News Releases
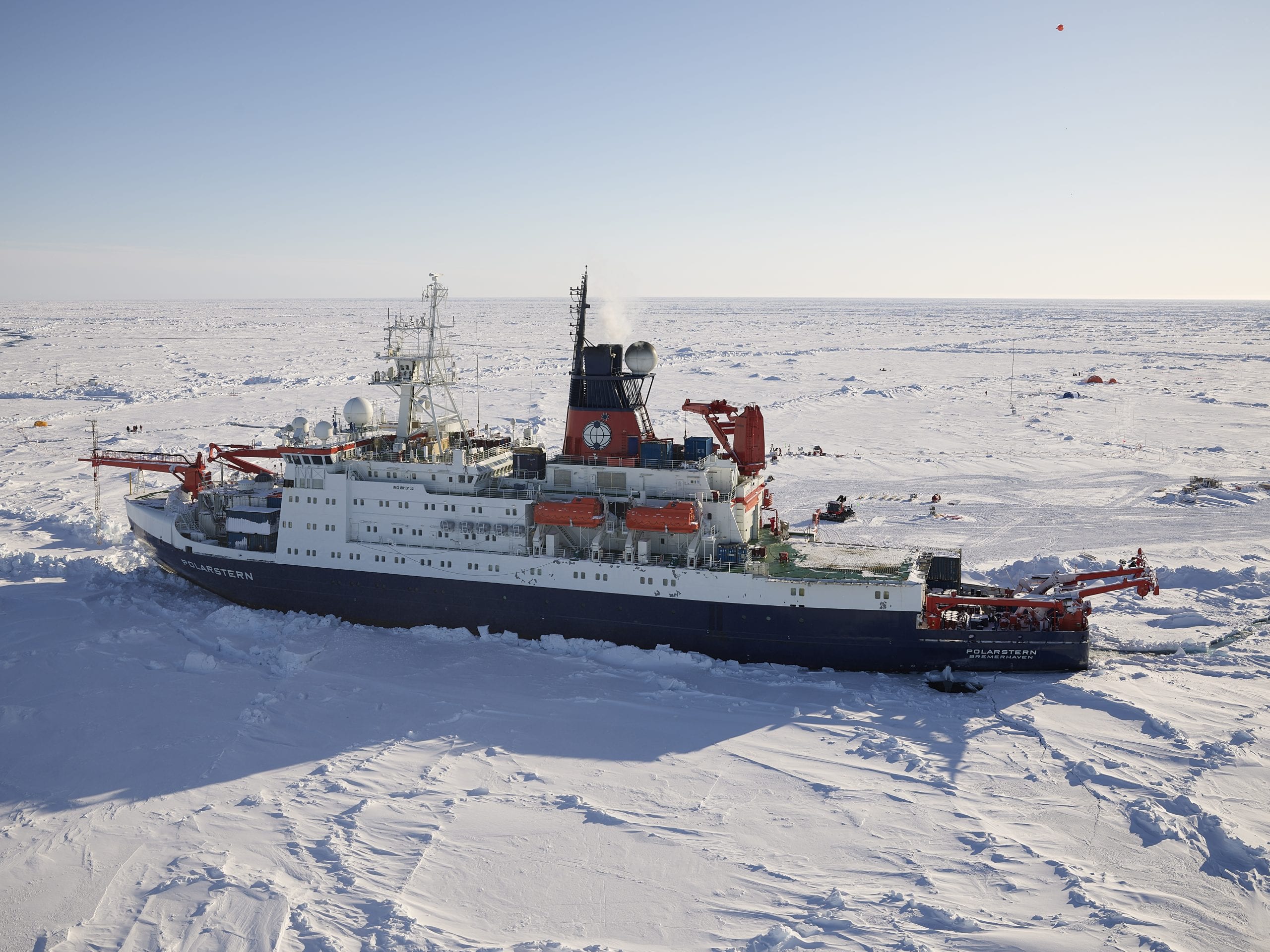
Epic Arctic Mission Ends
An epic mission ended as the German icebreaker Polarstern returned home Oct. 12, 2020, after being frozen near the top of the world for nearly a year to study all aspects of the Arctic system.
