News Releases
Study Provides Measurement of Nitrogen Removal by Local Shellfish
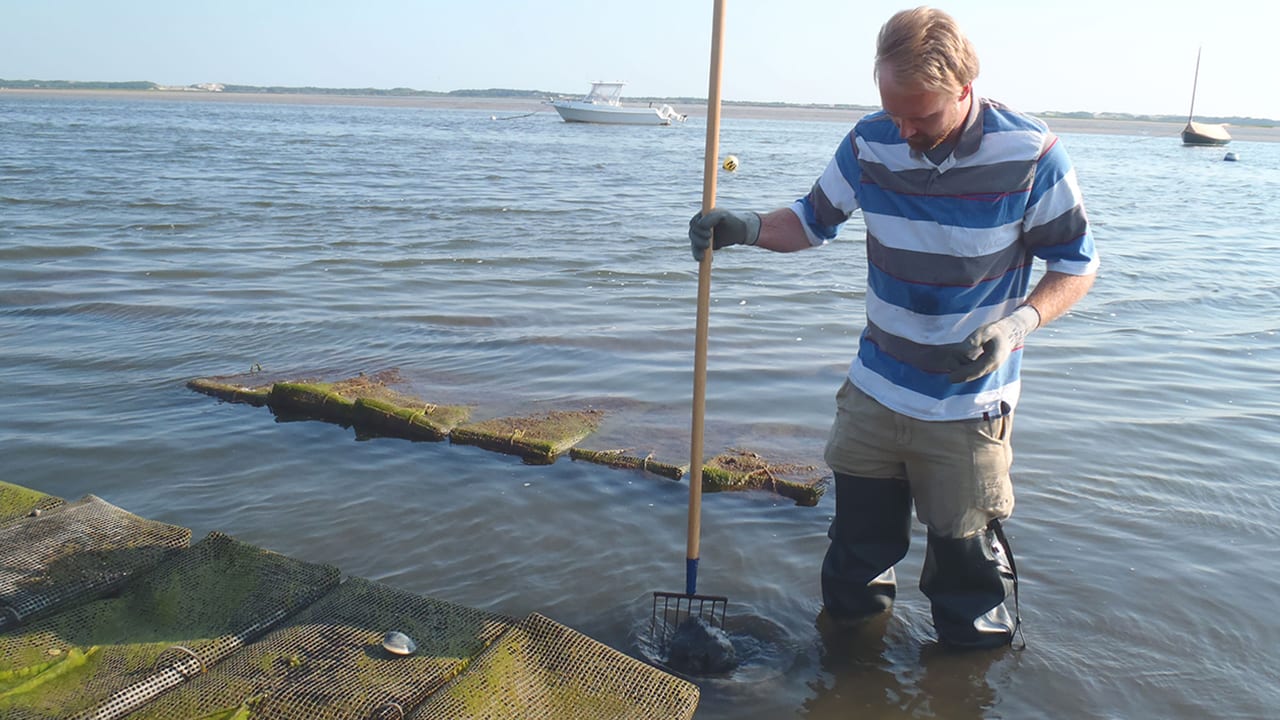
A new study by Woods Hole Sea Grant, Cape Cod Cooperative Extension, and the Mashpee Department of Natural Resources provides the first comprehensive measurement of nitrogen removed by shellfish harvested from waters off Cape Cod.
Read MoreResearch Enables Fishermen to Harvest Lucrative Shellfish on Georges Bank
Combined research efforts by scientists involved in the Gulf of Maine Toxicity (GOMTOX) project, funded by NOAA’s Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms (ECOHAB) program, and administered by the…
Read MoreRising acidity levels could trigger shellfish revenue declines, job losses
Changes in ocean chemistry — a consequence of increased carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from human industrial activity — could cause U.S. shellfish revenues to drop significantly in the next 50…
Read MoreUnderwater Microscope Helps Prevent Shellfish Poisoning Along Gulf Coast of Texas
Through the use of an automated, underwater cell analyzer developed at WHOI, researchers and coastal managers were recently able to detect a bloom of harmful marine algae in the Gulf of Mexico and prevent human consumption of tainted shellfish.
