Research Highlight
Climate change could lead to a dramatic temperature-linked decrease in essential omega-3 fatty acids
The effects of global climate change already are resulting in the loss of sea ice, accelerated sea level rise, and longer and more intense heat waves, among other threats. Now, the first-ever survey of planktonic lipids in the global ocean predicts a temperature-linked decrease in the production of essential omega-3 fatty acids, an important subset of lipid molecules.
Read MoreWHOI joins world leaders at UN Ocean Conference: June 27 – July 1, Lisbon, Portugal
Thousands of participants from around the world will converge in Lisbon beginning June 27 as part of the 2022 United Nations Ocean Conference. Among them will be representatives from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the world’s largest independent organization dedicated exclusively to ocean research, engineering, and education.
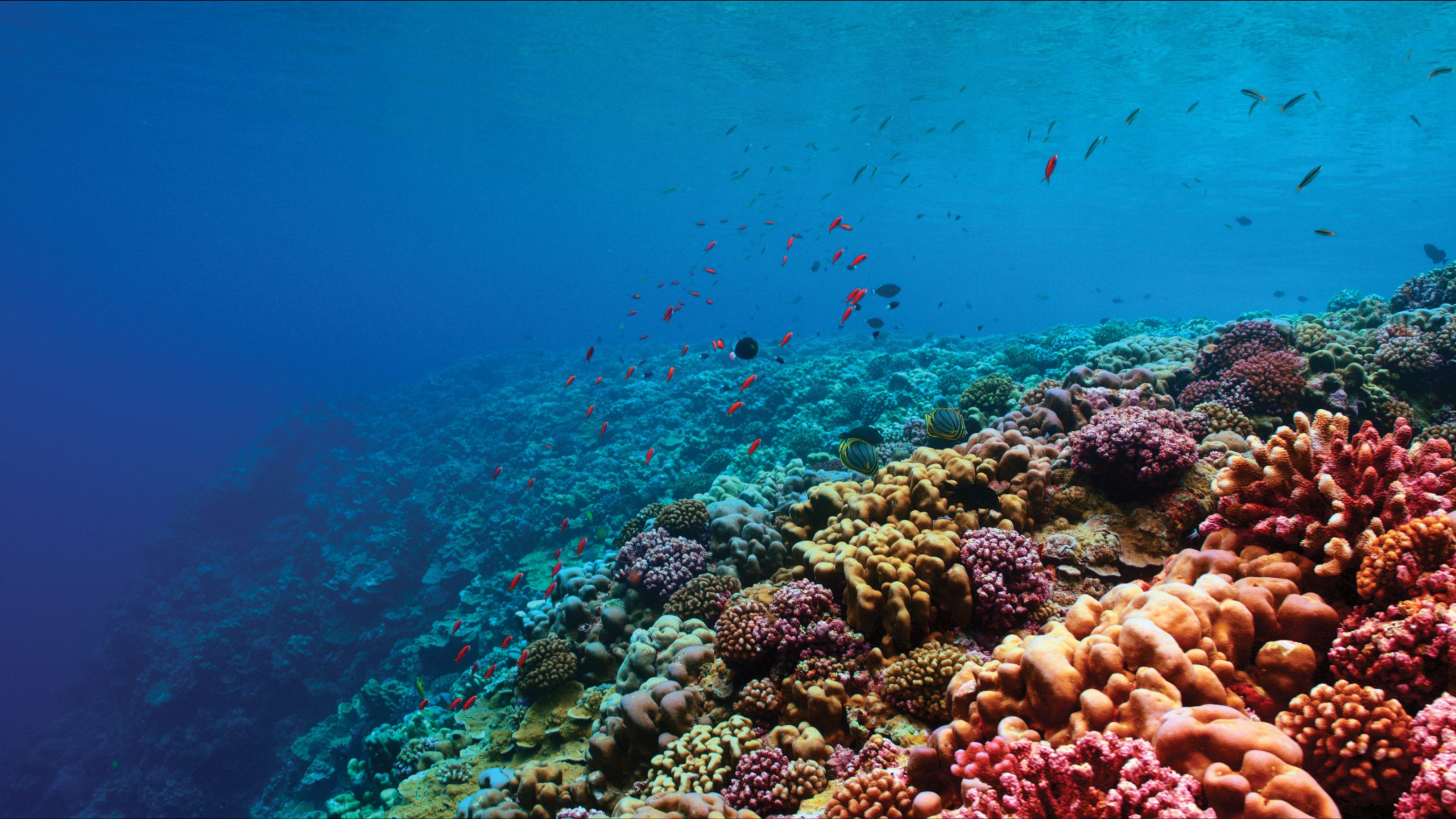
Read More4 Potential Solutions for Corals in Crisis
Racing against the clock, WHOI researchers and colleagues are developing innovative solutions to rebuild reefs and improve coral resiliency–before it’s too late.
