News Releases
WHOI Selected for Bicycle Friendly Business Award
The League of American Bicyclists recognized the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) with a Silver Bicycle Friendly Business award, which acknowledges efforts by the Institution that promote cycling to help ease traffic congestion, reduce greenhouse gas and pollution emissions, and encourage a healthy lifestyle among its employees.
Read MoreNew Robot Speeds Sampling of Ocean’s Biogeochemistry and Health
The world’s first underwater vehicle designed specifically to collect both biological and chemical samples from the ocean water column successfully completed sea trials off the coast of New England on July 9, 2017. The new autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV), named Clio, will help scientists better understand the inner workings of the ocean.
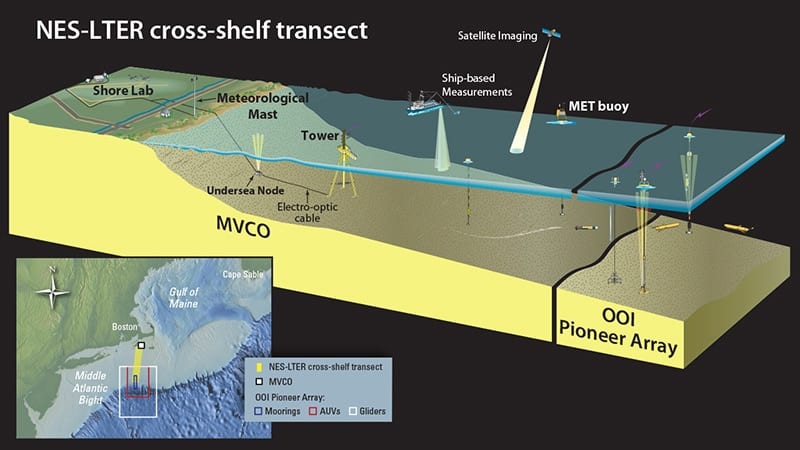
Read MoreA New Long-Term Ecological Research Site Announced for the Northeast U.S. Shelf
To better understand and manage the intricate ecosystem off the Northeast U.S. coast, the National Science Foundation has announced the selection of this critical ocean region for a new Long Term Ecological Research (LTER) site led by WHOI.
Read MoreWHOI Scientist Receives Camille and Henry Dreyfus Foundation Award
The Camille and Henry Dreyfus Foundation selected Mak Saito, a biogeochemist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), as one of eight awardees of a 2016 Postdoctoral Program in Environmental Chemistry grant.
Read MoreRiver Buries Permafrost Carbon at Sea
As temperatures rise, some of the carbon dioxide stored in Arctic permafrost meets an unexpected fate—burial at sea. As many as 2.2 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) per year are swept along by a single river system into Arctic Ocean sediment, according to a new study led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) researchers and published today in Nature. This process locks away the greenhouse gas and helps stabilize the earth’s CO2 levels over time, and it may help scientists better predict how natural carbon cycles will interplay with the surge of CO2 emissions due to human activities.
“The erosion of permafrost carbon is very significant,” says WHOI Associate Scientist Valier Galy, a co-author of the study. “Over thousands of years, this process is sequestering CO2 away from the atmosphere in a way that amounts to fairly large carbon stocks. If we can understand how this process works, we can predict how it will respond as the climate changes.”
Permafrost—the permanently frozen ground found in the Arctic and Antarctic and in some alpine regions—is known to hold billions of tons of organic material, including vast stores of CO2. Amid concerns about rising Arctic temperatures and their impact on permafrost, many researchers have directed their efforts to studying the permafrost carbon cycle—the processes through which the carbon circulates between the atmosphere, the soil and surface (the biosphere), and the sea. Yet how this cycle works and how it responds to the warming, changing climate remains poorly understood.
Galy and his colleagues from Durham University, the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, the NERC Radiocarbon Facility, Stockholm University, and the Universite Paris-Sud set out to characterize the carbon cycle in one particular piece of the Arctic landscape—northern Canada’s Mackenzie River, the largest river flowing into the Arctic Ocean from North America and that ocean’s greatest source of sediment. The researchers hypothesized that the Mackenzie’s muddy water might erode thawing permafrost along its path and wash that biosphere-derived material and the CO2 within it into the ocean, preventing the release of that CO2 into the atmosphere.
Read MoreAir Travel and Climate: A Potential New Feedback?
Global air travel contributes around 3.5 percent of the greenhouse gas emissions behind/driving anthropogenic climate change, according to the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). But what impact does a warming planet have on air travel and how might that, in turn, affect the rate of warming itself?
A new study by researchers at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and University of Wisconsin Madison found a connection between climate and airline flight times, suggesting a feedback loop could exist between the carbon emissions of airplanes and our changing climate. The study was published in this week’s Nature Climate Change.
