Press Room
Woods Hole, MA – The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has received $750,000 in funding from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) to develop next‐generation autonomous robotic technology for environmental monitoring of marine organisms and the seafloor at potential wind…
A prototype of an autonomous underwater vehicle capable of navigating complex underwater environments and of collecting data adaptively over long periods of time. Daniel Hentz / ©Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA – A grant by the National Science…
Experts from WHOI and Woodwell Climate Research Center are on the ground at COP26 in Glasgow, Scotland, sharing critical perspective on the implications of a warming Arctic
A new book by Michael Moore, veterinarian, and marine scientist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), examines the plight and future of the North Atlantic right whale, one of the most critically endangered species on the planet, and draws on Moore’s 40 years of fieldwork to offer possible solutions.
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the world’s independent leader in ocean discovery, exploration, and education, has welcomed Dr. Kilaparti Ramakrishna (Rama) as senior advisor to the President and Director on ocean and climate policy.
Woods Hole, MA – The mid-ocean “twilight zone” holds the key to several tantalizing questions about the marine food web and carbon-sequestering capacity of the ocean. But studying this vast and remote area is extremely difficult. Many inhabitants of the…
In October, the Board of Trustees of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) welcomed one new Board Member and named two new officers, as well as ten new Corporation Members
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has been selected by the U.S National Science Foundation (NSF) for phase one of a two-part Convergence Accelerator Program, a $21 million investment to advance use-inspired solutions addressing national-scale societal challenges. WHOI is one of sixteen teams across the US chosen to participate in Track E: The Networked Blue Economy, which aims to create a smart, integrated, connected, and open ecosystem for ocean innovation, exploration, and sustainable utilization.
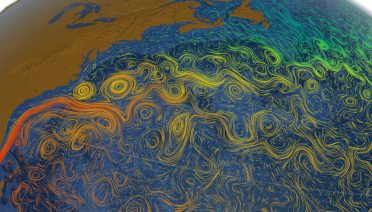
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) senior scientist of physical oceanography, Dr. Young-Oh Kwon, and WHOI adjunct scientist, Dr. Claude Frankignoul, have received a new research grant from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Modeling, Analysis, Predictions and Projections (MAPP) Program, funding their research project focusing on western boundary ocean currents and their correspondence with the atmosphere in relation to modern day climate.
Changes in the northern Alaskan Arctic ocean environment have reached a point at which a previously rare phenomenon-widespread blooms of toxic algae-could become more commonplace, potentially threatening a wide range of marine wildlife and the people who rely on…
Woods Hole, Mass. – The Nippon Foundation-GEBCO Seabed 2030 Project and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding in recognition of both organisations’ work to advance our understanding of ocean bathymetry. This will complement the goals…
Vertical Migration by artist group SUPERFLEX will be projected onto the facade of the United Nations’ 505-foot tower in New York, on 21-24 September 2021, coinciding with the 76th General Assembly and Climate Week NYC. The projection seeks to draw global attention to the critical role of the ocean in global climate, a primary focus of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Ocean Twilight Zone Project.
A new study led by Carolyn Tepolt, an associate scientist of biology at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, is investigating the adaptive mechanisms of the green crab along the west coast of North America, where it has shown extensive dispersal in the last decade despite minimal genetic diversity.
New collaborative research from the WHOI and five partner institutions published today in Nature Geoscience, reveals that during past periods glaciers and ice caps in coastal west Greenland experienced climate conditions much different than the interior of Greenland. Over the past 2,000 years, these ice caps endured periods of warming during which they grew larger rather than shrinking.
The new Center for Chemical Currencies of a Microbial Planet (C-CoMP) will focus on the chemical processes that underpin ocean ecosystems.
Sunlight was once thought to only fragment plastics in the marine environment into smaller particles that chemically resemble the original material and persist forever. However, scientists more recently have learned that sunlight also chemically transforms plastic into a suite of polymer-, dissolved-, and gas-phased products. Now, a new study finds that this chemical reaction can produce tens of thousands of water-soluble compounds, or formulas.
Some coral communities are becoming more heat tolerant as ocean temperatures rise, offering hope for corals in a changing climate. After a series of marine heatwaves hit the Phoenix Islands Protected Area (PIPA) in the central Pacific Ocean, a new study finds the impact of heat stress on the coral communities lessened over time.
On September 2, the remotely operated vehicle (ROV) Jason aided in the recovery of two underwater vehicles, ROV Hercules and Argus, that were stranded on the seafloor near British Columbia
A team led by Anne Cohen, a scientist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, received $1.75M in funding from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to study how coral reefs survive extreme heat events caused by climate change. The multidisciplinary project taps into expertise across four WHOI departments to uncover the oceanographic and biological processes that enable corals to survive marine heatwaves.
An ongoing collaborative effort by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), University of Massachusetts Dartmouth (UMassD), and Providence Public Library (PPL), has received a grant from FM Global. The project is investigating the role of historical weather data in current climate change research, and the increasingly urgent issues surrounding it.