Read MoreGeoscience technology company founded by MIT/WHOI Joint Program student awarded $3.8M from U.S. Department of Energy
Eden, a geoscience technology development company co-founded by Massachusetts Institute of Technology/Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Joint Program student Paris Smalls, will receive $3.8 million in federal funding from the U.S. Department of Energy Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E).
Read MoreArc volcanoes are wetter than previously thought, with scientific and economic implications
This increased amount of water has broad implications for understanding how Earth’s lower crust forms, how magma erupts through the crust, and how economically important mineral ore deposits form, according to a new paper led by authors from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
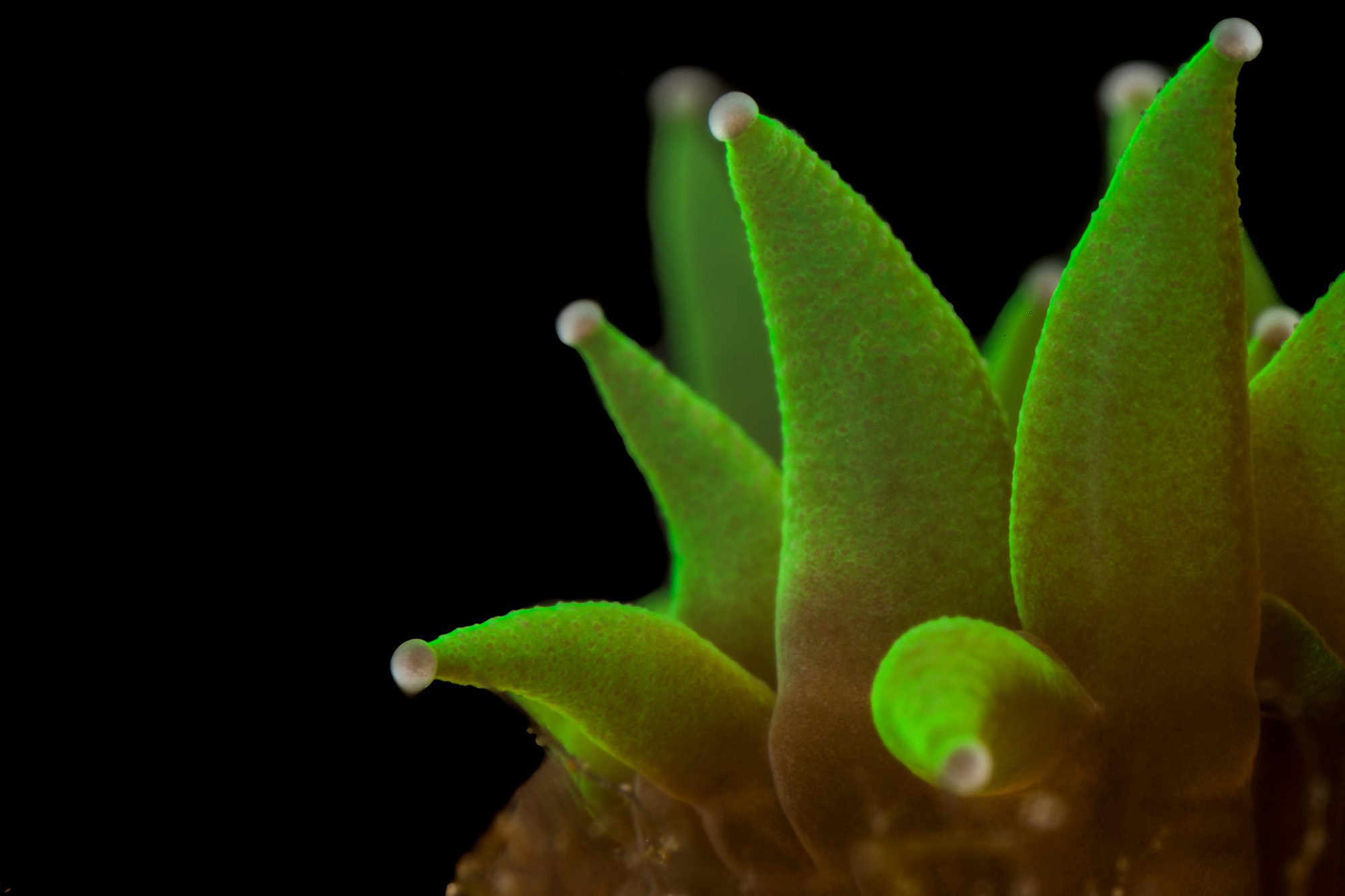
Read MoreReef architects
Exploring the many forms and functions of coral polyps with macro photography
Read More7 Places and Things Alvin Can Explore Now
With its new depth rating of 6500 meters (4 miles), WHOI’s human-occupied vehicle (HOV) Alvin is set to take scientists places they’ve never explored in person
Read MoreCan environmental DNA help us find lost US service members?
