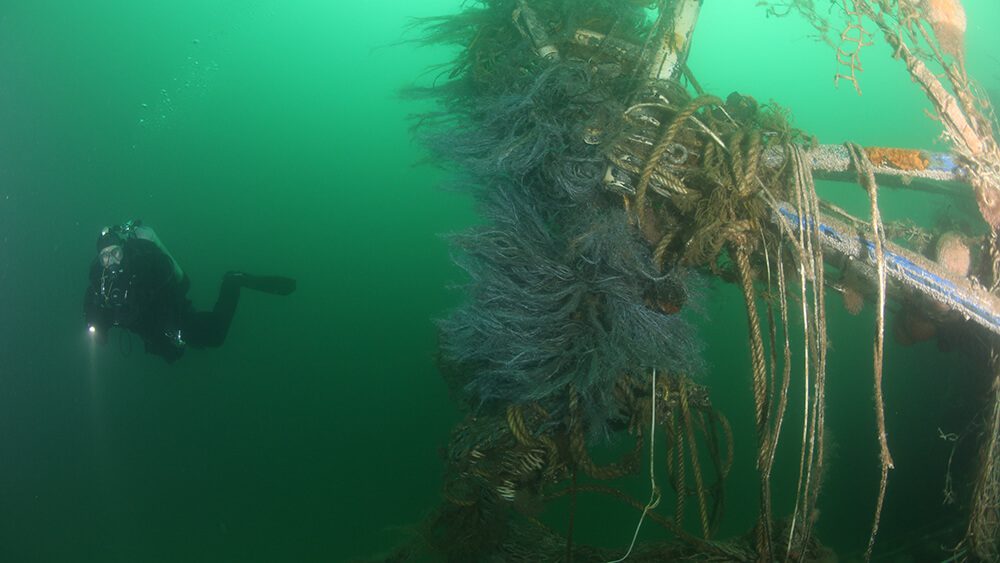
A new underwater robot could help preserve New England’s historic shipwrecks
WHOI’s ResQ ROV to clean up debris in prominent marine heritage sites
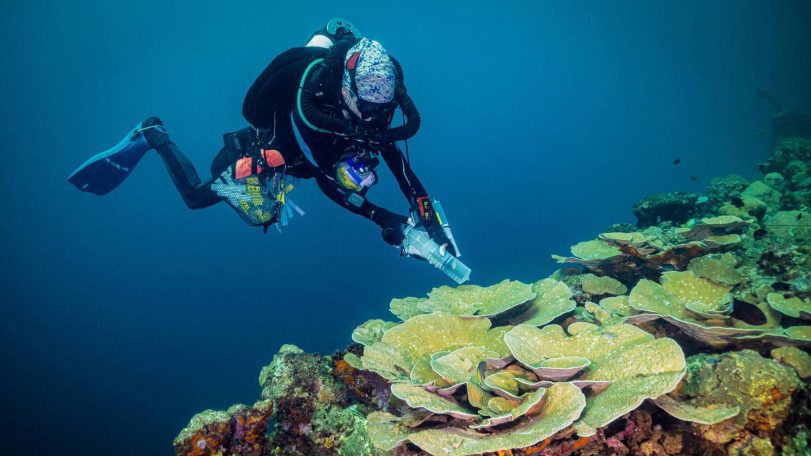
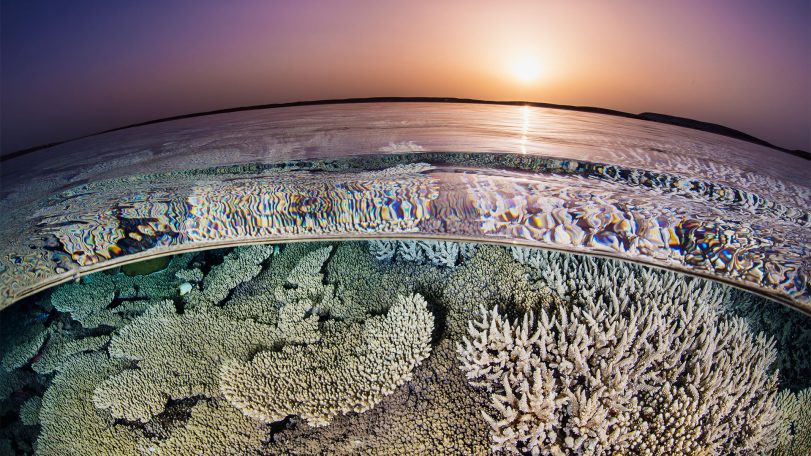
From ruin to reef
What Pacific wrecks are teaching us about coral resilience—and pollution
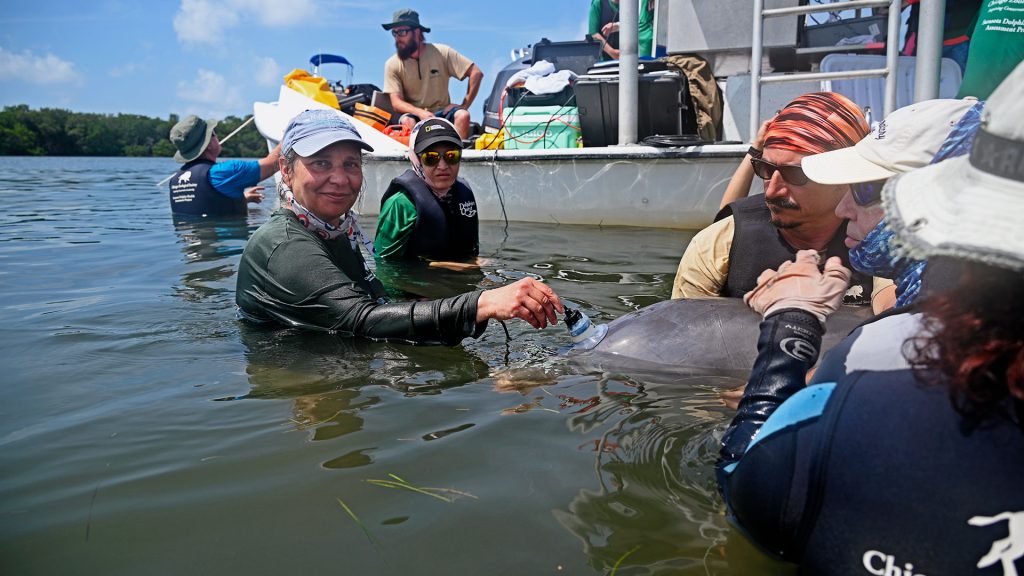
One researcher, 15,000 whistles: Inside the effort to decode dolphin communication
Scientists at WHOI analyze thousands of dolphin whistles to explore whether some sounds may function like words
Remembering Tatiana Schlossberg, a voice for the ocean
Environmental journalist and author Tatiana Schlossberg passed away after battling leukemia on December…
As the ocean warms, a science writer looks for coral solutions
Scientist-turned-author Juli Berwald highlights conservation projects to restore coral reefs
How an MIT-WHOI student used Google Earth to uncover a river–coral reef connection
Google Earth helps researcher decode how rivers sculpt massive breaks in coral reefs
The little big picture
