Multimedia
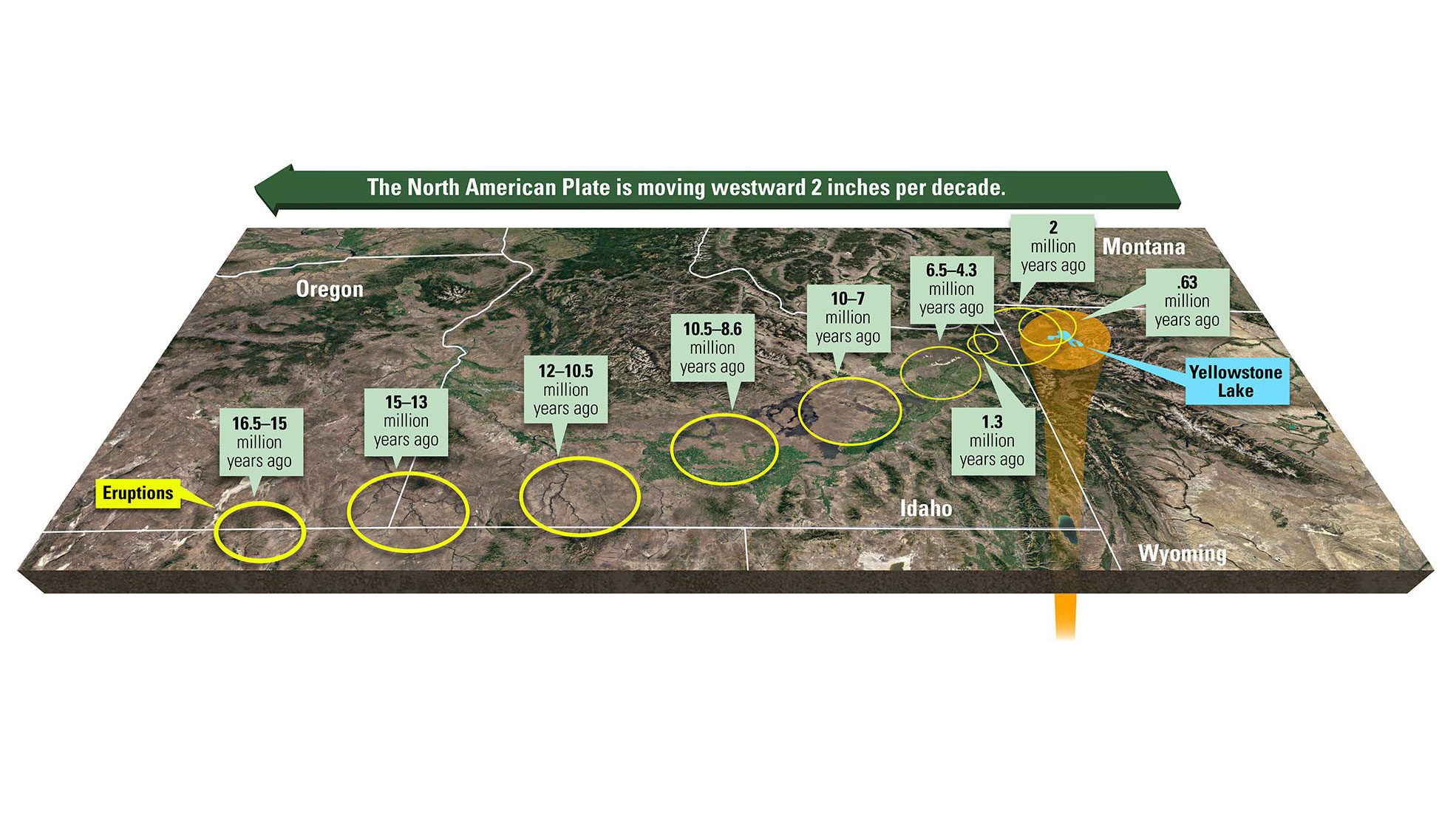
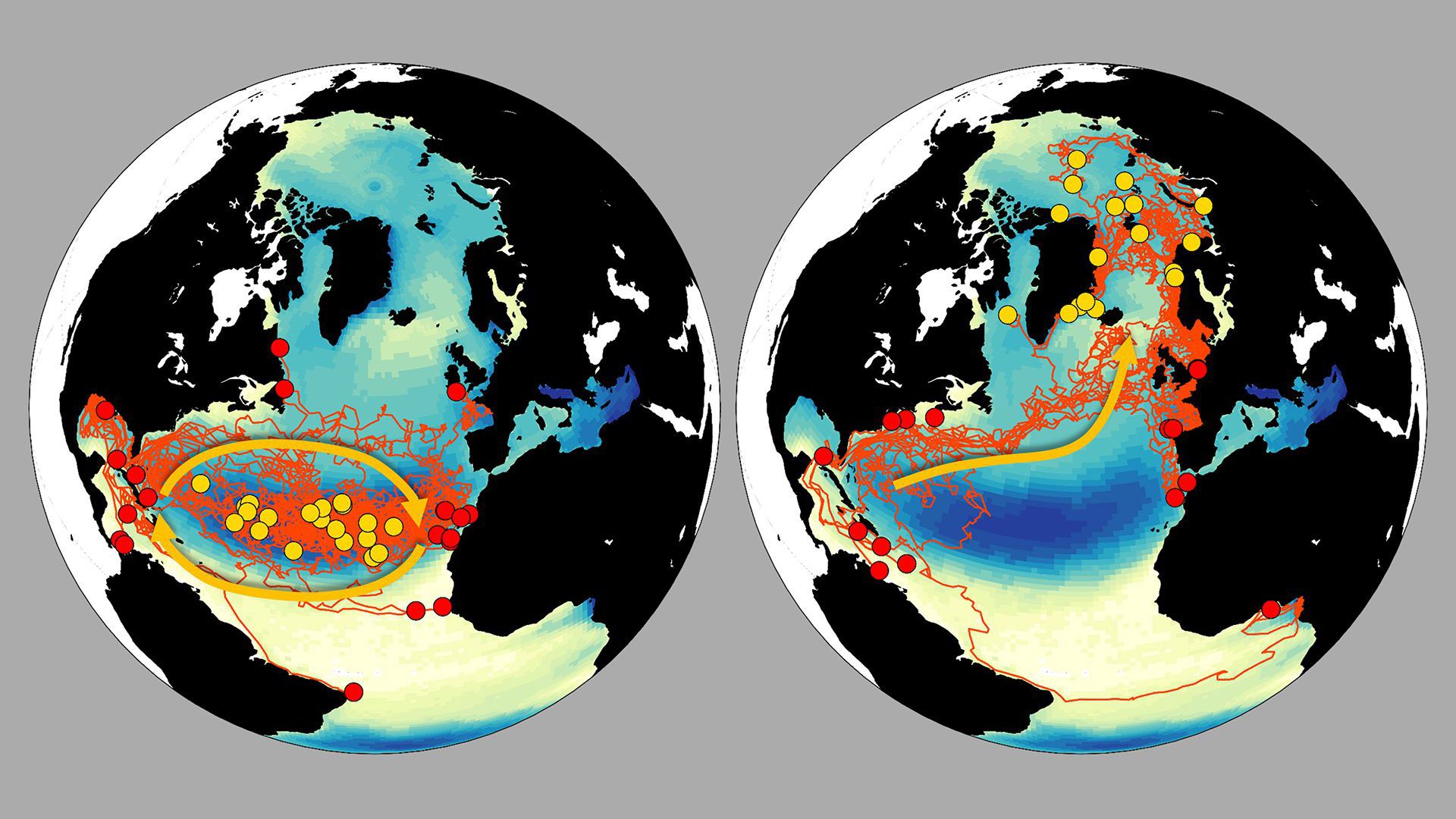
Eruptions along the North American Plate and Yellowstone hotspot
The North American Plate has slowly moved westward over an active magma chamber, leaving a trail of past eruptions. The hotspot now lies beneath Yellowstone Park.
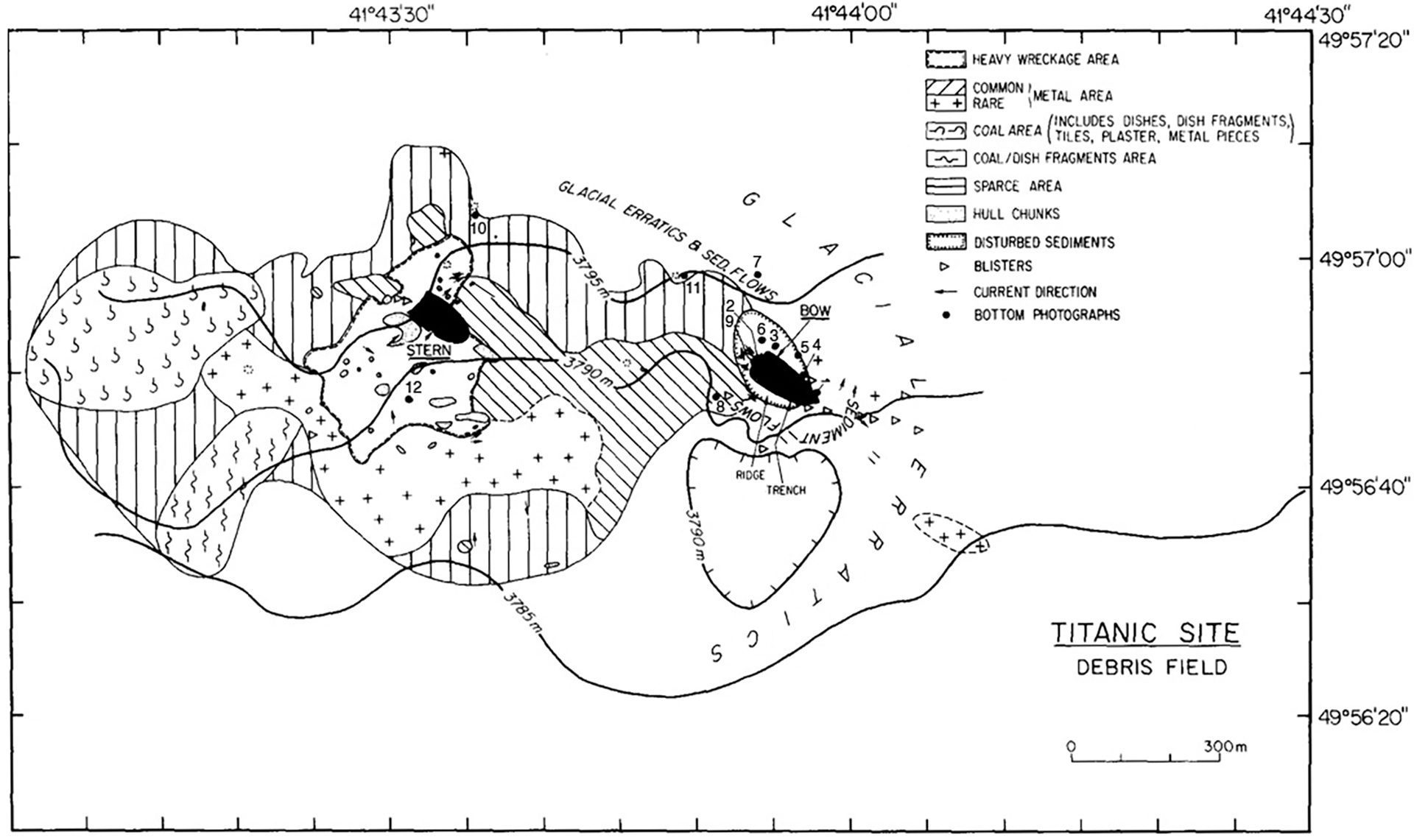
Read MoreTitanic debris-field
First map of Titanic shipwreck debris field, provides a detailed layout of the scattered remains, seafloor/ocean characteristics and existing photographs.
