News Releases
A new way of looking at plastics
WHOI researchers develop a new sustainability metric for plastic products
Read MoreOcean Pavilion Partners Unveil COP28 Dubai Ocean Declaration
Declaration recognizes the critical role of the ocean in regulating climate change, calls for increased ocean observations
Read MoreWHOI chemist given prestigious award
The award recognizes individuals who “materially increase the public’s knowledge of chemistry, chemical engineering, and related fields.”
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution Elects New Trustee and Corporation Members
The Board of Trustees of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) today welcomed one new Board Member and eight new Corporation Members.
Read MoreMapping the potential path of nuclear wastewater
WHOI Sea Grant will study spreading pathways from Pilgrim Nuclear Power Station
Read MoreWHOI Marine Chemist Shares Hard Won Advice for Communicating in the Face of Environmental Disasters
Science Communications in a Crisis: An Insider’s Guide draws on decades of experience
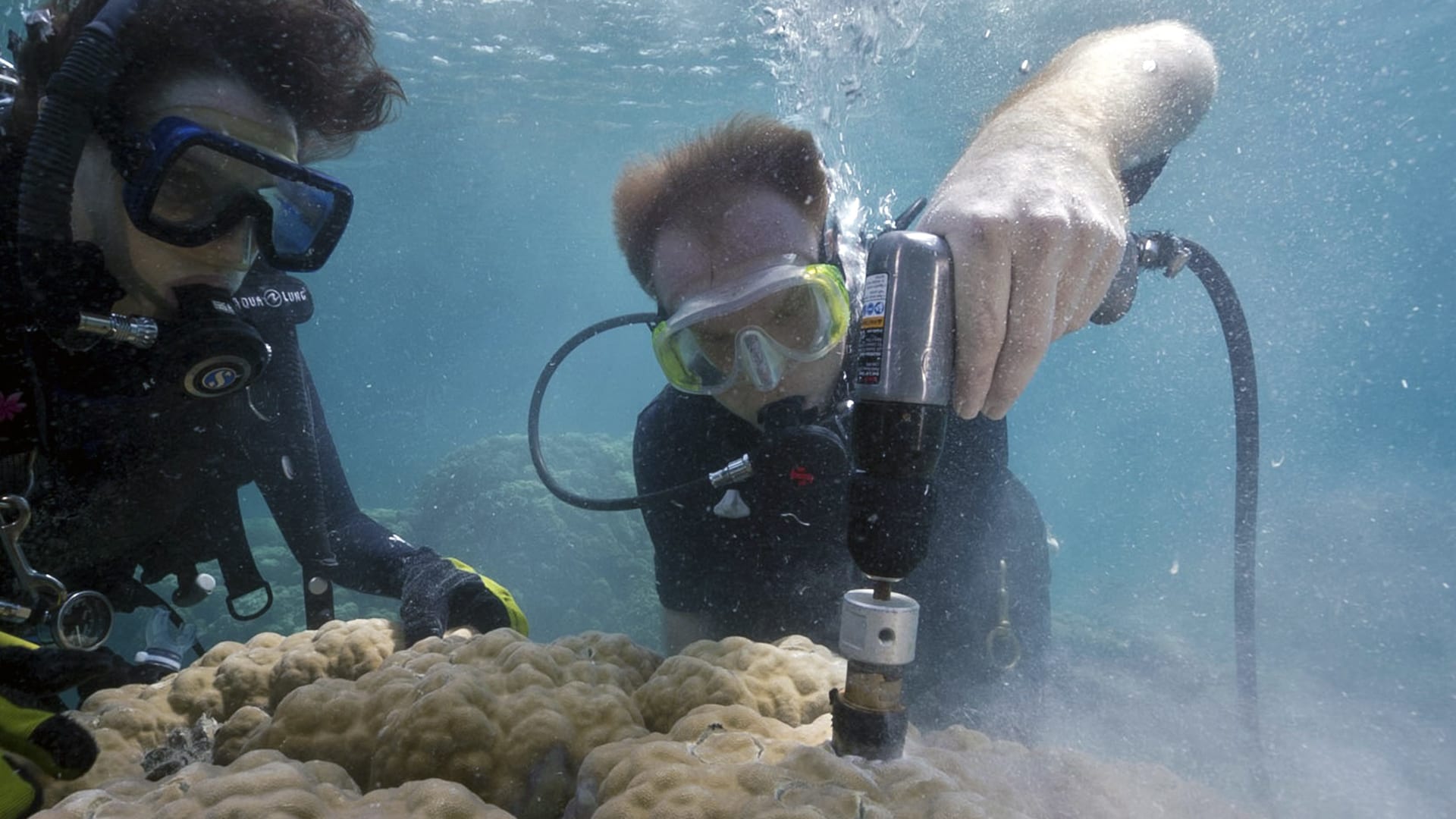
Read MoreToward a New Era of Reef Solutions
WHOI coral reef researchers propose a new technology-centered focus to study and conserve coral reefs