Read MoreNew Genetic Test Can Detect Clam Disease Crippling Shellfish Industry and Threatening Aquaculture Operations
A sensitive new genetic test can now detect a crippling disease called QPX occurring in clam beds from Cape Cod south to Virginia and north to Canada. Although it does…
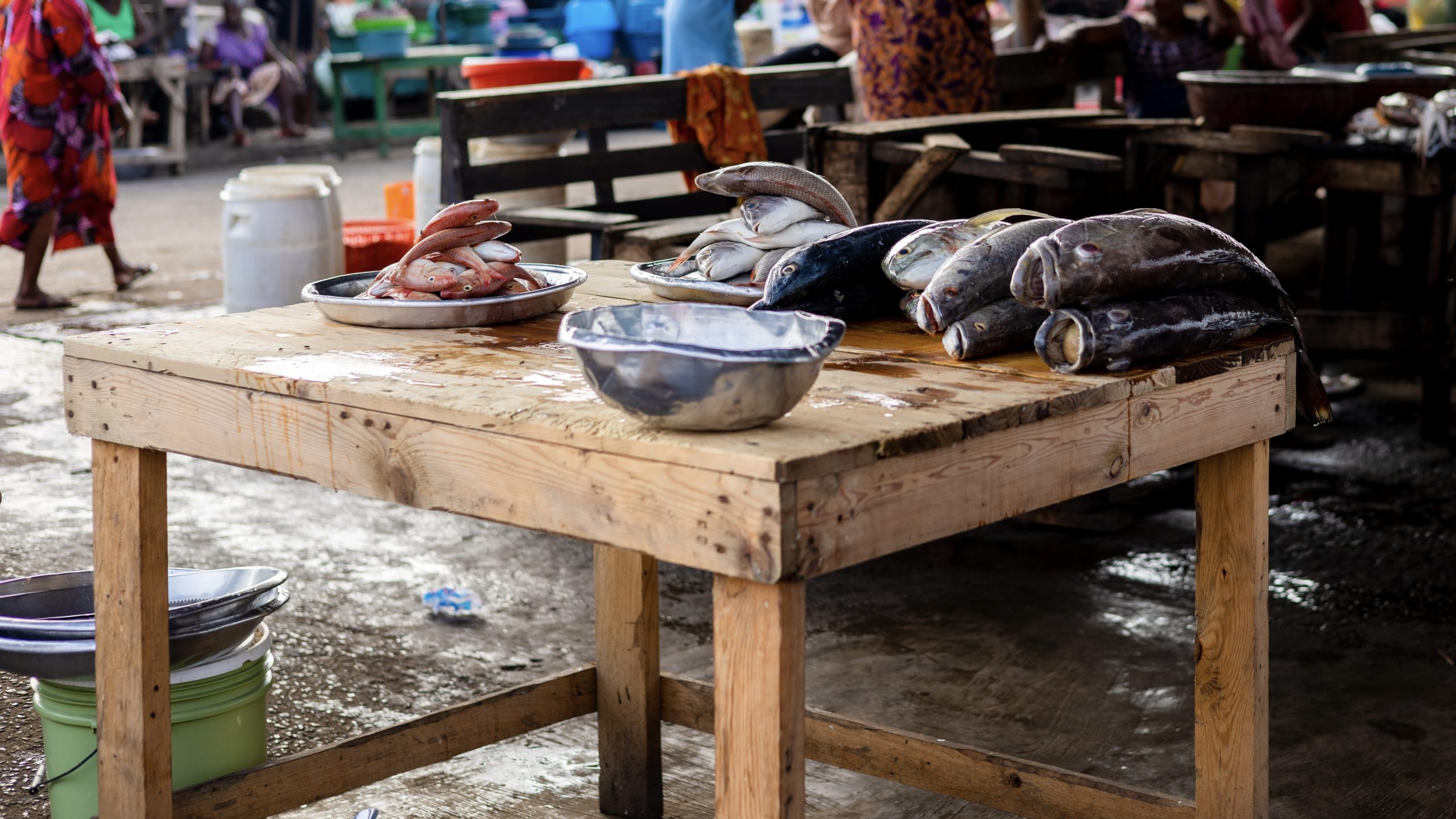
Read MoreFor developing countries, seafood imports are a nutritional bargain
Developing countries pay less for the nutrition in seafood imports than developed countries