Ocean scientists explore how eDNA may be able to help find and identify lost military personnel in the ocean
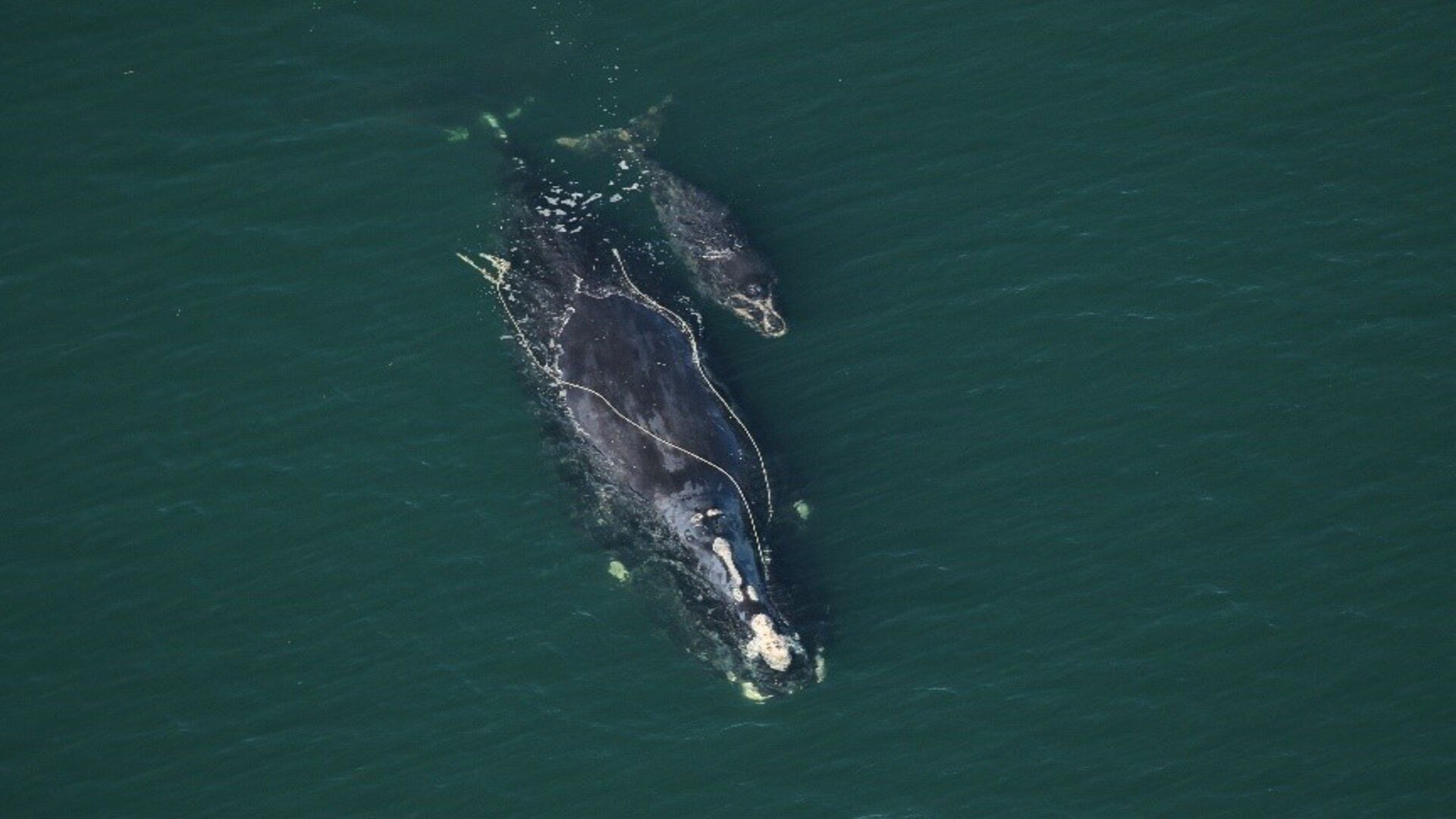
Read MoreSmaller female North Atlantic right whales, fewer calves
The declining body size of North Atlantic right whales may have critical consequences for the future of the species. New research, co-authored by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s senior scientist Michael Moore, shows that smaller females produce fewer calves.
