News Releases
UN-backed global research shows benefits of tracking ocean giants for marine conservation
WHOI researchers part of collaborative, international effort to increase Marine Protected Areas and other strategies
Read MoreSummer adventures await at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Discovery Center
New, interactive exhibits and fun learning experiences await visitors to Woods Hole, Mass.
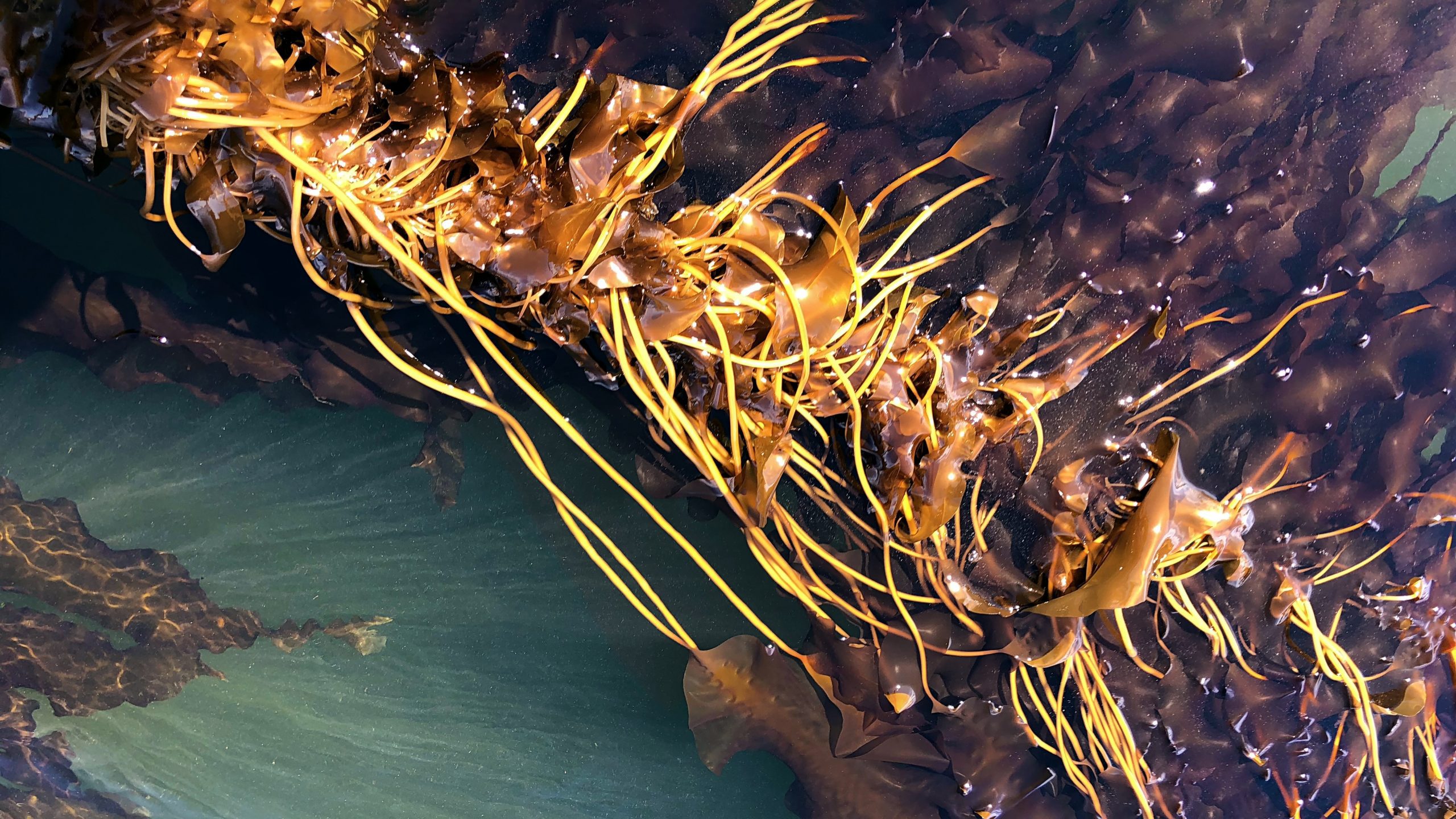
Read MoreNew global efforts to map and monitor kelp forests extend to South Africa and Namibia
A new expansion of kelpwatch.org, brings over 40 years of satellite-derived kelp canopy data to South Africa and Namibia, offering new insights into these vital underwater forest ecosystems.