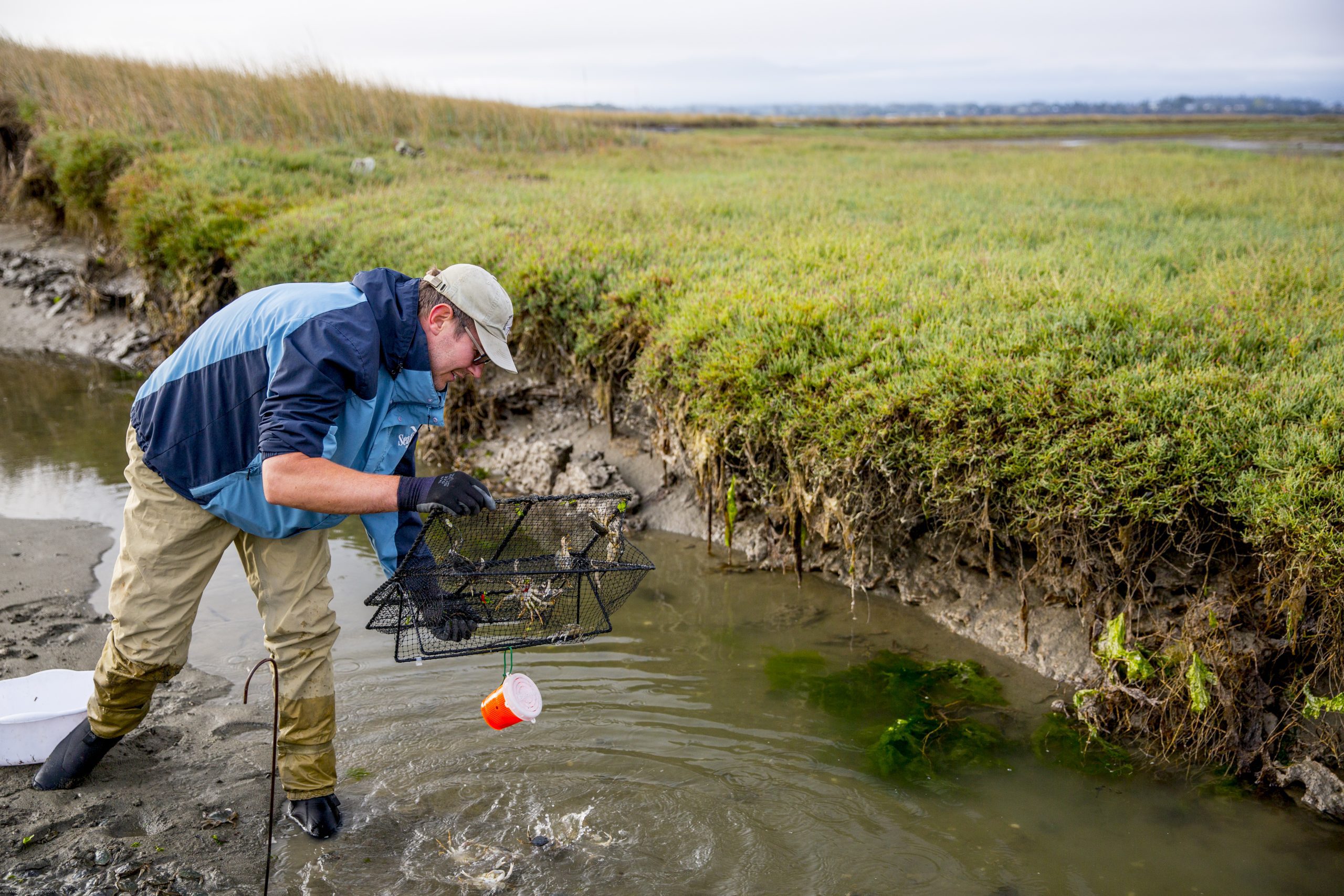
Read MoreResearchers to map the genome of the invasive European green crab
Washington Sea Grant will work with Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution to shed light on a highly invasive species
Read MoreThe Detection of a Massive Harmful Algal Bloom in the Arctic Prompts Real-Time Advisories to Western Alaskan Communities
The potent toxicity of the 2022 HAB event “posed an unprecedented risk to human and ecosystem health.”