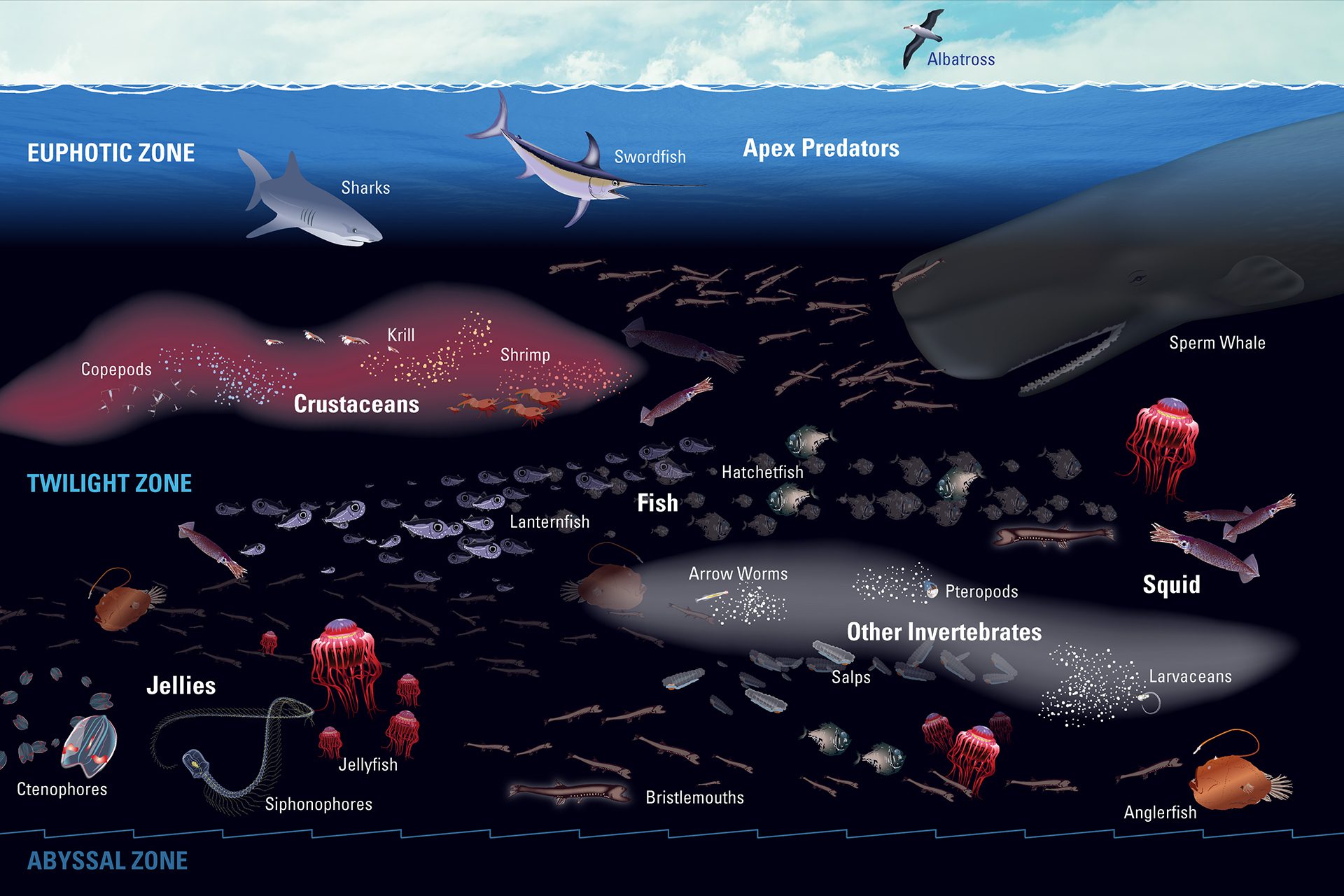
Read MoreBiomass of mesopelagic organisms in Ocean Twilight Zone (OTZ)
The ocean twilight zone hosts Earth’s largest animal migration and plays a key role in the climate by helping move carbon from the surface to the deep sea.
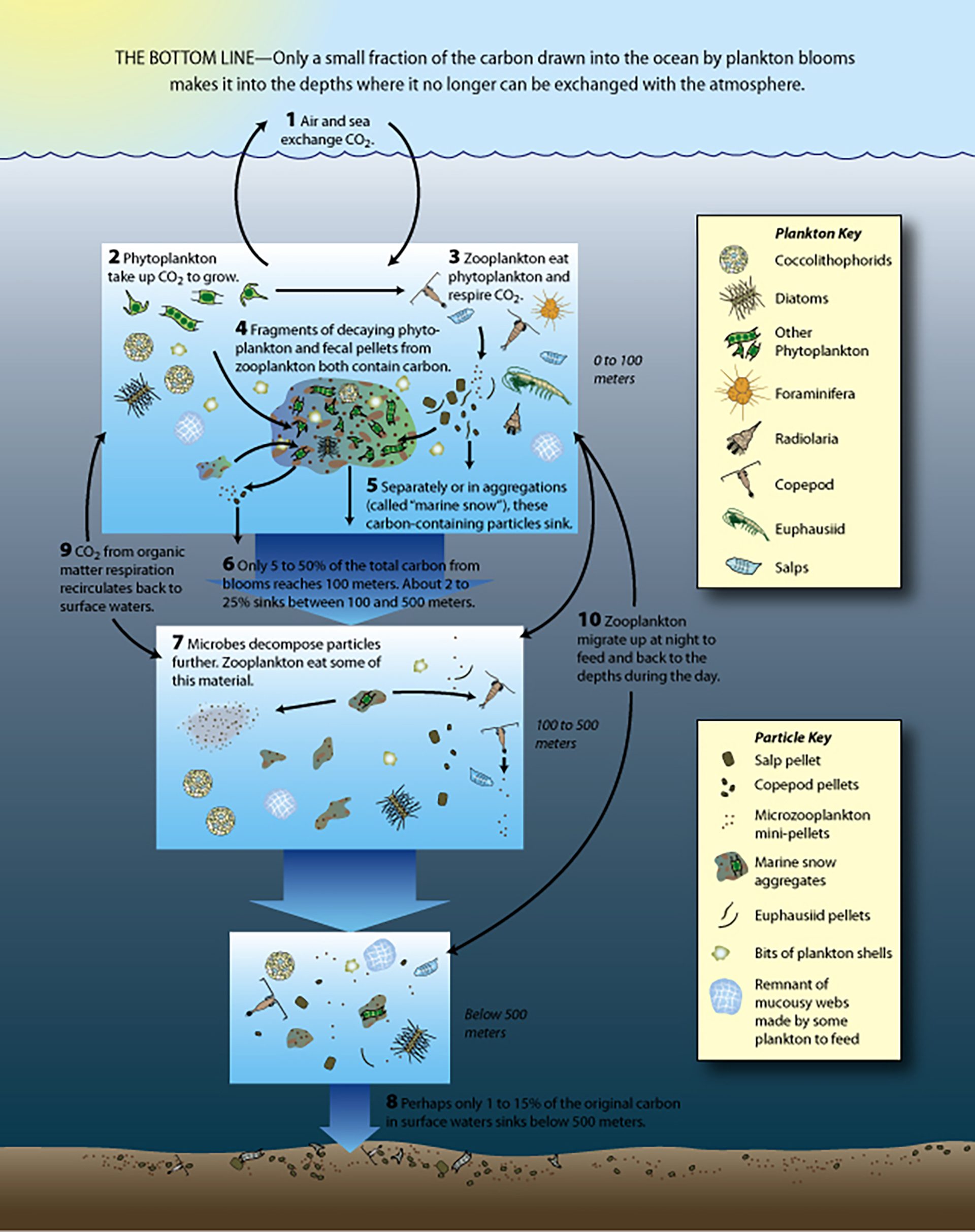
Read MoreCarbon drawn into the ocean by plankton sinks and dissipates with depth
Only a small fraction of the carbon drawn into the ocean by plankton blooms makes it into the depths where it no longer can be exchanged with the atmosphere.
