Deep Argo Observations of Antarctic Bottom Water in the Deep Fracture Zones of the Southwest Indian Ridge
Menezes, V. V., Robbins, P., Furey, H., & Mazloff, M. (2024). Deep Argo Observations of Antarctic Bottom Water in the Deep Fracture Zones of the Southwest Indian Ridge. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 129(7), e2024JC021165. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JC021165
The Madagascar Basin is the primary pathway for Antarctic Bottom Water to ventilate the entire western Indian Ocean as part of the Global Overturning Circulation. The only way for this water mass to reach this basin is by crossing the Southwest Indian Ridge through its deep fracture zones.
However, due to the scarcity of observations, the Antarctic Bottom Water presence has only been well established in the Atlantis II fracture zone. In May 2023, the Deep Madagascar Basin Experiment deployed three Deep SOLO Argo floats in the exit of the fracture zones that were more likely to transport Antarctic Bottom Water: Atlantis II, Novara, and Melville. These floats have been collecting temperature and salinity profiles every 3–5 days with high vertical resolution in the deep ocean. In the present paper, we use the first 7 months of float data to characterize the Antarctic Bottom Water in the deep fracture zone area, revisiting a half‐century puzzle about the Melville contribution. We also collected shipboard‐based profiles to calibrate float salinity and show it is within the Deep Argo program target accuracy. We find Antarctic Bottom Water in both Melville and Novara fracture zones, not only in Atlantis II. This is the first time the Novara contribution has been revealed. The floats also uncover their distinct properties, which may result from the different mixing histories.
Key Points:
- The floats collected the region’s largest temperature‐salinity data set to date, with adjusted salinity meeting the Deep Argo target accuracy
- The floats found a new abyssal ventilation source (Novara fracture zone) to the Madagascar Basin and solved the Melville inflow puzzle
- The abyssal layer is fresher at the Melville fracture zone and saltier at Atlantis II, with Novara having Intermediate water mass properties
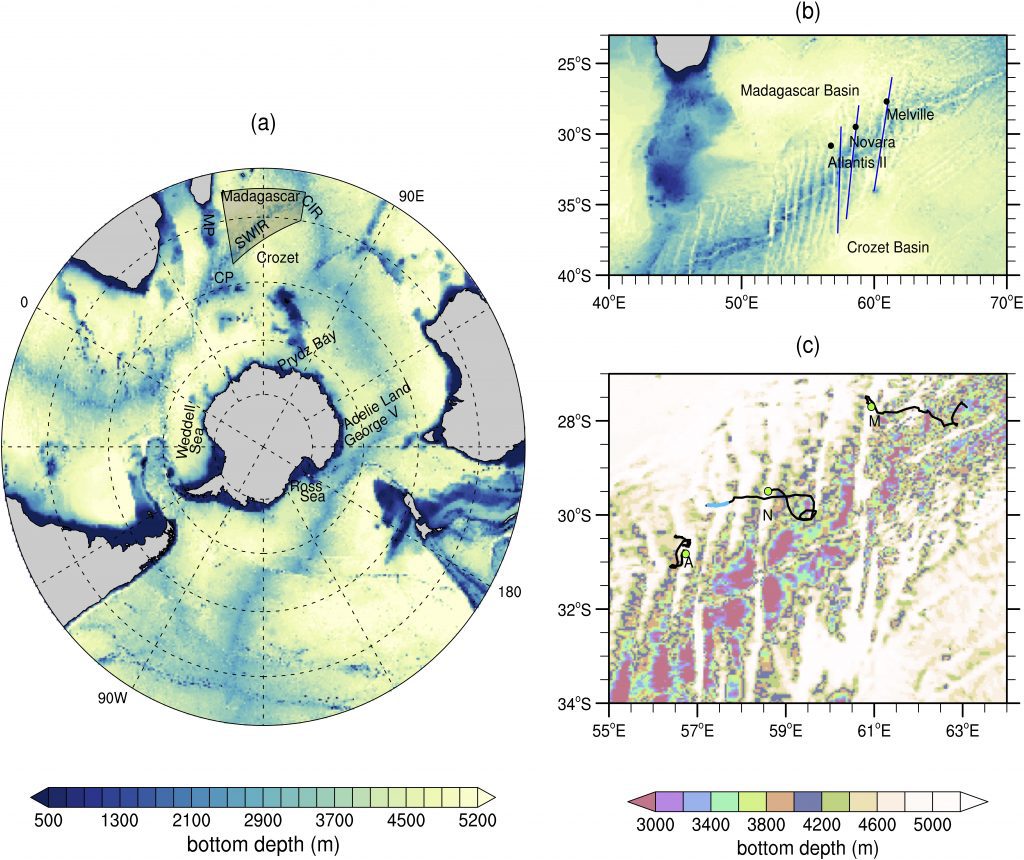
Figure 1. Bottom topography south of 20S with main bathymetric features: (a) large‐scale view; (b) Deep Argo float deployment positions (black dots) near three deep fracture zones (Atlantis II, Novara, and Melville) of the Southwest Indian Ridge; (c) float trajectories (black lines) overlaid to bottom topography. The topographic maps use reverse color schemes, such that deep features are mapped in light colors and shallow features in dark. SWIR stands for Southwest Indian Ridge, CIR for the Central Indian Ridge, and MP and CP for the Madagascar and Crozet Plateaus, respectively. In (b): blue lines mark the fracture zones as determined by GEBCO. In (c): a non‐sequential color map highlights the ridge and fracture zones, and A, N, and M labels identify trajectories from floats deployed near the Atlantis II, Novara, and Melville fracture zones, respectively. Green dots highlight the deployment positions. Image provided by Viviane Menezes.