Read MoreOn the crumbling edge
The race to ensure protection for the emperor penguin across the world
Read MoreFluid Flow Stimulates Chemosynthesis in a Greek Salad of Hydrothermal Microbes
A new study uses an innovative approach to examine the bay’s shallow-water hydrothermal system and the production of microbes there in situ and near natural conditions as a model to assess the importance of hydrothermal fluid circulation on chemosynthesis.
Read MoreTracking dispersal of baby fish for better reef conservation
To improve marine protected areas, WHOI scientists study the traffic patterns of juvenile reef fish
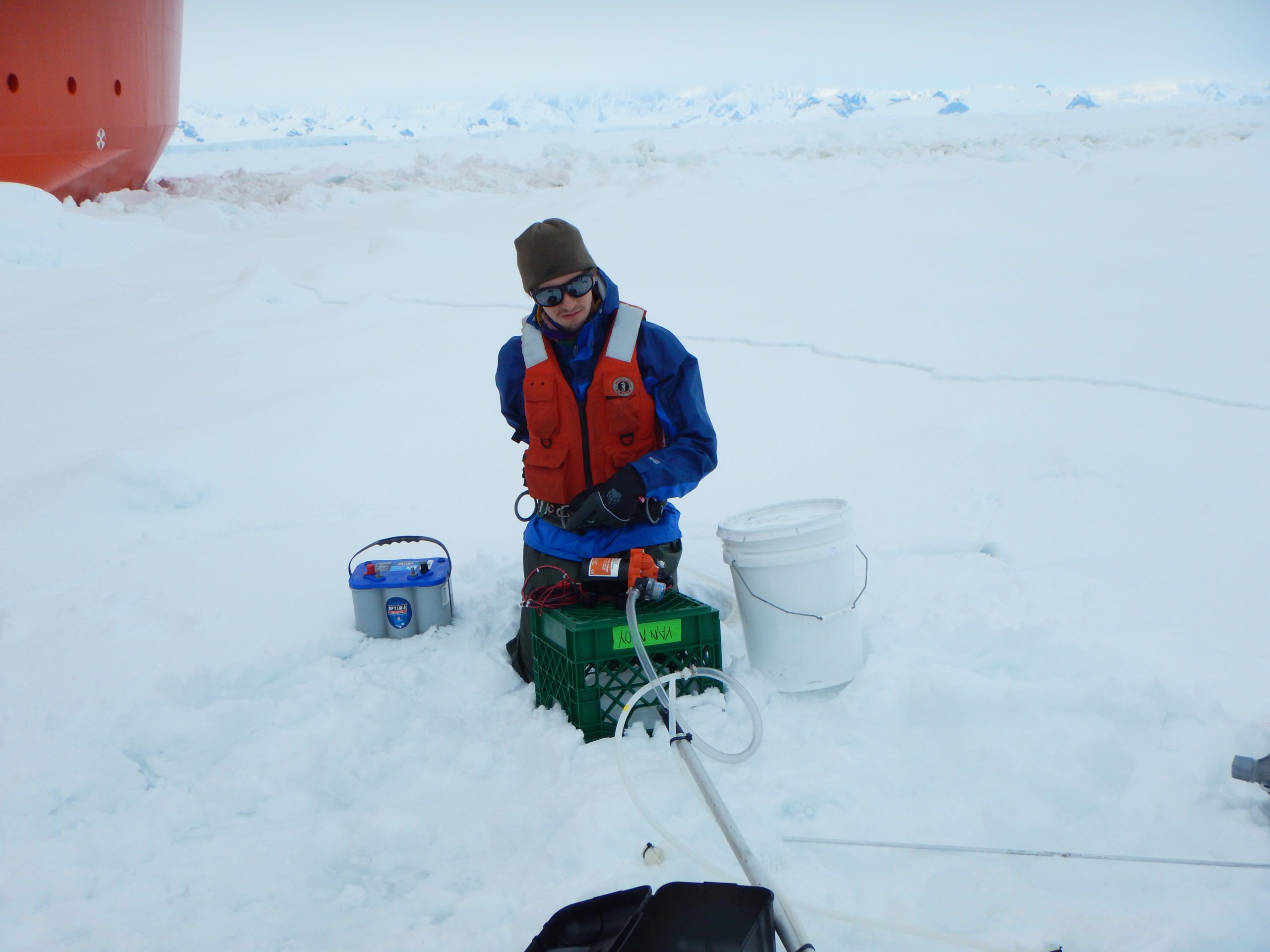
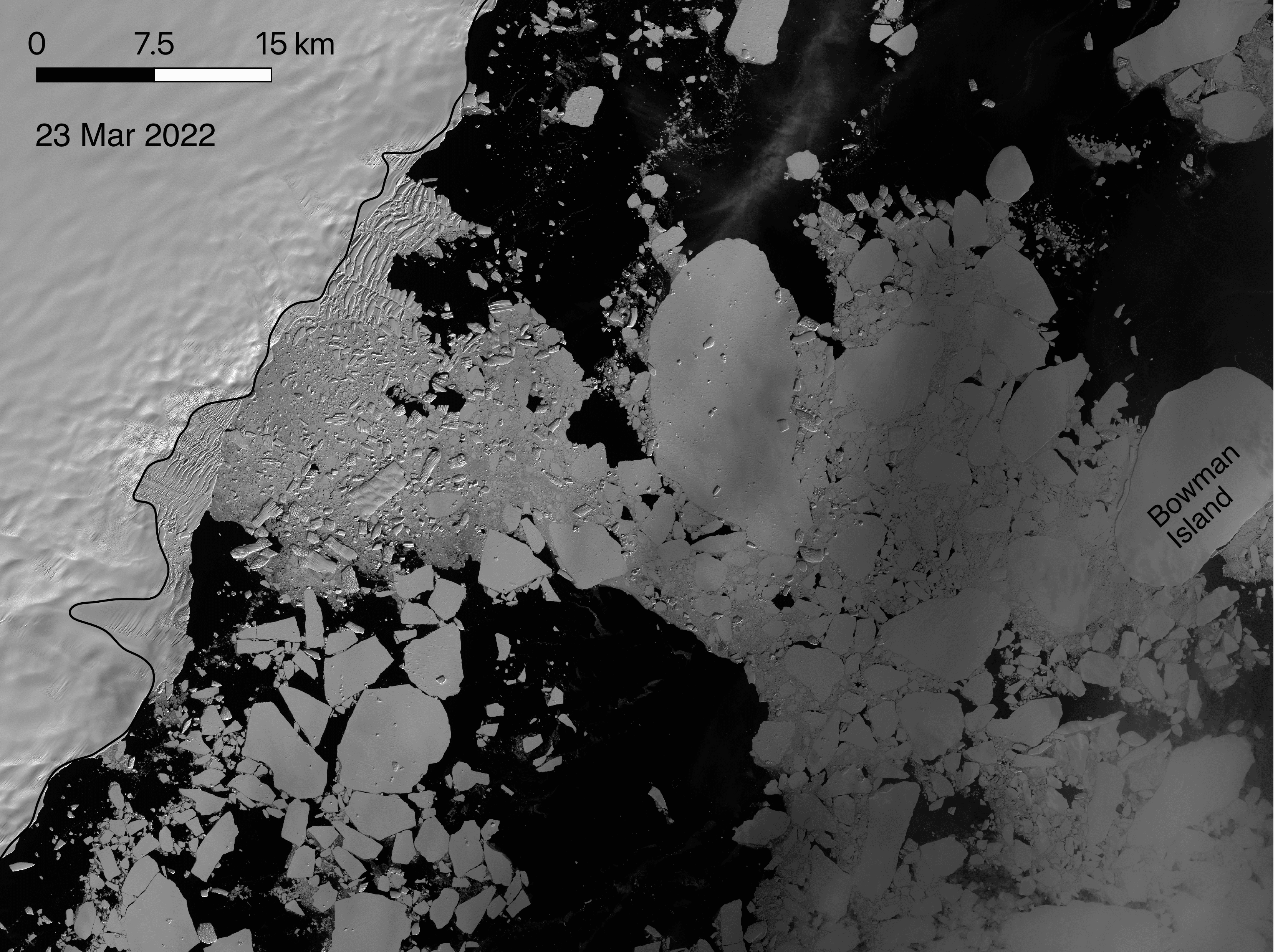
Read MoreScientists report complete collapse of East Antarctica’s Conger Ice Shelf
Satellite data has confirmed that an ice shelf about the size of Manhattan has completely collapsed in East Antarctica within days of record high temperatures. The Conger ice shelf, which had an approximate surface area of 1,200 sq km, collapsed around 15 March, scientists confirmed today.