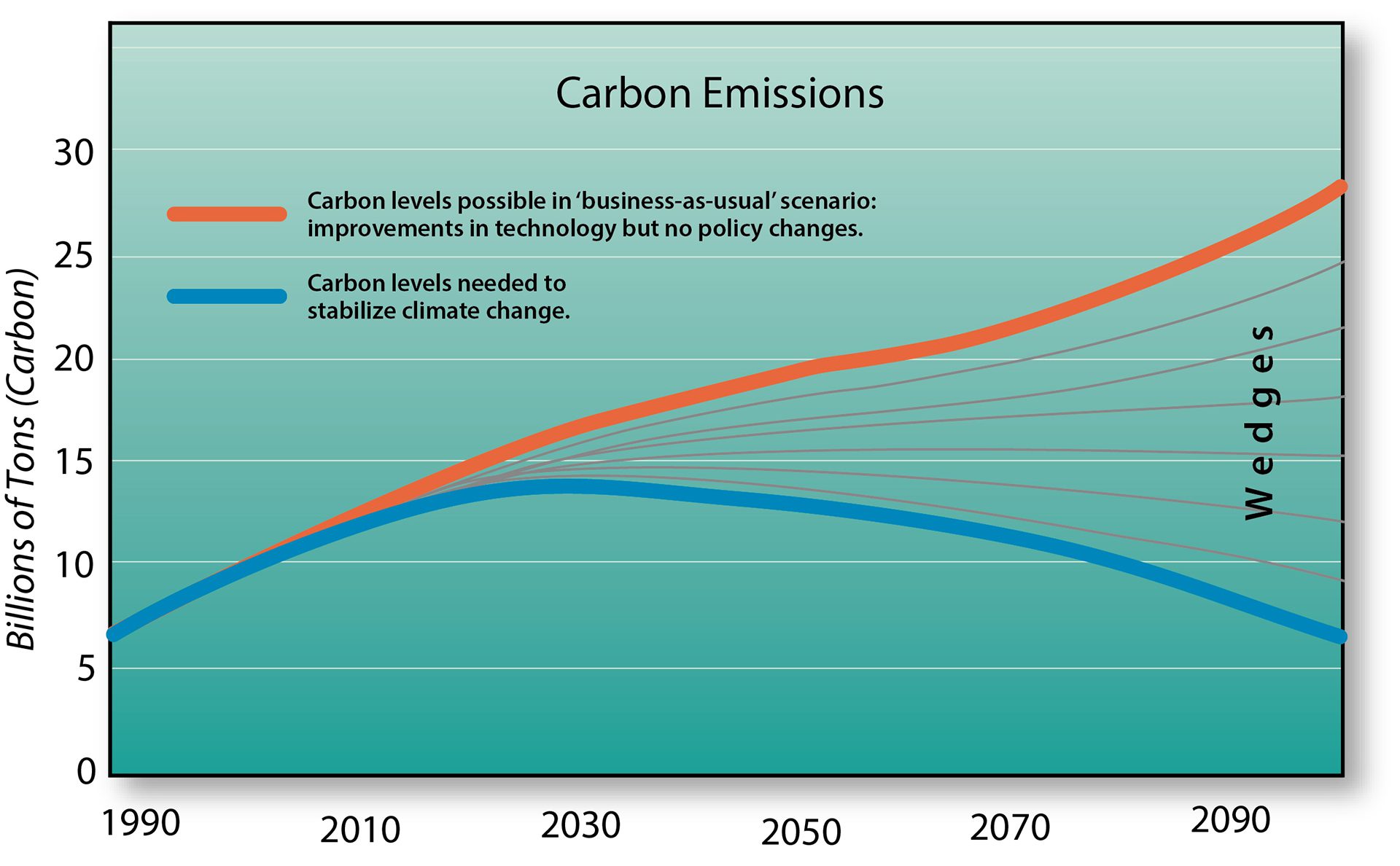
Read MoreCarbon emissions projection featuring possible reduction methods called "wedges"
Without climate action, emissions will keep rising. To close the gap, multiple solutions—including ocean iron—may be needed to reach carbon reduction targets.
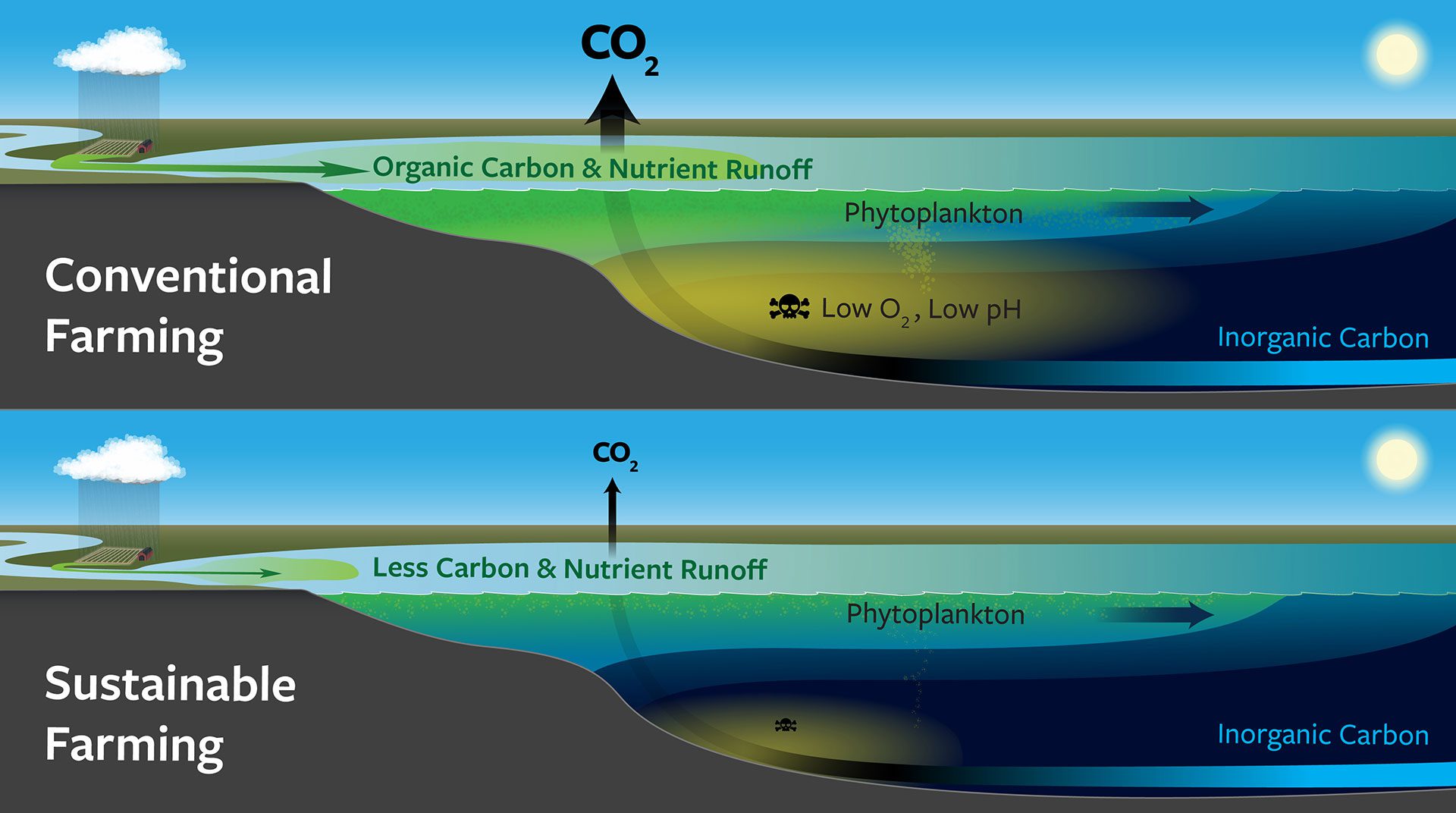
Read MoreCarbon without Borders, conventional vs sustainable farming
This illustration shows the difference between conventional and sustainable farming on land, and how that affects carbon and pH levels in the ocean.
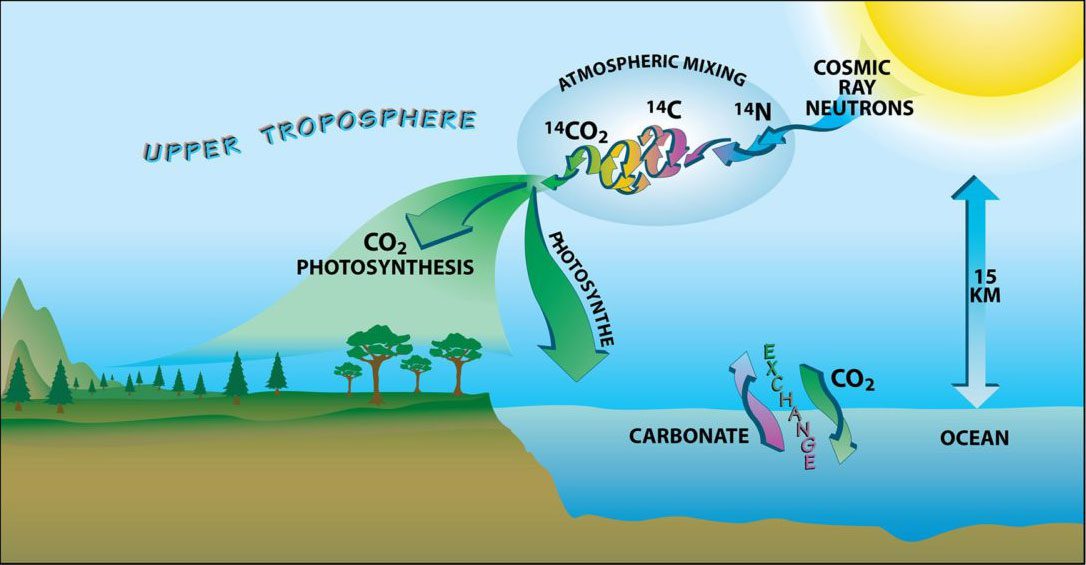
Read MoreCarbon-14 natural cycle
An illustration showing the natural carbon-14 cycle through the atmosphere, land and ocean.
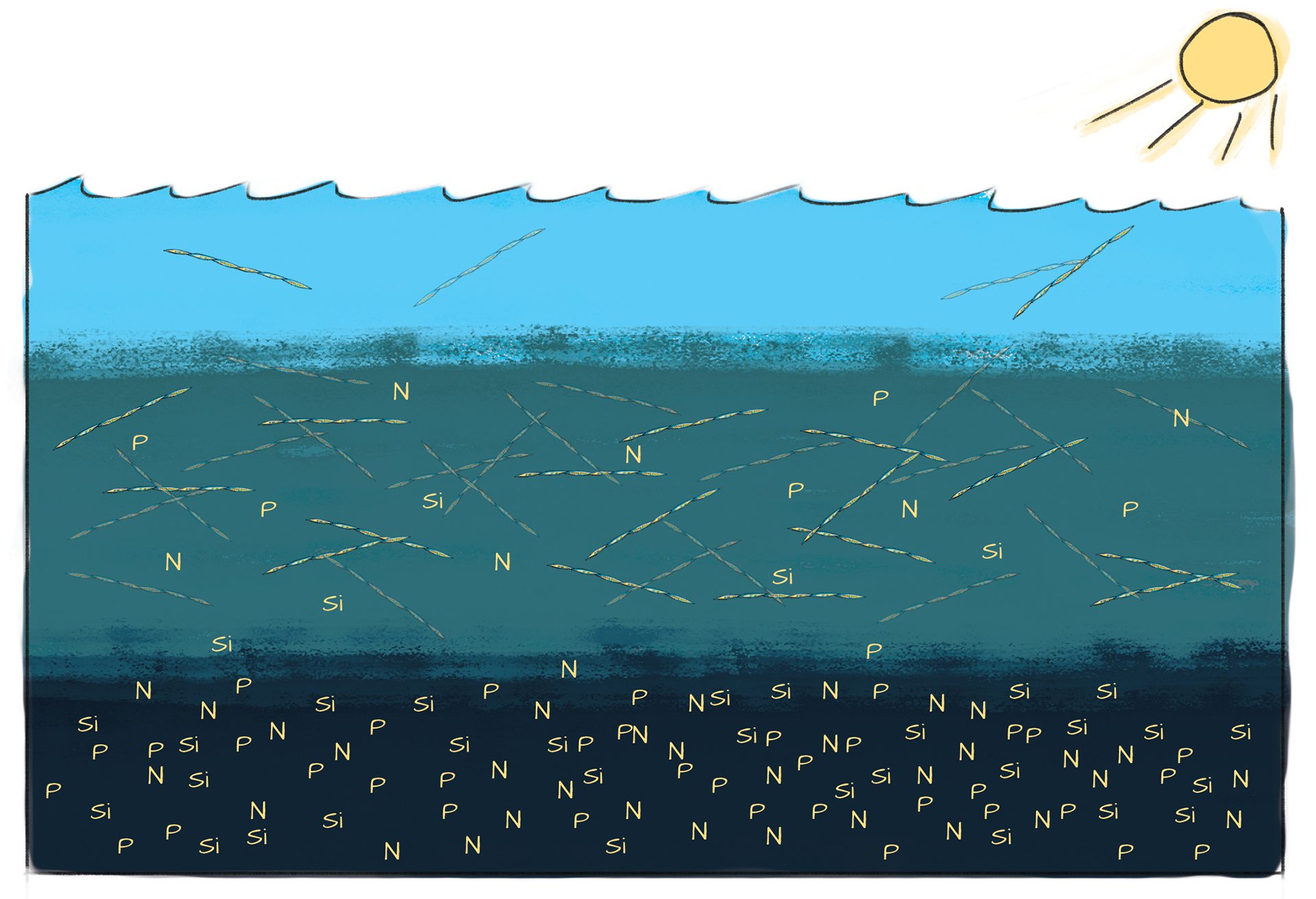
Read MoreChemical process by which phytoplankton and harmful algal blooms grown
Phytoplankton thrive where sunlight and nutrients overlap—often just below the surface—creating a “sweet spot” for growth that fuels ocean life and ecosystems.
