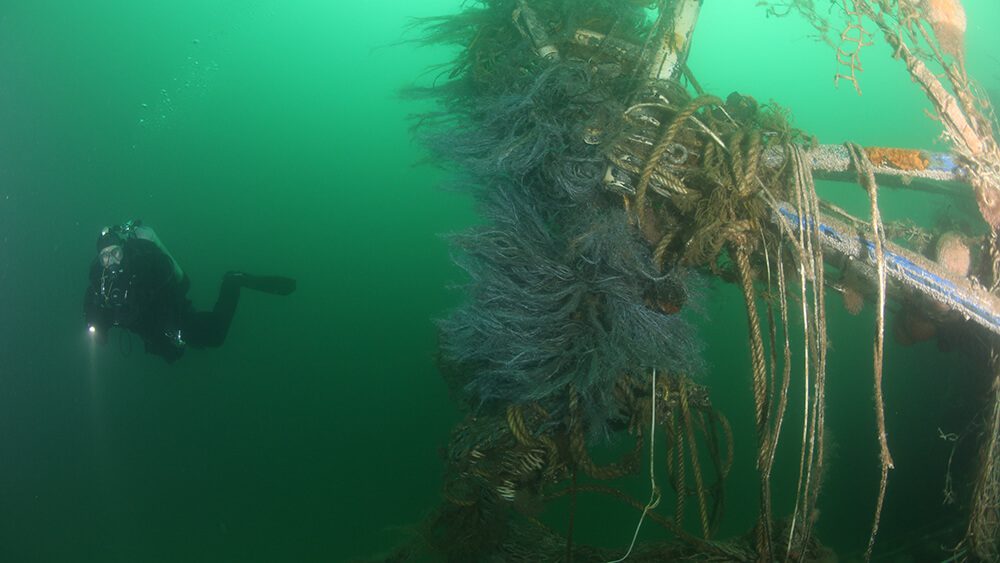
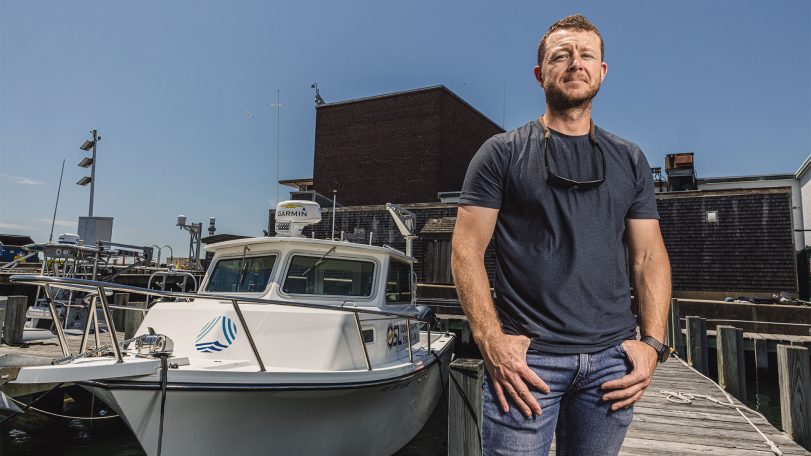
A new underwater robot could help preserve New England’s historic shipwrecks
WHOI’s ResQ ROV to clean up debris in prominent marine heritage sites
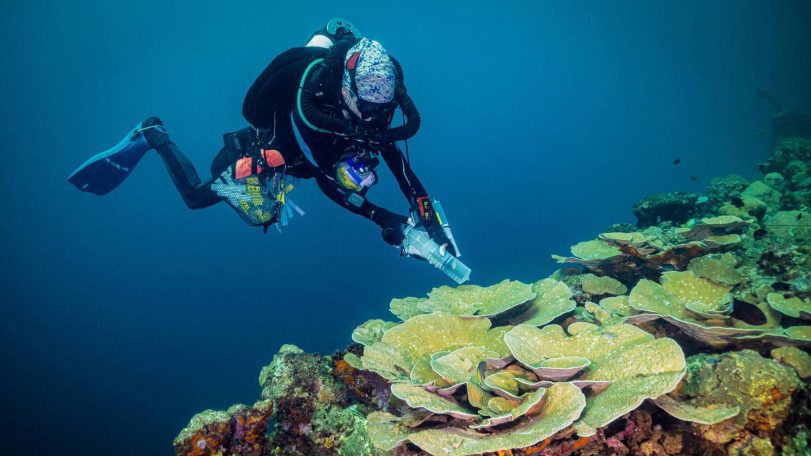
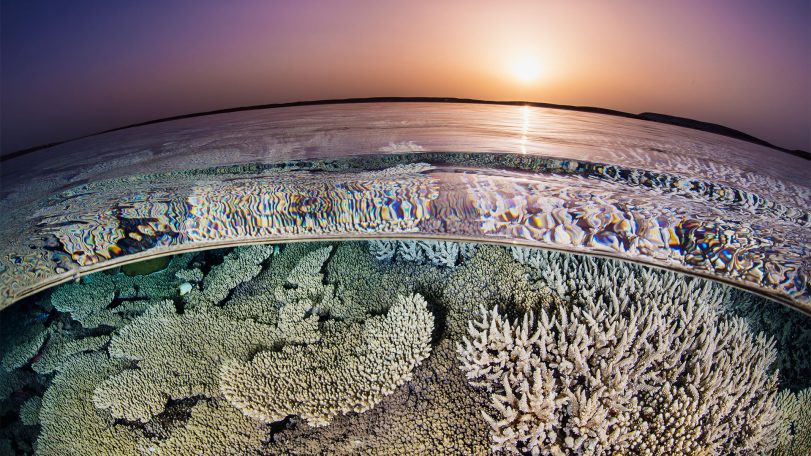
From ruin to reef
What Pacific wrecks are teaching us about coral resilience—and pollution
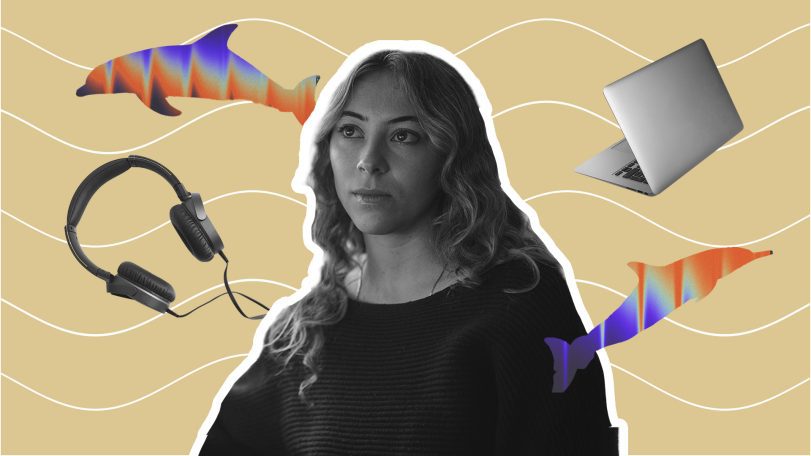
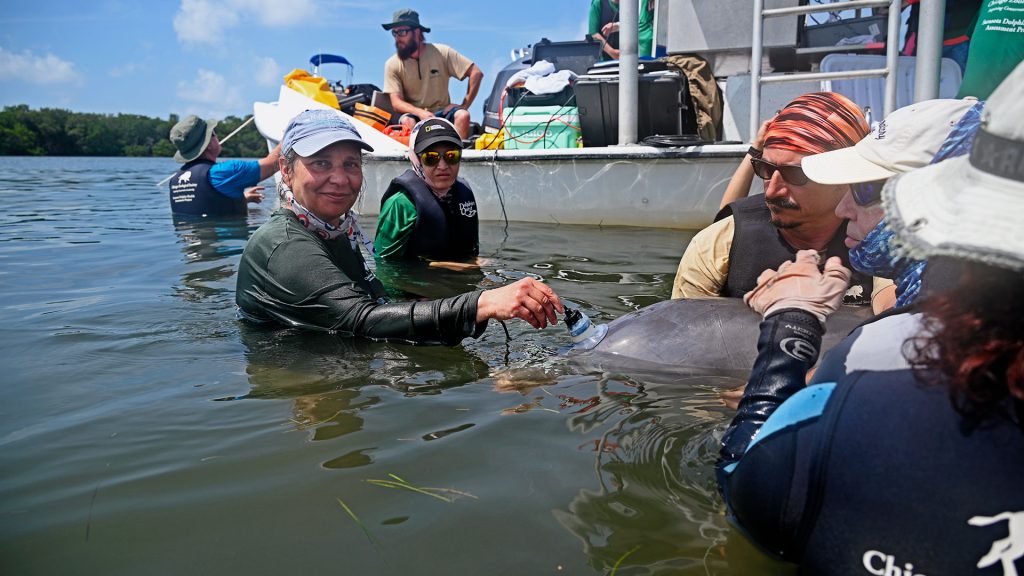
One researcher, 15,000 whistles: Inside the effort to decode dolphin communication
Scientists at WHOI analyze thousands of dolphin whistles to explore whether some sounds may function like words
Remembering Tatiana Schlossberg, a voice for the ocean
