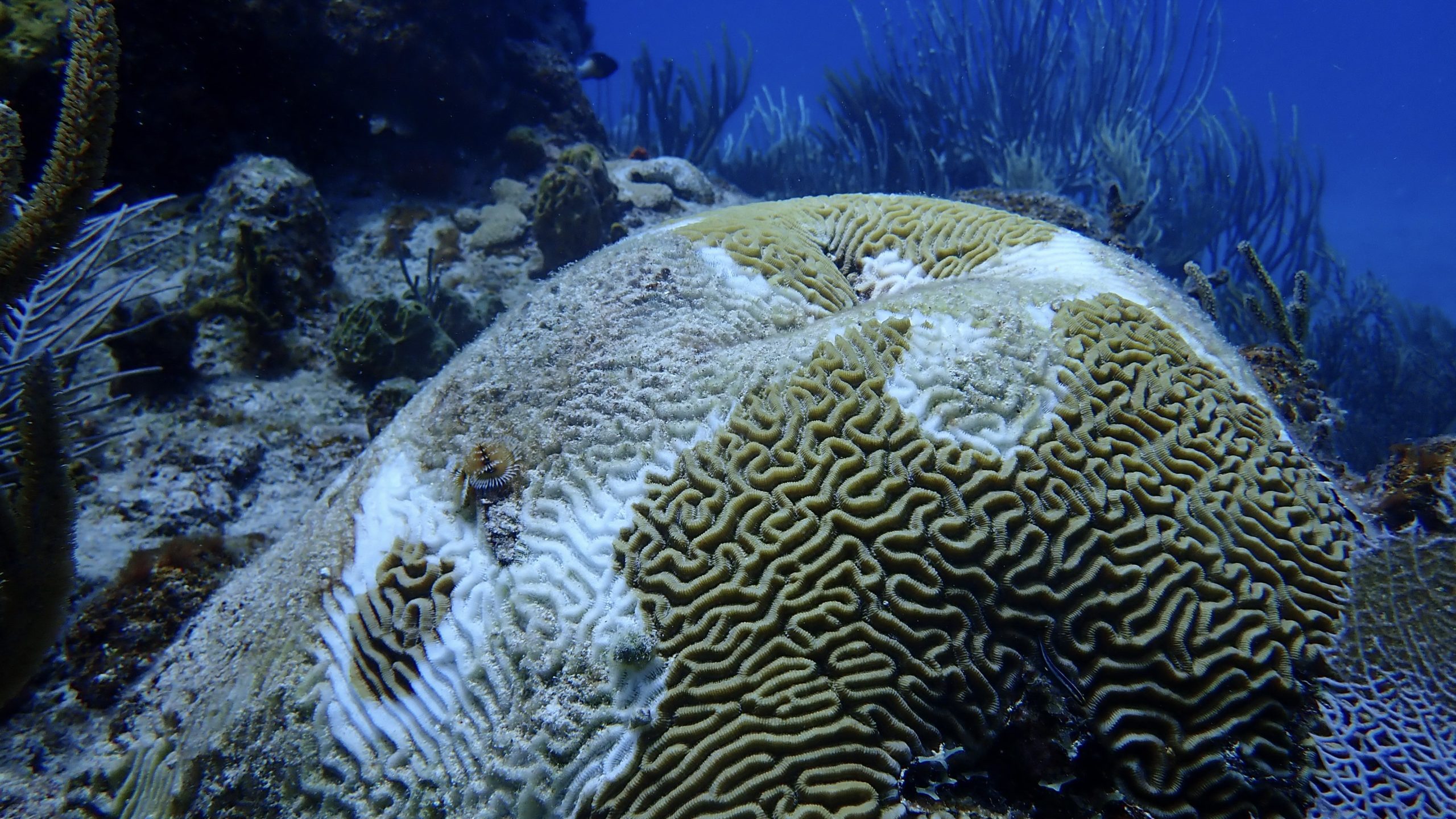
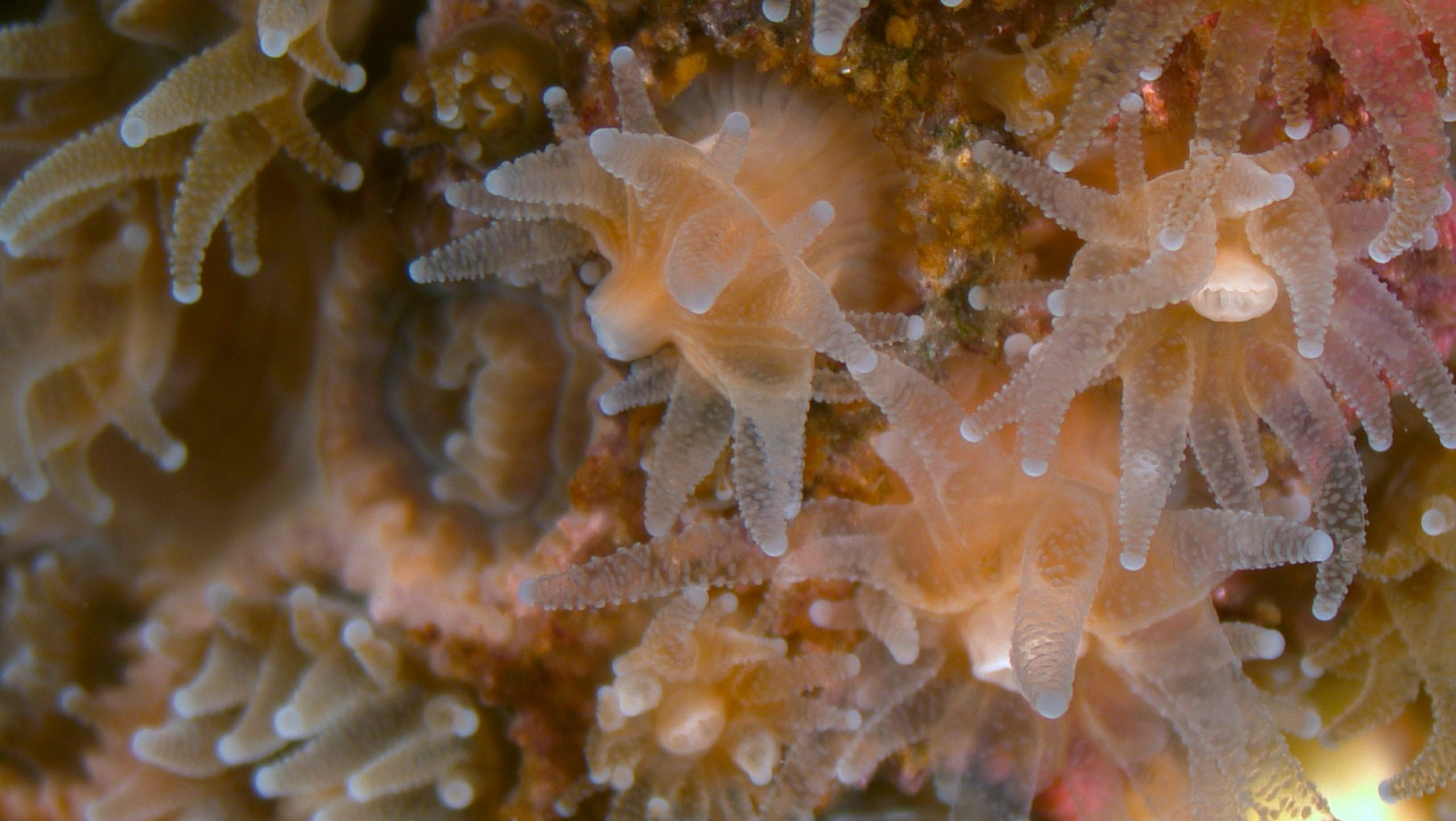
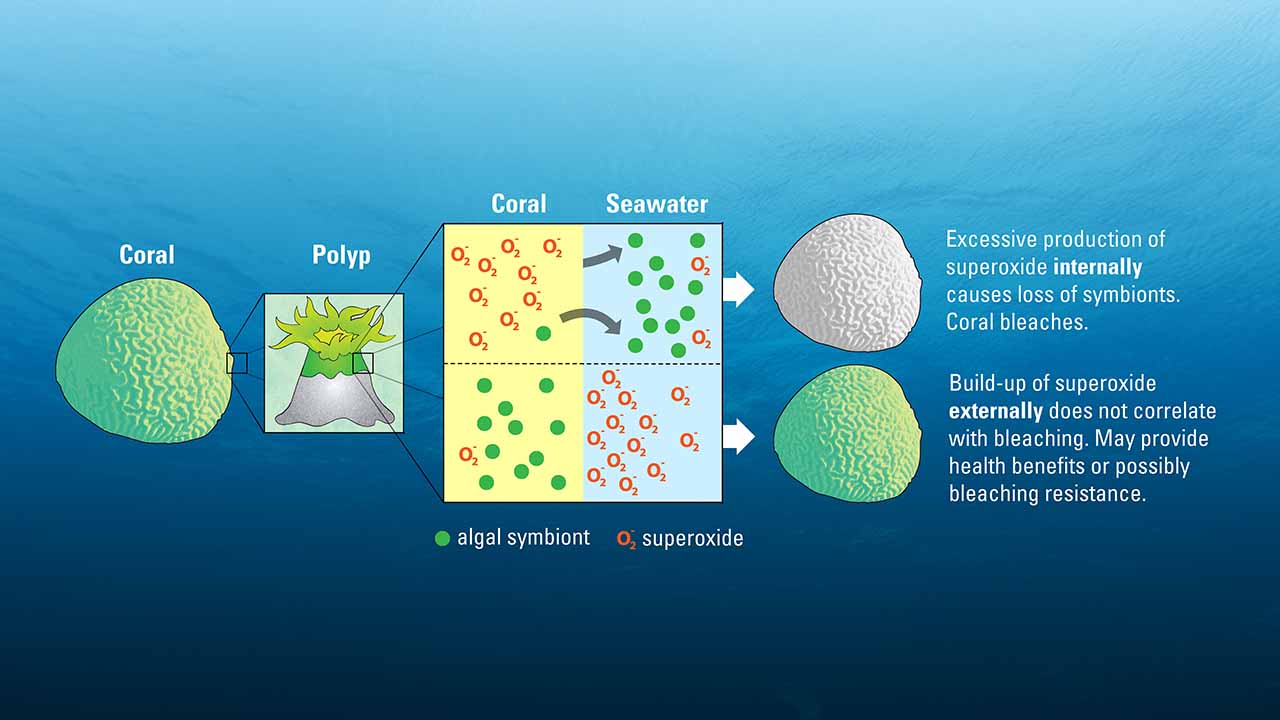
Read MoreNew Studies Take a Second