News Releases
Microbe Dietary Preferences Influence the Effectiveness of Carbon Sequestration in the Deep Ocean
A series of seemingly small processes helps carry carbon dioxide from the ocean’s surface to the deep sea, where it can be stored away for decades.
Read MoreCan adding iron to the ocean help it absorb CO2?
A newly published article spells out the work needed to assess the potential of ocean iron fertilization as a low cost, scalable, and rapidly deployable method of mCDR.
Read MoreFirst ever ocean-focused pavilion in the Blue Zone
Leading ocean science and philanthropic organizations to highlight the global ocean at UN climate conference
Read MoreThe ocean’s ‘biological pump’ captures more carbon than expected
Scientists have long known that the ocean plays an essential role in capturing carbon from the atmosphere, but a new study from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) shows that the efficiency of the ocean’s “biological carbon pump” has been drastically underestimated, with implications for future climate assessments.
Read MoreSurprising Enzymes Found in Giant Ocean Viruses
Findings could represent new drug targets for human pathogens A new study led by researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and Swansea University Medical School furthers our knowledge of…
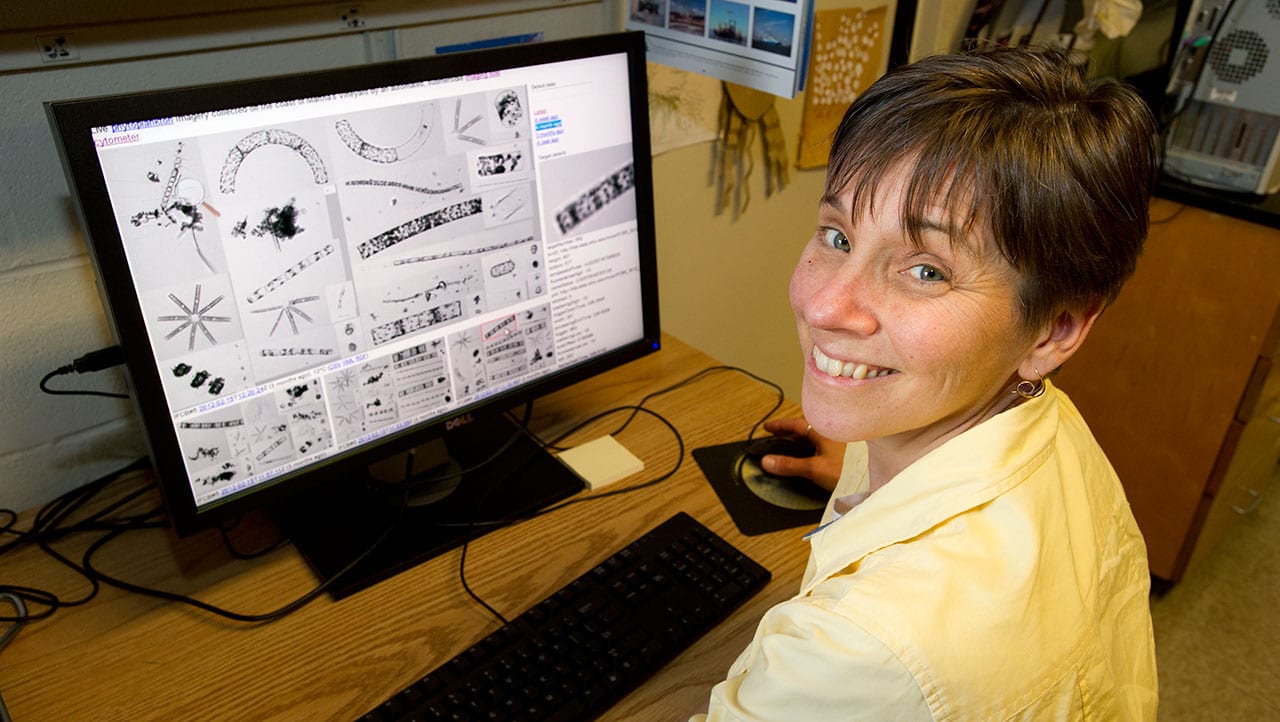
Read MoreHeidi Sosik Selected as a Fellow of The Oceanography Society
Heidi Sosik, a senior scientist in the Biology Department at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has been named a 2018 Fellow of The Oceanography Society (TOS). Sosik’s accomplishments will be formally recognized on Feb. 13, 2018, during a ceremony at the 2018 Ocean Sciences Meeting in Portland, Oregon.