Environmental journalist and author Tatiana Schlossberg passed away after battling leukemia on December…
As the ocean warms, a science writer looks for coral solutions
Scientist-turned-author Juli Berwald highlights conservation projects to restore coral reefs
How an MIT-WHOI student used Google Earth to uncover a river–coral reef connection
Google Earth helps researcher decode how rivers sculpt massive breaks in coral reefs
The little big picture
WHOI senior biologist Heidi Sosik on the critical need for long-term ocean datasets
Lessons from a lifetime of exploration
Award-winning ocean photographer Brian Skerry shares insights from a career spent around ocean life and science

and get Oceanus delivered to your door twice a year as well as supporting WHOI's mission to further ocean science.
Our Ocean. Our Planet. Our Future.
The ocean weather nexus, explained
The vital role of ocean observations in extreme weather forecasting
Breaking down plastics together
Through a surprising and successful partnership, WHOI and Eastman scientists are reinventing what we throw away
Three questions with Carl Hartsfield
Captain Hartsfield, USN retired, discusses the role ocean science plays in our national defense
The Ocean (Re)Imagined
How expanding our view of the ocean can unlock new possibilities for life
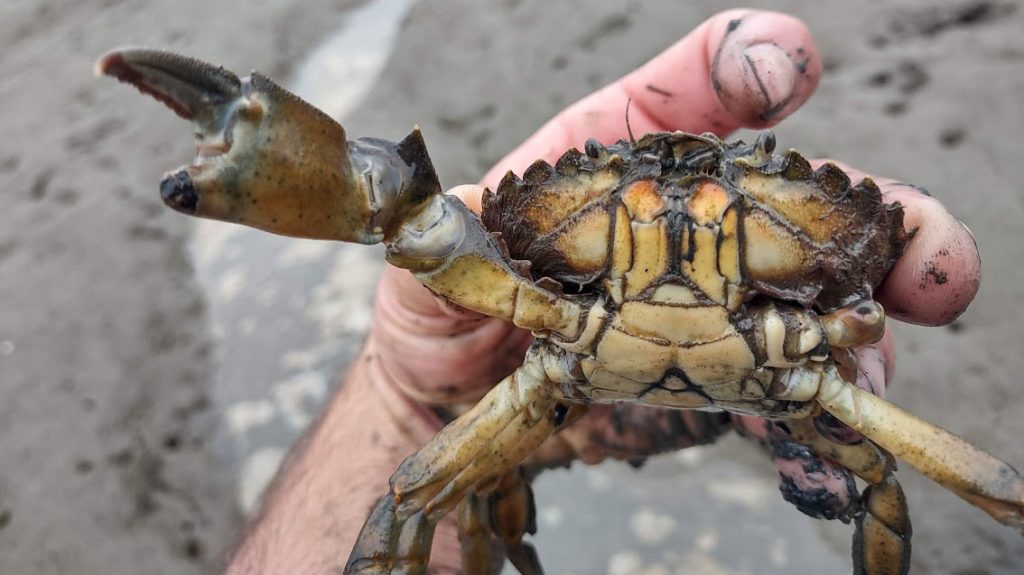
Body snatchers are on the hunt for mud crabs
WHOI biologist Carolyn Tepolt discusses the biological arms race between a parasite and its host
A polar stethoscope
Could the sounds of Antarctica’s ice be a new bellwether for ecosystem health in the South Pole?
