News Releases
Ancient groundwater records reveal regional vulnerabilities to climate change
New WHOI-led study shows the Southwest may be more sensitive to drying than the Pacific Northwest
Read MoreSea Surface Temperature Research Provides Clear Evidence of Human-Caused Climate Change
New oceanic research provides clear evidence of a human “fingerprint” on climate change and shows that specific signals from human activities have altered the seasonal cycle amplitude of sea surface temperatures.
Read MoreVitamin B12 adaptability in Antarctic algae has implications for climate change
Woods Hole, Mass. — Vitamin B12 deficiency in people can cause a slew of health problems and even become fatal. Until now, the same deficiencies were thought to impact certain…
Read MoreEvidence of Climate Change in the North Atlantic can be Seen in the Deep Ocean, Study Finds
Woods Hole, Mass. –Evidence of climate change in the North Atlantic during the last 1,000 years can be seen in the deep ocean, according to a newly published paper led…
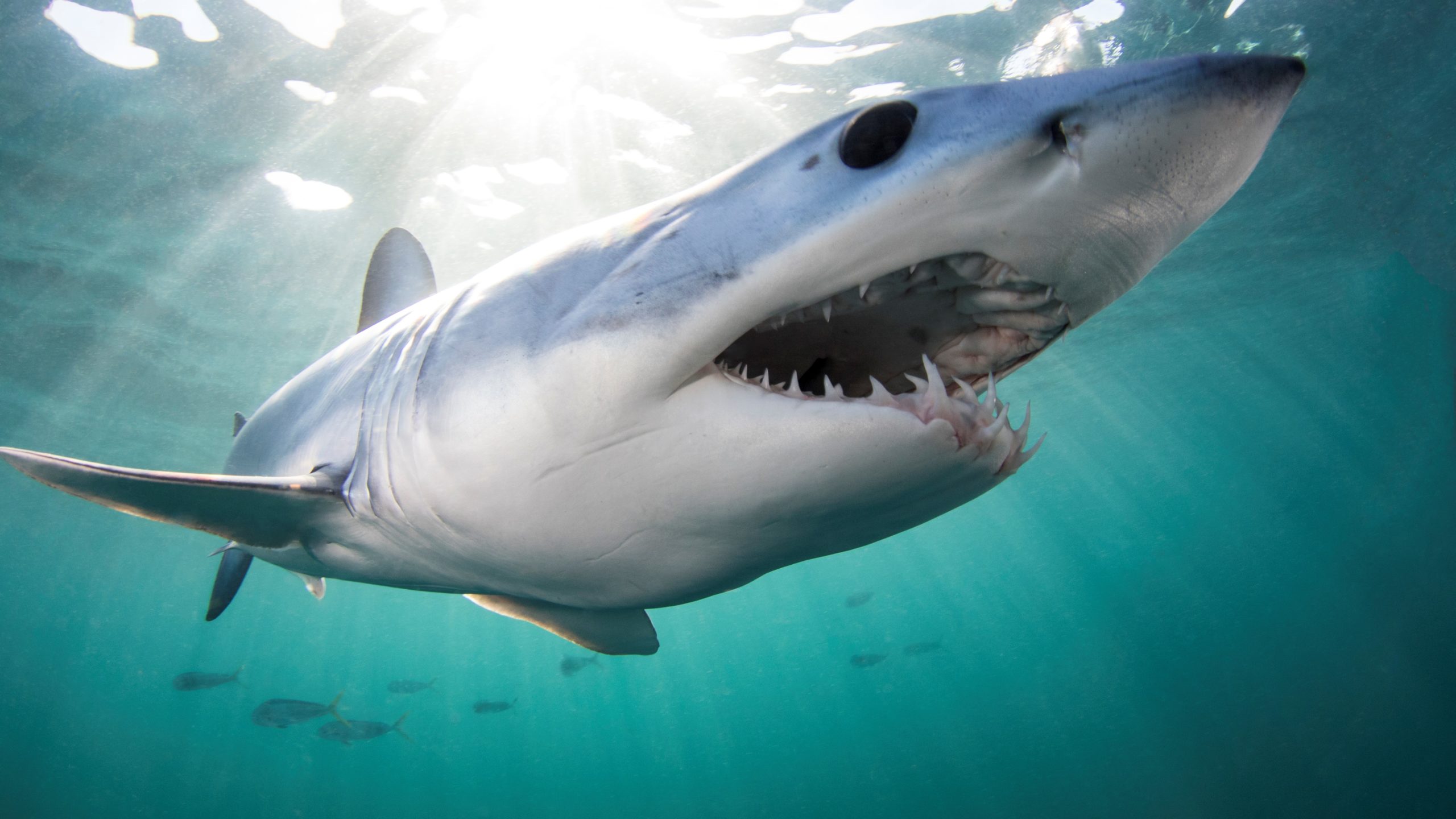
Read MoreTop Fish Predators Could Suffer Wide Loss of Suitable Habitat by 2100 Due to Climate Change
The impacts of climate change on habitats are already evident Woods Hole, MA — A study of 12 species of highly migratory fish predators—including sharks, tuna, and billfish such as…
Read MoreAtmospheric Research Provides Clear Evidence of Human-Caused Climate Change Signal Associated with CO2 Increases
Claims that Climate Change Is Natural are Inconsistent with Atmospheric Temperature Trends