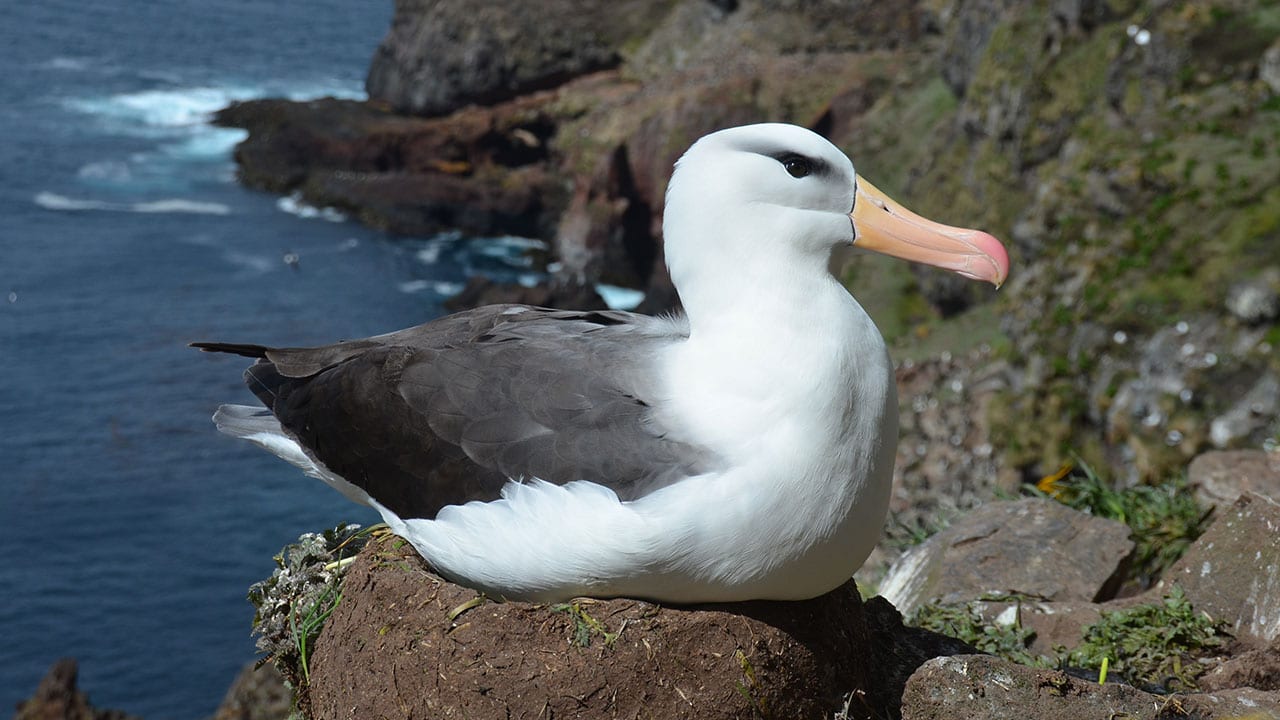
Read MoreMore Frequent Extreme Ocean Warming Could Further Endanger Albatross
As scientists grapple with the behavioral, ecological and evolutionary impacts of extreme climatic events, the journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B created a special June issue to explore what is known on the topic and pioneer new approaches to this challenging and rapidly expanding field of study. The issue, which was published online May 8, 2017, was co-edited by Wood Hole Oceanographic institution (WHOI) biologist Stephanie Jenouvrier.
Read MoreMajor Source of Methanol in the Ocean Identified
Scientists have long known methanol exists in the ocean, and that certain microbes love to snack on it, but they’ve been stymied by one key question: where does it come from? Researchers at WHOI have solved this mystery through the discovery of a massive ‘ and previously unaccounted for ‘ source of methanol in the ocean: phytoplankton.