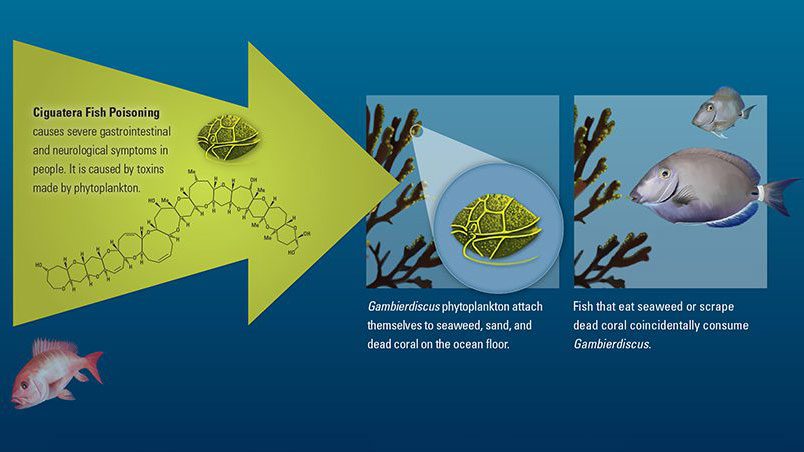
Read MoreCiguatera Fish Poisoning cycle
Ciquatera fish poisoning, caused by toxins made by phytoplankton, can cause several gastrointestinal and neurological symptoms in people.
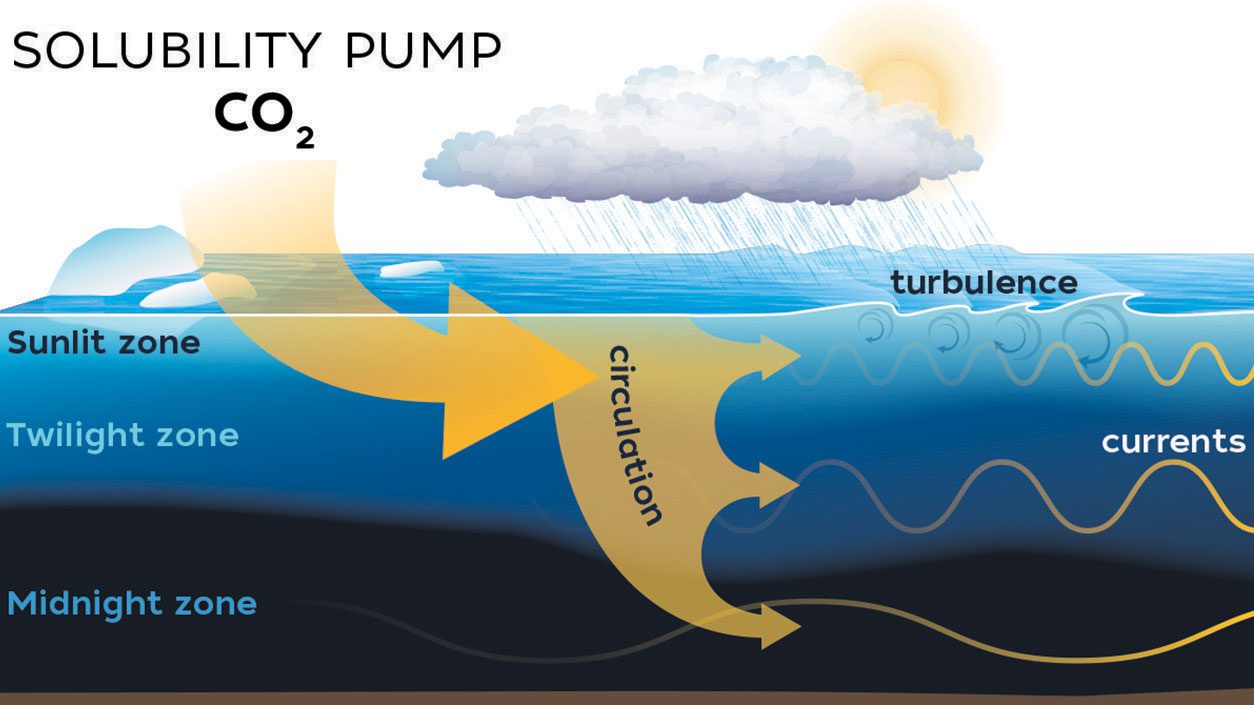
Read MoreCO Solubility Pump
Cold seawater absorbs CO? from the atmosphere, which sinks to the deep ocean via circulation, storing carbon long-term in the solubility pump process.
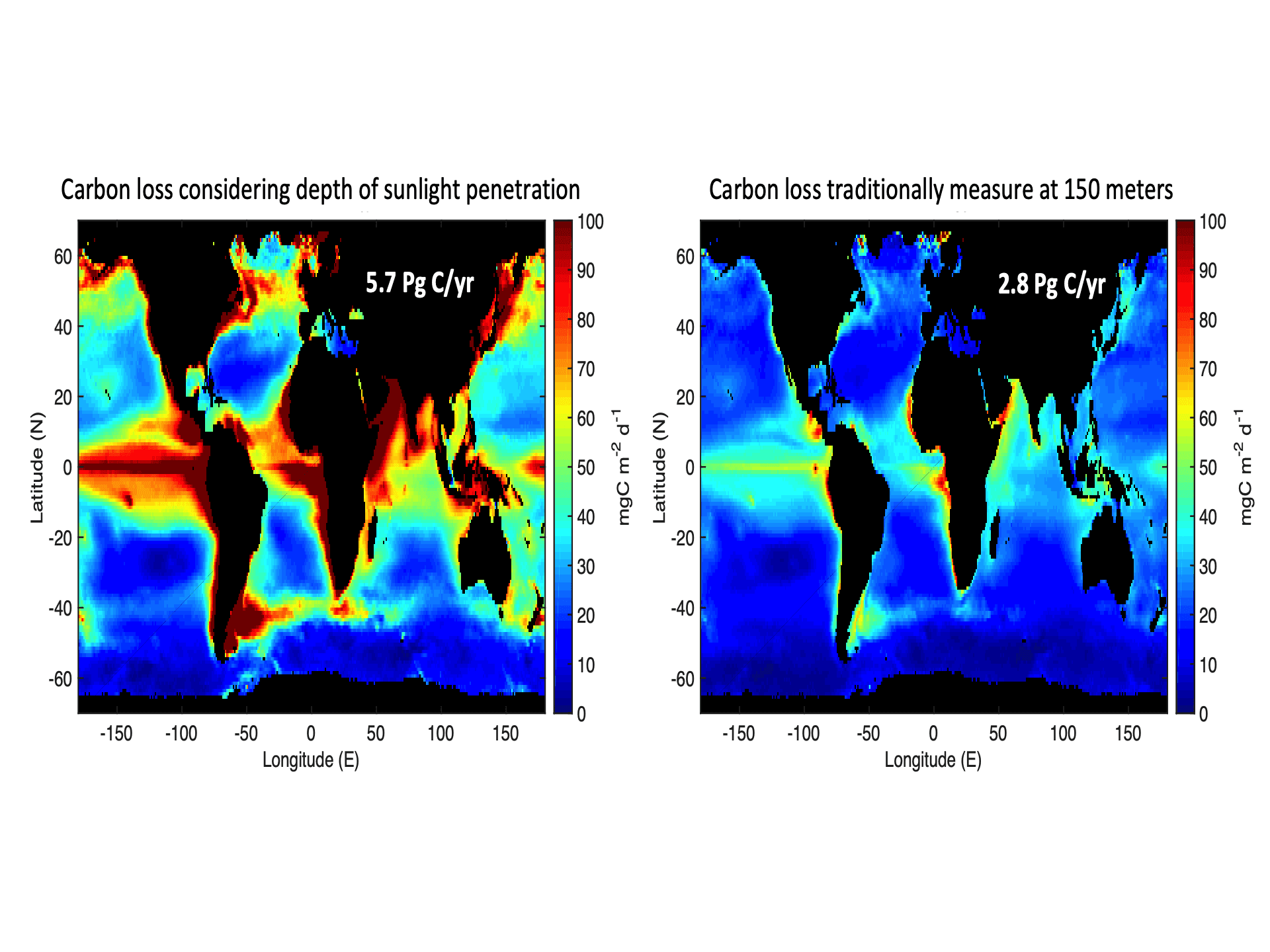
Read MoreComparing carbon loss considering different sunlight penetration depths
Global maps of ocean carbon estimates highlighting the need to account for sunlight (Buesseler et al., 2020).