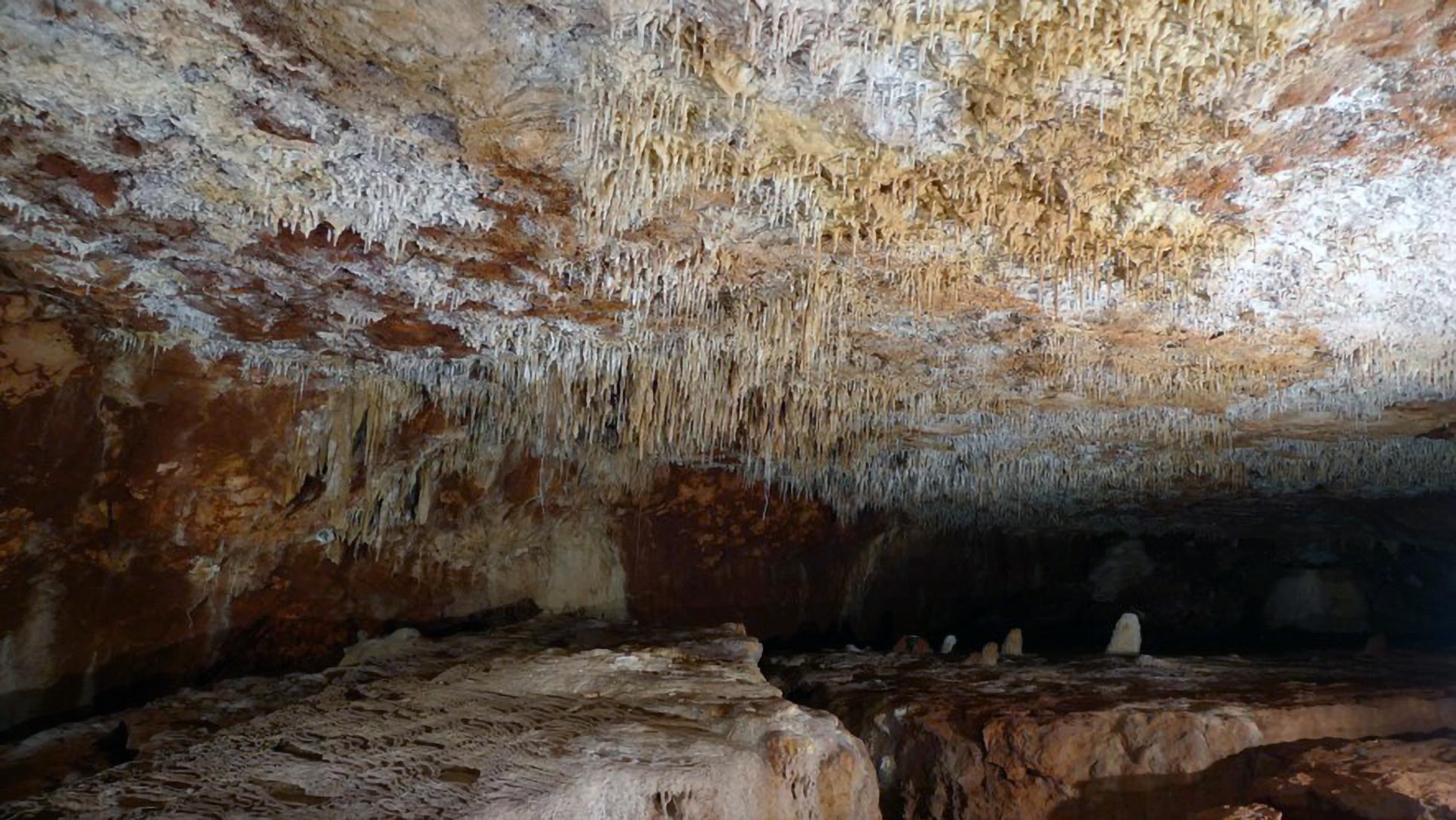
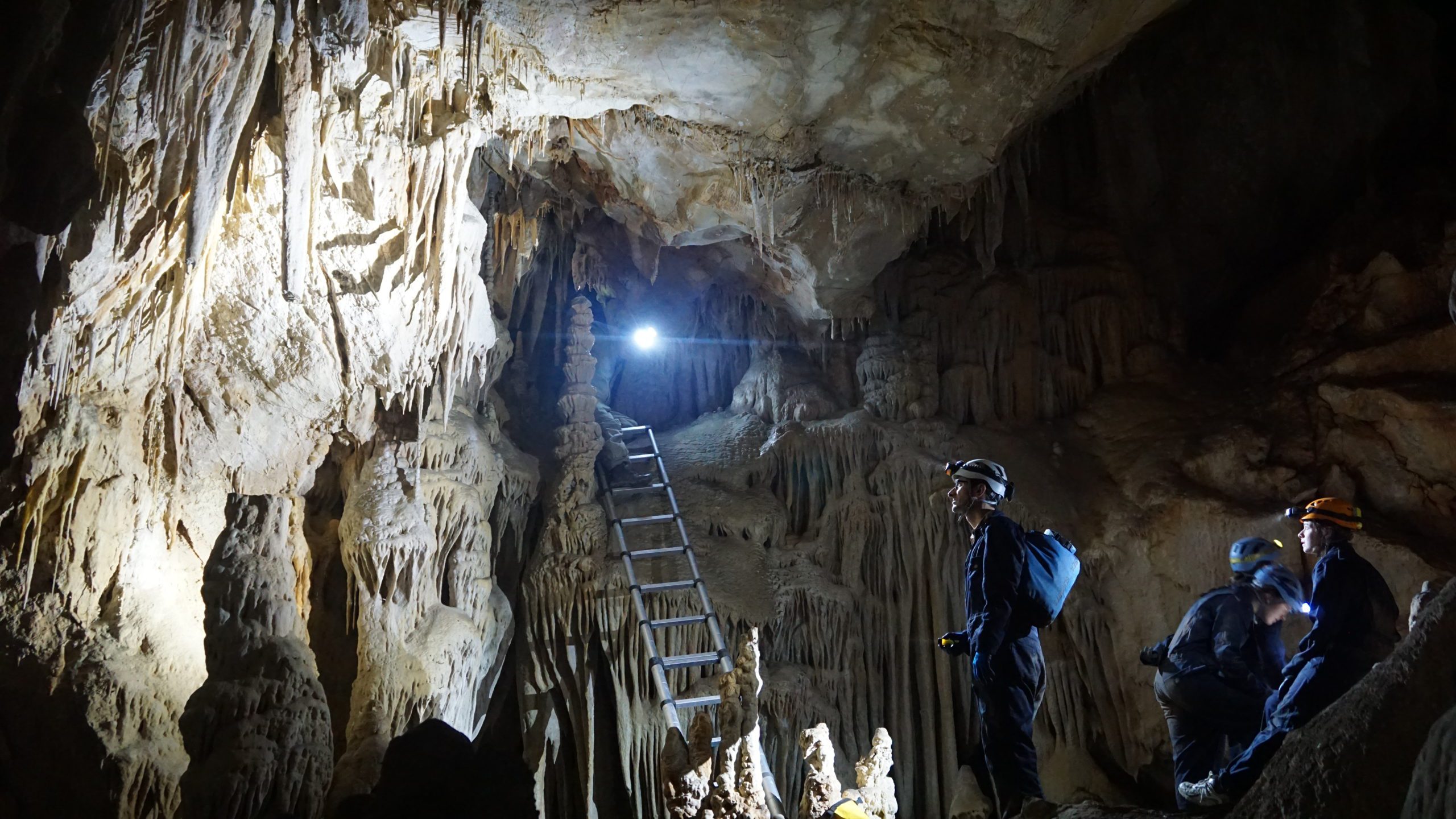
Read MoreResearch reveals new links behind climate change in Australia
A team of scientists, including those from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), have combined stalagmites and climate model simulations to reveal links between monsoon rains and tropical cyclones in Australia.
Read MoreScientists link the changing Azores High and the drying Iberian region to anthropogenic climate change
Projected changes in wintertime precipitation make agriculture in the Iberian region some of the most vulnerable in Europe, according to a new WHOI co-led study that links the changes to increased anthropogenic greenhouse gases.