Read MoreWoods Hole Center for Oceans and Human Health Receives Additional Five Years of Funding
The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) and National Science Foundation (NSF) have announced that the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will receive funding to continue operating the Woods Hole Center for Oceans and Human Health (WHCOHH).
Read MoreMapping the potential path of nuclear wastewater
WHOI Sea Grant will study spreading pathways from Pilgrim Nuclear Power Station
Read MoreNatural Wax Holds Promise to Replace Petroleum in Cosmetics and Personal Care Products
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and Western Washington University Sign License Agreement for Upwell Cosmetics to Make and Market a Marine Microalga-Derived Wax
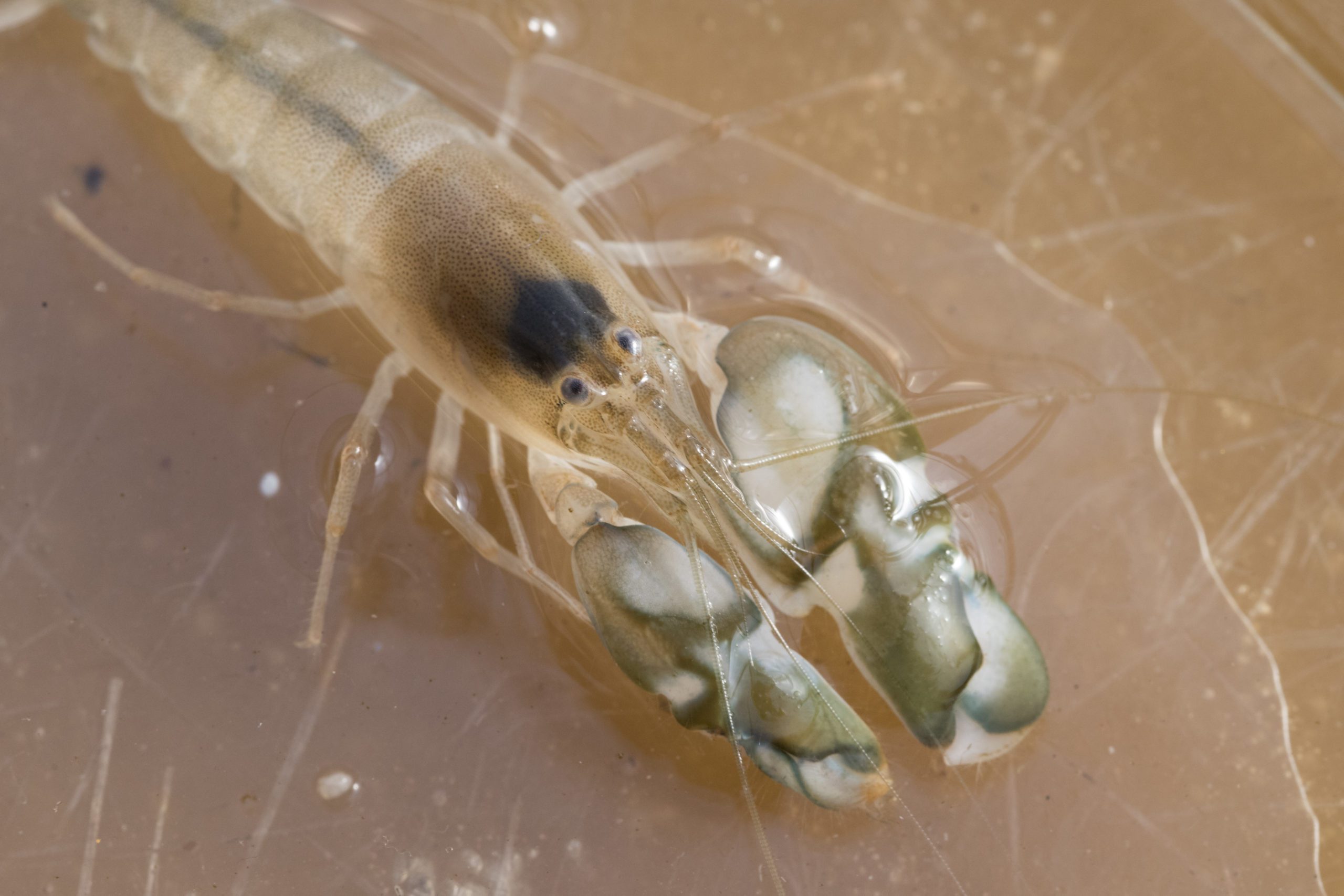
Read MoreAs oceans warm, snapping shrimp sound a warning
Research published by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists today in Frontiers in Marine Science confirmed their previous observations that rising temperatures increase the sound of snapping shrimp, a tiny crustacean found in temperate and tropical coastal marine environments around the world.
