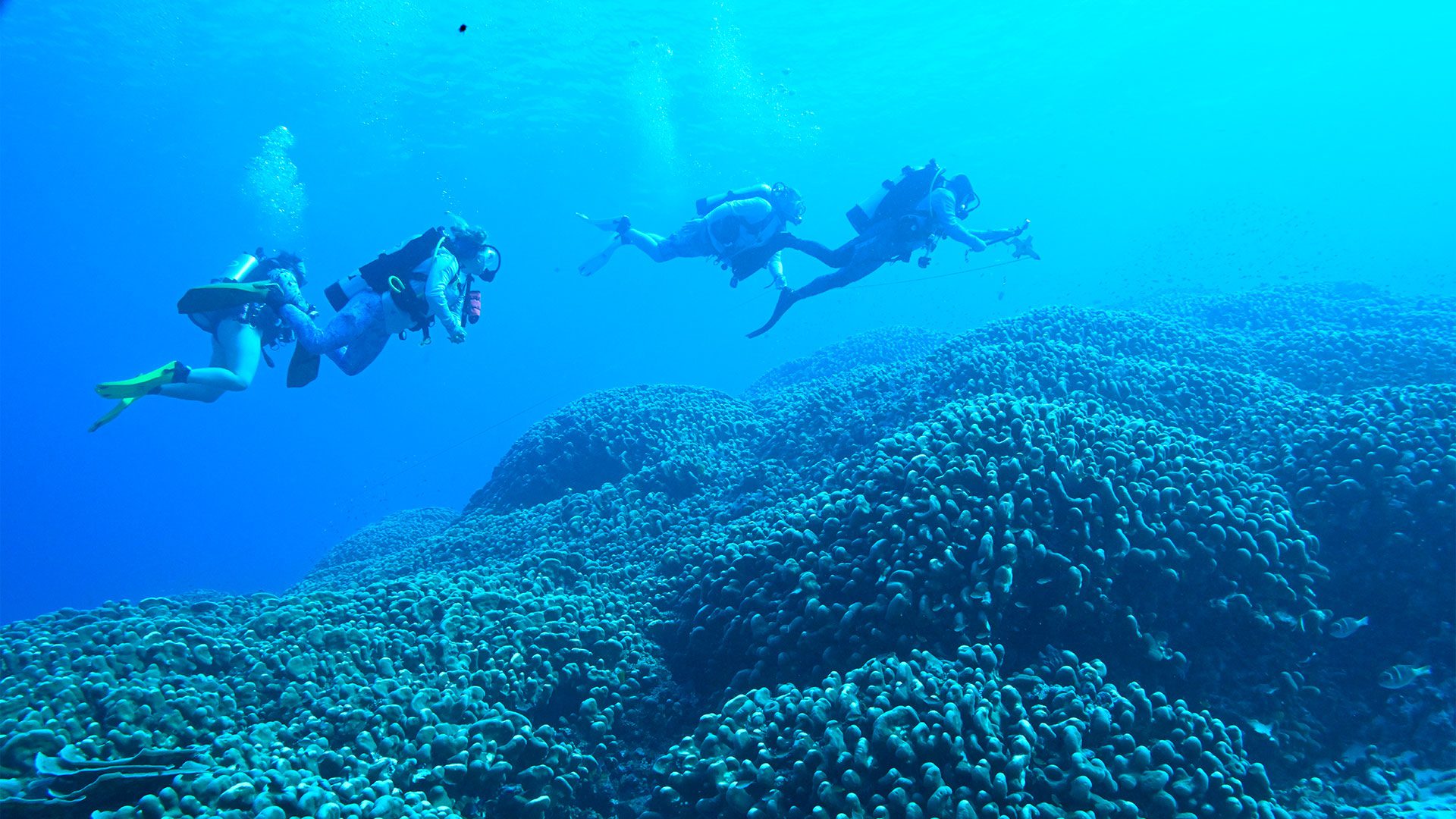
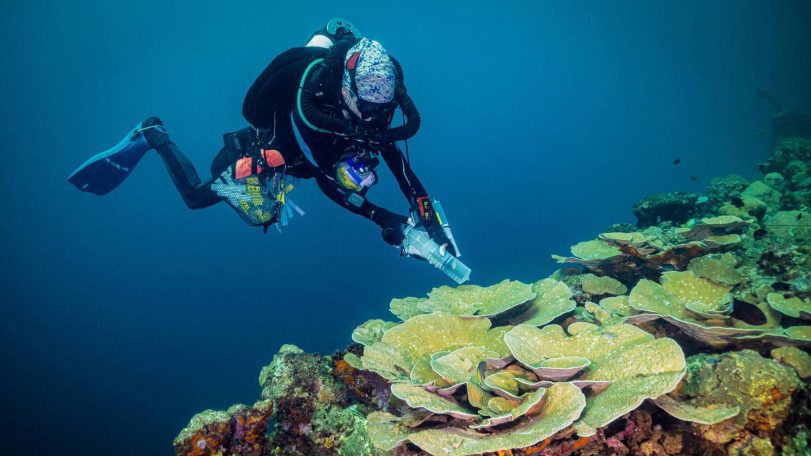
Inside the Solomon Islands’ hidden mega coral — a 300-year-old ocean giant
WHOI’s Reef Solutions team journeys to the world’s largest coral colony
From ruin to reef
What Pacific wrecks are teaching us about coral resilience—and pollution
One researcher, 15,000 whistles: Inside the effort to decode dolphin communications
Scientists at WHOI analyze thousands of dolphin whistles to explore whether some sounds may function like words
Remembering Tatiana Schlossberg, a voice for the ocean
Environmental journalist and author Tatiana Schlossberg passed away after battling leukemia on December…
As the ocean warms, a science writer looks for coral solutions