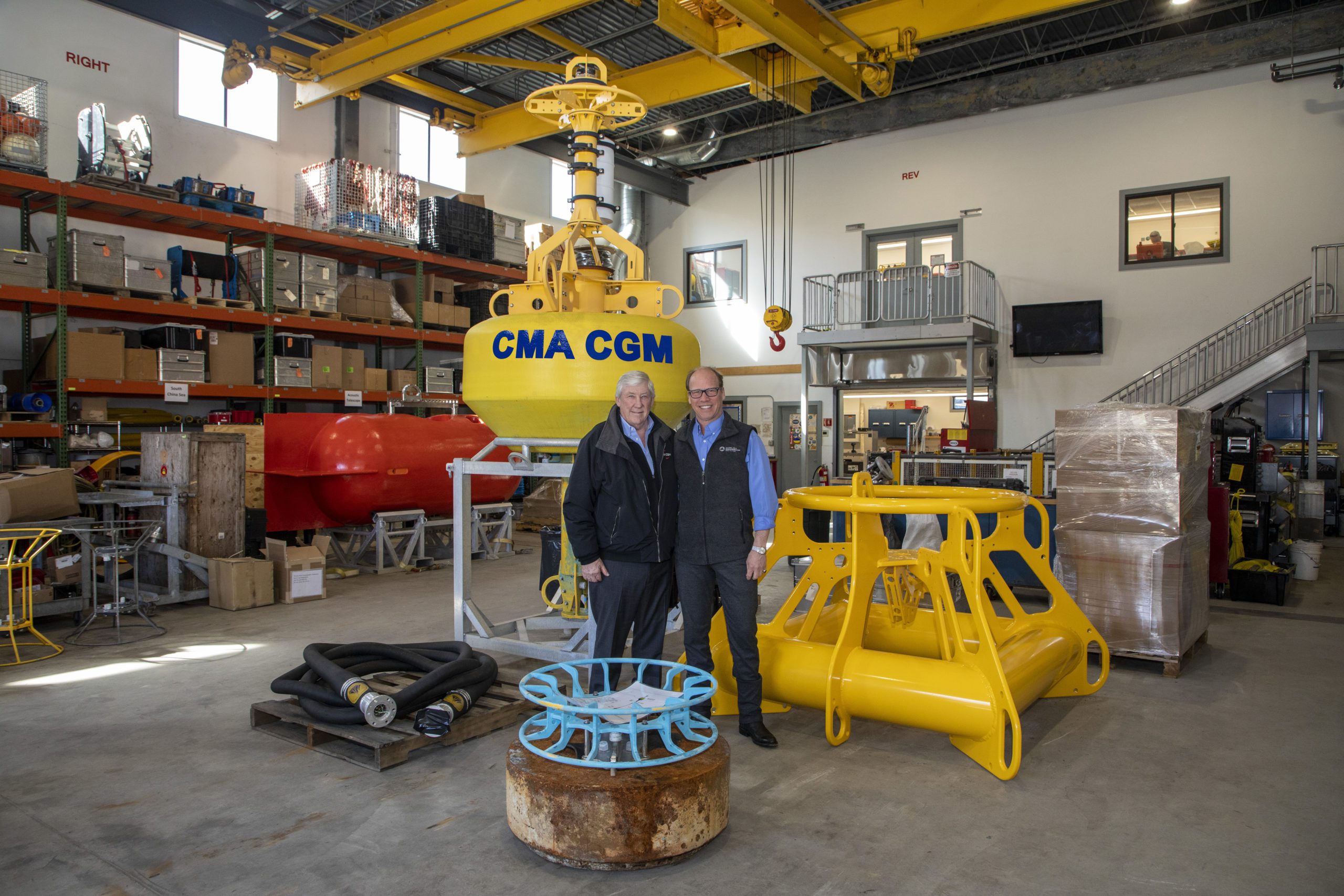
Read MoreWHOI collaborates with CMA CGM to increase protections for marine mammals
A collaboration between Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and the CMA CGM Group, a world leader in shipping and logistics, aims to increase whale detection efforts along the U.S East Coast, particularly for North Atlantic right whales, and reduce the potential for ship strikes along critical shipping routes.
Read MoreWHOI scientists discuss the chemistry behind Sri Lanka’s flaming plastic spill
Eight months after the M/V X-Press Pearl disaster in Sri Lanka, WHOI investigators talk about their research on the unique chemistry of the spilled plastic nurdles
Read MoreEvidence Bolsters Classification of a Major Spawning Ground for Atlantic Bluefin Tuna Off the Northeast U.S.
The Slope Sea off the Northeast United States is a major spawning ground for Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus), a new WHOI-led paper affirms. This finding likely has important implications for population dynamics and the survival of this fish.