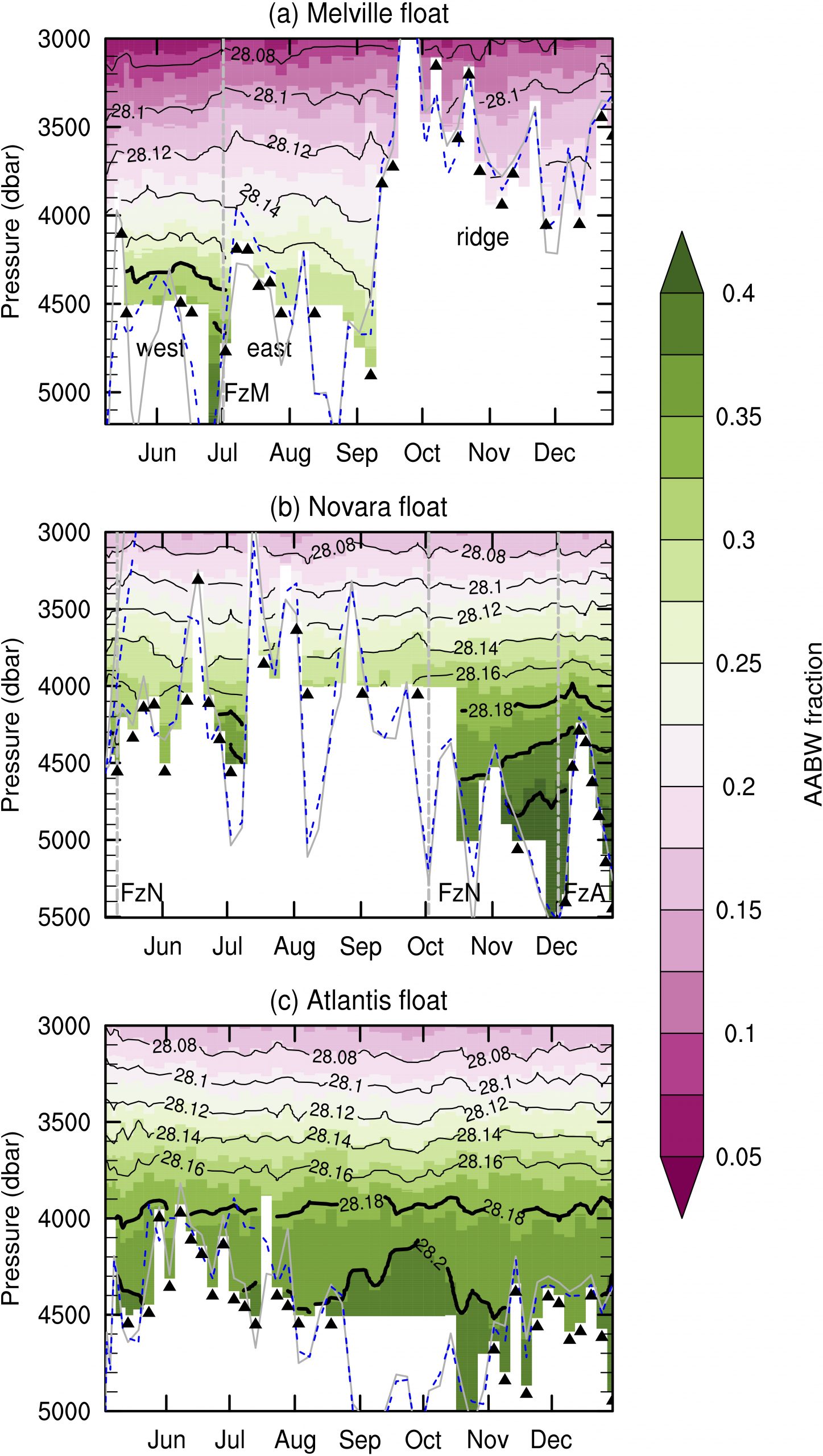
Figure 2. Antarctic Bottom Water contribution for the mixture from the water mass mixing analysis for the data collected by (a) Melville, (b) Novara, and (c) Atlantis floats. Black contours are neutral densities (γ) in kg/m3. Thick black contours highlight isopycnals γ ≥ 28.18 kg/m3. FzM stands for Melville fracture zone, FzN for Novara fracture zone, and FzA for Atlantis II fracture zone, and dashed gray lines indicate their positions in the data. Dashed blue contour shows the estimated seafloor from ETOPO‐2022 at the profiles’ coordinates, and the gray is from GEBCO‐2023. Black triangles show casts in which the float touched the seafloor. Image provided by Viviane Menezes.