Read MoreNew paper addresses the mix of contaminants in Fukushima wastewater
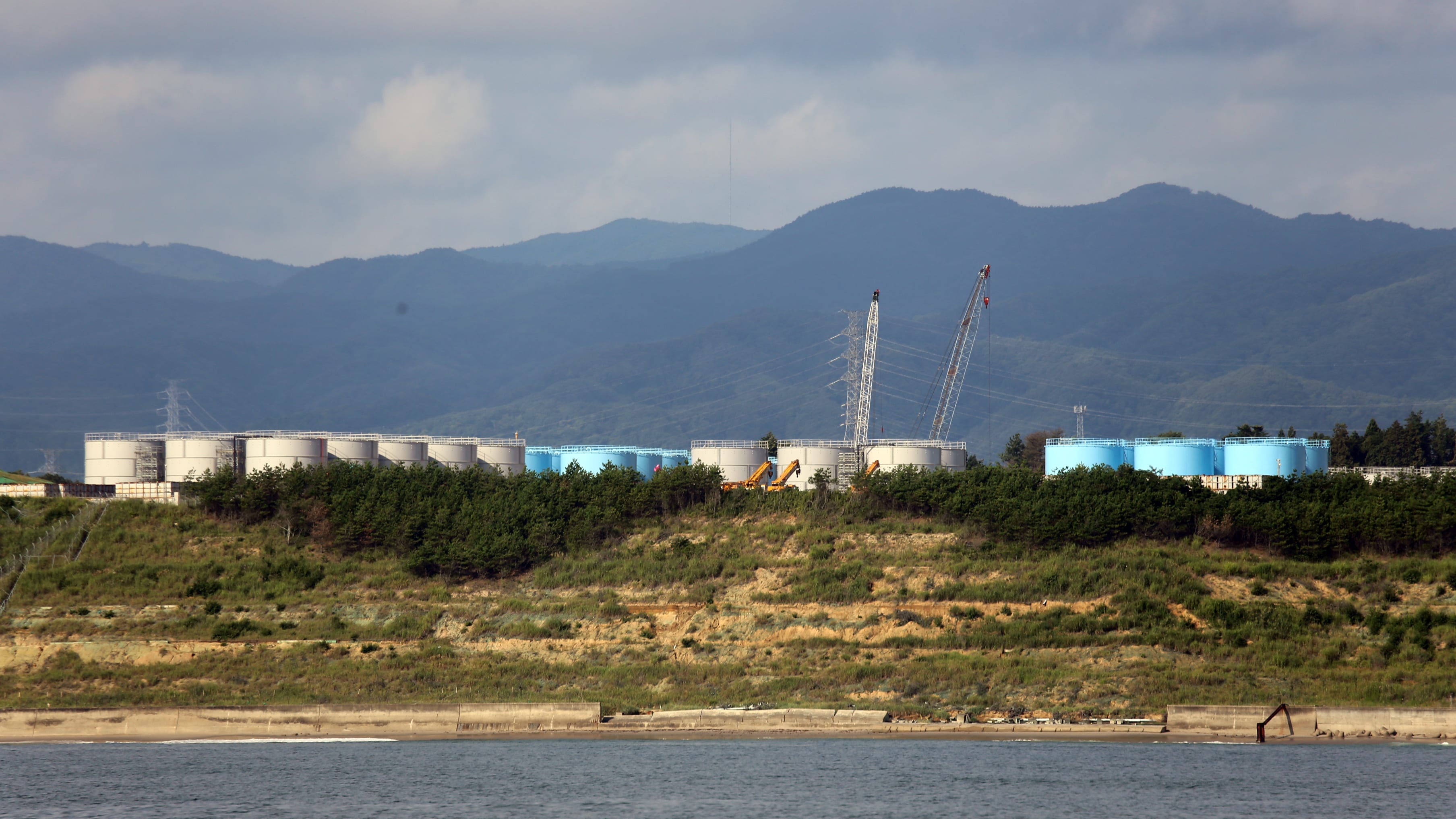
A new study in the journal Science addresses recent suggestions that treated wastewater from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant should be dumped in the ocean.
Read MoreFor Zombie Microbes, Deep-Sea Buffet is Just Out of Reach
Far below the ocean floor, sediments are teeming with bizarre zombie-like microbes. Although they’re technically alive, they grow in slow motion, and can take decades for a single cell to divide – something their cousins at the surface do in a matter of minutes. A new study from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is beginning to pick apart how they survive by examining their source of food, nearby molecules of organic carbon. The study helps further our understanding of the limitations of life on Earth and could help inform how life might exist on other planets.