WHOI senior biologist Heidi Sosik on the critical need for long-term ocean datasets
Lessons from a lifetime of exploration
Award-winning ocean photographer Brian Skerry shares insights from a career spent around ocean life and science

and get Oceanus delivered to your door twice a year as well as supporting WHOI's mission to further ocean science.
Our Ocean. Our Planet. Our Future.
The ocean weather nexus, explained
The vital role of ocean observations in extreme weather forecasting
Breaking down plastics together
Through a surprising and successful partnership, WHOI and Eastman scientists are reinventing what we throw away
Three questions with Carl Hartsfield
Captain Hartsfield, USN retired, discusses the role ocean science plays in our national defense
The Ocean (Re)Imagined
How expanding our view of the ocean can unlock new possibilities for life
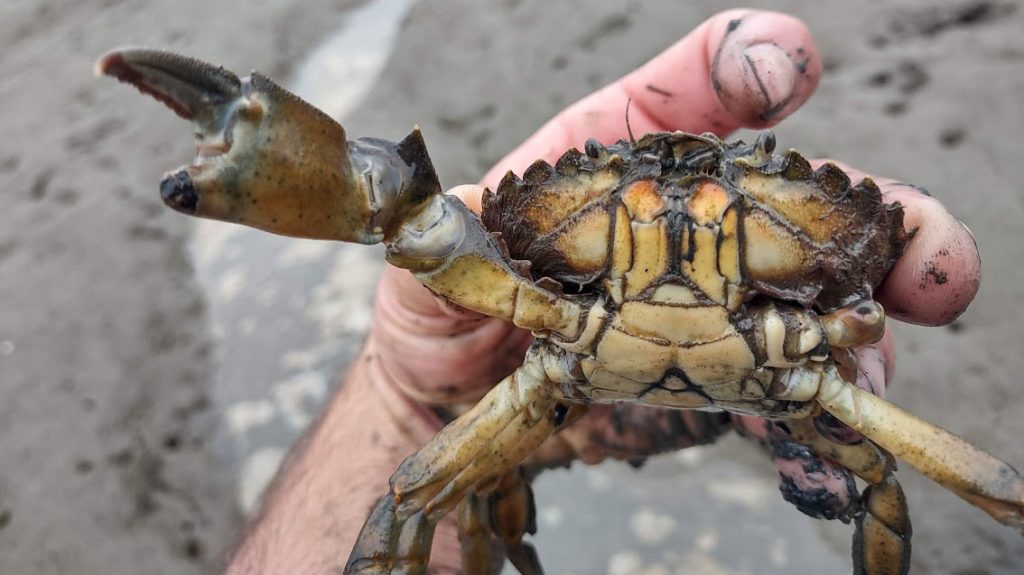
Body snatchers are on the hunt for mud crabs
WHOI biologist Carolyn Tepolt discusses the biological arms race between a parasite and its host
A polar stethoscope
Could the sounds of Antarctica’s ice be a new bellwether for ecosystem health in the South Pole?