Read MoreStudy Finds Growing Potential for Toxic Algal Blooms in the Alaskan Arctic
A warming Arctic presents potential new threats to humans and marine wildlife in the fast-changing region Changes in the northern Alaskan Arctic ocean environment have reached a point at…
Read MoreFlipping the “genetic paradox of invasions”
A new study led by Carolyn Tepolt, an associate scientist of biology at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, is investigating the adaptive mechanisms of the green crab along the west coast of North America, where it has shown extensive dispersal in the last decade despite minimal genetic diversity.
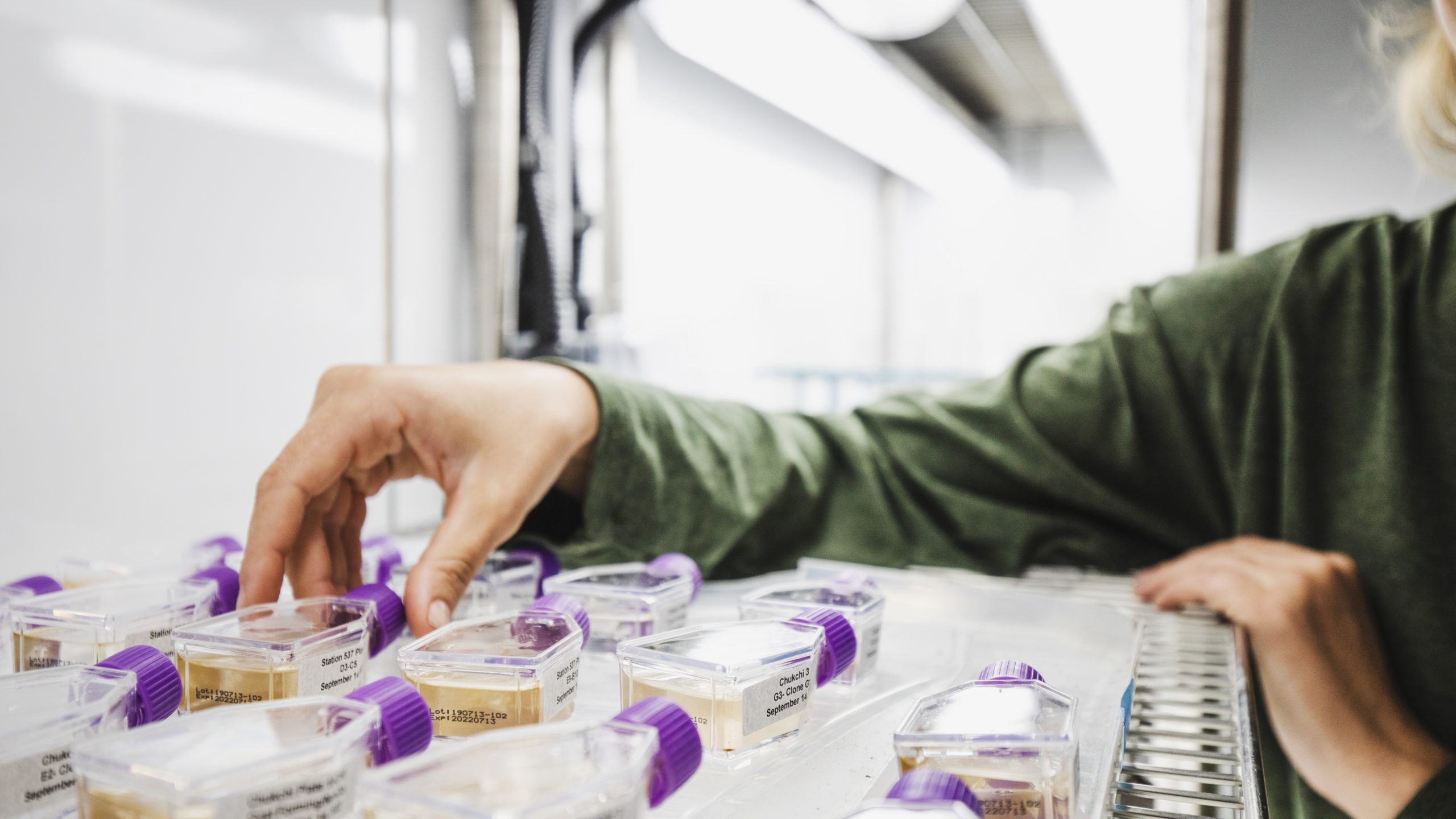
Read MoreFirst Global Statistical Analysis of Harmful Algal Blooms
International study finds no worldwide trend in blooms, but significant increases in some regions and of certain species, pointing to the need for better monitoring and data collection—especially in light…
Read MoreWHOI receives NOAA awards to study, predict harmful algal blooms
Projects will help enhance monitoring and determine socioeconomic impacts of blooms nationwide Researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) were recently named in a list of 17 new research projects…
Read MoreNOAA awards WHOI $2.9 million for harmful algal bloom research
NOAA’s National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science recently announced funding for 12 new research projects to better understand and predict harmful algal blooms (HABs) and improve our collective response to them.
Read MoreSea Grant Funds New Technology to Monitor for Harmful Algal Blooms
A new system using next generation robotic sensors to monitor coastal waters for disease-causing microalgae has been funded by the NOAA Sea Grant Program as part of a national strategic investment in aquaculture.
The PhytO-ARM (Phytoplankton Observing for Automated Real-time Management), under development by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) biologist Mike Brosnahan, will vastly improve our ability to detect harmful algal blooms (HABs) and the toxins they produce and provide aquaculturists, resource managers, and others detailed, real-time information about the bloom using a web-based, user-friendly dashboard.