Secrets from the blue mud
Microbes survive—and thrive—in caustic fluids venting from the seafloor

Looking for something specific?
We can help you with that. Check out our extensive conglomeration of ocean information.
Top 5 ocean hitchhikers
As humans traveled and traded across the globe, they became unwitting taxis to marine colonizers
Following the Polar Code
Crew of R/V Neil Armstrong renew their commitment to Arctic science with advanced polar training
Harnessing the ocean to power transportation
WHOI scientists are part of a team working to turn seaweed into biofuel
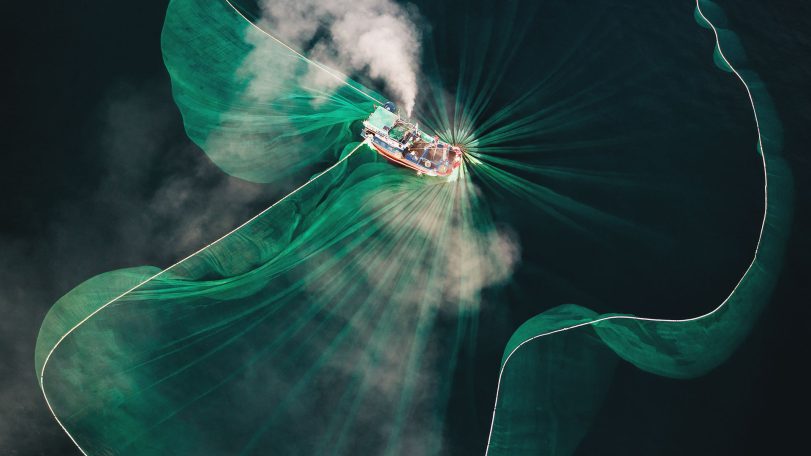
Casting a wider net
The future of a time-honored fishing tradition in Vietnam, through the eyes of award-winning photographer Thien Nguyen Noc
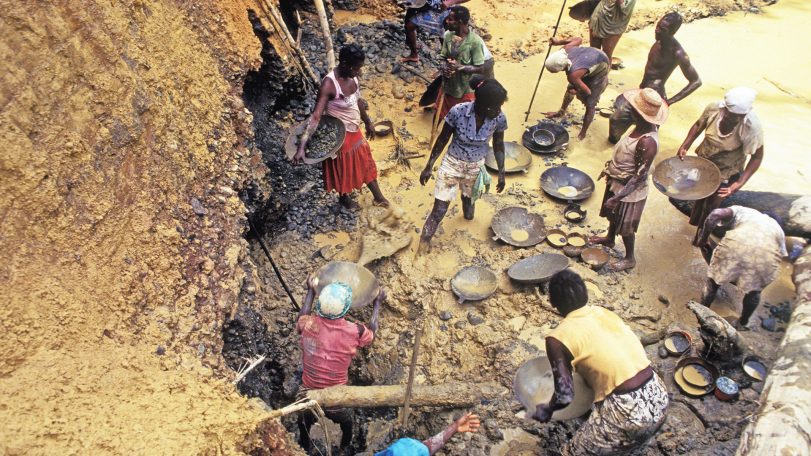
Gold mining’s toxic legacy
Mercury pollution in Colombia’s Amazon threatens the Indigenous way of life
How do you solve a problem like Sargassum?