Read MoreClimate change could lead to a dramatic temperature-linked decrease in essential omega-3 fatty acids
The effects of global climate change already are resulting in the loss of sea ice, accelerated sea level rise, and longer and more intense heat waves, among other threats. Now, the first-ever survey of planktonic lipids in the global ocean predicts a temperature-linked decrease in the production of essential omega-3 fatty acids, an important subset of lipid molecules.
Read MoreResilient Woods Hole releases new, interactive tools to prepare for climate change
ResilientWoodsHole (RWH) initiative releases new interactive website tools to further engage the local community in its collective goal of securing a climate-resilient future for the coastal village of Woods Hole
Read MoreThe ocean twilight zone’s role in climate change
A new report from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Ocean Twilight Zone (OTZ) project team offers a detailed look at the climate-altering processes that take place within the zone, in particular those that are driven by animals that migrate between the twilight zone and the surface each night to feed. This phenomenon is likely the biggest migration on Earth—yet it remains incredibly vulnerable to human exploitation.
Read MoreA recent reversal in the response of western Greenland’s ice caps to climate change
New collaborative research from the WHOI and five partner institutions published today in Nature Geoscience, reveals that during past periods glaciers and ice caps in coastal west Greenland experienced climate conditions much different than the interior of Greenland. Over the past 2,000 years, these ice caps endured periods of warming during which they grew larger rather than shrinking.
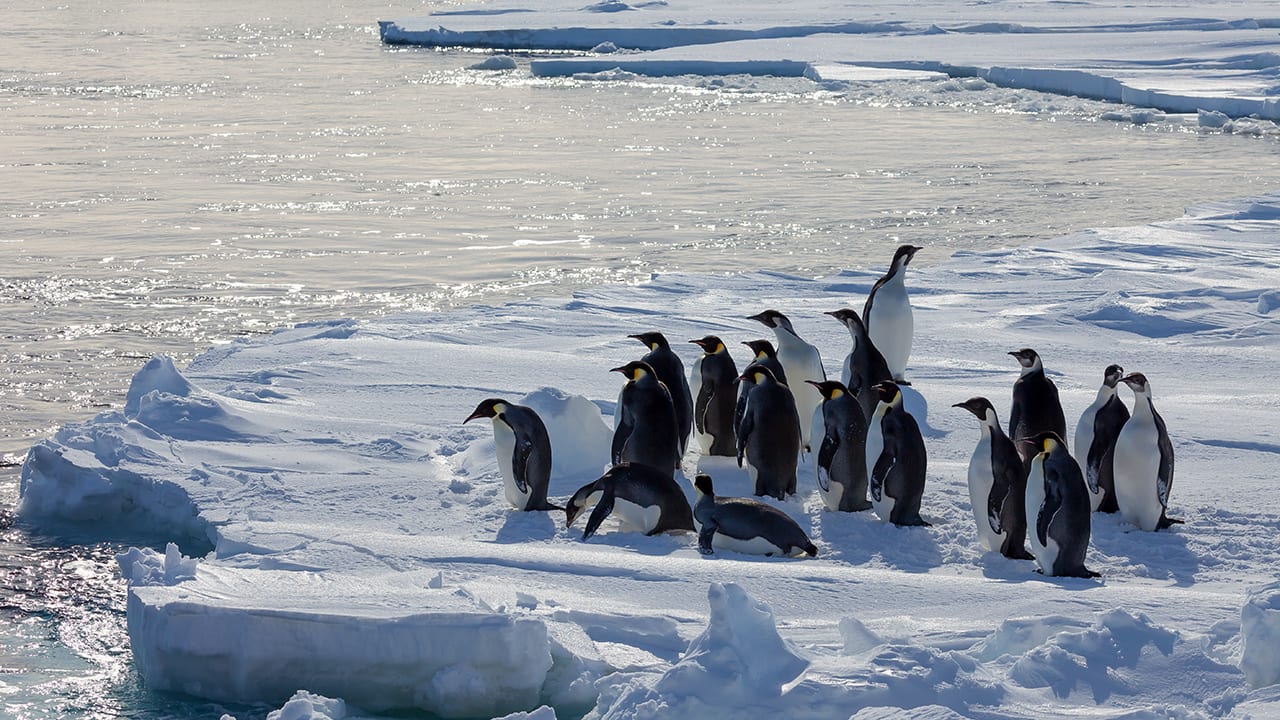
