Marine Chemistry & Geochemistry
Oil in Our Coastal Back Yard
On September 16, 1969, the barge Florida ran aground off Cape Cod, rupturing its hull and spilling 189,000 gallons of No. 2 fuel oil. Winds and waves pushed the oil onto the beaches and marshes of West Falmouth, Massachusetts, carrying with it dead lobsters, scup, and cod.
Read MoreLiving Large in Microscopic Nooks
Newly discovered deep-sea microbes rearrange thinking on the evolution of the Eart—and life on it.
Read MoreMixing Oil and Water
In recent decades scientists have made substantial progress in understanding how oil enters the oceans, what happens to it, and how it affects marine organisms and ecosystems. This knowledge has led to regulations, practices, and decisions that have helped us reduce sources of pollution, prevent and respond to spills, clean up contaminated environments, wisely dredge harbors, and locate new petroleum handling facilities.
Read MoreThe Remarkable Diversity of Seafloor Vents
Since 1982, I had spent most of my waking hours examining pieces of seafloor vent deposits that had been recovered during a routine dredging operation along the Juan de Fuca Ridge off the Pacific Northwest coast.
Read MoreWhen Seafloor Meets Ocean, the Chemistry Is Amazing
Scientists are discovering that abundant quantities of methane gas are continually seeping from the seafloor throughout the oceans. This widespread but overlooked natural phenomenon has potentially dramatic implications on world energy supplies, life in the oceans, and Earth’s climate.
Read MoreHow to Build a Black Smoker Chimney
Diving along the mid-ocean ridge at 21°N on the East Pacific Rise, scientists within the deep submersible Alvin peered through their tiny portholes two decades ago to see an astonishing sight: Clouds of billowing black “smoke” rising rapidly from the tops of tall rocky “chimneys.”
Read MoreThe Cauldron Beneath the Seafloor
Just over 20 years ago, scientists exploring the mid-ocean ridge system first made the spectacular discovery of black smokers—hydrothermal chimneys made of metal sulfide minerals that vigorously discharge hot, dark, particulate-laden fluids into the ocean.
Read MoreA New Way to Catch the Rain
The carbon budget of the upper ocean includes an important loss to the deep ocean due to a very slowly falling rain of organic particles, usually called sediment. As this sediment falls through the upper water column it is consumed, mainly by bacteria, and the carbon is recycled into nonsinking forms (dissolved or colloidal organic carbon or inorganic forms). Thus the sediment rain decreases with increasing depth in the water column, and only a tiny fraction reaches the deep sea floor, less than about one percent.
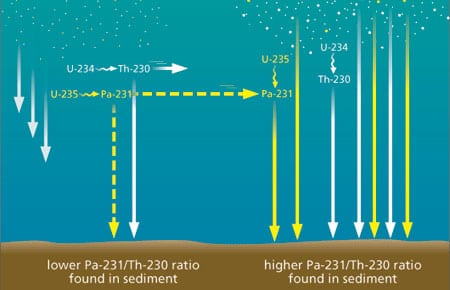
Read MoreGeochemical Archives Encoded in Deep-Sea Sediments Offer Clues for Reconstructing the Ocean’s Role in Past Climatic Changes
Geochemical Archives Encoded in Deep-Sea Sediments Offer Clues for Reconstructing the Ocean’s Role in Past Climatic Changes
Paleoceanographers are trying to understand the causes and consequences of global climate changes that have occurred in the geological past. One impetus for gaining a better understanding of the factors that have affected global climate in the past is the need to improve our predictive capabilities for future climate changes, possibly induced by the rise of anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere.
Transient Tracers Track Ocean Cimate Signals
Transient tracers provide us with a unique opportunity to visualize the effects of the changing climate on the ocean. They trace the pathways climate anomalies follow as they enter and move through the ocean and give us valuable information about rates of movement and amounts of dilution. This knowledge is important for developing ocean-climate models to predict long term climate changes.
Read More