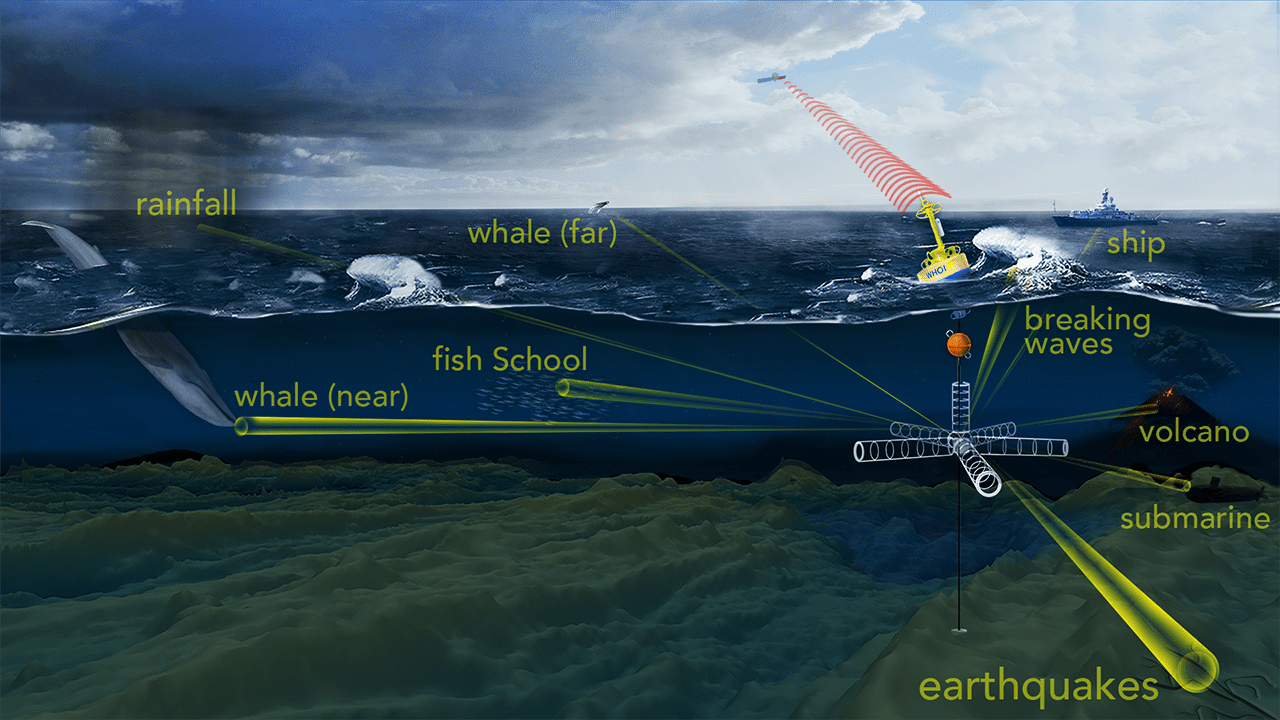
Read More$1 Million Grant to Build the WHOI-Keck Real Time 3-D Acoustic Telescope
A first-of-its-kind acoustic telescope is under development at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), funded by a $1 million grant from the W.M. Keck Foundation, that will permit researchers to…
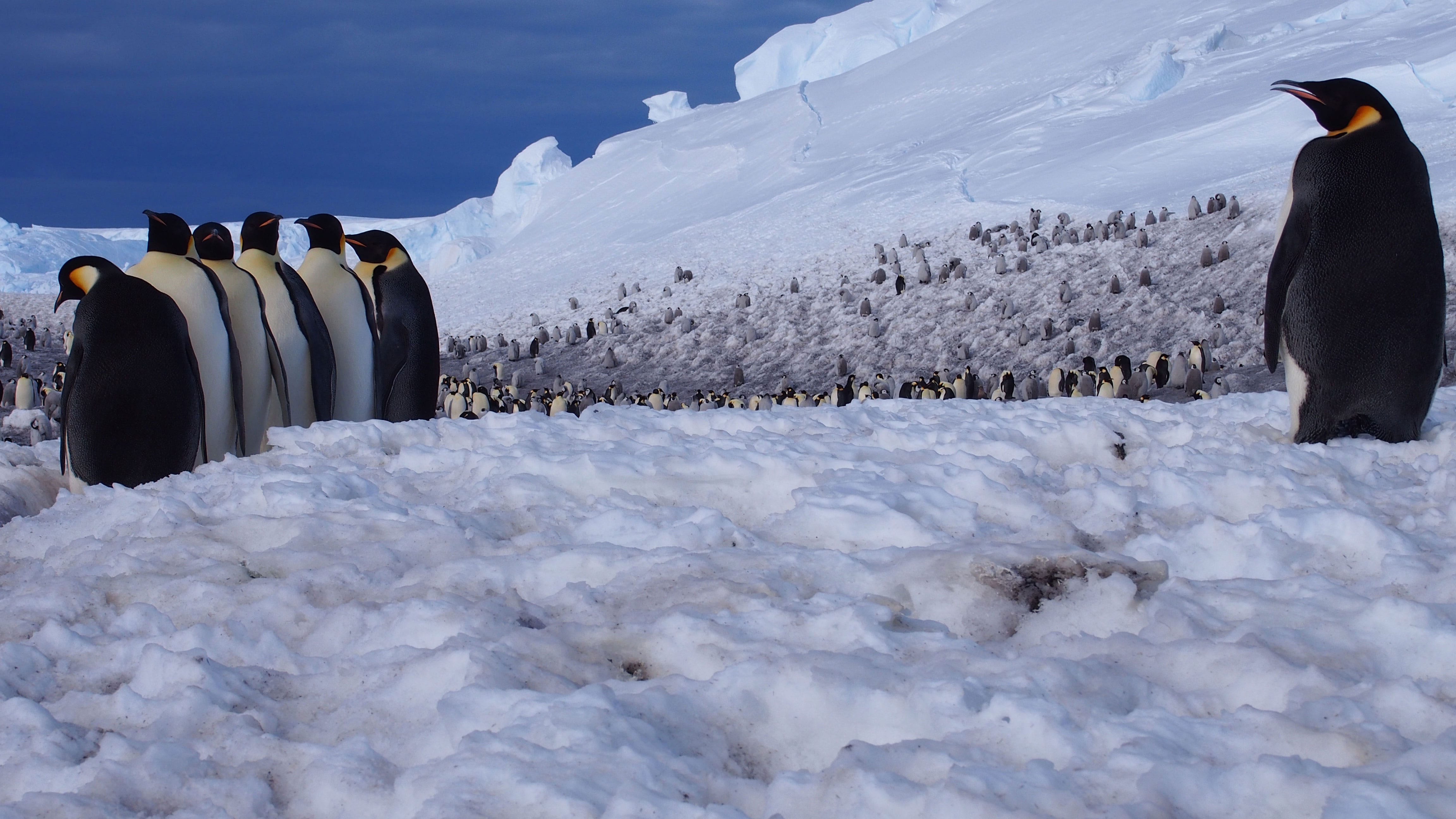
Read MoreAre Emperor Penguins Eating Enough?
For Emperor penguins waddling around a warming Antarctic, diminishing sea ice means less fish to eat. How the diets of these tuxedoed birds will hold up in the face of…
Read MoreHigher Levels of Fukushima Cesium Detected Offshore
Scientists monitoring the spread of radiation in the ocean from the Fukushima nuclear accident report finding an increased number of contaminated sites off the US West Coast, along with the highest detection level to date, from a sample collected about 1,600 miles west of San Francisco. The level of cesium in the sample is 50 percent higher than other samples collected, but is still more than 500 times lower than US government safety limits for drinking water and well below limits of concern for direct exposure while swimming, boating, or other recreational activities.
Ken Buesseler, a marine radiochemist with the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and director of the WHOI Center for Marine and Environmental Radioactivity, was among the first to begin monitoring radiation in the Pacific, organizing a research expedition to the area just three months after the start of the ongoing accident. Through a citizen science sampling effort, Our Radioactive Ocean, as well as research funded by the National Science Foundation, Buesseler and his colleagues are using sophisticated sensors to measure minute levels of ocean-borne radioactivity from Fukushima. In 2015, they have added more than 50 new sample locations in the Pacific to the more than 200 previously collected and posted on the Our Radioactive Ocean web site.
Read MoreTrace Amounts of Fukushima Radioactivity Detected Along Shoreline of British Columbia
Scientists at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have for the first time detected the presence of small amounts of radioactivity from the 2011 Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in a seawater sample from the shoreline of North America. The sample, which was collected on February 19 in Ucluelet, British Columbia, with the assistance of the Ucluelet Aquarium, contained trace amounts of cesium (Cs) -134 and -137, well below internationally established levels of concern to humans and marine life.