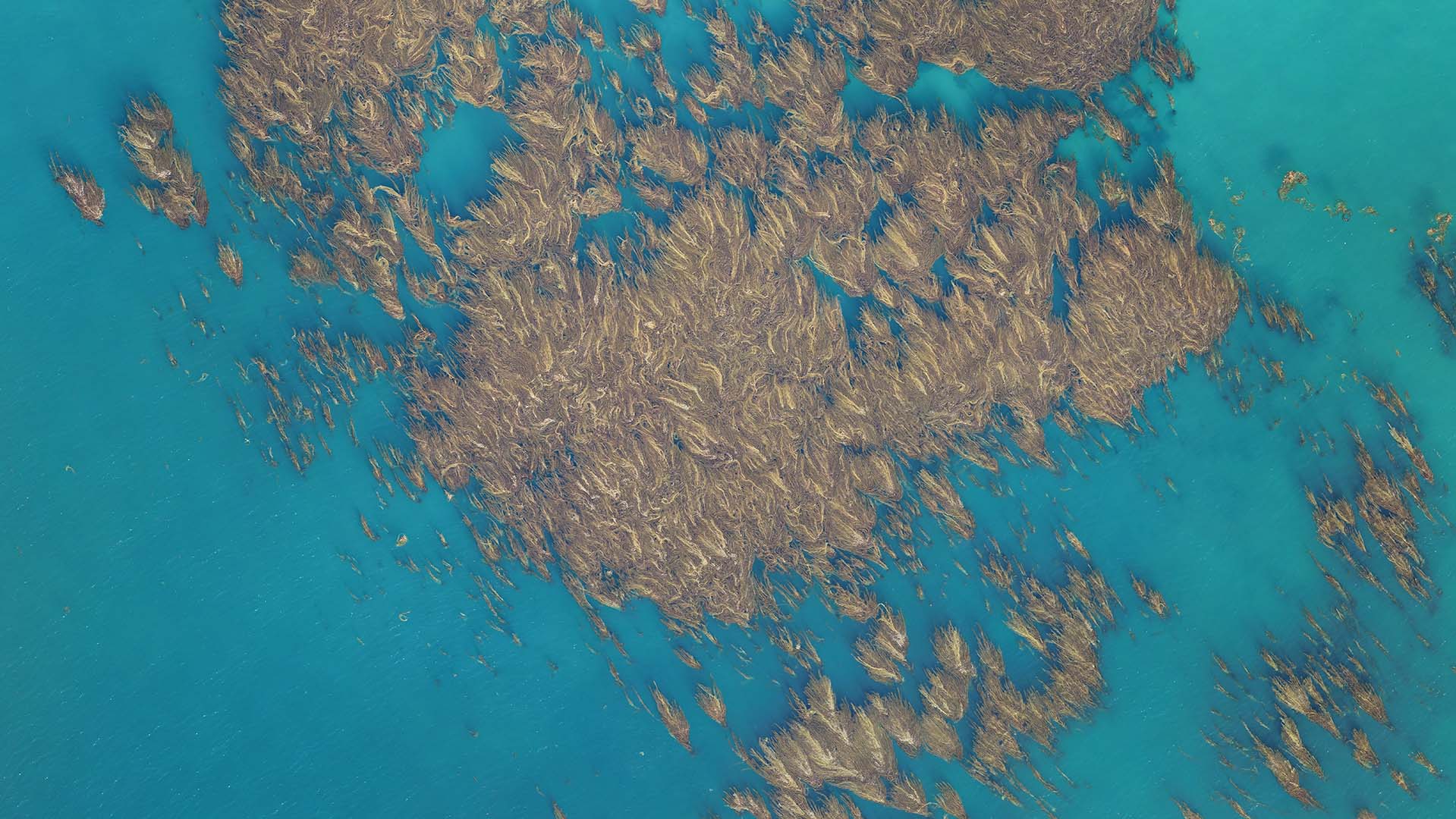
Read MoreResearch suggests giant kelp has different factors that bear on its growth dynamics
The macroalga giant kelp, which is an iconic and important ecosystem-structuring species found off the coast of California and many other coastlines, can grow 100-feet long within 1-2 years. Now, researchers using novel remote sensing observations have found that different factors may bear on the spatial growth dynamics of the Macrocystis pyrifera kelp, which is the largest species of algae in the world.
Read MoreOcean data gives Northeast fishermen an edge against a warming ocean
Fishermen successfully brace against warm water wave from Gulf Stream, thanking greater access to data from the WHOI Shelf Fleet Program
Read MoreTropical fish…up north? How ocean physics play a role in altering water temperature and salinity
A study led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution scientists is explaining why warm and salty water along with warm water fish species, such as the deep-sea dwelling Gulf Stream flounder and Black Sea bass, were found far inshore in New England in the middle of winter 2017. How did this happen? Researchers say it is due to an intrusion of offshore water from the open ocean onto the Northeast U.S. Shelf, caused by eddies (a circular current of water) and wind.