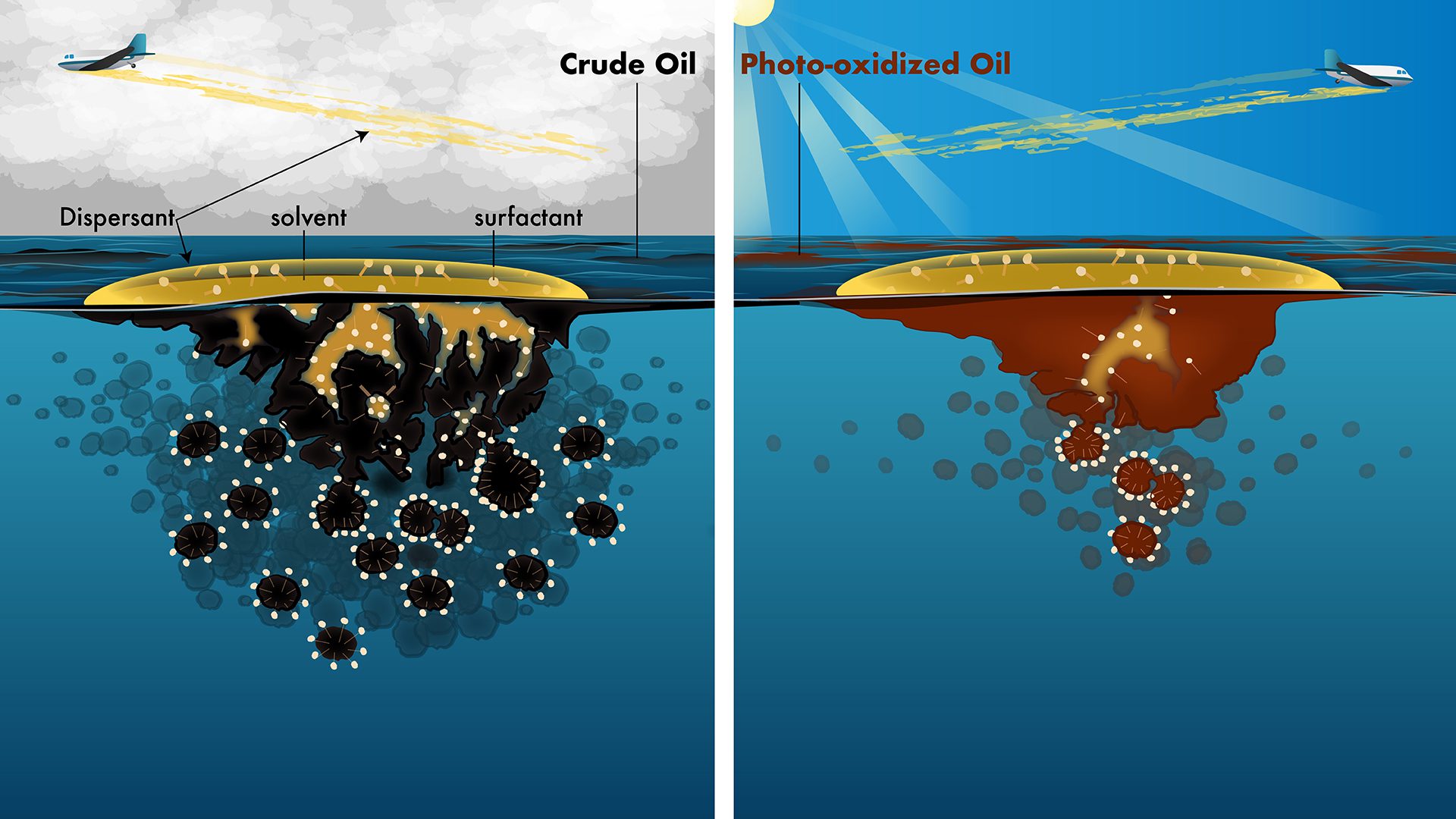
Read MoreComparison of oil dispersant effectiveness in different weather
Sunlight changes oil chemistry on the ocean surface, reducing dispersant effectiveness by limiting how well surfactants break oil into small droplets.
Read MoreComparison of radioactivity sources in the ocean
The background level of radiation in the ocean varies around the globe. The primary source has been nuclear weapons testing in the Pacific Ocean.
Read MoreTransport of microplastics in the North Atlantic
Global maps illustrating how microplastics may travel through the North Atlantic and Arctic, based on global transport simulations.
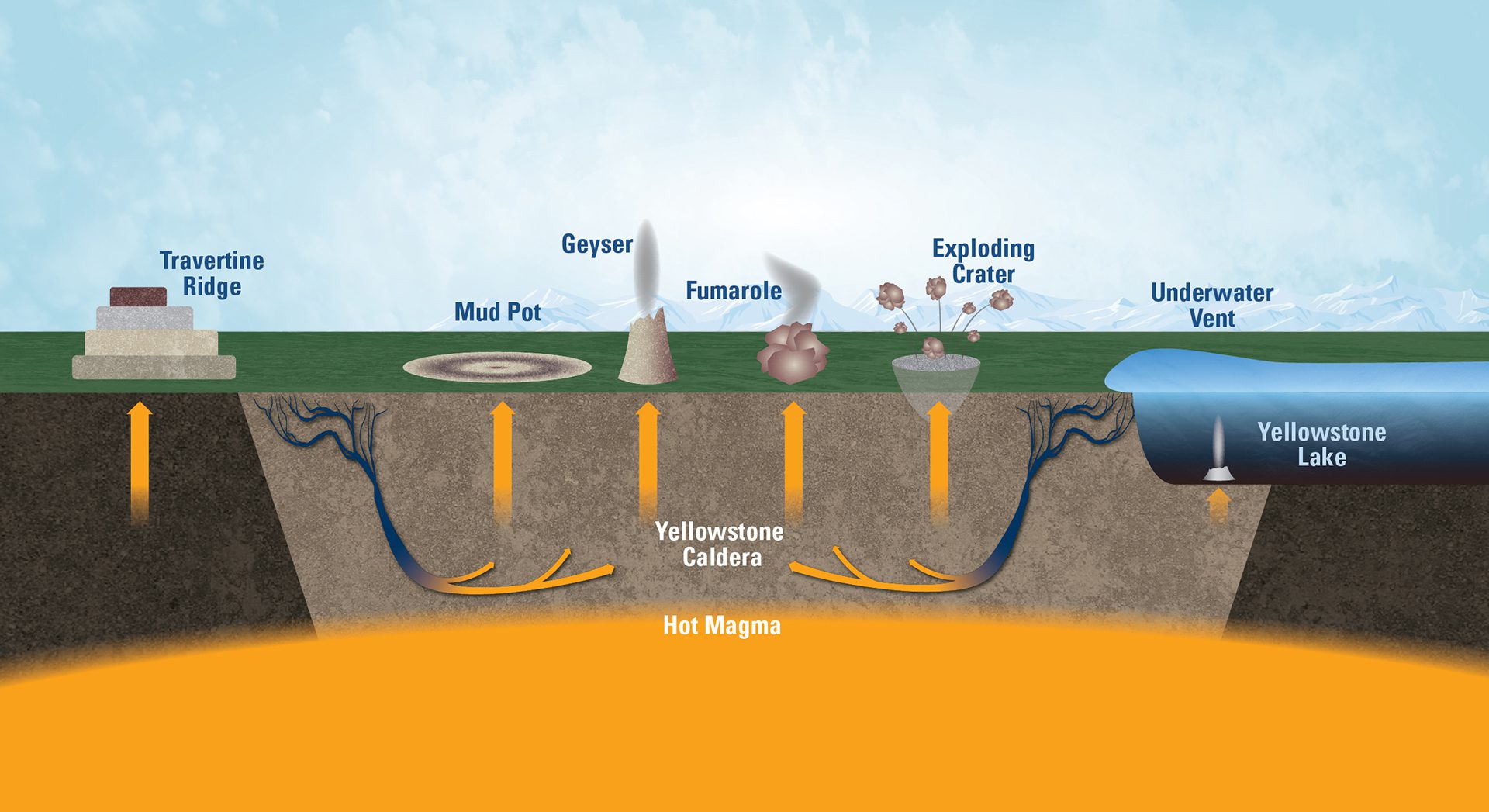
Read MoreConceptual cross-section view of Yellowstone Lake geothermal dynamics
Yellowstone’s colorful pools and geysers are surface features of a vast geothermal system that stretches beneath the northern half of Yellowstone Lake.
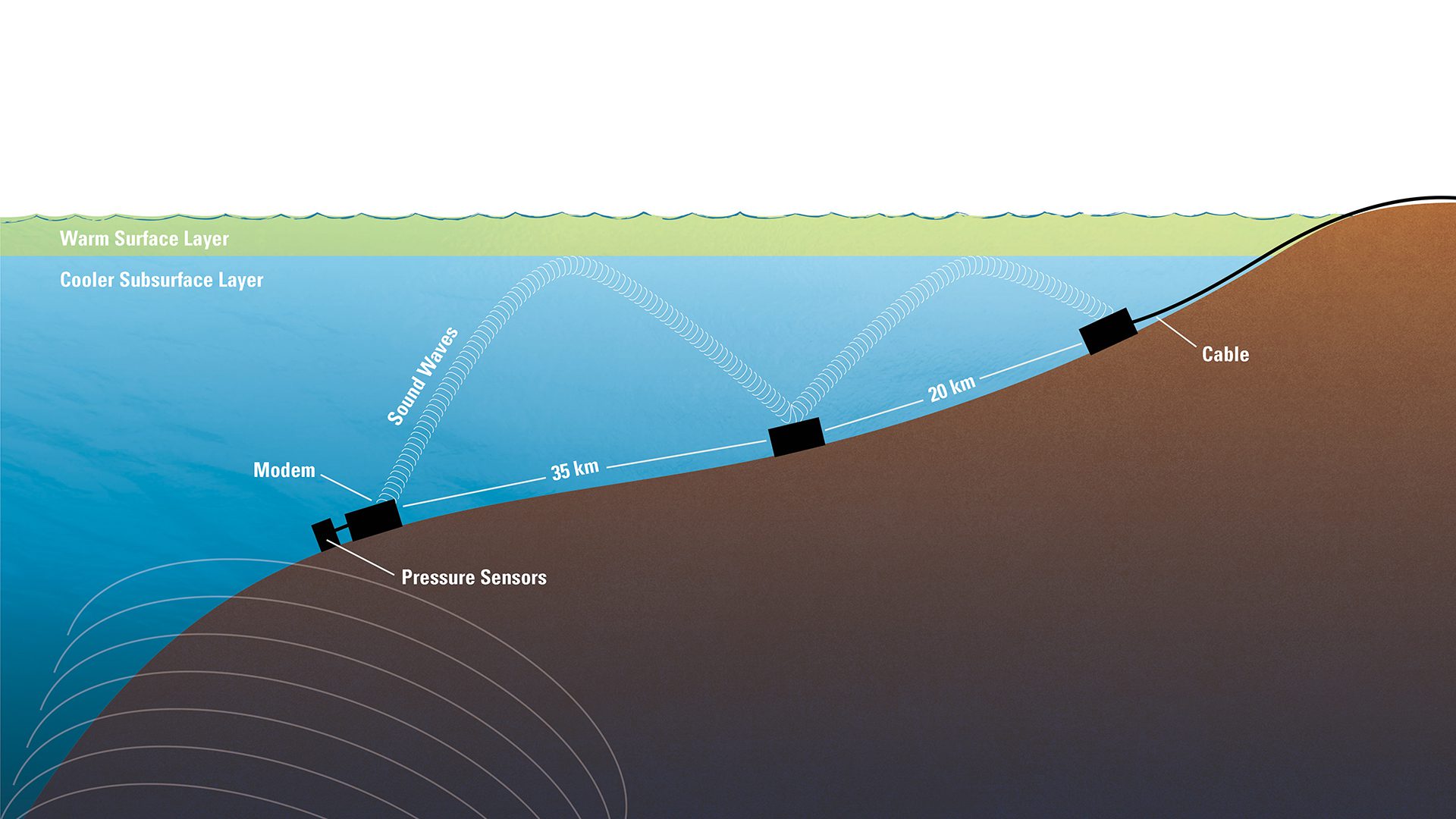
Read MoreConfiguration of tsunami warning pressure sensor system
Tsunami pressure sensors send underwater sound signals that bounce off warm surface layers to relay stations, triggering alerts sent to officials on shore.