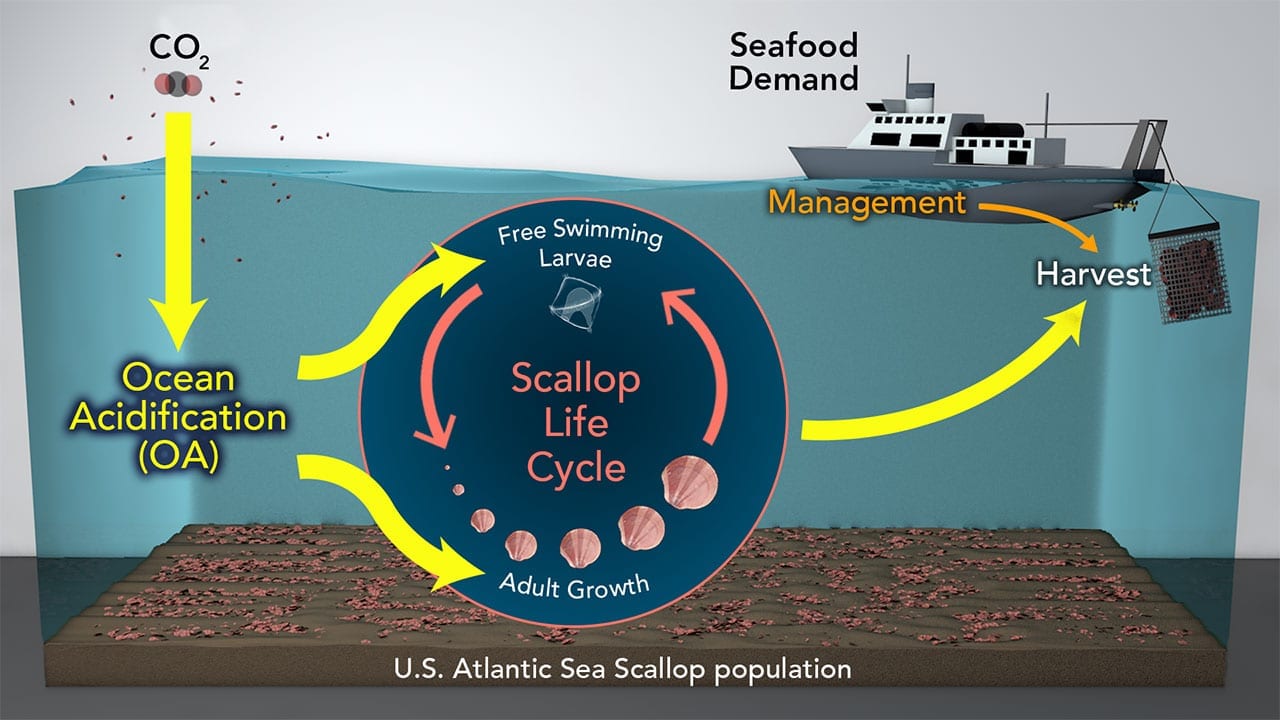
Read MoreOcean Acidification May Reduce Sea Scallop Fisheries
Each year, fishermen harvest more than $500 million worth of Atlantic sea scallops from the waters off the east coast of the United States. A new model created by scientists…
Read MoreWoods Hole Sea Grant Awards Funds to Six New Coastal Projects
The Woods Hole Sea Grant program has awarded researchers from WHOI and other Massachusetts academic organizations funds for new projects, representing a total anticipated investment of nearly $1.5 million.
Read MoreHeidi Sosik Selected as a Fellow of The Oceanography Society
Heidi Sosik, a senior scientist in the Biology Department at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has been named a 2018 Fellow of The Oceanography Society (TOS). Sosik’s accomplishments will be formally recognized on Feb. 13, 2018, during a ceremony at the 2018 Ocean Sciences Meeting in Portland, Oregon.
Read MoreBay State Aquaculture Projects Get Green Light from National Sea Grant Program
Two new grants to the Woods Hole Sea Grant program totaling more than $650,000 are part of a national strategic investment in aquaculture and will support research aimed at expanding aquaculture production in Massachusetts.
Read MoreDon Anderson Selected for Prestigious Ketchum Award for Coastal Research
Senior Scientist Don Anderson will receive WHOI’s prestigious 2017 Bostwick H. Ketchum Award, which honors an internationally recognized scientist who demonstrates an innovative approach to coastal research, leadership in the scientific community, and who forges a link between coastal research and societal issues.
