An Experiment to Dye For
Researchers trace movement of water using airborne laser
Tracking the motion of the ocean can be tricky. Water sloshes and streams in all directions—pushed and pulled by winds, tidal forces, Earth’s rotation, and differences in heat and salt. To understand the ocean on both global and local scales, researchers strive to sort out the sometimes predictable but often chaotic movements of water. It isn’t easy.
Sometimes oceanographers resort to tagging the water the way ornithologists might tag a bird to see where it travels. They mark parcels of water by releasing harmless dyes or chemicals from ships, taking samples of the water, and using the dyes to trace the flow.
“We let nature diffuse the dye, which amplifies motion so we can watch the patches of water move,” said Miles Sundermeyer, a visiting investigator in the WHOI Applied Ocean Physics and Engineering Department (AOPE), an assistant professor at the University of Massachusetts Dartmouth, and a 1998 graduate of the MIT/WHOI Joint Program in Oceanography.
One problem with tracers, however, is that the “tagged” water disperses faster than a ship can survey it. The motion of the ship itself also disturbs the natural movement scientists want to study.
To overcome these limitations—and to better understand the processes responsible for mixing in the upper ocean—scientists Jim Ledwell and Gene Terray in the AOPE Department and Sundermeyer collaborated on a pilot project—literally and figuratively.
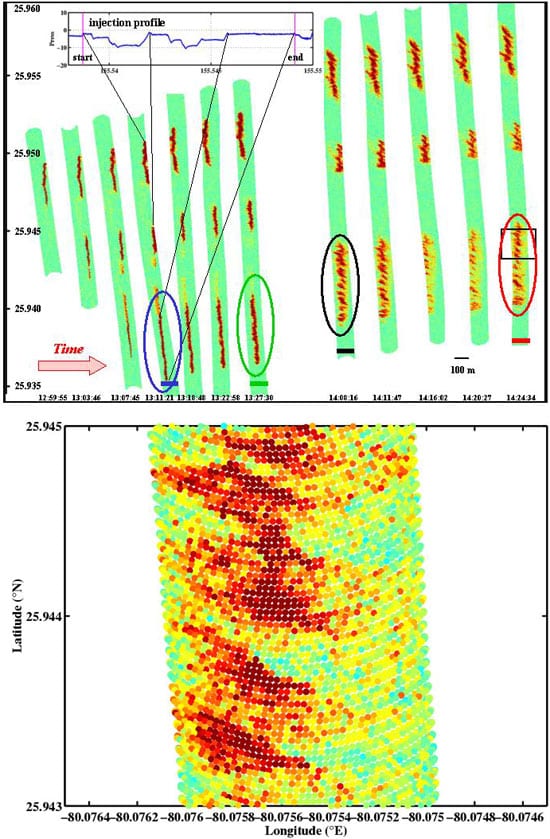
The team devised an experiment to map the motion of fluorescent dye in the ocean by surveying it from an airplane equipped with a Light Detection and Ranging instrument. LIDAR uses pulses of laser light and their reflection to detect motion in much the same way radar uses radio signals to detect echoes bouncing off objects.
Working 10 kilometers (5.4 nautical miles) southeast of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., Terray, Sundermeyer, and WHOI Summer Student Fellow Sandeep Bohra injected fluorescent rhodamine dye into Atlantic waters from the fantail of Florida Atlantic University’s research vessel Stephan. They streamed the dye continuously in a straight line over 1.5 kilometers (about 1 mile), releasing it at varying depths from the surface to 5 to 10 meters (16 to 33 feet) deep.
Colleagues from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and Optech Inc., flew an airplane back and forth over the dye track, pulsing infrared and green laser light into a 100-meter (330-foot) swath of ocean. The laser chemically “excited” the red dye, which emitted flashes of fluorescent yellow-orange light that were recorded by a receiver on the plane.
While the ship made just three surveys of the dye patches, the airborne surveyors made 21 passes in about 1.5 hours (roughly every four minutes). Compared with the few still “snapshots” of water motion taken by the ship, the LIDAR images seemed like a motion picture.
“We couldn’t measure these movements with conventional current-measuring technologies because the velocities are too small,” said Terray. “The combination of the tracer and LIDAR is like having a big pointer that allows us to observe the displacement of the dye. We don’t just want to quantify the mixing and stirring. We want to get at the physics of how it happens.”