Scientist-turned-author Juli Berwald highlights conservation projects to restore coral reefs
How an MIT-WHOI student used Google Earth to uncover a river–coral reef connection
Google Earth helps researcher decode how rivers sculpt massive breaks in coral reefs
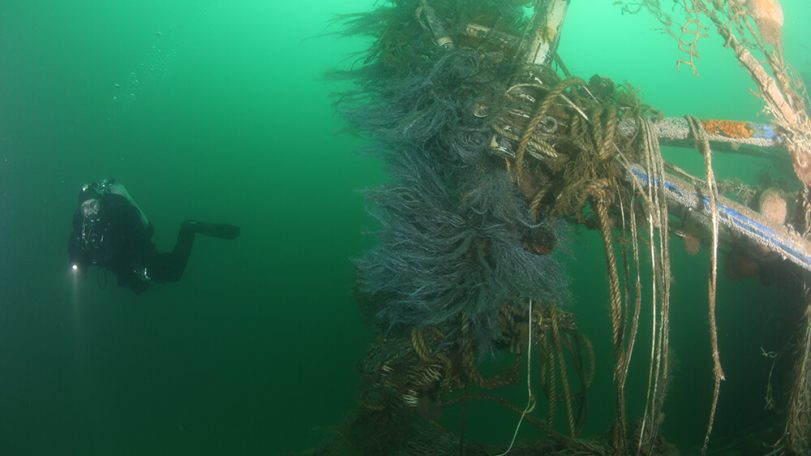
A new underwater robot could help preserve New England’s historic shipwrecks
WHOI’s ResQ ROV to clean up debris in prominent marine heritage sites
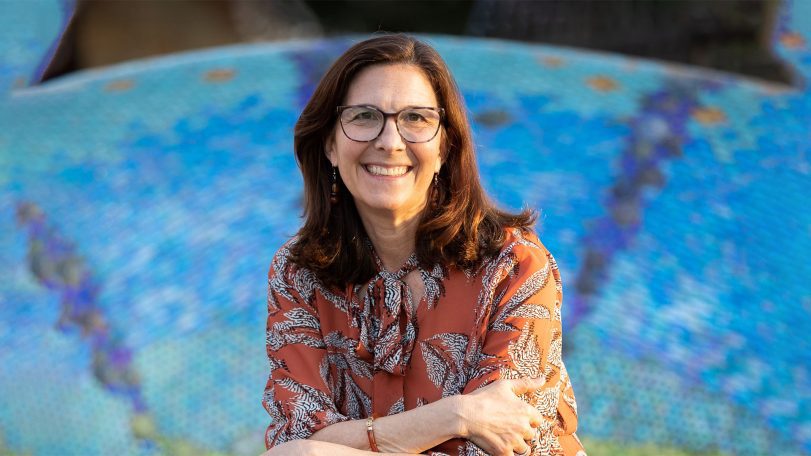
The little big picture
WHOI senior biologist Heidi Sosik on the critical need for long-term ocean datasets

and get Oceanus delivered to your door twice a year as well as supporting WHOI's mission to further ocean science.