Look at Coral Bleaching Culprit
A new study from WHOI indicates that superoxide’a natural toxin believed to be the main culprit behind coral bleaching’may actually play a beneficial role in coral health and resilience.
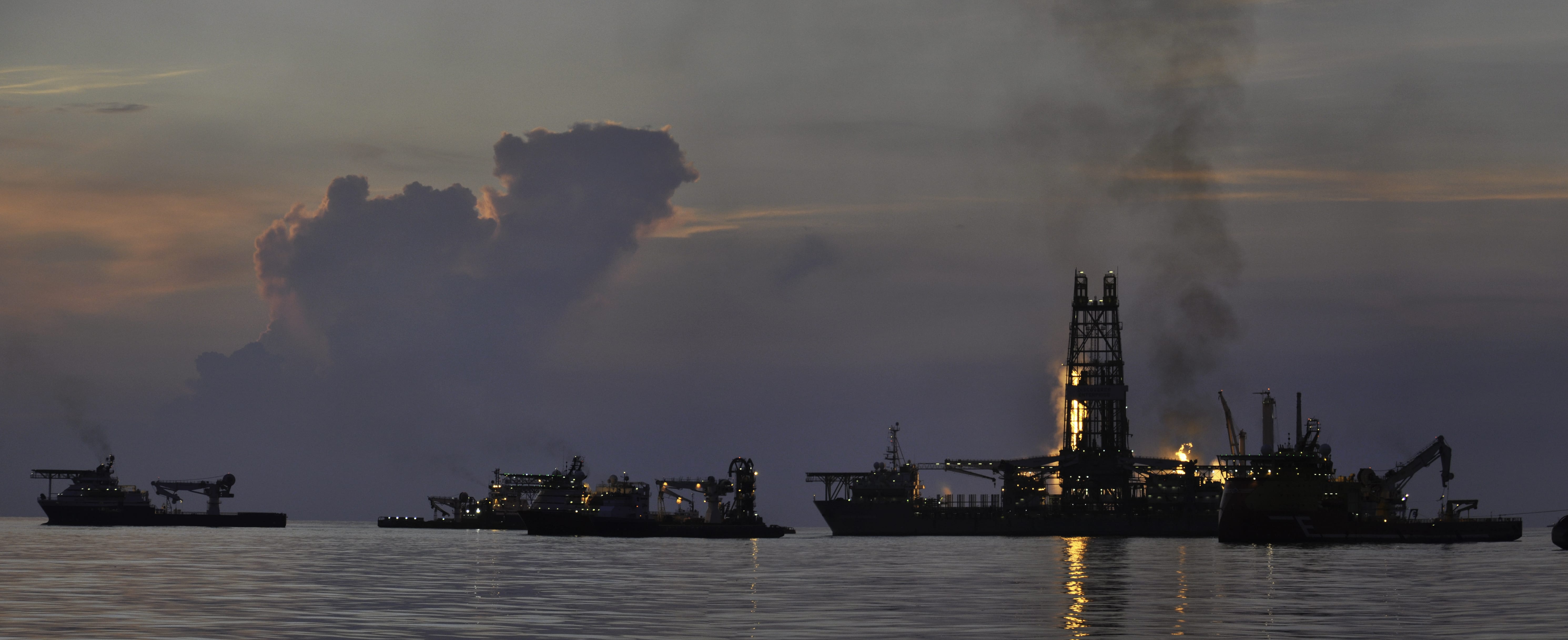
Read MoreWhat did scientists learn from Deepwater Horizon?