Read MoreStudy finds bio-based cellulose acetate plastic used in consumer goods disintegrates in ocean much faster than assumed
Woods Hole, MA — Cellulose diacetate (CDA), a bio-based plastic widely used in consumer goods, disintegrates, and degrades in the ocean far quicker than previously assumed, according to a new…
Read MoreAn ocean of opportunity
Ocean experts explore the potential risks and rewards of ocean-based solutions to climate change
Read MoreA curious robot is poised to rapidly expand reef research
WHOI scientists with the Coral Catalyst Team are leveraging a new, artificially intelligent robot to automate coral reef health assessments
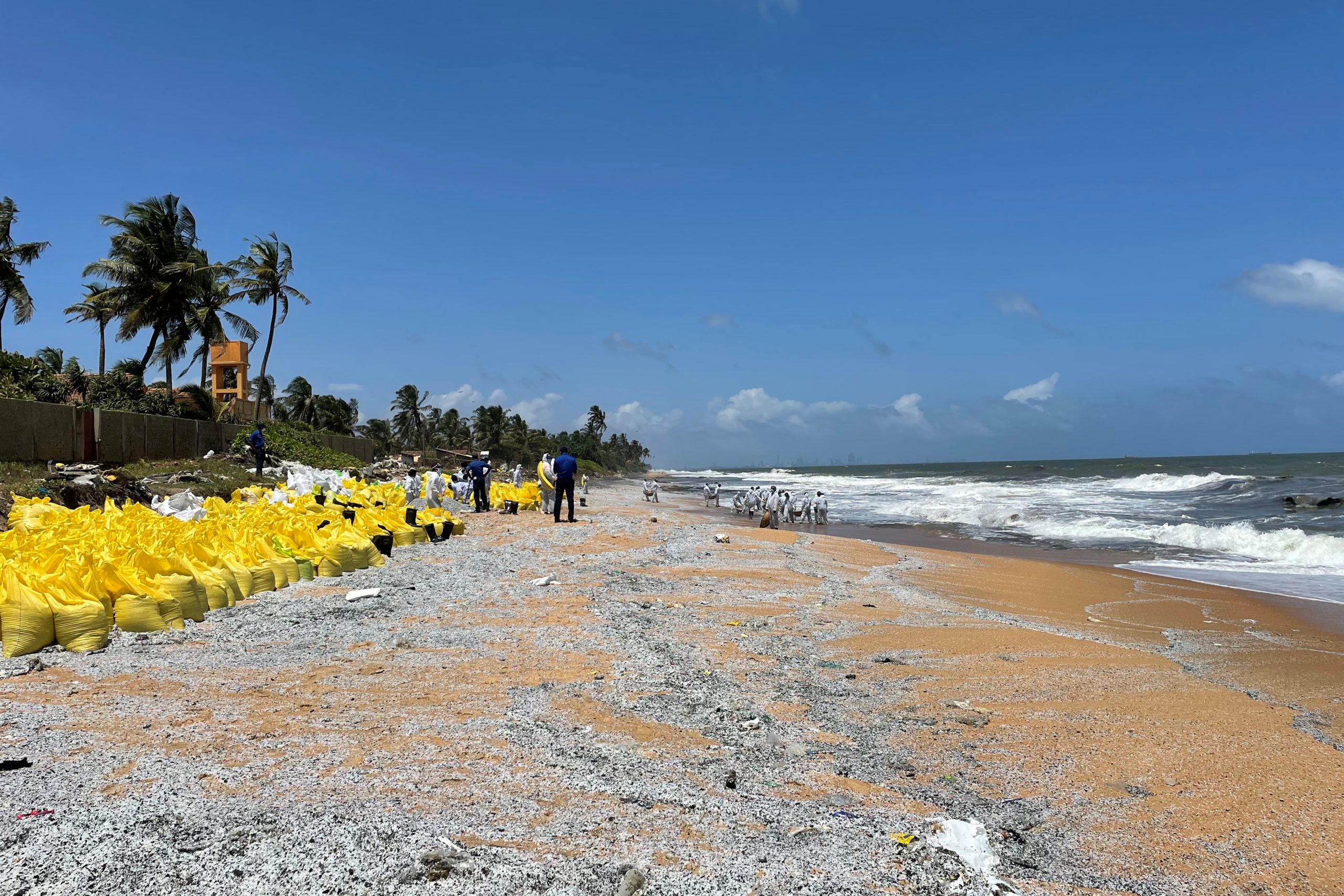
Read MoreStudy outlines challenges to ongoing clean-up of burnt and unburnt nurdles along Sri Lanka’s coastline
When a fire broke out on the deck of the M/V XPress Pearl cargo ship on May 20, 2021, an estimated 70-75 billion pellets of preproduction plastic material, known as nurdles, spilled into the ocean and along the Sri Lankan coastline. That spill of about 1,500 tons of nurdles, many of which were burnt by the fire, has threatened marine life and poses a complex clean-up challenge. A new peer-reviewed study characterizes how the fire modified the physical and chemical properties of the nurdles and proposes that these properties affected their distribution along the coast.
Read MoreA coral reef kickstart
WHOI’s Reef Solutions Initiative takes a multi-disciplinary approach to investigate solutions for ailing coral reefs
Read More