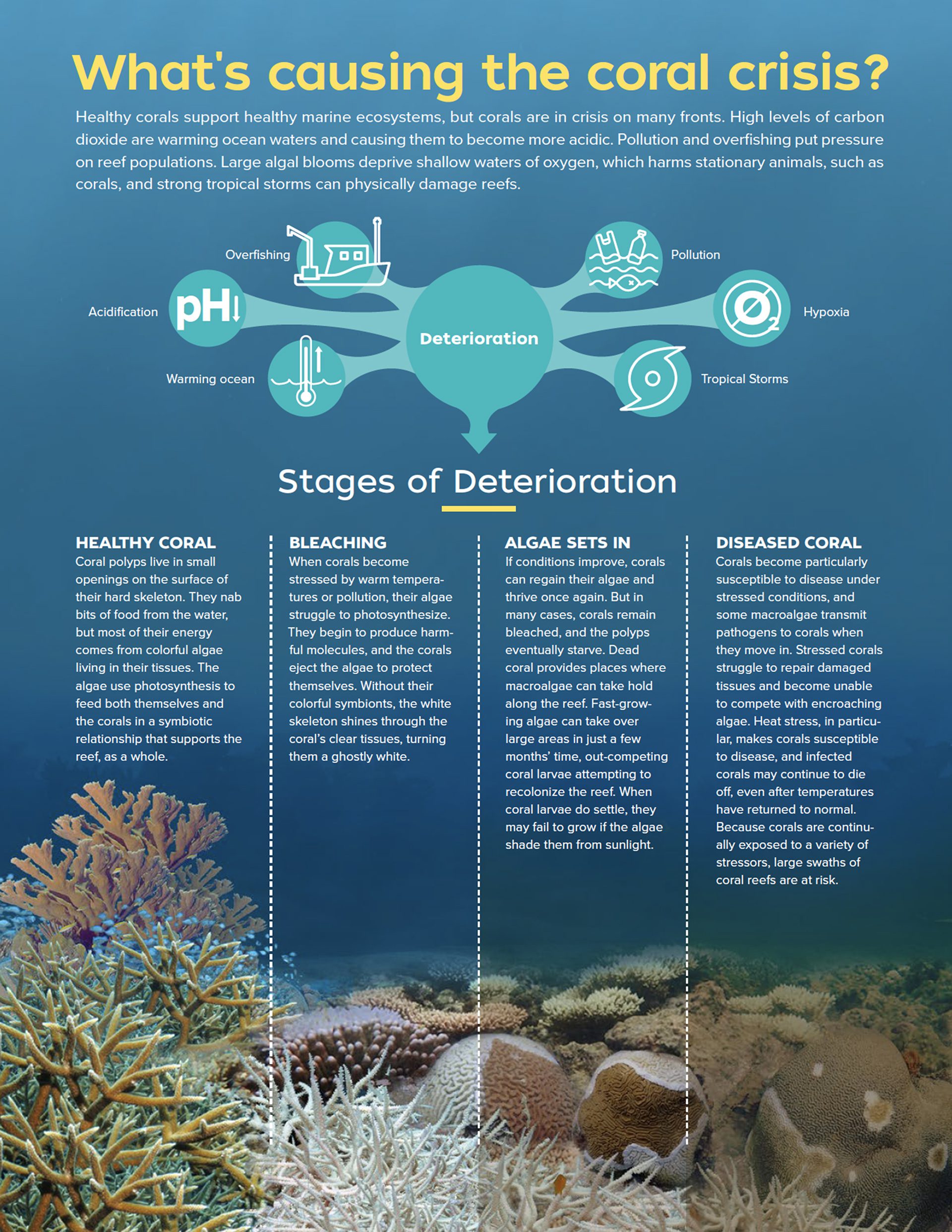
Read MoreCoral reef deterioration stages
Healthy corals support healthy marine ecosystems, but corals are in crisis on many fronts.
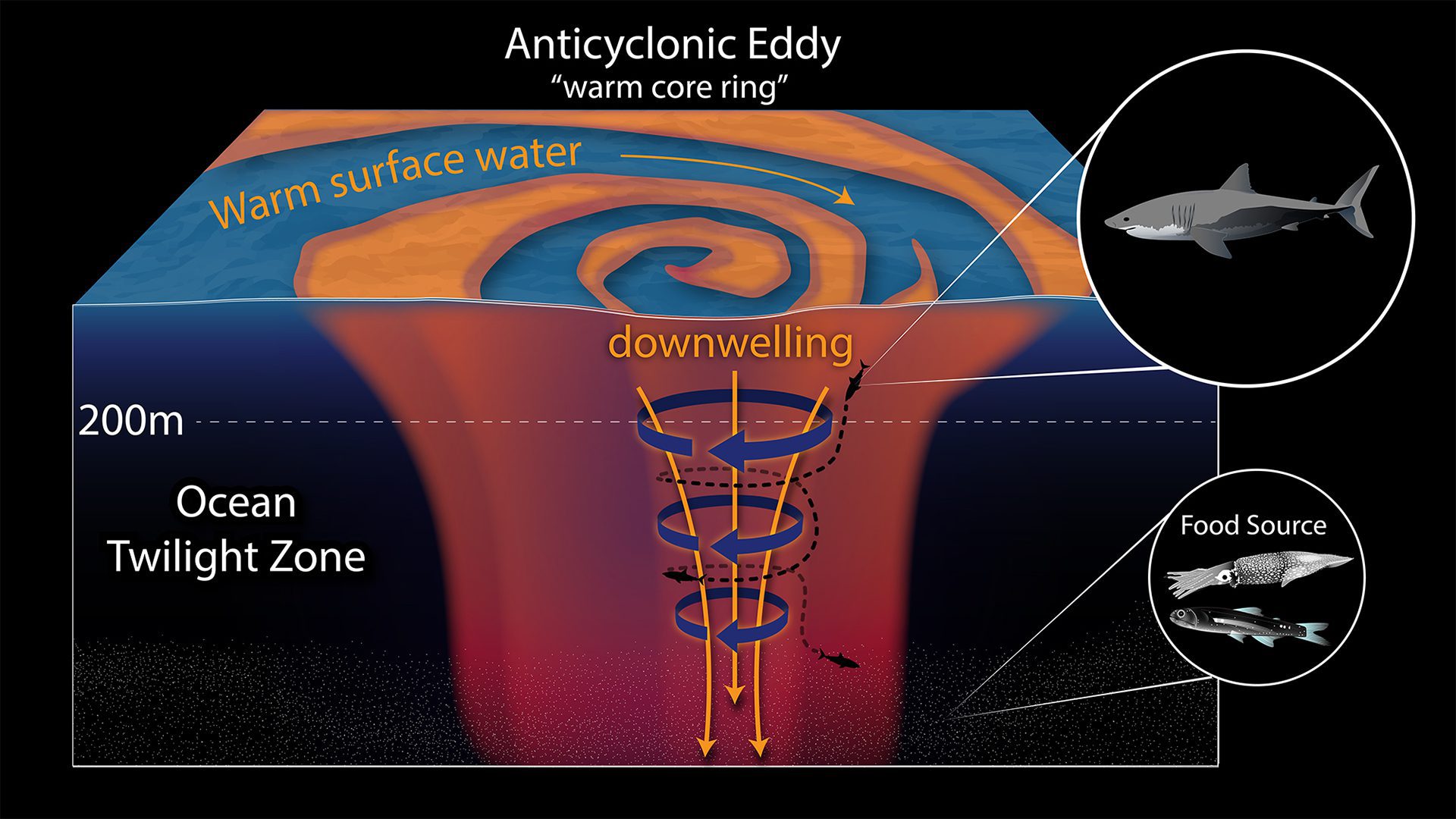
Read MoreCross-section of an anticyclonic eddy, warm core ring used for food sourcing
White sharks use warm, swirling anticyclonic eddies from the Gulf Stream to dive deeper and hunt efficiently in the ocean twilight zone, saving energy.
