Fishing for Answers off Fukushima
October 25, 2012
Japan’s “triple disaster,” as it has become known, began on March 11, 2011, and remains unprecedented in its scope and complexity. To understand the lingering effects and potential public health implications of that chain of events, scientists are turning to a diverse and widespread sentinel in the world’s ocean: fish.
Events on March 11 began with a magnitude 9.0 earthquake, the fourth largest ever recorded. The earthquake in turn spawned a massive 40-foot tsunami that inundated the northeast Japanese coast and resulted in an estimated 20,000 missing or dead. Finally, the wave caused catastrophic damage to the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant, resulting in the largest accidental release of radiation to the ocean in history, 80 percent of which ended up in the Northwest Pacific Ocean.
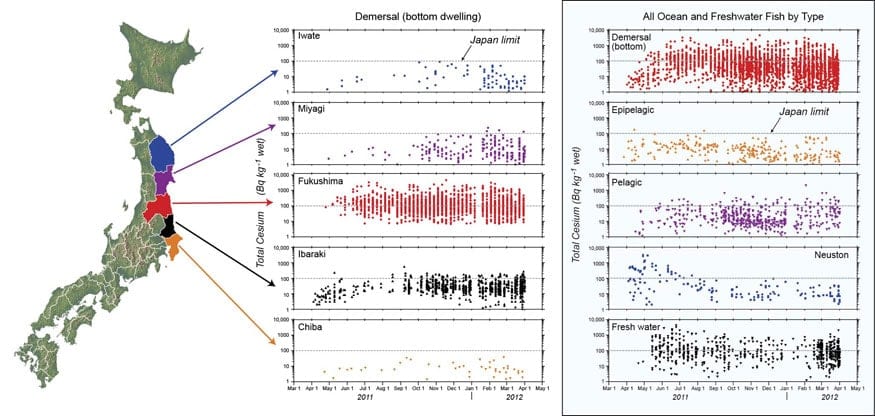
In a Perspectives article appearing in October 26, 2012, issue of the journal Science, WHOI marine chemist Ken Buesseler analyzed data made publicly available by the Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) on radiation levels in fish, shellfish and seaweed collected at ports and inland sites in and around Fukushima Prefecture. The picture he draws from the nearly 9,000 samples describes the complex interplay between radionuclides released from Fukushima and the marine environment.
In it, Buesseler shows that the vast majority of fish caught off the northeast coast of Japan remain below limits for seafood consumption, even though the Japanese government tightened those limits in April 2012. Nevertheless, he also finds that the most highly contaminated fish continue to be caught off the coast of Fukushima Prefecture, as could be expected, and that demersal, or bottom-dwelling fish, consistently show the highest level of contamination by a radioactive isotope of cesium from the damaged nuclear power plant. He also points out that levels of contamination in almost all classifications of fish are not declining, although not all types of fish are showing the same levels, and some are not showing any appreciable contamination.
As a result, Buesseler concludes that there may be a continuing source of radionuclides into the ocean, either in the form of low-level leaks from the reactor site itself or contaminated sediment on the seafloor. In addition, the varying levels of contamination across fish types points to complex methods of uptake and release by different species, making the task of regulation and of communicating the reasons behind decision-making to the fish-hungry Japanese public all the more difficult.
“To predict the how patterns of contamination will change over time will take more than just studies of fish,” said Buesseler, who led an international research cruise in 2011 to study the spread of radionuclides from Fukushima. “What we really need is a better understanding of the sources and sinks of cesium and other radionuclides that continue to drive what we’re seeing in the ocean off Fukushima.”
To help achieve this, Buesseler and his colleague Mitsuo Uematsu at the University of Tokyo are organizing a scientific symposium in Tokyo on November 12 and 13 to present the most current findings available about how radionuclides from Fukushima Dai-ichi have affected the ocean, marine life, seafood, policy decisions, and media coverage to date. The event will also include a free public colloquium in Tokyo on November 14 to help spread information about the lessons learned to the broadest possible audience.
This work was supported by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, non-profit organization on Cape Cod, Mass., dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930 on a recommendation from the National Academy of Sciences, its primary mission is to understand the ocean and its interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate a basic understanding of the ocean’s role in the changing global environment.