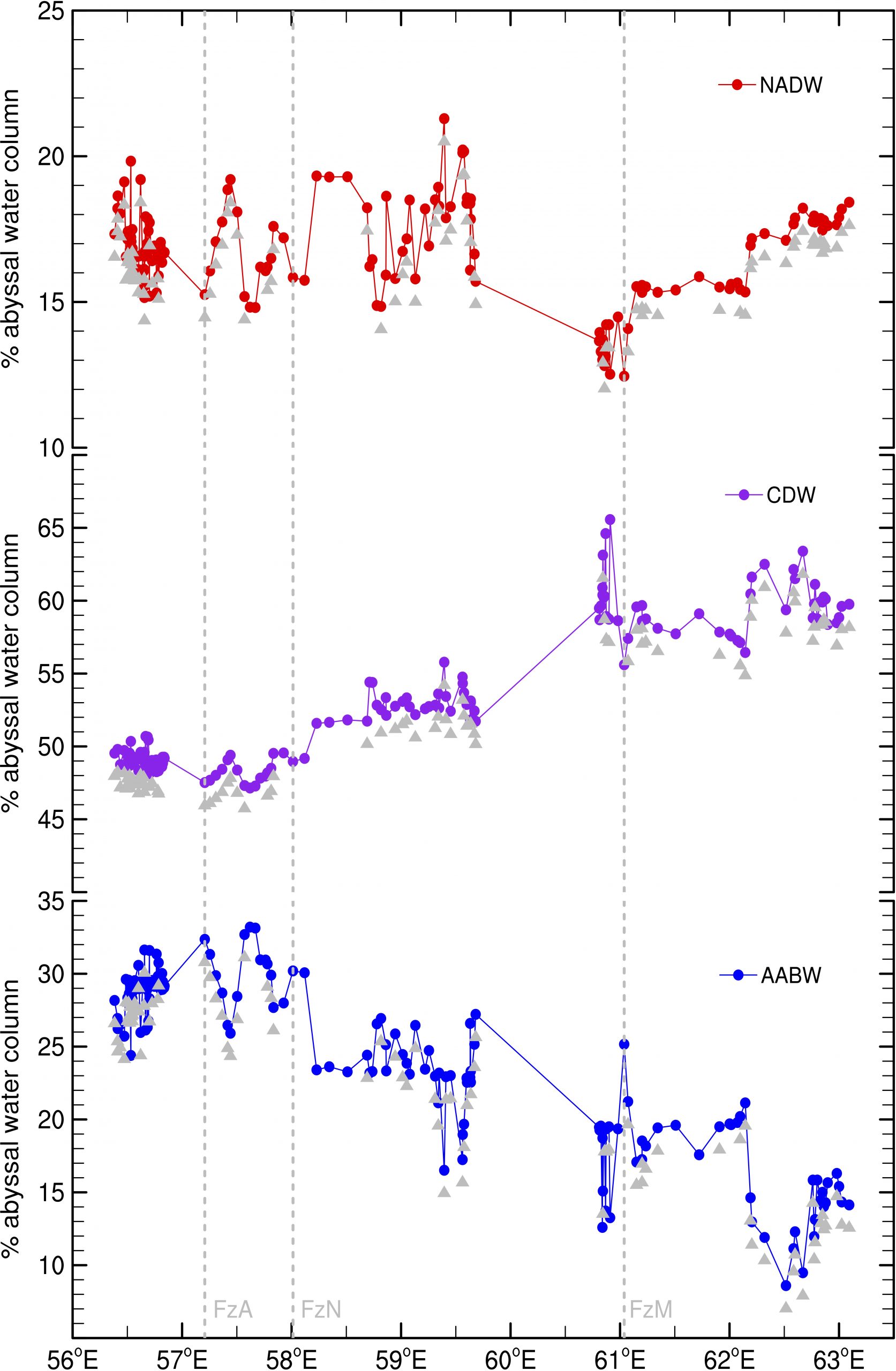
Figure 3. Normalized thickness for North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW; top panel), Circumpolar Deep Water (CDW; mid), and Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW; bottom) as a function of longitude. Dashed gray lines indicate the data in the valleys of the fracture zones: Atlantis II (FzA), Novara (FzN), and Melville (FzM). Gray triangles show all casts in which the float touched the seafloor. Image provided by Viviane Menezes.