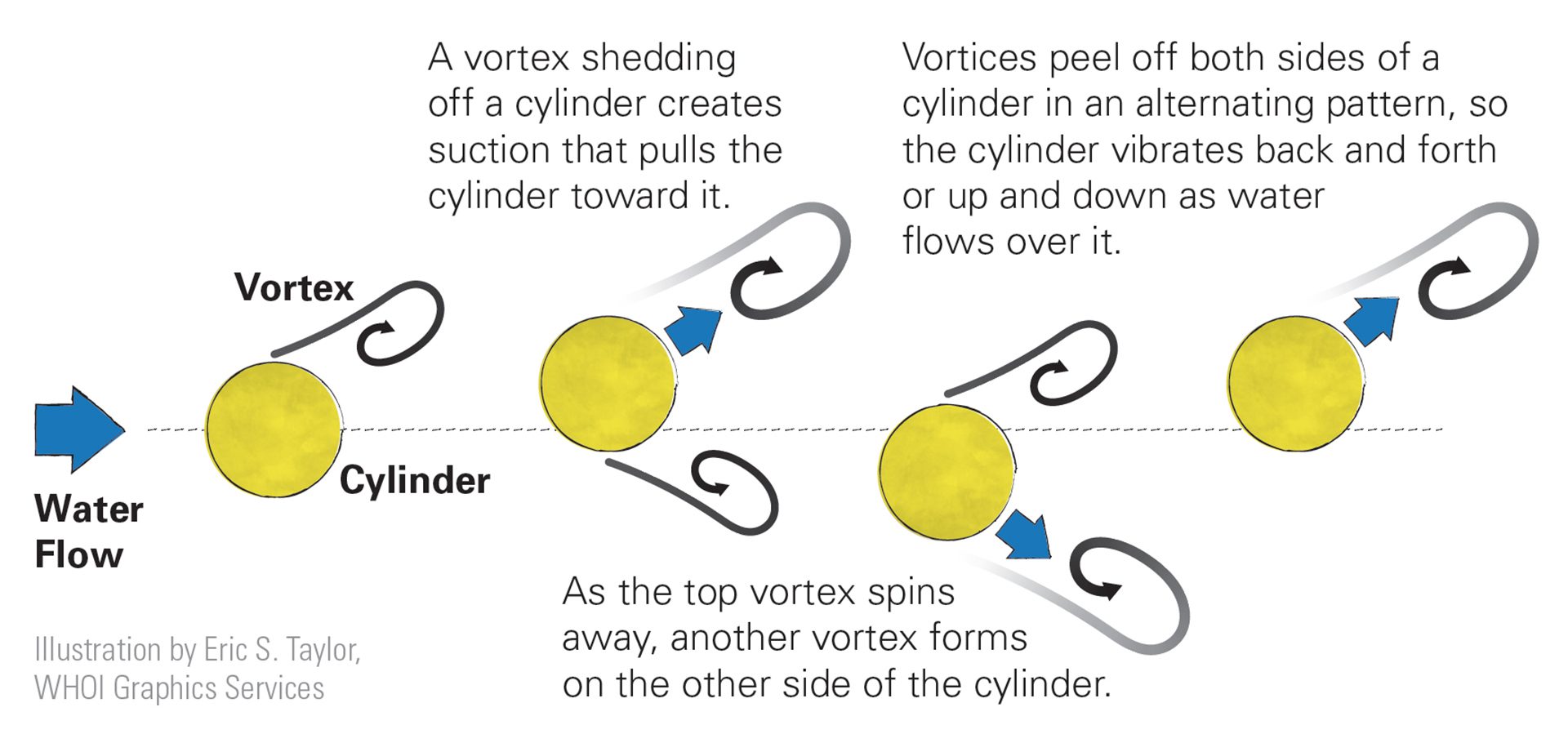
Read MoreCurrent vortices peeling off cylinders
Fluid usually doesn’t flow smoothly around cylindrical objects. Instead, the flow breaks away from the object into vortices, similar to those made by fish.
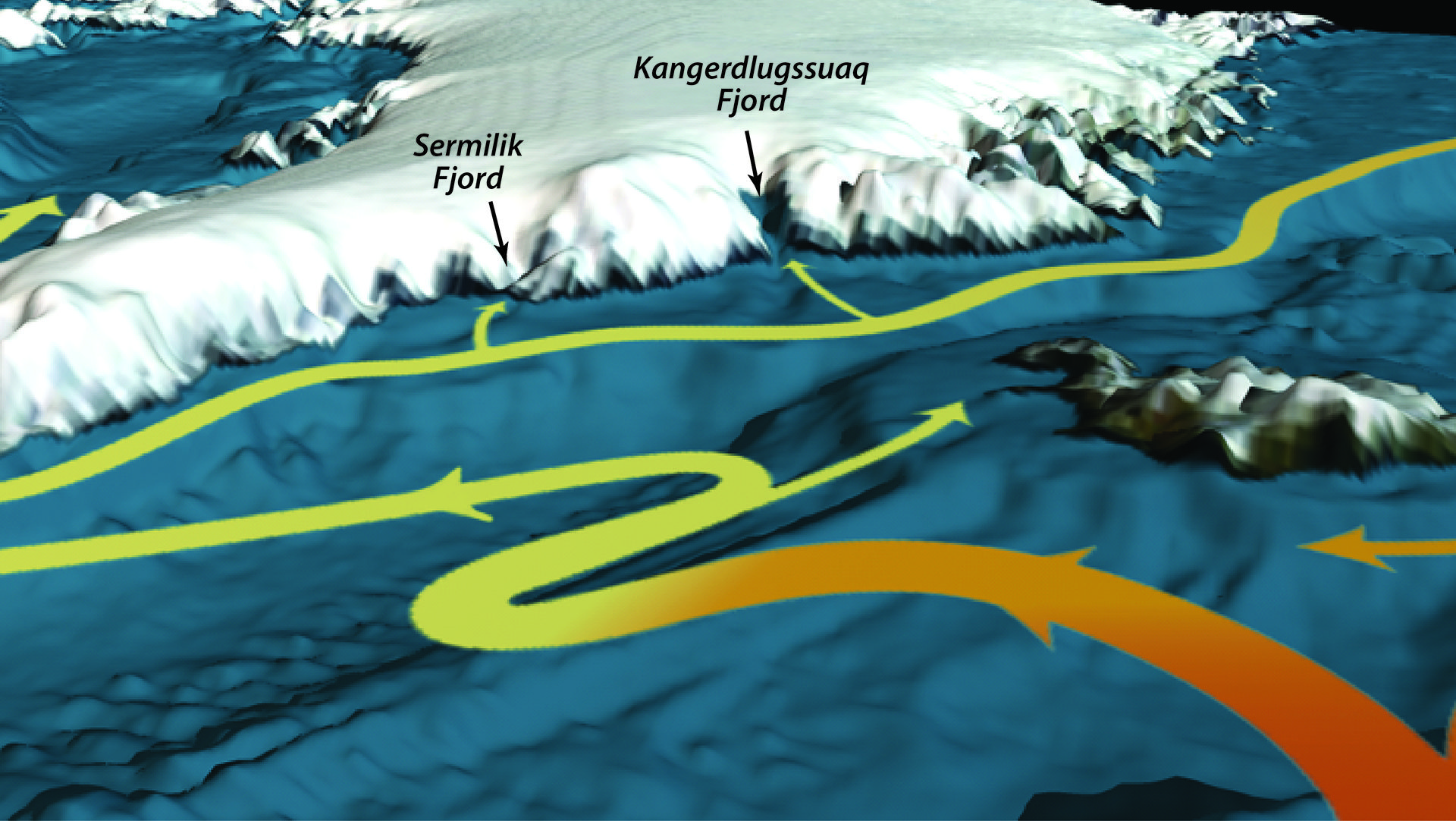
Read MoreGreenland circulation
Map illustrating North Atlantic currents flowing into two Greenland fjords, combined with seafloor bathymetry.
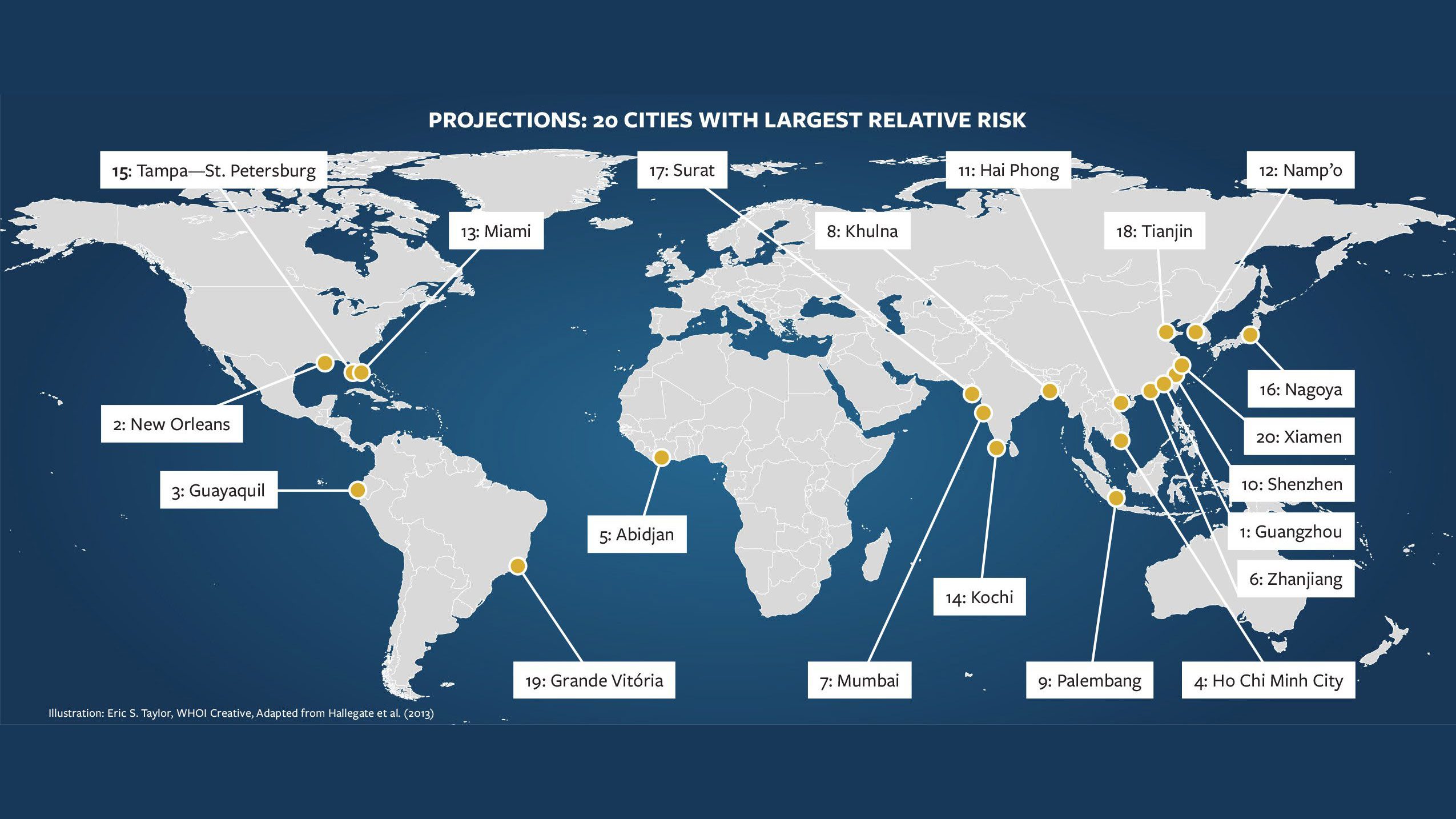
Read MoreCities and sea level impact
2013 map highlighting 20 cities projected to be at risk due to sea level rise.