Secrets from the blue mud
Microbes survive—and thrive—in caustic fluids venting from the seafloor

Looking for something specific?
We can help you with that. Check out our extensive conglomeration of ocean information.
Top 5 ocean hitchhikers
As humans traveled and traded across the globe, they became unwitting taxis to marine colonizers
Following the Polar Code
Crew of R/V Neil Armstrong renew their commitment to Arctic science with advanced polar training
Harnessing the ocean to power transportation
WHOI scientists are part of a team working to turn seaweed into biofuel
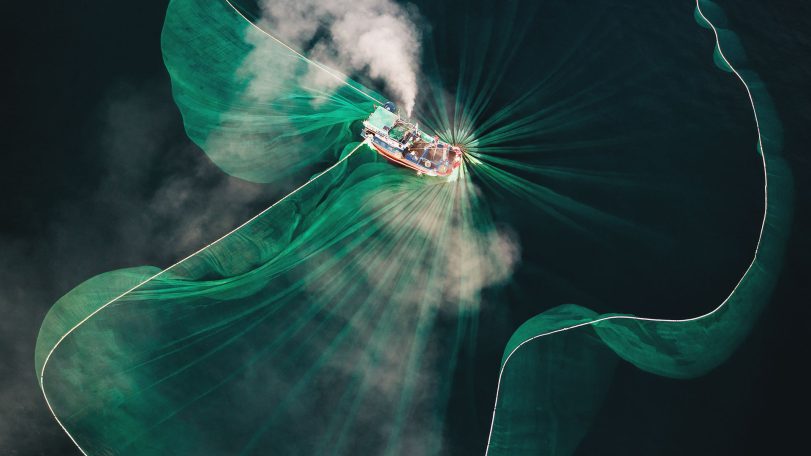
Casting a wider net
The future of a time-honored fishing tradition in Vietnam, through the eyes of award-winning photographer Thien Nguyen Noc
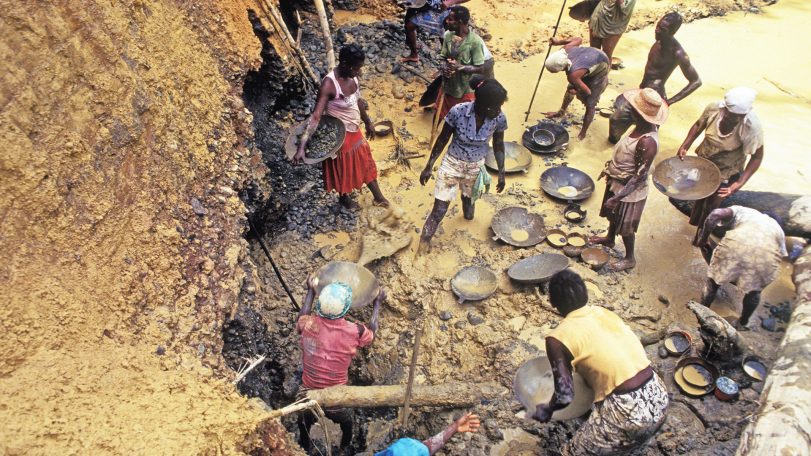
Gold mining’s toxic legacy
Mercury pollution in Colombia’s Amazon threatens the Indigenous way of life
How do you solve a problem like Sargassum?