Read MoreNew Museum Program Focuses on Impacts of Fukushima on the Ocean
Four years after the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant accident, Japan is still recovering and rebuilding from the disaster. In March 2011 one of the largest earthquakes ever recorded shook Japan, creating a devastating tsunami and damaging the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant. The accident resulted in the largest unintentional release of radioactivity into the ocean in history.
On the fourth anniversary of the disaster, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and the Long Beach, CA-based Aquarium of the Pacific will debut a new program about ocean radioactivity motivated by the Fukushima nuclear accident. The program will be projected daily in the Aquarium’s Ocean Science Center on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Science on a Sphere® and will be made available to more than 100 institutions around the world through NOAA’s SOS Network with a capacity to reach over 50 million combined visitors.
Read MoreStudy Supplies Insight into Behavior of African Monsoon
Think of the Sahara and you will conjure images of a vast desert landscape, with nothing but sand as far as the eye can see. But for a period of about 10,000 years, the Sahara was characterized by lush, green vegetation and a network of lakes, rivers and deltas.
This “green Sahara” occurred between 14,800 and 5,500 years ago during what is known as the “African Humid Period.” Why and how it ended is the subject of scientific study that holds important information for predicting the region’s response to future climate change.
In a study published this week in Nature Geoscience, a team of researchers provides new insight into the behavior of the African monsoon at the end of the African Humid Period and the factors that caused it to collapse.
Read MoreRadioactive Ocean Website Garners Public Support
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has teamed up with the public to build the most comprehensive and up-to-date dataset on marine radiation levels in the aftermath of the 2011 Fukushima…
Read MoreThree Years after Fukushima: Tracking Radionuclides in the Pacific Ocean
Scientists have been keeping a close eye on how radionuclides from the Japanese power plant are being transported in the Pacific Ocean since the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident…
Read MoreRadioactive Ocean Website a Success
With concern among the public over the plume of radioactive ocean water from Fukushima arriving on the West Coast of North America and no U.S. government or international plan to…
Read MoreHow Radioactive is Our Ocean?
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) marine chemist Ken Buesseler began sampling and analyzing seawater surrounding the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant three months after the 2011 disaster. Today, he launched…
Read MoreWHOI to Host Public Event on Fukushima and the Ocean
Japan’s “triple disaster,” as it has become known, began on March 11, 2011, with a magnitude 9.0 earthquake—the fourth largest ever recorded. Following the quake, a 40 to 50-foot tsunami…
Read MoreFishing for Answers off Fukushima
Japan’s “triple disaster,” as it has become known, began on March 11, 2011, and remains unprecedented in its scope and complexity. To understand the lingering effects and potential public health…
Read MoreSampling the Pacific for Signs of Fukushima
An international research team is reporting the results of a research cruise they organized to study the amount, spread, and impacts of radiation released into the ocean from the tsunami-crippled…
Read MoreStudy Links Major Shifts in Indian Civilizations to Past Changes in Monsoon
A fundamental shift in the Indian monsoon has occurred over the last few millennia, from a steady humid monsoon that favored lush vegetation to extended periods of drought, reports a new study led by researchers at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI). The study has implications for our understanding of the monsoon’s response to climate change.
Read MoreSpecial Fukushima Session at 2012 Ocean Sciences Meeting
The March 11, 2011, earthquake, tsunami, and subsequent radioactivity releases from the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plants resulted in the largest accidental release of radiation to the ocean in history.…
Read MoreResearchers Assess Radioactivity Released to the Ocean from the Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Facility
The impact on the ocean of releases of radioactivity from the Fukushima nuclear power plants remains unclear. But a new study by U.S. and Japanese researchers analyzes the levels of radioactivity discharged from the facility in the first four months after the accident and draws some basic conclusions about the history of contaminant releases to the ocean.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution Hosts Visit by Senator Scott Brown
On Monday, Aug. 15, U.S. Senator Scott Brown visited the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the world-renowned research and education organization based on Cape Cod. The visit was Browns first to WHOI.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution to Lead Expedition to Measure Radioactive Contaminants in the Pacific Ocean
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will lead the first international, multidisciplinary assessment of the levels and dispersion of radioactive substances in the Pacific Ocean off the Fukushima nuclear power plant—a research effort funded by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
Read More