Read MoreWhere Iron and Water Mix
A new study by researchers from University of Washington (UW), Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), and the University of Southern California, demonstrates that chemical-laden plumes erupted from vents at one section of Mid Ocean Ridge in the SE Pacific can be traced all the way across the Pacific for more than 4000 kilometers. Further, the study shows how the iron transported by this process is ultimately brought to the surface oceans of Antarctica where it is serves as a key life-sustaining micro-nutrient supporting up to 30 percent of all the organic carbon uptake in that ocean.
Read MoreRevealing the Ocean’s Hidden Fertilizer
A new study by a research team from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and Columbia University reveals for the first time a marine phosphorus cycle that is much more complex than previously thought. The work also highlights the important but previously hidden role that some microbial communities play in using and breaking down forms of this essential element.
Read MoreStudy Reveals How Rivers Regulate Global Carbon Cycle
Humans concerned about climate change are working to find ways of capturing excess carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and sequestering it in the Earth. But Nature has its own methods for the removal and long-term storage of carbon, including the world’s river systems, which transport decaying organic material and eroded rock from land to the ocean.
While river transport of carbon to the ocean is not on a scale that will bail humans out of our CO2 problem, we don’t actually know how much carbon the world’s rivers routinely flush into the ocean – an important piece of the global carbon cycle.
But in a study published May 14 in the journal Nature, scientists from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) calculated the first direct estimate of how much and in what form organic carbon is exported to the ocean by rivers. The estimate will help modelers predict how the carbon export from global rivers may shift as Earth’s climate changes.
Read MoreStudy Offers Economical Solutions for Maintaining Critical Delta Environments
Millions of people across the world live or depend on deltas for their livelihoods. Formed at the lowest part of a river where its water flow slows and spreads into…
Read MoreDoney receives A.G. Huntsman Award for Excellence in Marine Science
WHOI Senior Scientist Scott Doney has been awarded the 2013 A.G. Huntsman Award for Excellence in Marine Science. He will receive the award later this year at the Bedford Institute…
Read MoreDeep Biosphere Harbors Active, Growing Communities of Microorganisms
The deep biosphere—the realm of sediments far below the seafloor—harbors a vast ecosystem of bacteria, archaea, and fungi that are actively metabolizing, proliferating, and moving, according a new study by…
Read MoreWHOI Research Projects Awarded $5.2 M to Support Marine Microbial Research
There are more microbes in a bucket of seawater than there are people on Earth. Despite their abundance, humans are only just beginning to fathom the complex role marine microbes…
Read MoreWHOI Scientist Receives Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation Marine Microbiology Initiative Investigator Award
Mak Saito, a biogeochemist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, has been selected for a Marine Microbiology Initiative (MMI) investigator award by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation. Saito is one…
Read MoreHuman Impact Felt on Black Sea Long Before Industrial Era
When WHOI geologist Liviu Giosan first reconstructed the history of how the Danube River built its delta, he was presented with a puzzle. In the delta’s early stages of development,…
Read MoreMelting Sea Ice Threatens Emperor Penguins, Study Finds
At nearly four feet tall, the Emperor penguin is Antarctica’s largest sea bird—and thanks to films like “March of the Penguins” and “Happy Feet,” it’s also one of the continent’s…
Read MoreNew Study by WHOI Scientists Provides Baseline Measurements of Carbon in Arctic Ocean
Scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have conducted a new study to measure levels of carbon at various depths in the Arctic Ocean. The study, recently published in…
Read MoreWHOI Study Sheds Light on Tunicate Evolution
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) researchers have filled an important gap in the study of tunicate evolution by genetically sequencing 40 new specimens of thaliaceans, a gelatinous type of tunicate. Their study was featured on the cover of the June issue of the Journal of Plankton Research.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution to Lead Expedition to Measure Radioactive Contaminants in the Pacific Ocean
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will lead the first international, multidisciplinary assessment of the levels and dispersion of radioactive substances in the Pacific Ocean off the Fukushima nuclear power plant—a research effort funded by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
Read MoreNovel Ocean-Crust Mechanism Could Affect World’s Carbon Budget
The Earth is constantly manufacturing new crust, spewing molten magma up along undersea ridges at the boundaries of tectonic plates. The process is critical to the planet?s metabolism, including the cycle of underwater life and the delicate balance of carbon in the ocean and atmosphere. Now, scientists at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have observed ocean crust forming in an entirely unexpected way?one that may influence those cycles of life and carbon and, in turn, affect the much-discussed future of the world?s climate.
Read MoreWHOI To Mark New Lab with Groundbreaking Celebration
Equipped with an $8.1 million federal Recovery Act grant and a shovel, the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will celebrate the groundbreaking of its new Laboratory for Ocean Sensors and Observing Systems (LOSOS) at 11 a.m. on Wednesday, Aug. 4, at the Clark Laboratory on the Institution?s Quissett Campus.
Read MoreMystery Solved: Marine Microbe Is Source of Rare Nutrient
A new study of microscopic marine microbes, called phytoplankton, by researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and the University of South Carolina has solved a ten-year-old mystery about the…
Read More