An important yet prolific seaweed with massive blooms worries scientists
Ancient seas, future insights
WHOI scientists study the paleo record to understand how the ocean will look in a warmer climate
Rising tides, resilient spirits
As surrounding seas surge, a coastal village prepares for what lies ahead
Whistle! Chirp! Squeak! What does it mean?
Avatar Alliance Foundation donation helps WHOI researcher decode dolphin communication
Outposts in the Ocean
Oceanographers and climatologists have something in common with politicians and stock market analysts: They are all trying to get a grasp on a complex, ever-shifting system.
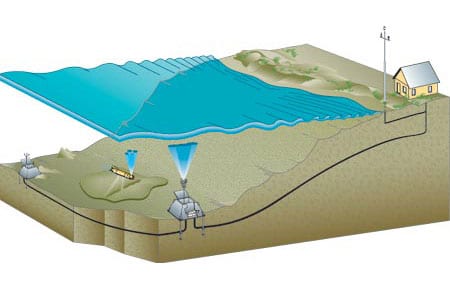
New Coastal Observatory Is Born
The Martha’s Vineyard Observatory will have sensors mounted on two seafloor nodes, at depths of about 5 and 15 meters, respectively, connected to a shore station via a buried cable. Instruments mounted on the nodes will continually monitor mean sea and wave heights, current strengths, seawater turbulence, subsurface sediment movement, sunlight intensity, and the temperature, salinity, and carbon dioxide levels of the ocean?s waters.
Launching the Argo Armada
The Argo program proposes to disperse 3,000 floats, like the one below, throughout the oceans to collect data on oceanic conditions that can be periodically transmitted to shore via satellite.
Putting H2O in the Ocean
A major obstacle impeding our ability to understand many of the earth’s fundamental, ongoing dynamics–quite frankly–has been a dearth of electrical outlets and phone jacks on the seafloor.
Where the Surf Meets the Turf
The gentle lapping of waves on the beach is a metaphor for enduring tranquility. However, the thin zone where the surf meets the turf is one of the most turbulent, complex, fast-moving, constantly changing places on Earth.
ALISS in Wonderland
In 1985, Cindy Van Dover, then a graduate student in biology in the MIT/WHOI Joint Program, discovered a novel light-sensing organ on a unique species of shrimp that lives at high-temperature, black smoker chimneys on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. If this photoreceptor were indeed some sort of primitive “eye,” the question instantly arose: At depths of some 3,600 meters, where sunlight cannot penetrate, what are these shrimp looking at? The search for a source of light in deep-sea hydrothermal environments began.
How to Build a Black Smoker Chimney
Diving along the mid-ocean ridge at 21°N on the East Pacific Rise, scientists within the deep submersible Alvin peered through their tiny portholes two decades ago to see an astonishing sight: Clouds of billowing black “smoke” rising rapidly from the tops of tall rocky “chimneys.”
Hitting the Hotspots
The great volcanic mid-ocean ridge system stretches continuously around the globe for 60,000 kilometers, nearly all of it hidden beneath the world’s oceans.
Life on the Seafloor and Elsewhere in the Solar System
The RIDGE program (Ridge Inter-Disciplinary Globe Experiments) was sharply focused on the global spreading center system, but the program’s goals were broadly defined. RIDGE was designed to explore the causes, consequences, and linkages associated with the physical, chemical, and biological processes that transfer mass and energy from the interior to the surface of the planet along the mid-ocean ridges.
Deep-Sea Diaspora
When spectacular biological communities were first discovered at hydrothermal vents in 1977, biologists puzzled over two main questions: How did these oases of large and abundant animals persist in the deep sea, where food is typically scarce? And how did these unusual species, which occur only at vents, manage to colonize new vents and avoid extinction when old vents shut down?
The Cauldron Beneath the Seafloor
Just over 20 years ago, scientists exploring the mid-ocean ridge system first made the spectacular discovery of black smokers—hydrothermal chimneys made of metal sulfide minerals that vigorously discharge hot, dark, particulate-laden fluids into the ocean.
“Nothing Could Diminish the Excitement Of Seeing the Animals for the First Time”
The scientists who made the surprising discovery of teeming life around hydrothermal vents of the Galápagos Rift in 1977 were geologists and geochemists. They had not expected to find spectacular colonies of previously unknown, large animals on the deep seafloor.