Cruise
Log: Tuesday, April 6, 2004
|
March
|
|
Sun
|
Mon
|
Tue
|
Wed
|
Thu
|
Fri
|
Sat
|
|
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
|
7
|
8
|
9
|
10
|
11
|
12
|
13
|
|
14
|
15
|
16
|
17
|
18
|
19
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
April
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16
|
17
|
|
18
|
19
|
20
|
21
|
22
|
23
|
24
|
|
25
|
26
|
27
|
28
|
29
|
30
|
|
|
| |
|
| Team
CO2: Kim Currie and Burns Macaskill in the lab (Matt Walkington). |
| |
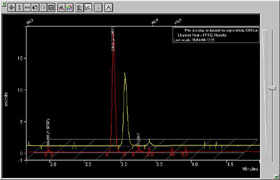 |
|
Chromatograms showing the quantity of DMS in the water (Credit: Steve
Archer). |
| |
 |
| Crooning
albatross (Photo by Murray Smith). |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
 |
|
Ribbon plot of pCO2 showing variations in different water masses with
different temperatures and biology (Credit: Kim Currie). |
A sign
of things to come?
Contributors: Kim Currie (NIWA)
Burns Macaskill (NIWA)
Steve Archer (PML, UK)
It's a clear, calm, low-flux
day here in the patch, though we are hardly aware of that in our lab down
in the bowels of the ship. The CO2 lab is below the water line - a nice
stable place in the ship, though we can't tell if it's day or night, sunny
or cloudy. Twice a day we emerge to take water samples from the CTD casts
(in-patch and out-patch stations) then it's back below to analyze the water
for pH and alkalinity, from which we calculate total inorganic carbon concentration.
In the lab we also have two systems carrying out measurements while underway
- taking near-surface water from the ship's seawater supply to analyze for
pCO2 and pH. The data is used to determine the carbonate chemistry of the
seawater. Phytoplankton use carbon from the water for photosynthesis, so
as a bloom develops there is a concurrent decrease in the carbon concentration,
resulting in a decrease in pCO2 and an increase in pH. While tantalizing
changes have been seen in the biology, a dramatic bloom has not yet developed
(which is of great interest to the biologists) and so we cannot yet see
any change in these seawater chemical properties.
 |
| Careful
sampling of pH from the rosette (Photo by Matt Walkington). |
Team CO2 consists of
two people: Kim Currie (NIWA, Dunedin) and Burns Macaskill (NIWA, Hamilton).
Malcolm Reid (University of Otago) gives shore-based assistance. A decrease
in pCO2 in the surface water will lead to an enhanced flux of atmospheric
carbon dioxide into the ocean. Our data will be combined with that from
the atmospheric CO2 measurements (Rona Thompson), and the piston velocity
determinations (David Ho and Cliff Law).
There's a smidgen of
a hint of a rise in the concentration of dimethyl sulphide in the water
today. Dimethyl sulphide (or DMS) is one of the climate-relevant gases that
we are interested in (see Dawn Devries' explanation on April
4). It is derived from a compound produced by microalgae and a complex
network of processes governs how much DMS enters the atmosphere, where it
may have a cooling effect on the planet. For possibly the first time (you
don't always know what other research is going on in parallel around the
world), we have the capability of looking at both the processes in the water
column that produce DMS (Graham Jones, Karl Safe and myself) and the really
novel capability to measure its transfer rate and fate in the atmophere
at sea (Mike Harvey, Murray Smith, Jill Cainey and Dawn Devries).
The figure illustrates
the chromatograms from 6th and 4th April for the surface waters in the
iron enriched patch. The two large peaks correspond to the quantity of
DMS. Due to the detection method, the difference is exaggerated in the
figure but the increase is real enough to get excited about. Is it going
to continue to rise and is this different from the surrounding waters
without the added iron? There have been a number of tantalizing indicators
that the microalgae are starting to escape the constraints that have held
their population growth in check. If they do break free, we could be in
for an interesting few days. If they don't, one of the fascinating questions
to come out of our study will be what's holding them back?
During the day
the small RHIB workboat of the Tangaroa was deployed several times, the
met balloon was released and Murray and Mike were doing some vertical
profiling of DMS concentration in the atmosphere. The sunny weather gave
an opportunity to measure some of the gases generated by sunlight interactions
in the near-surface waters. Deck incubation experiments are investigating
the effects of micronutrients, light levels and grazing on phytoplankton
growth. This data may help explain why a bloom has not yet developed.
A further infusion of iron and tracer gas (SF6) will be released this
evening. Next Day>>
 |
| The
Tangaroa produces a fun wave; it is likely that many marine animals
including the cetaceans can sense chemicals like DMS, even at low
seawater concentrations (Photo by Steve Archer). |
|