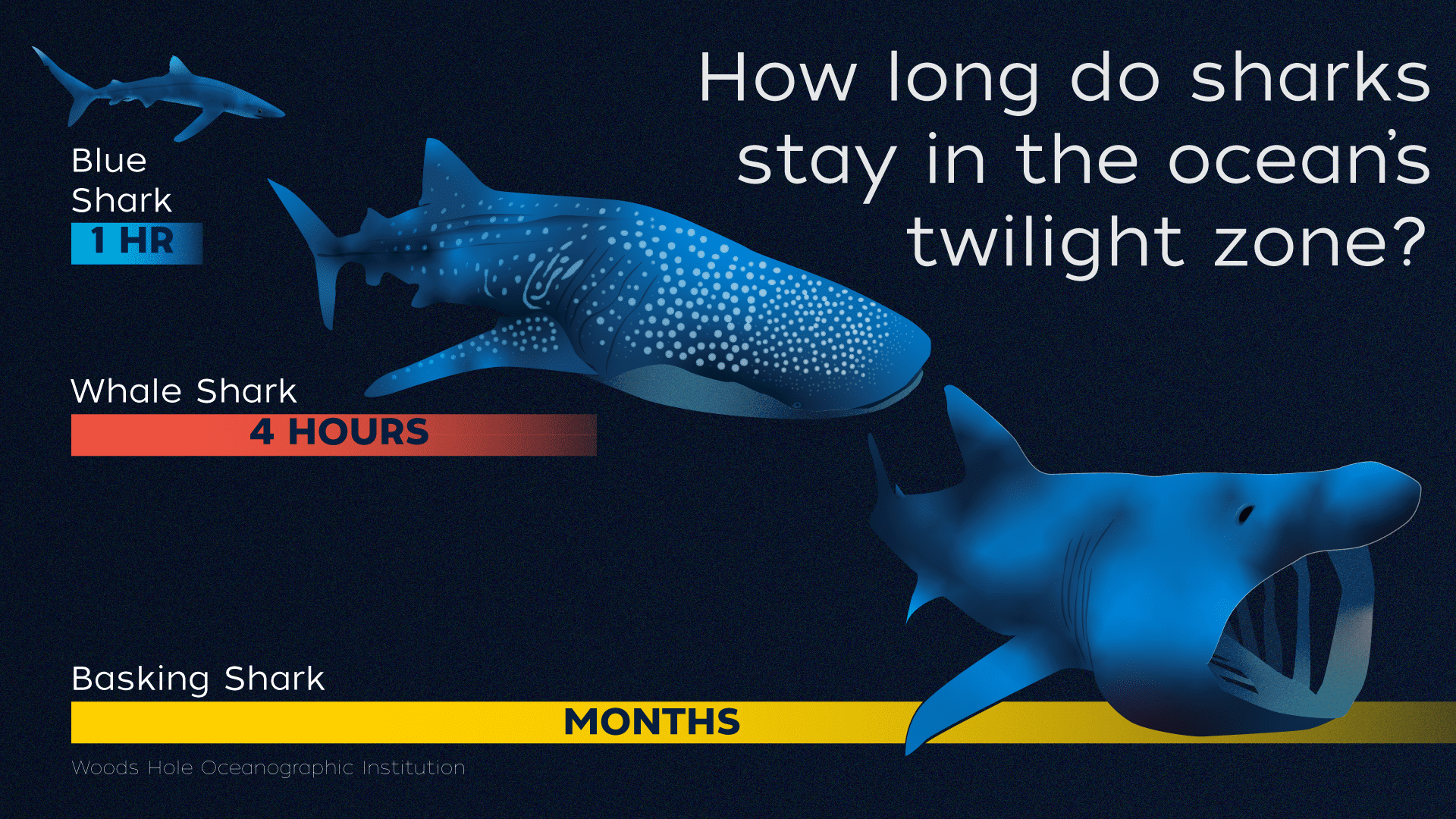News Releases
Swirling Currents Deliver Phytoplankton Carbon to Ocean Depths
A new paper published March 26 in the journal Science that highlights the significant role that swirling currents, or eddies, play in pushing non-sinking carbon to ocean depths.
Read MoreHow Do Phytoplankton Survive Scarcity of a Critical Nutrient?