The researchers foresee a time when they can look at how individual eddies form, circulate, and dissipate in the ocean. And since the LIDAR technique allows scientists to peek beneath the surface, they also hope to examine the way water mixes from the surface to the depths. A three-dimensional picture of the mixing process is not out of the question. And we wouldn’t need those funny plastic glasses to see it.
This project was funded by the Cecil H. and Ida M. Green Technology Innovation Fund, the Rinehart Access to the Sea Initiative, the Office of Naval Research, and the Rinehart Access to the Sea Initiative.
Slideshow

Slideshow
- WHOI scientists are exploring an experimental technique to track the complex movements of water in the oceans using harmless fluorescent dyes and airplanes equipped with Light Detection and Ranging instruments. To detect motion, LIDAR uses pulses of laser light, which cause the flowing dye to fluoresce, even underwater. (Illustration by Jack Cook, WHOI)
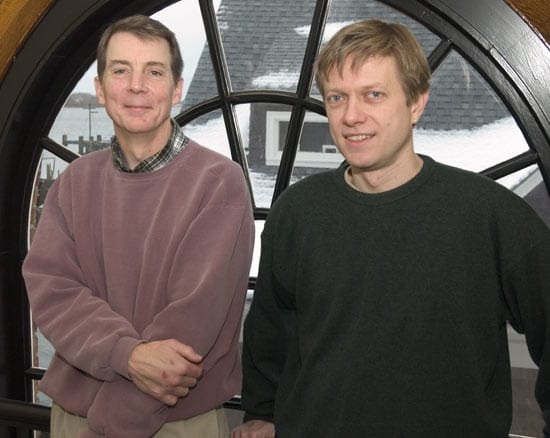
- Gene Terray (left), research specialist in the Applied Ocean Physics and Engineering (AOPE) Department, and Miles Sundermeyer, guest investigator in AOPE, recently experimented with airborne lasers as a tool for studying the vertical and horizontal movement of water masses in the ocean. (Photo by Tom Kleindinst, WHOI)
- WHOI Summer Student Fellow Sandeep Bohra (from the University of Minnesota) holds a dye injection line over the fantail of R/V Stephan as the WHOI-led research team poured harmless Rhodamine WT dye into the ocean about 10 kilometers (6 miles) southeast of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. WHOI Research Specialist Gene Terray stands in the foreground. (Courtesy of Miles Sundermeyer, University of Massachusetts, Dartmouth)
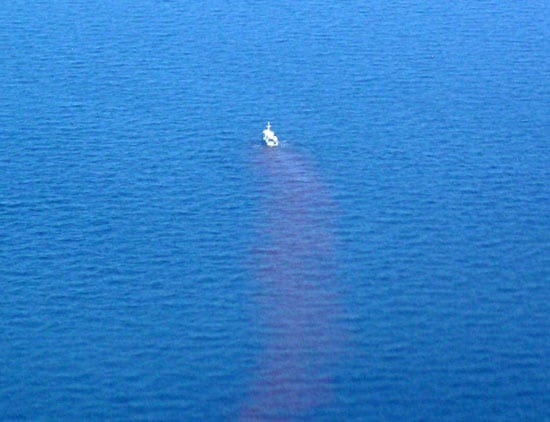
- Passengers aboard an U.S. Army Corps of Engineers plane spotted the trail of dye in the Atlantic Ocean as they approached with their airborne LIDAR instruments. The pilot needed to be able to see the dye streak from R/V Stephan from several miles away in order to properly align the flight path.
- Data collected by the LIDAR instruments on north-south flights show the dispersion of the rhodamine dye on the surface over time by currents in the ocean. The dots represent the intensity of the fluorescing light emitted by the dye in the water after being pulsed by the laser, revealing stronger and weaker concentrations of dye.
Related Articles
- Mary Sears and the race to solve the ocean in World War II
- Go with the flow
- Ocean in Motion
- Saving Tico
- The long journey of Bottle No. 71645
- The ocean currents behind Brazil’s pollution problem
- Ocean data gives Northeast fishermen an edge against a warming ocean
- Tracking change in the Arctic Ocean
- A tunnel to the Twilight Zone
- Diving in Eddies
- Following the Eddies
- Of Wings, Waves, and Winds
- The Oceans Have Their Own Weather Systems