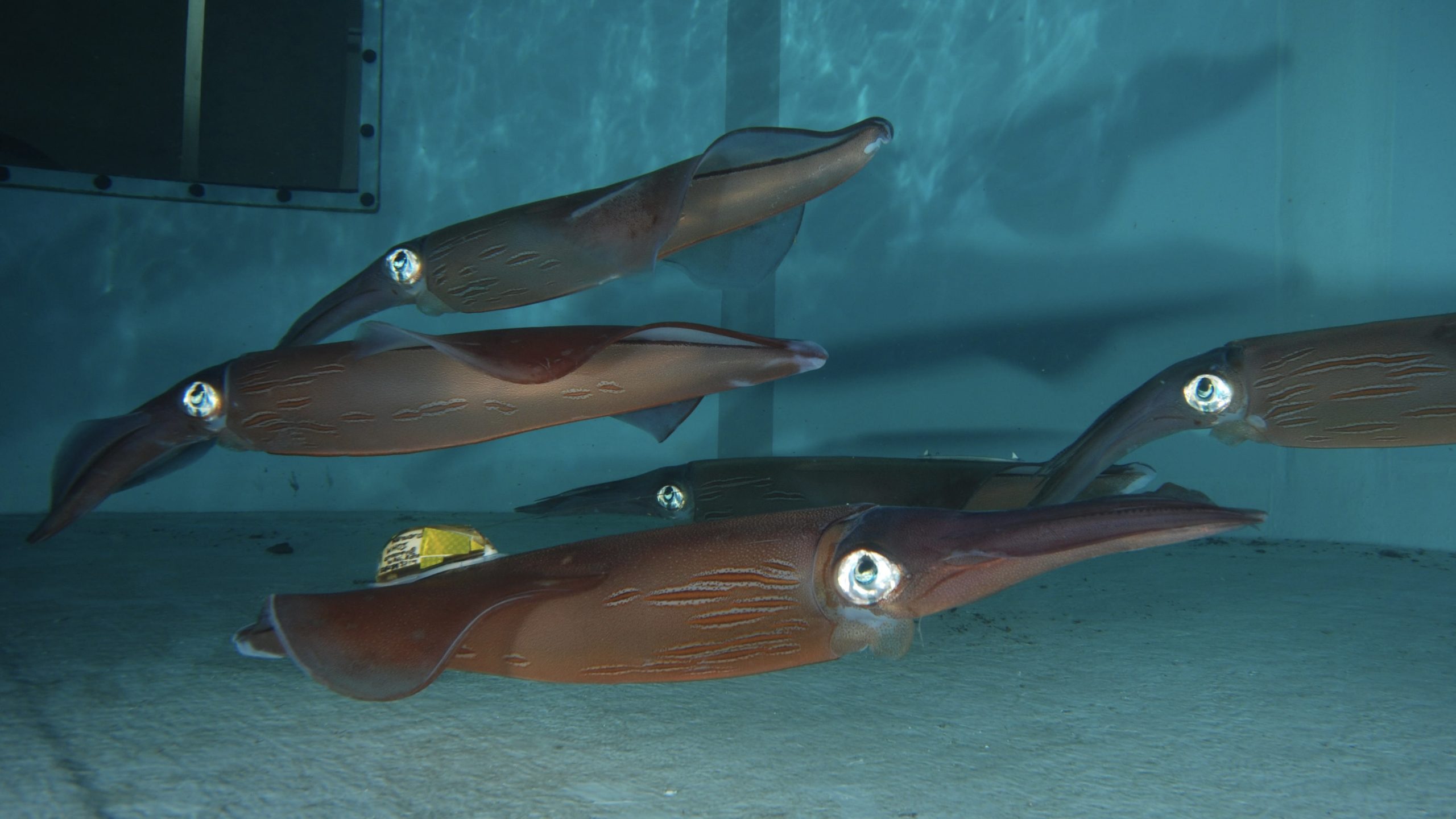
Read MoreA new tagging method for fragile marine species
Newly developed bioadhesive sensors (BIMS) are effective and less invasive than traditional tagging. Scientists can attach them with a thin layer of dried-hydrogel in less than 20 seconds.