Our Ocean. Our Planet. Our Future.
Lessons from a lifetime of exploration
Award-winning ocean photographer Brian Skerry shares insights from a career spent around ocean life and science
The ocean weather nexus, explained
The vital role of ocean observations in extreme weather forecasting
Breaking down plastics together
Through a surprising and successful partnership, WHOI and Eastman scientists are reinventing what we throw away
Three questions with Carl Hartsfield
Captain Hartsfield, USN retired, discusses the role ocean science plays in our national defense
The Ocean (Re)Imagined
How expanding our view of the ocean can unlock new possibilities for life
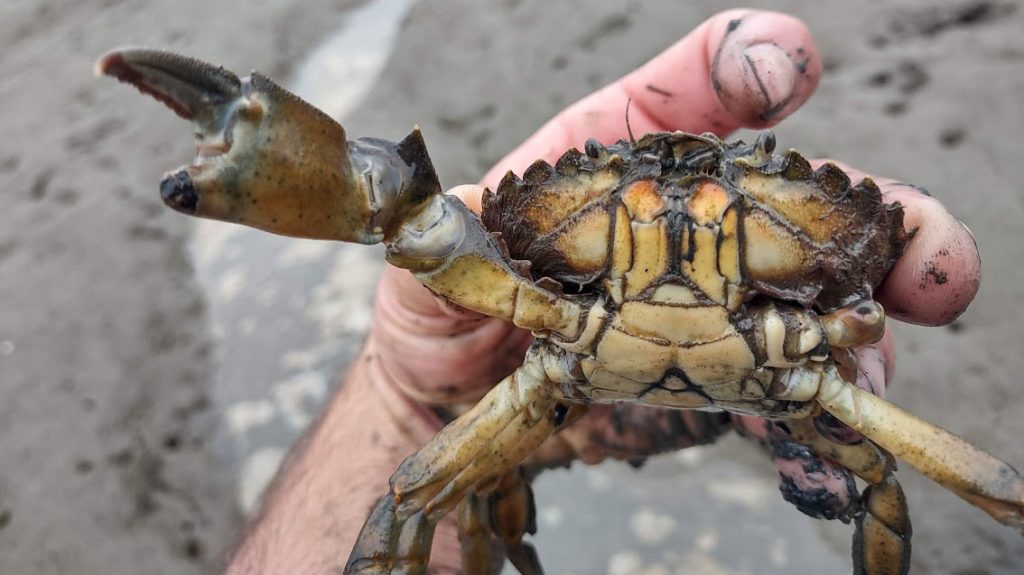
Body snatchers are on the hunt for mud crabs
WHOI biologist Carolyn Tepolt discusses the biological arms race between a parasite and its host
A polar stethoscope
Could the sounds of Antarctica’s ice be a new bellwether for ecosystem health in the South Pole?
Secrets from the blue mud
Microbes survive—and thrive—in caustic fluids venting from the seafloor

Looking for something specific?
We can help you with that. Check out our extensive conglomeration of ocean information.