Read MoreShifting Winds, Ocean Currents Doubled Endangered Galapagos Penguin Population
New research suggests shifts in wind currents over the past three decades, possibly due to climate change and natural variability, have nudged the Equatorial Undercurrent north. The changing current expanded the nutrient-rich, cold water farther north along the coasts of the two islands, likely bolstering algae and fish numbers in the cold pool. This allowed the penguin population to double over the past 30 years, swelling to more than 1,000 birds by 2014, according to the new study.
Read MoreRevealing the Ocean’s Hidden Fertilizer
A new study by a research team from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and Columbia University reveals for the first time a marine phosphorus cycle that is much more complex than previously thought. The work also highlights the important but previously hidden role that some microbial communities play in using and breaking down forms of this essential element.
Read MoreOcean Bacteria Get ‘Pumped Up’
In a new study published April 27 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and their colleague from Rutgers University discovered a surprising new short-circuit to the biological pump. They found that sinking particles of stressed and dying phytoplankton release chemicals that have a jolting, steroid-like effect on marine bacteria feeding on the particles. The chemicals juice up the bacteria’s metabolism causing them to more rapidly convert organic carbon in the particles back into CO2 before they can sink to the deep ocean.
Read More
Swirling Currents Deliver Phytoplankton Carbon to Ocean Depths
A new paper published March 26 in the journal Science that highlights the significant role that swirling currents, or eddies, play in pushing non-sinking carbon to ocean depths.
Read MoreRadioactive Ocean Website Garners Public Support
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has teamed up with the public to build the most comprehensive and up-to-date dataset on marine radiation levels in the aftermath of the 2011 Fukushima…
Read MoreThree Years after Fukushima: Tracking Radionuclides in the Pacific Ocean
Scientists have been keeping a close eye on how radionuclides from the Japanese power plant are being transported in the Pacific Ocean since the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident…
Read MoreStudy explores complex physical oceanography in East China Sea
Just days before a team of researchers from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and National Taiwan University set out to conduct fieldwork in the East China Sea, Typhoon Morakot—one of…
Read MoreScientists Discover Thriving Colonies of Microbes in Ocean ‘Plastisphere’
Scientists have discovered a diverse multitude of microbes colonizing and thriving on flecks of plastic that have polluted the oceans—a vast new human-made flotilla of microbial communities that they have…
Read MoreScientists Discover New Trigger for Immense North Atlantic Ocean Spring Plankton Bloom
On this July 4th week, U.S. beachgoers are thronging their way to seaside resorts and parks to celebrate with holiday fireworks. But across the horizon and miles out to sea…
Read MoreSpecial Fukushima Session at 2012 Ocean Sciences Meeting
The March 11, 2011, earthquake, tsunami, and subsequent radioactivity releases from the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plants resulted in the largest accidental release of radiation to the ocean in history.…
Read MoreResearchers Assess Radioactivity Released to the Ocean from the Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Facility
The impact on the ocean of releases of radioactivity from the Fukushima nuclear power plants remains unclear. But a new study by U.S. and Japanese researchers analyzes the levels of radioactivity discharged from the facility in the first four months after the accident and draws some basic conclusions about the history of contaminant releases to the ocean.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution to Lead Expedition to Measure Radioactive Contaminants in the Pacific Ocean
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will lead the first international, multidisciplinary assessment of the levels and dispersion of radioactive substances in the Pacific Ocean off the Fukushima nuclear power plant—a research effort funded by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
Read MoreCan a Dose of Iron Supplements Improve the Health of the Ocean and Climate?
Researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will host a public forum next week to discuss the pros and cons of ?iron fertilization? of the oceans as a means to mediate global warming.
Read MoreScientists, Policymakers, and Industry Leaders Gather to Discuss Ocean Iron Fertilization
Scientists at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution will host an international, interdisciplinary conference on the proposed use of ?iron fertilization? of the ocean as a means to combat rising concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Read MoreOceanic Storms Create Oases in the Watery Desert
A research team led by Dennis McGillicuddy of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution has shown that episodic, swirling current systems known as eddies act to pump nutrients up from the deep ocean to fuel such blooms.
Read MoreOcean’s “Twilight Zone” Plays Important Role in Climate Change
A major study has shed new light on the dim layer of the ocean called the “twilight zone”where mysterious processes affect the ocean’s ability to absorb and store carbon dioxide…
Read More