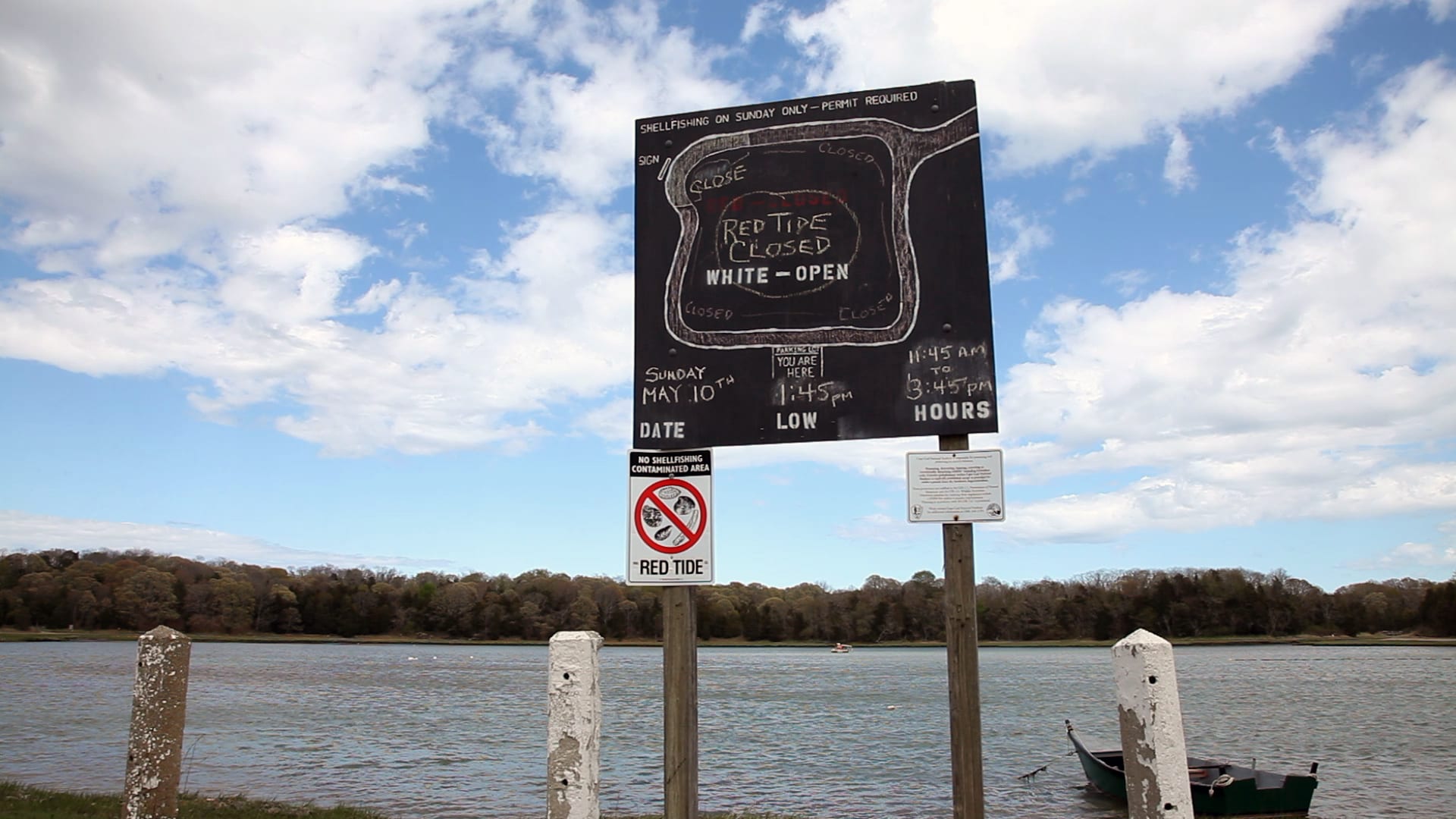
Read MoreGulf of Maine Red Tide Bloom Expected to Be Similar to Past Three Years
New England’s spring and summer red tides will be similar in extent to those of the past three years, according to the 2015 Gulf of Maine red tide seasonal forecast. The forecast is the eighth seasonal Gulf of Maine red tide forecast funded by NOAA and issued by scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and North Carolina State University.
The forecast is part of a larger NOAA effort to deliver ecological forecasts that support human health and well-being, coastal economies, and coastal and marine stewardship.
Red tide, a type of harmful algal bloom (HAB) caused by the alga Alexandrium fundyense, produces a toxin that can lead to paralytic shellfish poisoning, which can result in serious or even fatal illness in humans who eat contaminated shellfish. In 2005, an unusually large red tide event caused $23 million in lost shellfish sales in Massachusetts and Maine.
Read More