Read MoreExcess Nutrients Lead to Dramatic Ecosystem Changes in Cape Cod’s Waquoit Bay
The Bay Is a harbinger for estuaries worldwide, say researchers
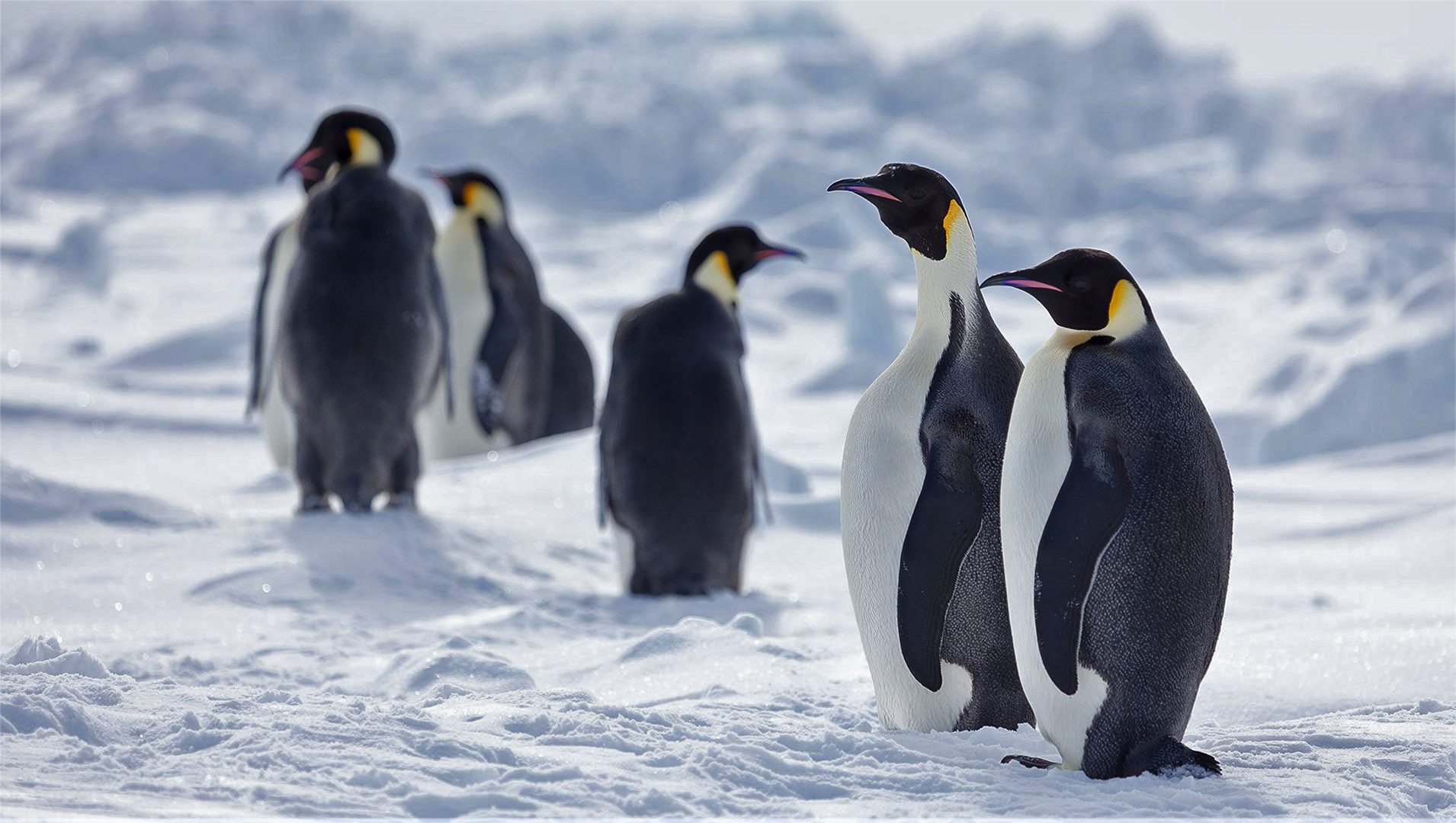
Read MoreEmperor penguins granted protections under Endangered Species Act
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution among research groups that offer key findings to support federal protection of species, increasingly under siege by climate change
Read MoreWHOI-led projects receive UN endorsement as part of Decade of Ocean Science
Four projects led or co-led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientists were named on World Ocean Day by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) to receive Endorsed Action status as part of the UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development 2021-2030.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s “Ocean Encounters” nominated for Webby Award
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s virtual education series, Ocean Encounters, has been nominated for a People’s Voice Webby Award in the Virtual and Remote – Series, Health and Science category, and was also named an honoree in the Virtual and Remote: Best Series category.