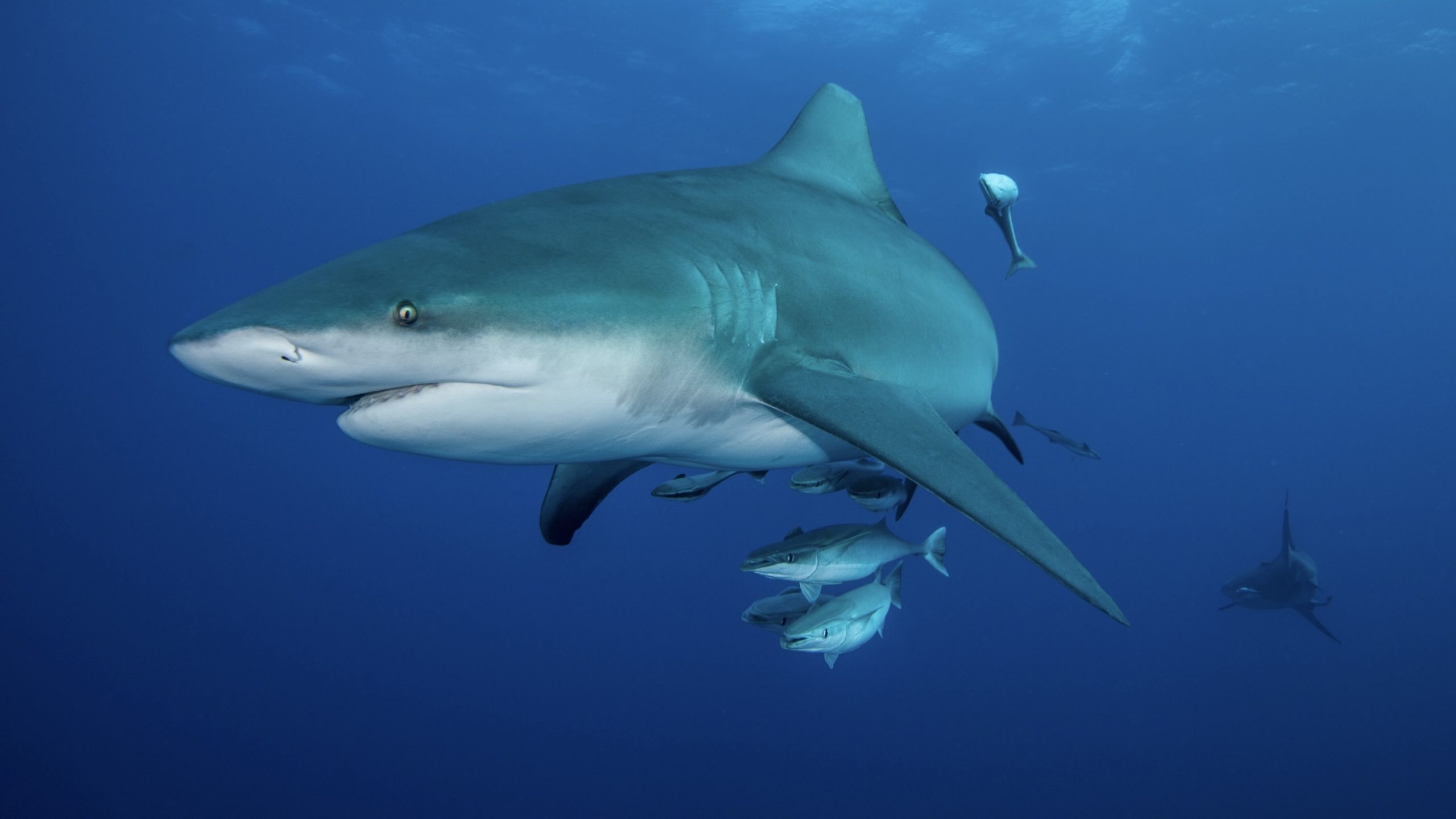
Read MoreHow marine predators find food hot spots in open ocean “deserts”
A new study led by scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and University of Washington Applied Physics Laboratory (UW APL) finds that marine predators, such as tunas, billfishes and sharks, aggregate in anticyclonic, clockwise-rotating ocean eddies (mobile, coherent bodies of water). As these anticyclonic eddies move throughout the open ocean, the study suggests that the predators are also moving with them, foraging on the high deep-ocean biomass contained within.
Read More