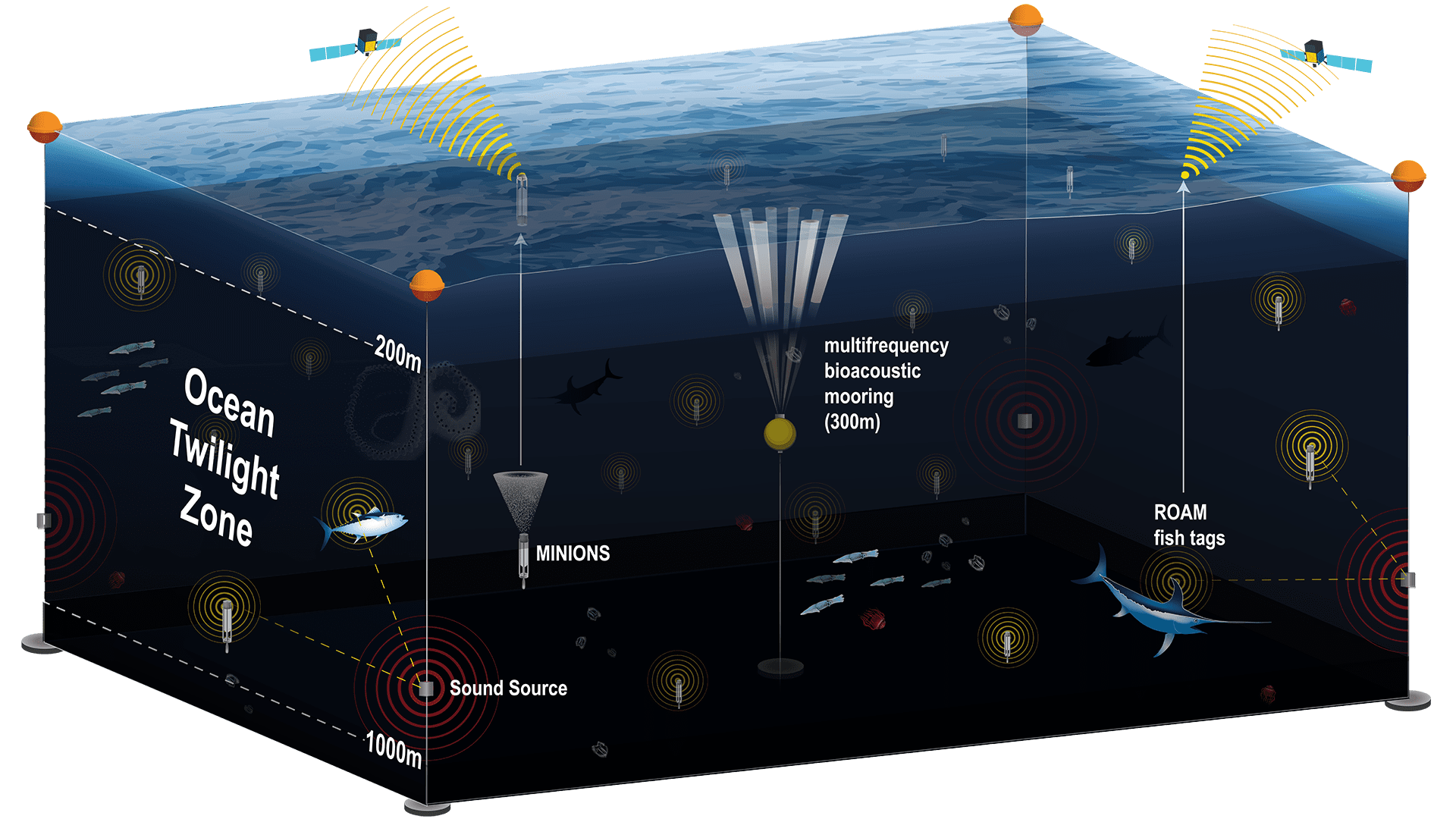
Read MoreAcoustic Sensing Cube in the Ocean Twilight Zone
An ocean network could provide a comprehensive view of the twilight zone, or mesopelagic, using several different technologies including moored buoys equipped with acoustic survey systems
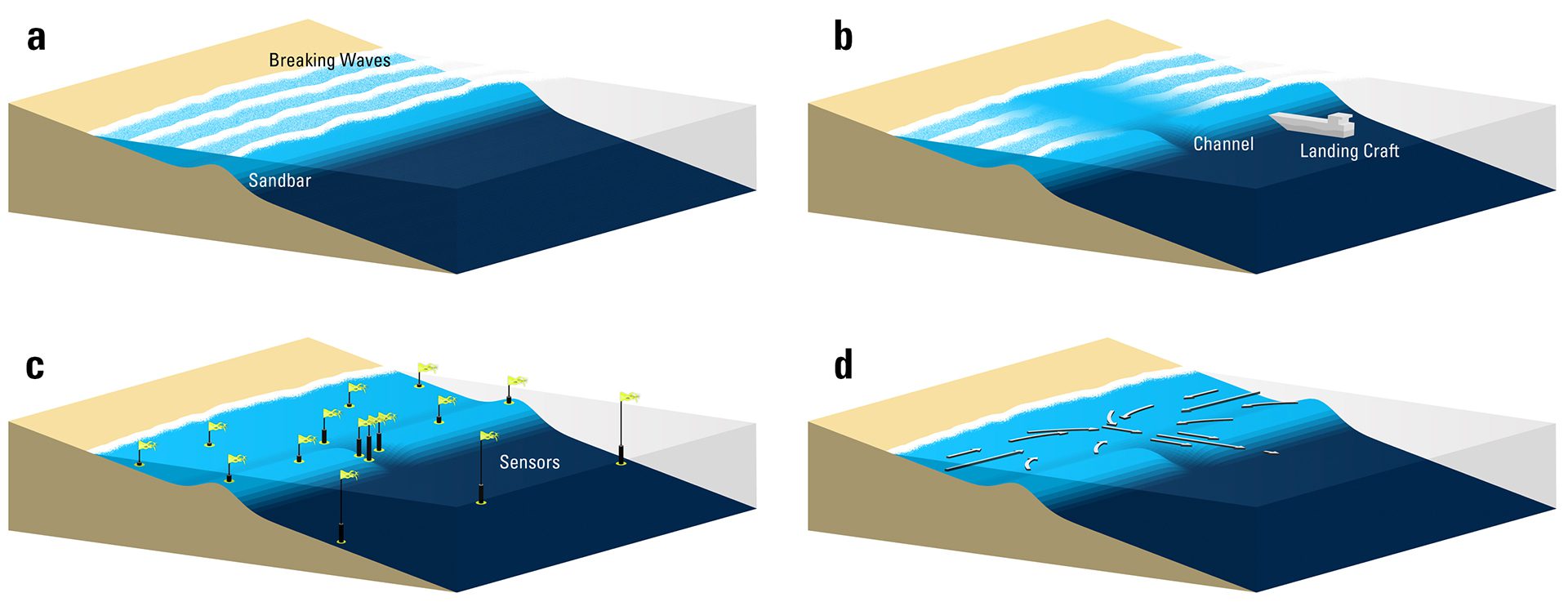
Read MoreAnatomy of a rip current
Waves push water toward shore, but it escapes fast through narrow gaps—rip currents form as water funnels out to sea through these hidden channels.
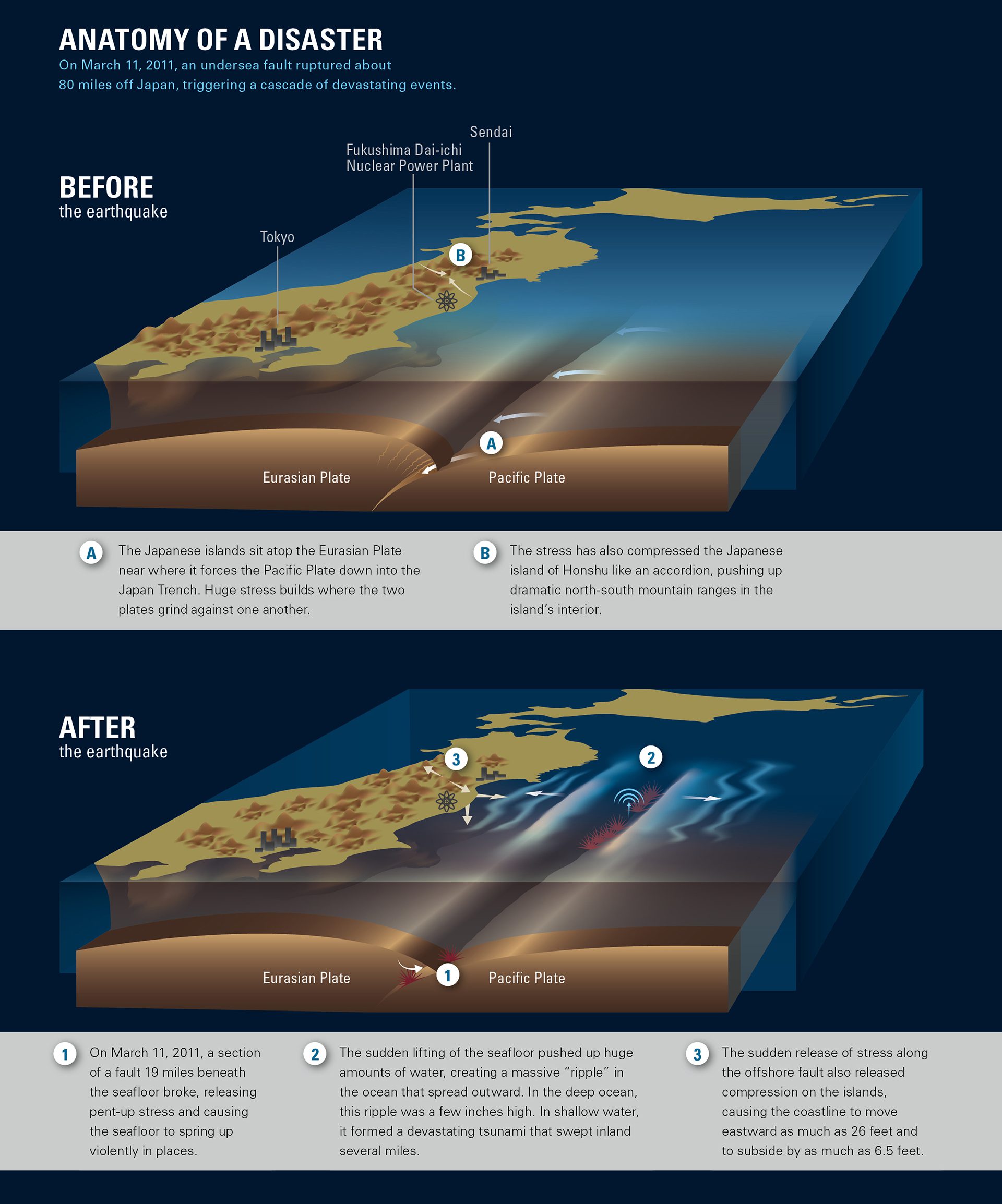
Read MoreAnatomy of the Fukushima earthquake and tsunami
Before and after the Fukushima earthquake and tsunami.
Read More