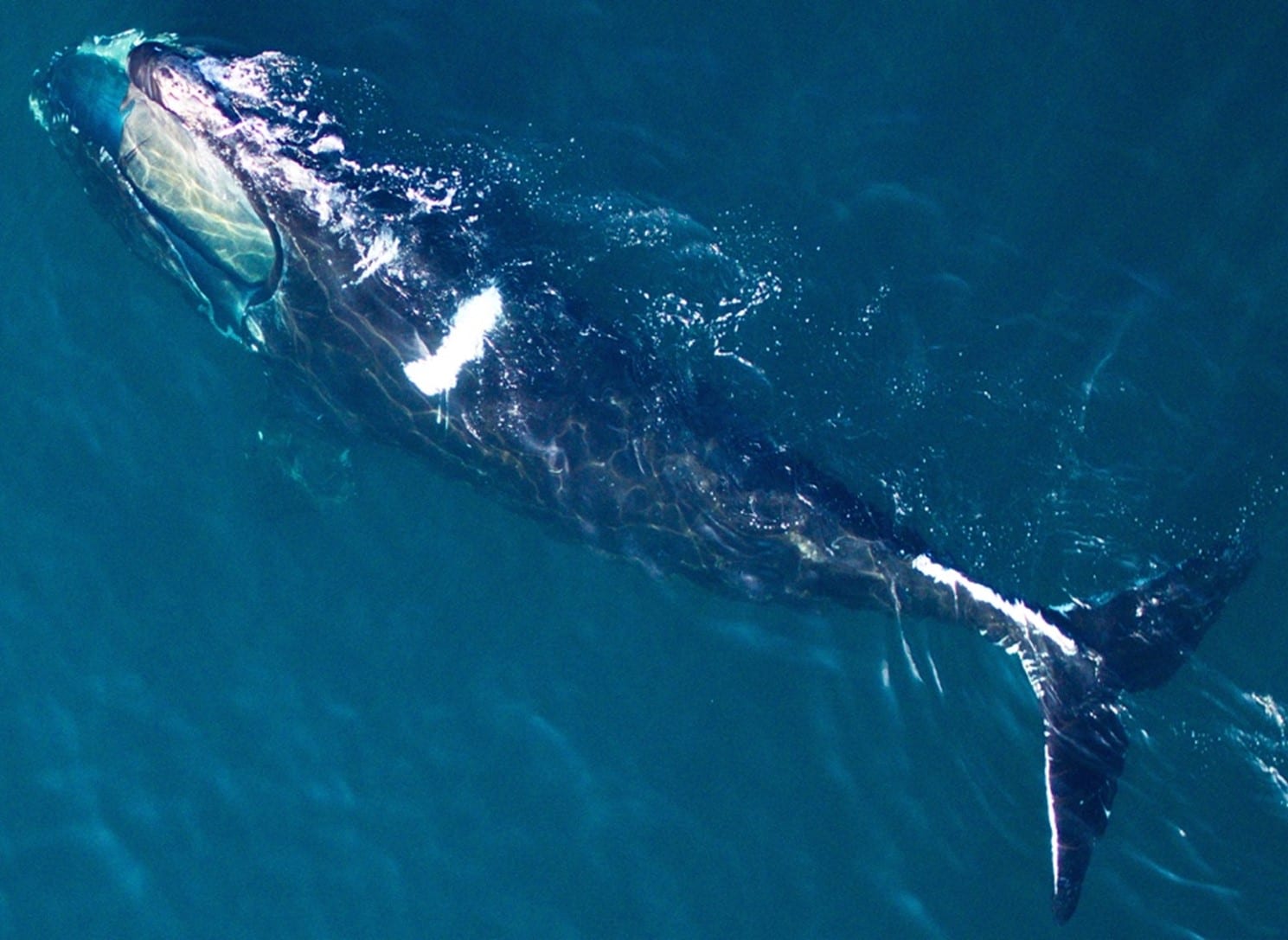
Read MoreWHOI collaborates with CMA CGM to increase protections for marine mammals
A collaboration between Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and the CMA CGM Group, a world leader in shipping and logistics, aims to increase whale detection efforts along the U.S East Coast, particularly for North Atlantic right whales, and reduce the potential for ship strikes along critical shipping routes.