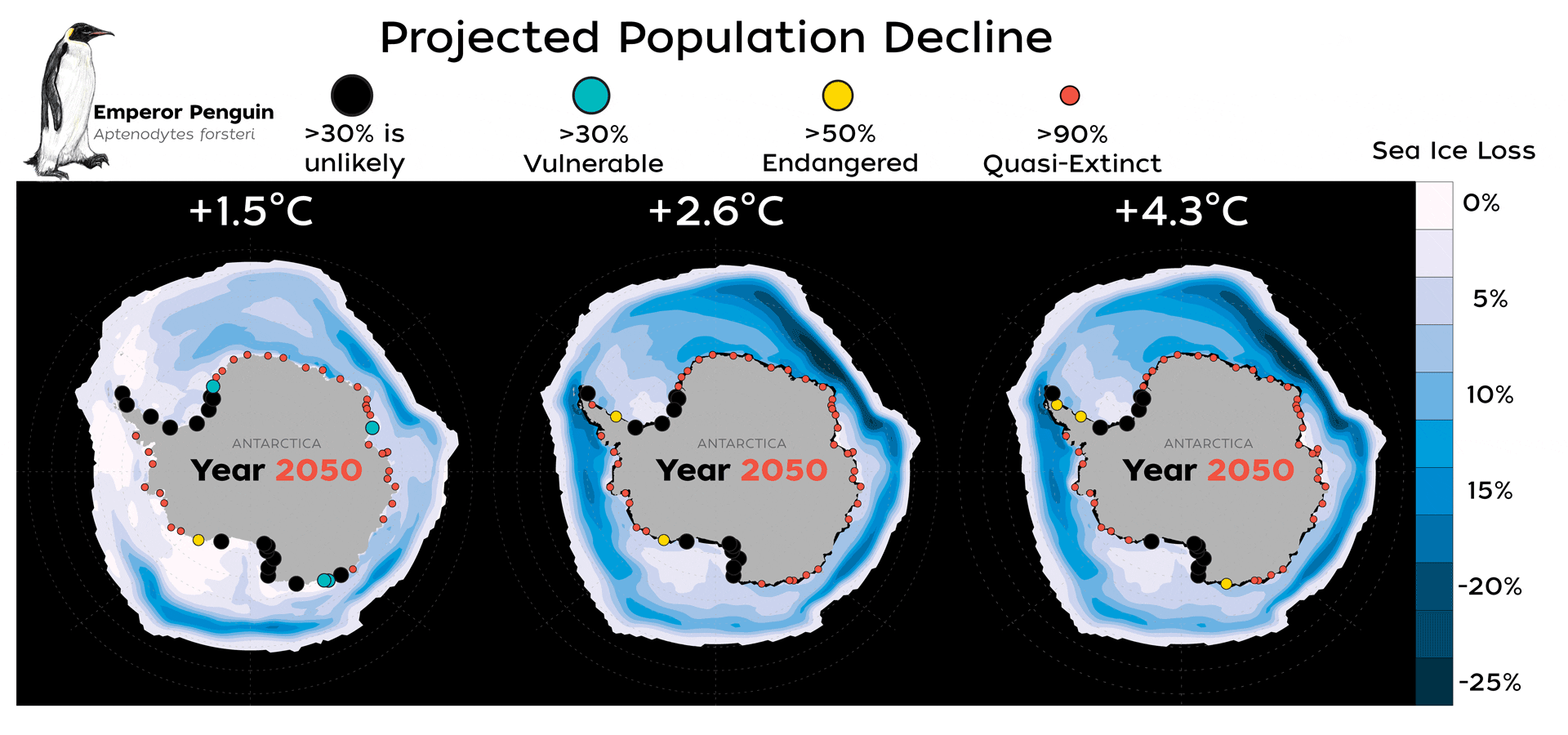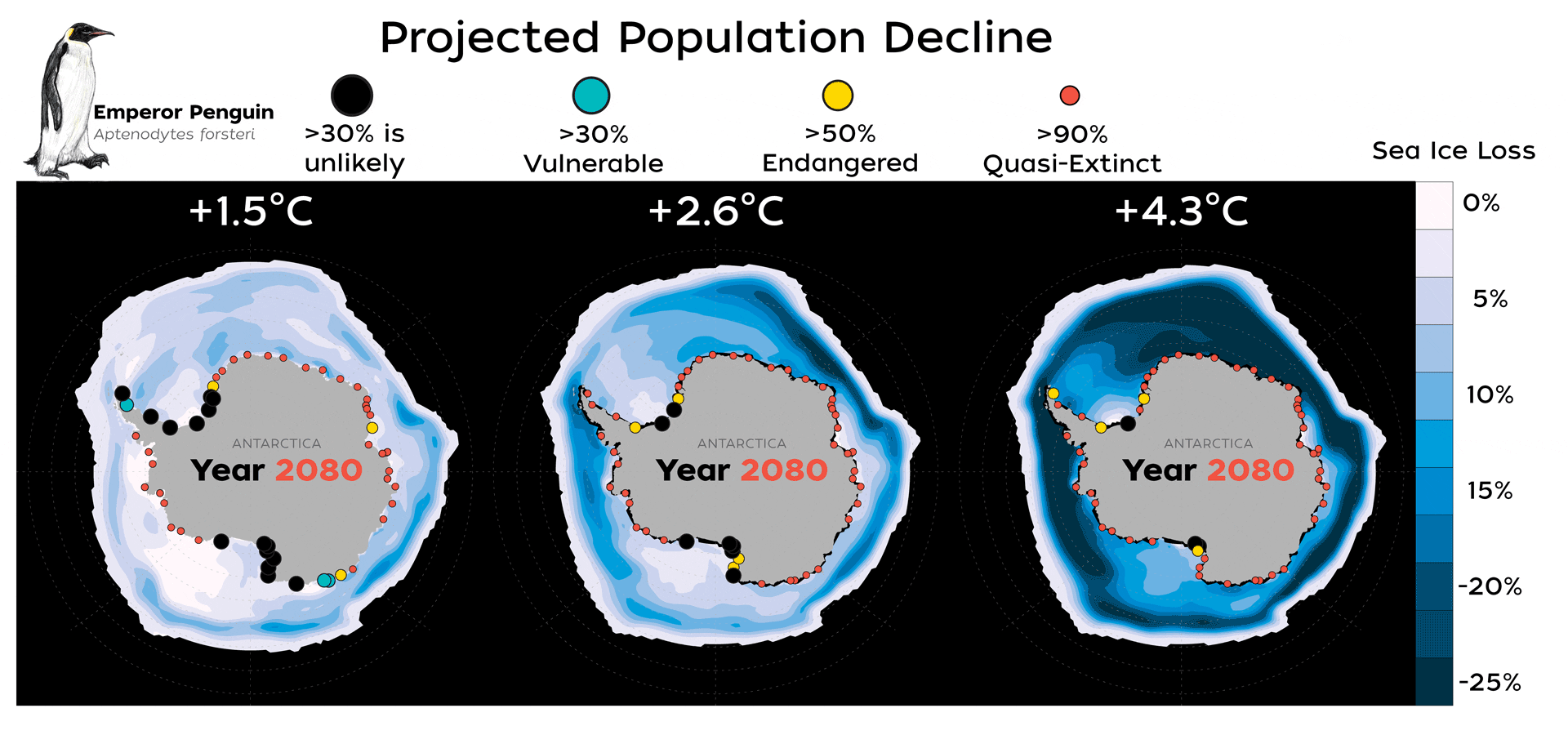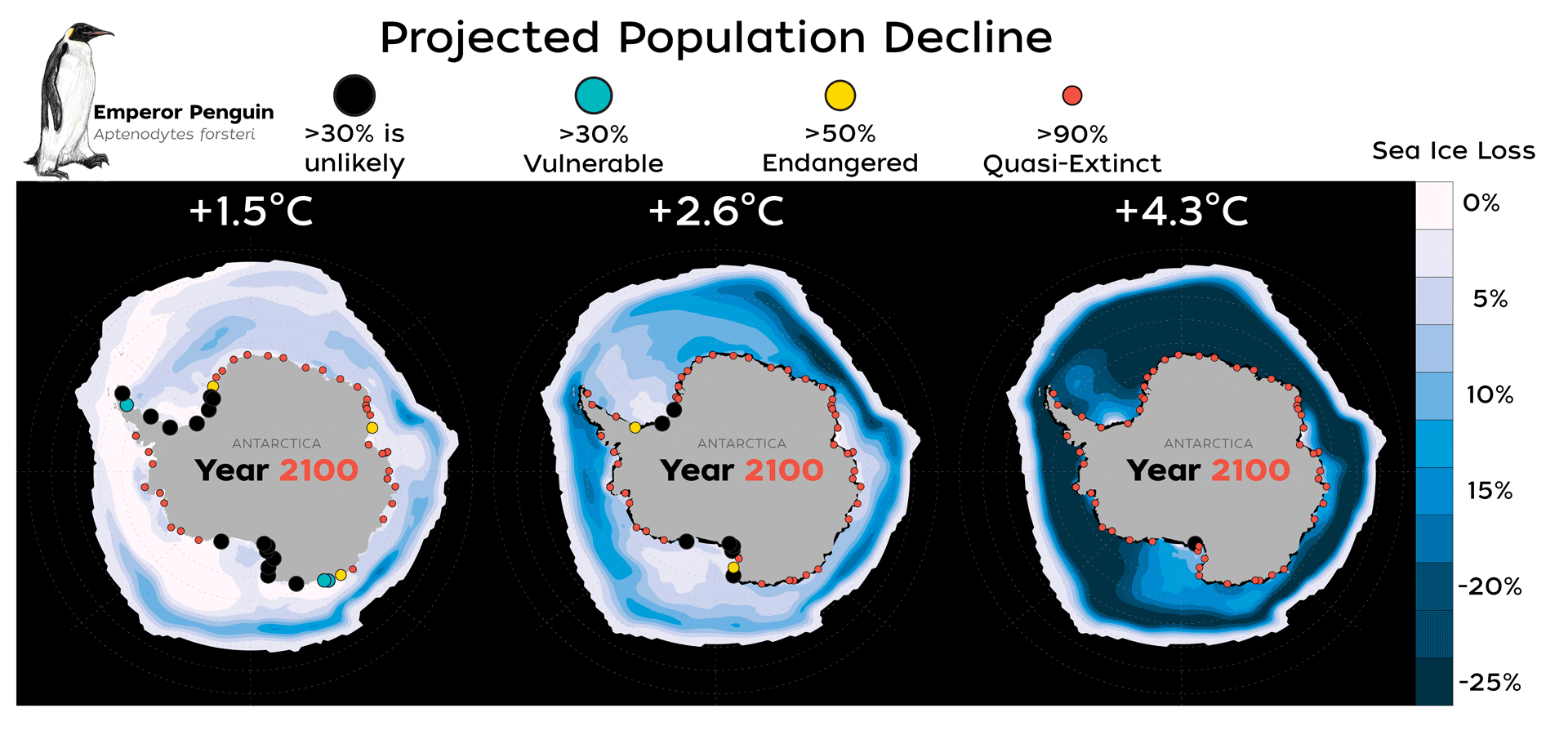
Read MoreNew Study Finds Emperor Penguins Increasingly Threatened by Climate Change
A new study published today in Global Change Biology provides valuable new data that highlights how species extinction risk is accelerating due to rapid climate change and an increase in extreme climate events, such as glacial calving and sea ice loss.
Read MoreSome Forams Could Thrive with Climate Change, Metabolism Study Finds
Oceanic deoxygenation is increasingly affecting marine ecosystems. A new paper that examines two foram species found that they demonstrated great metabolic versatility to flourish in hypoxic and anoxic sediments where there is little or no dissolved oxygen, inferring that the forams’ contribution to the marine ecosystem will increase with the expansion of oxygen-depleted habitats.
Read MoreClimate Change Can Destabilize the Global Soil Carbon Reservoir, New Study Finds
The vast reservoir of carbon that is stored in soils probably is more sensitive to destabilization from climate change than has previously been assumed, according to a new study by…
Read MoreAntarctic Ice Sheet Loss Expected to Affect Future Climate Change
The research team reports that their new models with the added ice melt information reveal important interacting processes and demonstrate a need to accurately account for meltwater input from ice sheets in order to make confident climate predictions.
Read MoreStudy reveals Missoula Floods impact on past abrupt climate changes
A new study shows for the first time how massive flood events in the eastern North Pacific Ocean—known as the Missoula Floods—may have in part triggered abrupt climate changes in the Northern Hemisphere during the last deglaciation (approximately 19,000–11,700 years ago).