Phytoplankton—tiny, photosynthetic organisms—are essential to life on Earth, supplying us with roughly half the oxygen we breathe. Like all other life forms, phytoplankton require the element phosphorus to carry out…
Read MoreScientists Discover Huge Phytoplankton Bloom in Ice Covered Waters
A team of researchers, including scientists from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), discovered a massive bloom of phytoplankton beneath ice-covered Arctic waters. Until now, sea ice was thought to block…
Read MorePhytoplankton Cell Membranes Challenge Fundamentals of Biochemistry
Get ready to send the biology textbooks back to the printer. In a new paper published in Nature, Benjamin Van Mooy, a geochemist with the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI),…
Read MoreBacteria hitching a ride on “marine snow” may slow the ocean’s carbon sink
New study reveals how microbes dissolve calcium carbonate ballast, altering the ocean’s biological carbon pump
Read MorePreliminary results from the first EPA-permitted ocean alkalinity enhancement (OAE) field trial
LOC-NESS project team shares findings at annual Ocean Sciences Meeting
Read MoreScientists outline case for next-generation ocean iron fertilization field trials
A new paper argues that larger, longer studies with rigorous monitoring and clear safeguards are needed to accurately assess OIF as a potential long-term CO2 storage solution.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution and CMA CGM expand their partnership
CMA CGM, which has long been committed to preserving biodiversity through multiple initiatives in the U.S. and worldwide, will support two key WHOI projects
Read MoreInnovative partnerships advancing ocean observations
WHOI’s Science RoCs aims to equip commercial vessels with sensors to measure physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the ocean along the world’s major shipping routes
Read MoreWHOI senior scientist named 2024 MacArthur Fellow
Benjamin Van Mooy receives “genius grant” for his research on biogeochemical networks and the impacts of climate change on ocean health
Read MoreMicrobe Dietary Preferences Influence the Effectiveness of Carbon Sequestration in the Deep Ocean
A series of seemingly small processes helps carry carbon dioxide from the ocean’s surface to the deep sea, where it can be stored away for decades.
Read MoreCan adding iron to the ocean help it absorb CO2?
A newly published article spells out the work needed to assess the potential of ocean iron fertilization as a low cost, scalable, and rapidly deployable method of mCDR.
Read MoreThe Detection of a Massive Harmful Algal Bloom in the Arctic Prompts Real-Time Advisories to Western Alaskan Communities
The potent toxicity of the 2022 HAB event “posed an unprecedented risk to human and ecosystem health.”
Read MoreSpring 2024: Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Elects New Trustees and Corporation Members
At Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s (WHOI’s) Spring Joint Meeting of the Board and Corporation today, Institution leaders elected three new Trustees and seven new Corporation Members.
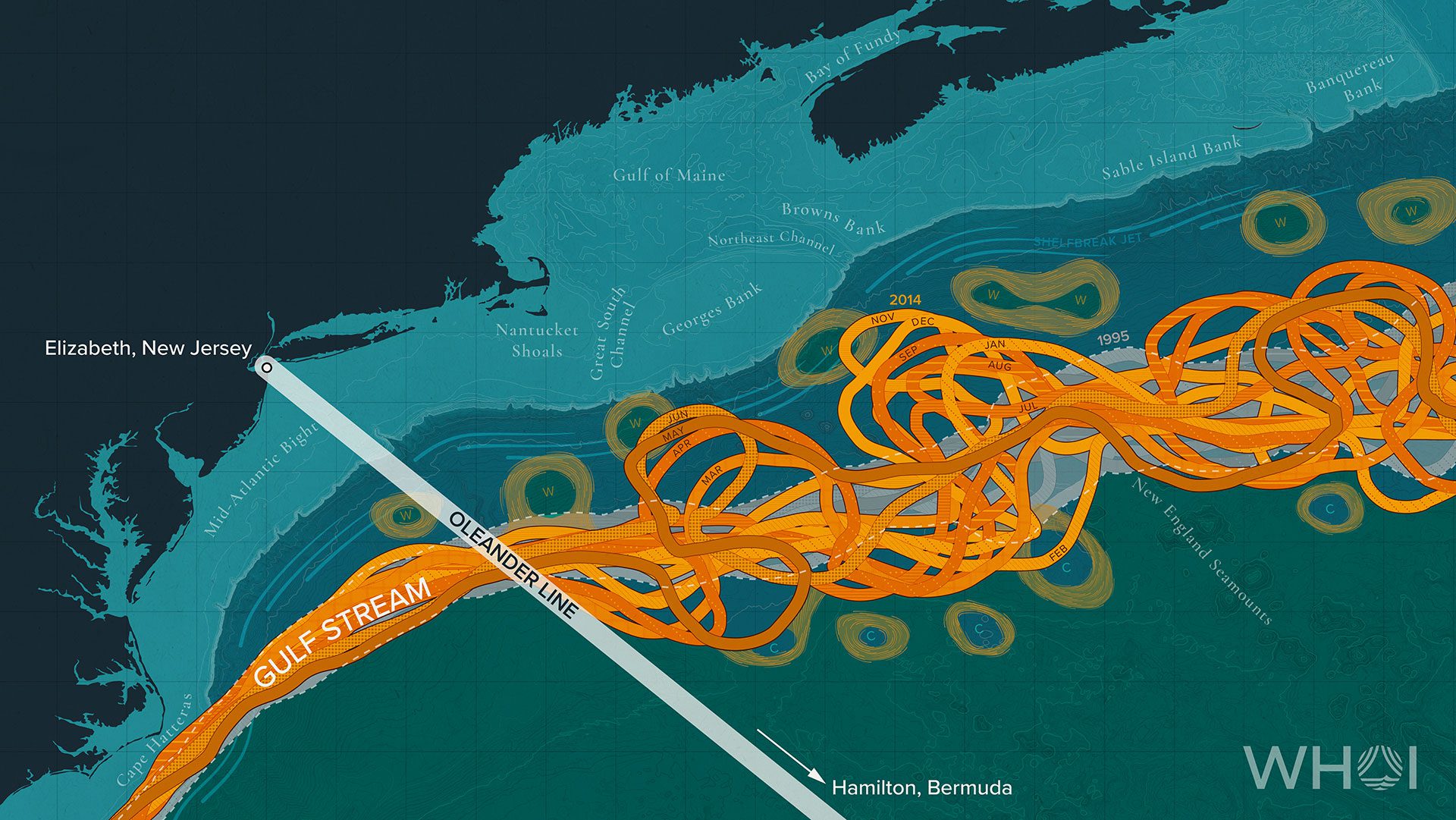
Read MoreFor microscopic organisms, ocean currents act as ‘expressway’ to deeper depths, study finds
New research shows how tiny plant-like organisms hitch a ride on ocean currents to reach darker and deeper depths, where they impact carbon cycling and microbial dynamics in the subtropical oceans.
Read MoreVitamin B12 adaptability in Antarctic algae has implications for climate change
Woods Hole, Mass. — Vitamin B12 deficiency in people can cause a slew of health problems and even become fatal. Until now, the same deficiencies were thought to impact certain…
Read MoreWHOI Awarded Funding to Support Research and Development of Marine Carbon Dioxide Removal
WHOI researchers are among the 17 projects that have been awarded funding by NOAA’s Ocean Acidification Program on behalf of the National Oceanographic Partnership Program (NOPP).
Read MoreWHOI scientists receive 2022 Simons Early Career Investigator Awards
Two Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution scientists have received prestigious Simons Early Career Investigator in Marine Microbial Ecology and Evolution Awards. Maria Pachiadaki and Harriet Alexander are both assistant scientists at WHOI, focusing on different aspects of microbial ecology.
Read MoreBen Van Mooy awarded by Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography
WHOI senior scientist and Dept. Chair honored for phosphorus and lipid cycling research
Read MoreShark Week 2021: Sharks and the Ocean’s Twilight Zone
How large marine predators use the twilight zone to thrive, and survive Woods Hole, MA (July 11, 2021) — Sharks are some of the largest fish in the ocean, known…
Read MorePapers Explore Massive Plankton Blooms with Very Different Ecosystem Impacts
Two papers explore the distribution and abundance of plankton and what conditions lead to big plankton blooms with vastly different potential impacts on the ecosystem.
Read MoreNew multi-institutional grant will support a fleet of robotic floats
The National Science Foundation approved a $53 million grant to build a global network of chemical and biological sensors that will monitor ocean health.
Read MoreWHOI receives NOAA awards to study, predict harmful algal blooms
Projects will help enhance monitoring and determine socioeconomic impacts of blooms nationwide Researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) were recently named in a list of 17 new research projects…
Read MoreThe $500 billion question: what’s the value of studying the ocean’s biological carbon pump?
A new study puts an economic value on the benefit of research to improve knowledge of the biological carbon pump and reduce the uncertainty of ocean carbon sequestration estimates.
Read More