Read MoreWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution-led study explores effects of noise on marine life
New research shows turtles can experience temporary hearing loss from an excess of underwater noise. This high volume of sound, referred to as underwater noise pollution, can be caused by passing ships and offshore construction. These preliminary findings were part of a Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution-led study that is being presented at the 2022 Ocean Sciences Meeting..
Read MoreEarth BioGenome Project begins genome sequencing in earnest
The Deep-Ocean Genomes Project is an ambitious effort co-led by WHOI and the University of Connecticut (UConn) to obtain fundamental new knowledge of the organization, evolution, functions, and interactions of life in one of Earth’s least-understood regions: the deep ocean.
Read MoreWHOI shares details on microplastic detection project
A project led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution’s Chemical Sensors Lab is moving researchers closer to an in-field microplastics sensor that measures the amount of plastic particles in water.
Read MoreStudy finds bio-based cellulose acetate plastic used in consumer goods disintegrates in ocean much faster than assumed
Woods Hole, MA — Cellulose diacetate (CDA), a bio-based plastic widely used in consumer goods, disintegrates, and degrades in the ocean far quicker than previously assumed, according to a new…
Read MoreDevelopment of a curious robot to study coral reef ecosystems awarded $1.5 million by the National Science Foundation
A prototype of an autonomous underwater vehicle capable of navigating complex underwater environments and of collecting data adaptively over long periods of time. Daniel Hentz / ©Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution…
Read MoreSunlight can break down marine plastic into tens of thousands of chemical compounds, study finds
Sunlight was once thought to only fragment plastics in the marine environment into smaller particles that chemically resemble the original material and persist forever. However, scientists more recently have learned that sunlight also chemically transforms plastic into a suite of polymer-, dissolved-, and gas-phased products. Now, a new study finds that this chemical reaction can produce tens of thousands of water-soluble compounds, or formulas.
Read MoreSome coral reefs are keeping pace with ocean warming
Some coral communities are becoming more heat tolerant as ocean temperatures rise, offering hope for corals in a changing climate. After a series of marine heatwaves hit the Phoenix Islands Protected Area (PIPA) in the central Pacific Ocean, a new study finds the impact of heat stress on the coral communities lessened over time.
Read MoreEmperor penguins, recommended as threatened species under Endangered Species Act
Today, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) announced a proposal to list the emperor penguin as a threatened species under the Endangered Species Act.
Read MoreWhat happens to marine life when oxygen is scarce?
A new study co-led by WHOI postdoctoral scholar Maggie Johnson looks closely at the changes occurring in both coral reef and microbial communities near Bocas del Toro during sudden hypoxic events, which occur when there is little to no oxygen in a given area of water.
Read MoreNorthern Star Coral Study Could Help Protect Tropical Corals
Worldwide, coral reefs are in crisis. Researchers at WHOI and Roger Williams University are finding that studying the recovery of this local New England species from a laboratory induced stressor could help better understand how to protect endangered tropical corals around the world.
Read MoreWHOI and NOAA Fisheries Release New North Atlantic Right Whale Health Assessment Review
North Atlantic right whales are critically endangered and declining. Climate change, vessel strikes, entanglements and noise engender poor health and reproductive failure, and are major threats to individuals and the species. Trauma reduction measures and applying new tools to assess and enhance their health, are critically important.
Read MoreOcean acidification causing coral ‘osteoporosis’ on iconic reefs
Scientists have long suspected that ocean acidification is affecting corals’ ability to build their skeletons, but it has been challenging to isolate its effect from that of simultaneous warming ocean…
Read More