An important yet prolific seaweed with massive blooms worries scientists
Ancient seas, future insights
WHOI scientists study the paleo record to understand how the ocean will look in a warmer climate
Rising tides, resilient spirits
As surrounding seas surge, a coastal village prepares for what lies ahead
Whistle! Chirp! Squeak! What does it mean?
Avatar Alliance Foundation donation helps WHOI researcher decode dolphin communication
Which Way Will the Wind Blow?
Wind energy is the fastest-growing sector of the global electric power industry, and several companies have proposed to build large wind turbines and utility-scale electric power-generating facilities in the coastal waters of the United States. Such facilities could change the way people use the ocean, and the public is divided over the costs and benefits. The environmental and economic benefits of renewable, nonpolluting sources of energy are clear. But there may be side effects from the placement of modern wind farms in the ocean, including the degradation of seascapes, impacts on birds and marine animals, and the disruption of existing patterns of human use of the ocean. The laws and regulations related to the placement of wind turbines in the ocean are at best rudimentary and inchoate; at worst, they are non-existent. Marine scientists and engineers can make an important contribution to this growing public debate by clarifying our understanding of the nature of these side effects. They might also inform public policies that balance the value of various ocean resources with the rights and interests of all who wish to use them.
Is Life Thriving Deep Beneath the Seafloor?
In 1991, scientists aboard the submersible Alvin were in the right spot at the right time to witness something extraordinary. They had sailed into the aftermath of a very recent volcanic eruption on the seafloor and found themselves in a virtual blizzard. They were densely surrounded by flocs of white debris, composed of sulfur and microbes, which drifted more than 30 meters above the ocean bottom. The seafloor was coated with a 10-centimeter-thick layer of the same white material. This vast volume of microbes did not come from the ocean. The eruption had flushed it out from beneath the seafloor.
Unraveling the Tapestry of Ocean Crust
Most people know that oceans cover about 70 percent of Earth’s surface. Fewer people realize that the crust beneath oceans and continents is fundamentally different. Why this is so remains a mystery that scientists are still trying to solve.
The Grass is Greener in the Coastal Ocean
Stretching from inland rivers and bays to the edge of the continental shelf, the coastal ocean accounts for about 10 percent of the ocean’s surface area. Yet this relatively small sliver of ocean contains about half of all the microscopic plants adrift in our seas.
A Sea Change in Ocean Drilling
Stretching from inland rivers and bays to the edge of the continental shelf, the coastal ocean accounts for about 10 percent of the ocean’s surface area. Yet this relatively small sliver of ocean contains about half of all the microscopic plants adrift in our seas.
How the Isthmus of Panama Put Ice in the Arctic
The long lag time has always puzzled scientists: Why did Antarctica become covered by massive ice sheets 34 million years ago, while the Arctic Ocean acquired its ice cap only about 3 million year ago?
Paving the SeafloorBrick by Brick
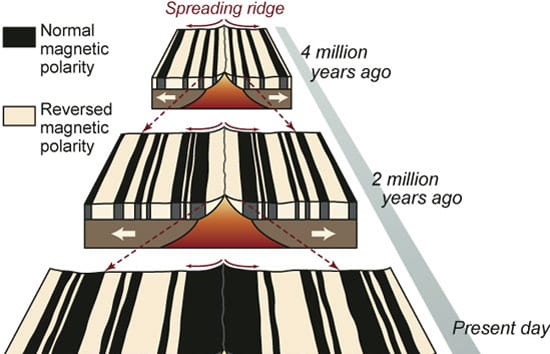
Most of Earth’s crust is manufactured at the bottom of the sea. Deep beneath the waves and beyond our view, magma erupts along a 40,000-mile volcanic mountain chain that bisects the ocean floors and encircles the globe. The lava flowing from these mid-ocean ridges solidifies into new ocean crust that spreads out and paves the surface of our planet.