Top 5 ocean hitchhikers
As humans traveled and traded across the globe, they became unwitting taxis to marine colonizers
Following the Polar Code
Crew of R/V Neil Armstrong renew their commitment to Arctic science with advanced polar training
Harnessing the ocean to power transportation
WHOI scientists are part of a team working to turn seaweed into biofuel
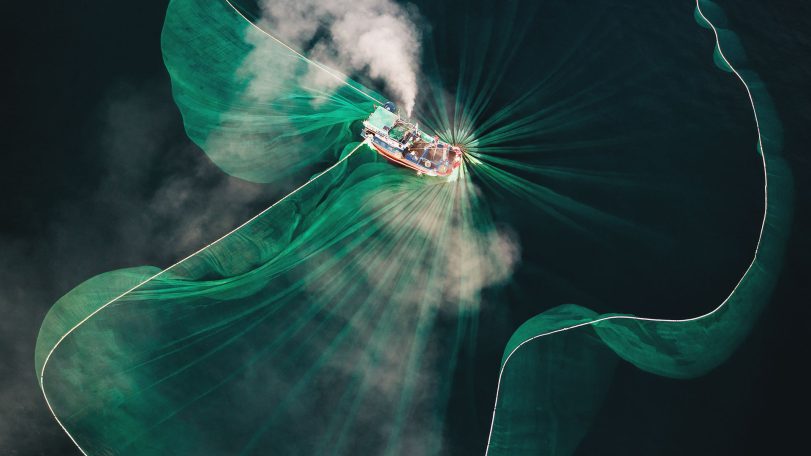
Casting a wider net
The future of a time-honored fishing tradition in Vietnam, through the eyes of award-winning photographer Thien Nguyen Noc
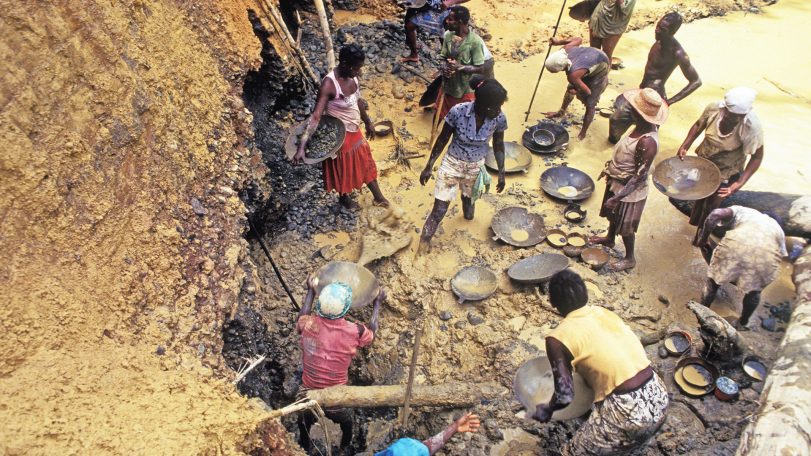
Gold mining’s toxic legacy
Mercury pollution in Colombia’s Amazon threatens the Indigenous way of life
How do you solve a problem like Sargassum?
An important yet prolific seaweed with massive blooms worries scientists
Ancient seas, future insights
WHOI scientists study the paleo record to understand how the ocean will look in a warmer climate
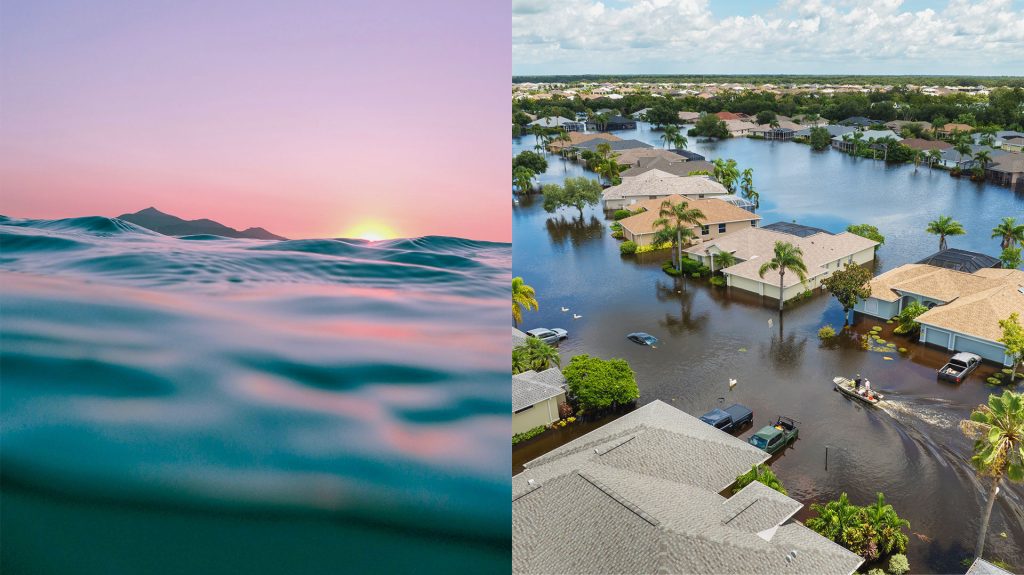
Rising tides, resilient spirits
As surrounding seas surge, a coastal village prepares for what lies ahead
The New Wave of Coastal Ocean Observing
Estuaries are the borderlands between salt and freshwater environments, and they are incredibly diverse both biologically and physically. The diversity and the high energy of the ecosystem make estuaries remarkably resilient. With a better understanding of these systems, we can reverse
their decline and restore the ecological richness of these valuable, albeit muddy, environments.