Ten years after the Deepwater Horizon explosion caused the largest accidental marine oil spill in history, WHOI marine geochemists Elizabeth Kujawinski and Christopher Reddy review what they— and their science colleagues from around the world—have learned.
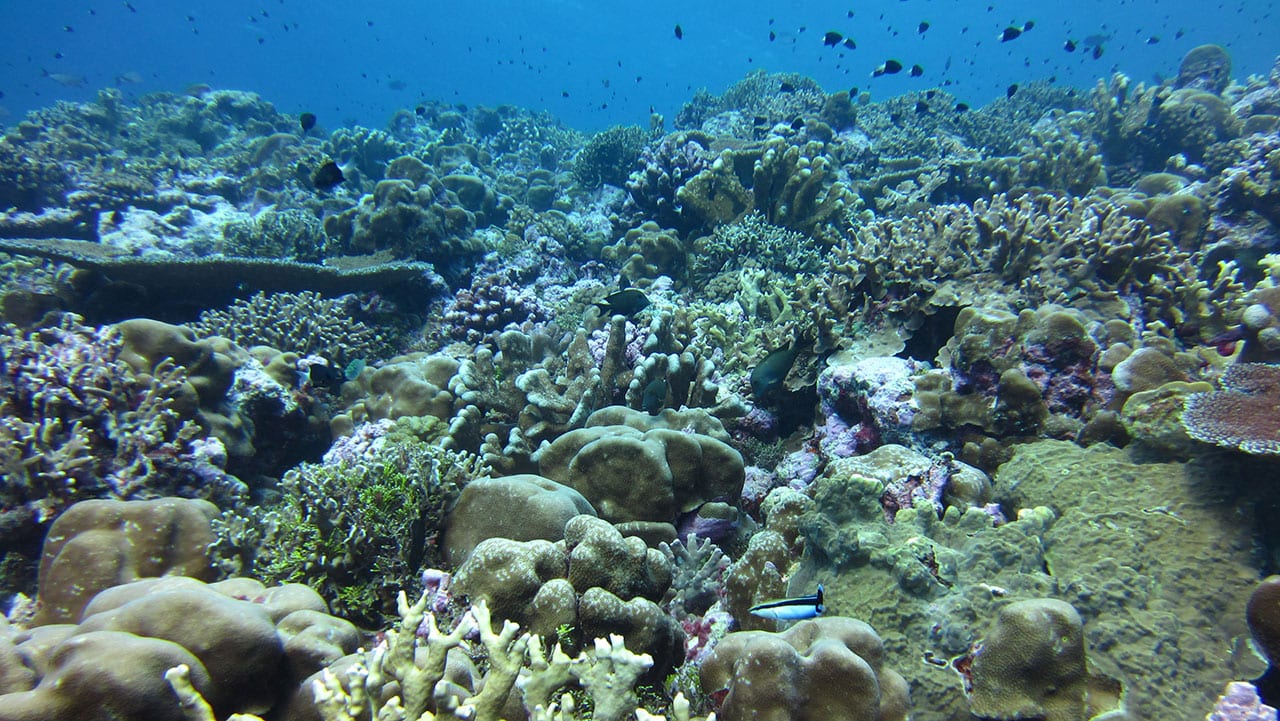
Read MoreTravel Distances of Juvenile Fish Key to Better Conservation
WHOI scientists and their international colleagues conducted the largest, most comprehensive study of larval dispersal at coral reefs. Their findings have important implications for the sizing and spacing of marine reserves.
Read MoreStudy Assesses Nations’ Vulnerabilities to Reduced Mollusk Harvests from Ocean Acidification
Changes in ocean chemistry due to increased carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are expected to damage shellfish populations around the world, but some nations will feel the impacts much sooner and more intensely than others, according to a study by scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
Read More