The Evolutionary Puzzle of Seafloor Life
Most of Earth’s crust is manufactured at the bottom of the sea. Deep beneath the waves and beyond our view, magma erupts along a 40,000-mile volcanic mountain chain that bisects the ocean floors and encircles the globe. The lava flowing from these mid-ocean ridges solidifies into new ocean crust that spreads out and paves the surface of our planet.
Listening Closely to ‘See’ Into the Earth
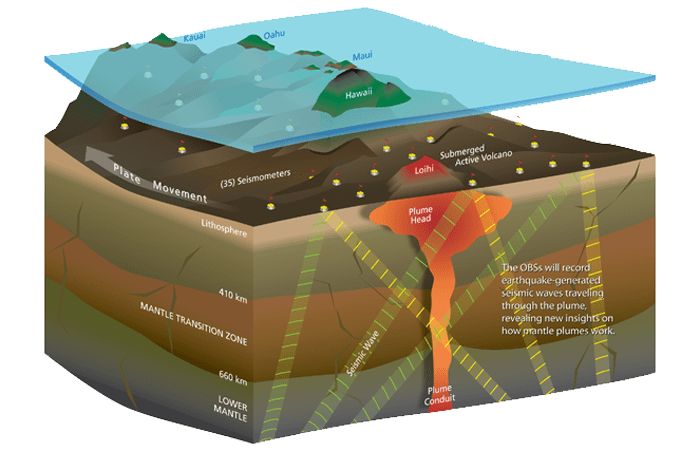
Today, excitement and anticipation is growing because of new generations of seismographs designed for use in the oceans. These new instruments will comprise a new national pool of instruments for use by the scientific community.
Shifting Continents and Climates
Sixty-five millions years ago, dinosaurs had just become extinct, and mammals were starting to dominate the planet.
Moving Earth and Heaven
The mountains rise, are lashed by wind and weather, and erode. The rivers carry mud and debris from the mountains into the ocean, where they settle onto the relatively tranquil seafloor and are preserved. The sediments bear evidence about where they came from, what happened to them, and when. By analyzing, measuring, and dating these seafloor sediments, scientists can piece together clues to reconstruct when and how fast their mountain sources rose to great heights millions of years ago, and how the climate and other environmental conditions may have changed in response.
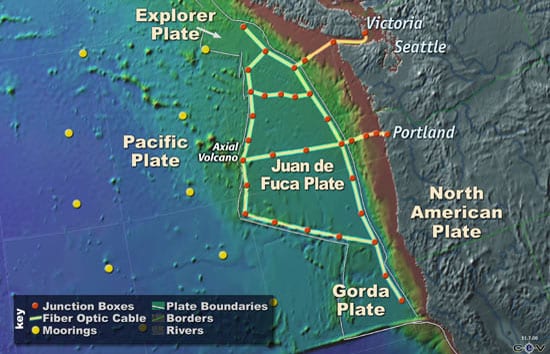
Seeding the Seafloor with Observatories
Scientists extend their reach into the deep with pioneering undersea cable networks
H2O (Hawaii-2 Observatory) – In 1998, scientists used the remotely operated vehicles (ROV) Jason and Medea to create the pioneering long-term seafloor observatory called H2O (Hawaii-2 Observatory). They spliced an abandoned submarine telephone cable into a termination frame. The frame relays power and communications to a junction box, which serves as an electrical outlet for scientific instruments.