Red Tides and Dead Zones
The most widespread, chronic environmental problem in the coastal ocean is caused by an excess of chemical nutrients. Over the past century, a wide range of human activities—the intensification of agriculture, waste disposal, coastal development, and fossil fuel use—has substantially increased the discharge of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other nutrients into the environment. These nutrients are moved around by streams, rivers, groundwater, sewage outfalls, and the atmosphere and eventually end up in the ocean.
Water Flowing Underground
Groundwater discharge appears to be an important factor for determining the chemistry of the coastal ocean. As fresh groundwater flows toward the sea, it rises up over denser, salty water. The fresh and salty water mix along the interface, and the resulting fluid discharges at the shoreline. This interface between underground water masses has recently been described as a “subterranean estuary,” a mixing zone between fresh and salty water analogous to the region where a river meets the ocean.
Rising Sea Levels and Moving Shorelines
Changes to the shoreline are inevitable and inescapable. Shoals and sandbars become islands and then sandbars again. Ice sheets grow and shrink, causing sea level to fall and rise as water moves from the oceans to the ice caps and back to the oceans. Barrier islands rise from the seafloor, are chopped by inlets, and retreat toward the mainland. Even the calmest of seas are constantly moving water, sand, and mud toward and away from the shore, and establishing new shorelines.
The Growing Problem of Harmful Algae
Harmful algal blooms are natural and they are not new. But ocean scientists are growing concerned that they are now all too common. The unprecedented growth of human activities in coastal watersheds—including agriculture, aquaculture, industry, housing, and recreation—has drastically increased the amount of fertilizer flowing into coastal waters and fueled unwanted algal growth.
Introducing…the Asian Oyster
As native oysters decline, officials seek to restore fishery with disease-resistant species “O Oysters,” said…
Scientists Muster to Help Right Whales
It is a sad irony that we have cataloged individual photographs of the remaining North Atlantic right whales and given each of them unique numbers and sometimes names, yet still know too little about their physiology, behavior, and habitats to take effective steps toward ensuring their survival as a species.
Whither the North Atlantic Right Whale?
“Today only a remnant of the population survives, no more than 350 whales clustered in calving and feeding grounds along the eastern seaboard of North America. Only occasional right whale sightings in the Gulf of St. Lawrence or in the waters between Iceland, Greenland, and Norway give echoes of their once substantially greater range.
Revealing the Ocean’s Invisible Abundance
Finding minuscule life forms in a seemingly infinite ocean isn’t trivial. But in recent years, oceanographers have been developing new techniques and instruments to identify and count marine microorganisms. Year by year, we are learning more and more about them and discovering that they are even more numerous, varied, and important than we previously thought.
Shedding Light on Light in the Ocean
Light in the ocean is like light in no other place on Earth. It is a world that is visibly different from our familiar terrestrial world, and one that marine animals, plants, and microbes are adapted to in extraordinary ways. Light behaves very differently when it moves from air into water. It moves through the expansive depths of an ocean that is devoid of solid surfaces. These and other factors combine to create an environment that has no equivalent on land.
Oil in Our Coastal Back Yard
On September 16, 1969, the barge Florida ran aground off Cape Cod, rupturing its hull and spilling 189,000 gallons of No. 2 fuel oil. Winds and waves pushed the oil onto the beaches and marshes of West Falmouth, Massachusetts, carrying with it dead lobsters, scup, and cod.
Shaping the Beach, One Wave at a Time
For years, scientists who study the shoreline have wondered at the apparent fickleness of storms, which can devastate one part of a coastline, yet leave an adjacent part untouched. How can this be? The answer lies in the physics of the nearshore region?the stretch of sand, rock, and water between the dry land behind the beach and the beginning of deep water far from shore.