Applied Ocean Physics & Engineering
Where Are Mines Hiding on the Seafloor?
Eternally and incessantly, waves and currents stir up sand from the seafloor near the coast. Sediments get suspended in the ocean, carried onshore and off, and deposited elsewhere. In the process, objects on the seafloor—natural and unnatural—can get buried and uncovered.
Read MoreThe New Wave of Coastal Ocean Observing
Estuaries are the borderlands between salt and freshwater environments, and they are incredibly diverse both biologically and physically. The diversity and the high energy of the ecosystem make estuaries remarkably resilient. With a better understanding of these systems, we can reverse
their decline and restore the ecological richness of these valuable, albeit muddy, environments.
Read MoreFive WHOI Researchers Recognized for Contributions to Science and Education
Five researchers have been recognized by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) for their contributions to ocean sciences research and education. All will receive funding provided by the endowed awards…
Read MoreShaping the Beach, One Wave at a Time
For years, scientists who study the shoreline have wondered at the apparent fickleness of storms, which can devastate one part of a coastline, yet leave an adjacent part untouched. How can this be? The answer lies in the physics of the nearshore region?the stretch of sand, rock, and water between the dry land behind the beach and the beginning of deep water far from shore.
Read MoreSeeding the Seafloor with Observatories
Scientists extend their reach into the deep with pioneering undersea cable networks
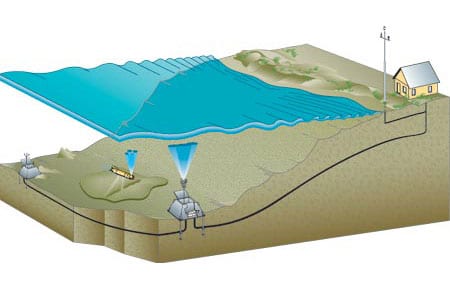
H2O (Hawaii-2 Observatory) – In 1998, scientists used the remotely operated vehicles (ROV) Jason and Medea to create the pioneering long-term seafloor observatory called H2O (Hawaii-2 Observatory). They spliced an abandoned submarine telephone cable into a termination frame. The frame relays power and communications to a junction box, which serves as an electrical outlet for scientific instruments.
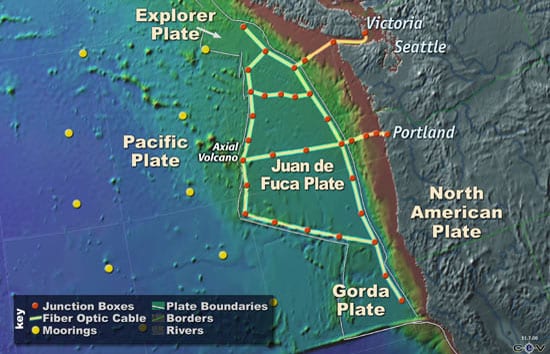
NEPTUNE: A Fiber-Optic ‘Telescope’ to Inner Space
NEPTUNE is a proposed system of high-speed fiber- optic submarine cables linking a series of seafloor nodes supporting thousands of assorted measuring instruments, video equipment, and robotic vehicles that could upload power and download data at undersea docks. Unlike conventional telephone cables, which supply power from shore in a straight line, end to end, NEPTUNE would operate like a power grid, distributing power simultaneously and as needed throughout the network. Working much like a campus data network (with nodes analogous to buildings and each instrument like a workstation), NEPTUNE would provide real-time transmission of data and two-way communications.
Read MoreSeafloor to Surface to Satellite to Shore
The next great leap in our understanding of the earth-ocean system will require us to put our “eyes” and “ears” in the ocean to observe the dynamic processes going on there as they are happening, in real time.
Read MoreNew Coastal Observatory Is Born
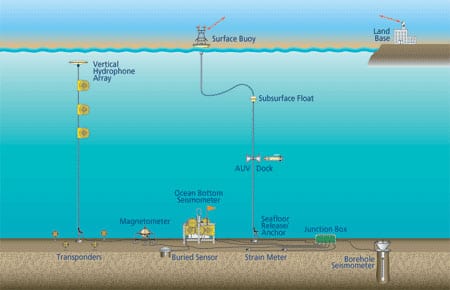
The Martha’s Vineyard Observatory will have sensors mounted on two seafloor nodes, at depths of about 5 and 15 meters, respectively, connected to a shore station via a buried cable. Instruments mounted on the nodes will continually monitor mean sea and wave heights, current strengths, seawater turbulence, subsurface sediment movement, sunlight intensity, and the temperature, salinity, and carbon dioxide levels of the ocean?s waters.
Read MorePutting H2O in the Ocean
A major obstacle impeding our ability to understand many of the earth’s fundamental, ongoing dynamics–quite frankly–has been a dearth of electrical outlets and phone jacks on the seafloor.
Read MoreWhere the Surf Meets the Turf
The gentle lapping of waves on the beach is a metaphor for enduring tranquility. However, the thin zone where the surf meets the turf is one of the most turbulent, complex, fast-moving, constantly changing places on Earth.
Read MoreALISS in Wonderland
In 1985, Cindy Van Dover, then a graduate student in biology in the MIT/WHOI Joint Program, discovered a novel light-sensing organ on a unique species of shrimp that lives at high-temperature, black smoker chimneys on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. If this photoreceptor were indeed some sort of primitive “eye,” the question instantly arose: At depths of some 3,600 meters, where sunlight cannot penetrate, what are these shrimp looking at? The search for a source of light in deep-sea hydrothermal environments began.
Read More“What a Year!”
Four technologies that have been developing separately for some time were brought together this year by WHOI’s Deep Submergence Laboratory (DSL) to serve three very different user communities. With images from the towed vehicle Argo II and the remotely operated vehicle Jason, DSL scientists and engineers created mosaic images of a sunken British cargo ship and 20-meter-tall hydrothermal vent chimneys, both in the Pacific Ocean, and ancient shipwreck sites in the Mediterranean. The three expeditions thus served the marine safety, scientific, and archaeological communities.
Read More