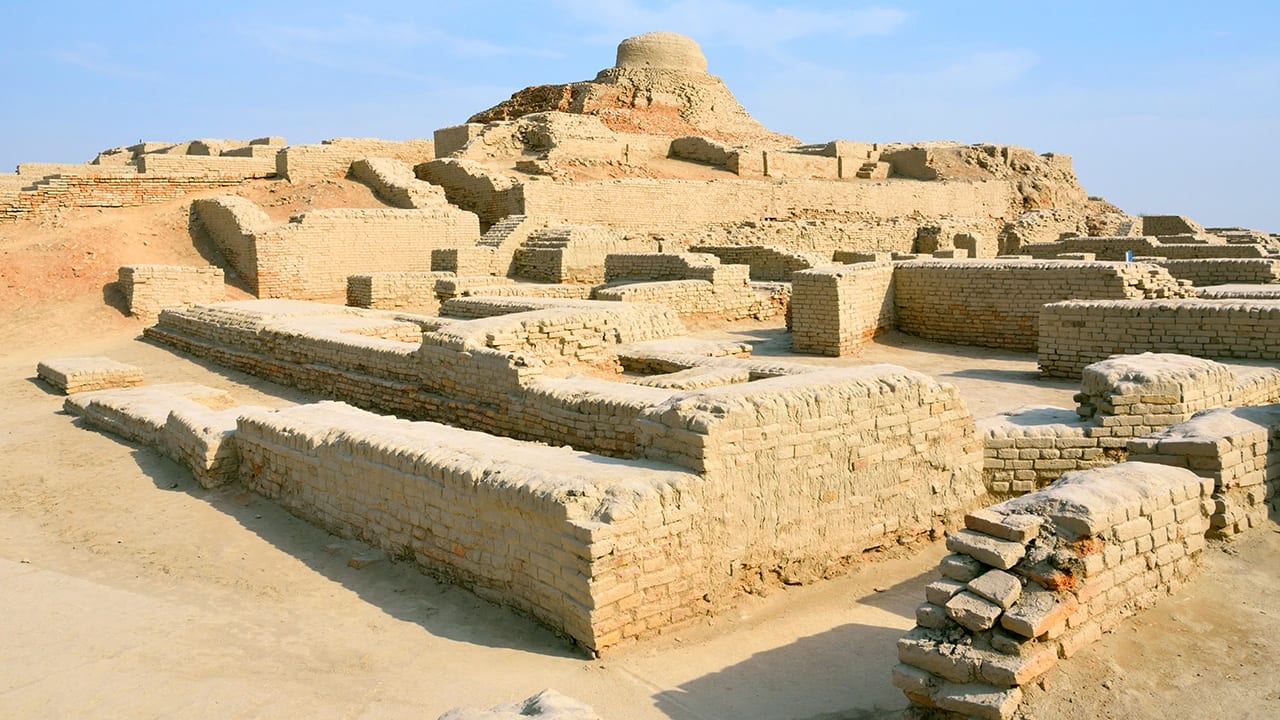
Read MoreClimate Change Likely Caused Migration, Demise of Ancient Indus Valley Civilization
More than 4,000 years ago, the Harappa culture thrived in the Indus River Valley of what is now modern Pakistan and northwestern India, where they built sophisticated cities, invented sewage systems that predated ancient Rome’s, and engaged in long-distance trade with settlements in Mesopotamia. Yet by 1800 BCE, this advanced culture had abandoned their cities, moving instead to smaller villages in the Himalayan foothills. A new study from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) found evidence that climate change likely drove the Harappans to resettle far away from the floodplains of the Indus.
Read MoreFinding New Homes Won’t Help Emperor Penguins Cope with Climate Change
Unlike other species that migrate successfully to escape the wrath of climate change, a new study shows that dispersal may help sustain global Emperor penguin populations for a limited time, but, as sea ice conditions continue to deteriorate, the 54 colonies that exist today will face devastating declines by the end of this century.
Read MoreStudy Reveals Climate Change Impacts on Buzzards Bay
Utilizing 22 years of data collected by a network of citizen scientists, researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and their colleagues at the Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program, the Buzzards Bay Coalition, and the Marine Biological Laboratory found that average summertime temperatures in embayments throughout Buzzards Bay warmed by almost 2 degrees Celsius—roughly 4 degrees Fahrenheit.
Read MoreClimate Change Will Irreversibly Force Key Ocean Bacteria into Overdrive
A new study from University of Southern California and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) shows that changing conditions due to climate change could send Tricho into overdrive with no way to stop – reproducing faster and generating lots more nitrogen. Without the ability to slow down, however, Tricho has the potential to gobble up all its available resources, which could trigger die-offs of the microorganism and the higher organisms that depend on it.
Read MoreClimate Change Winners and Losers
The Antarctic Peninsula, the northern most region of Antarctica, is experiencing some of the most dramatic changes due to climate warming, including population declines of some penguin species. This is…
Read MoreWHOI Hosts Public Forum and Art Exhibit on Impacts of Climate Change to Polar Animals
No place on the planet is more vulnerable to climate change than the polar regions of the Arctic and the Antarctic. Warming waters and the loss of sea ice are…
Read MoreClimate Change Led to Collapse of Ancient Indus Civilization, Study Finds
A new study combining the latest archaeological evidence with state-of-the-art geoscience technologies provides evidence that climate change was a key ingredient in the collapse of the great Indus or Harappan Civilization almost 4000 years ago. The study also resolves a long-standing debate over the source and fate of the Sarasvati, the sacred river of Hindu mythology.
Read More