Raising Awareness
News
NEWS RELEASES
Mountain Erosion May Add Carbon Dioxide to Atmosphere
Scientists have long known that steep mountain ranges can draw carbon dioxide (CO2) out of the atmosphere as erosion exposes new rock, it also starts a chemical reaction between minerals on hill slopes and CO2 in the air, weathering the rock and using CO2 to produce carbonate minerals like calcite.
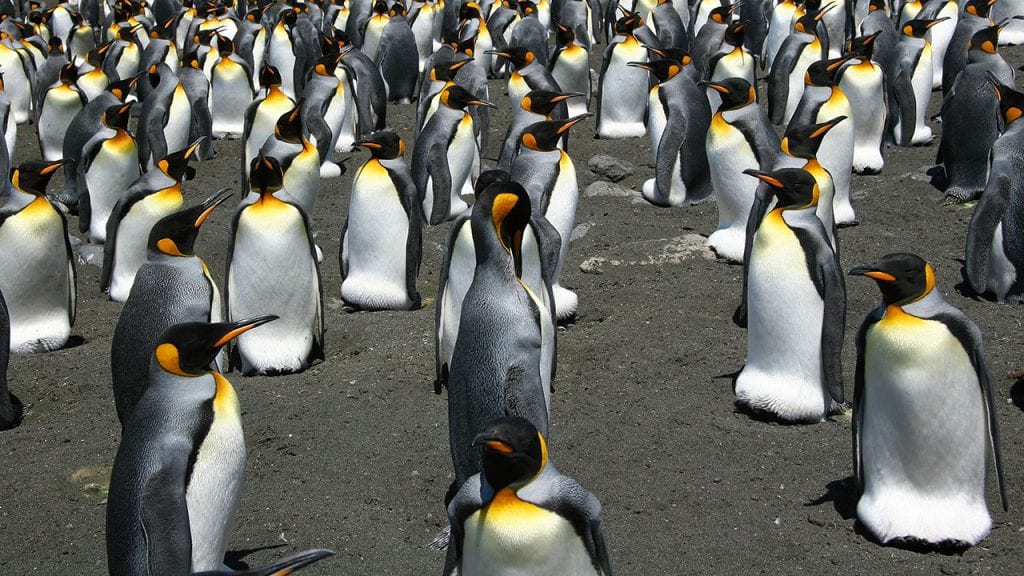
Penguins Go Through the Flow
Colonies of breeding king penguins behave much like particles in liquids do, according to new study by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and international colleagues. This “liquid ” organization and structure enables breeding colonies to protect themselves against predators while also keeping members together.
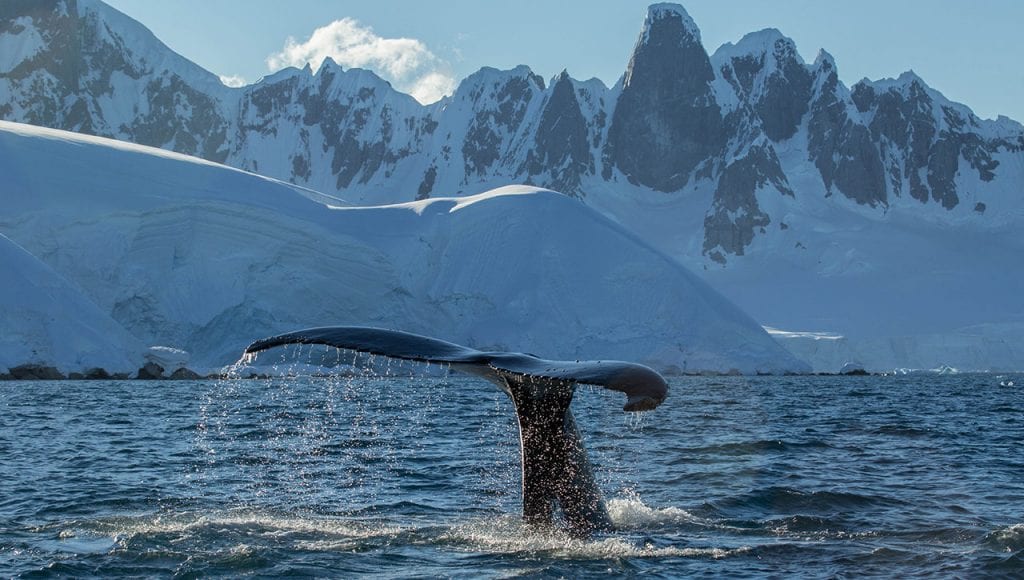
Monitoring Bacteria on Whale Skin
Just like with humans, the skin on marine mammals serves as an important line of defense against pathogens in their environment. A new study sheds light on the skin microbiome – a group of microorganisms that live on skin – in healthy humpback whales, which could aid in future efforts to monitor their health.
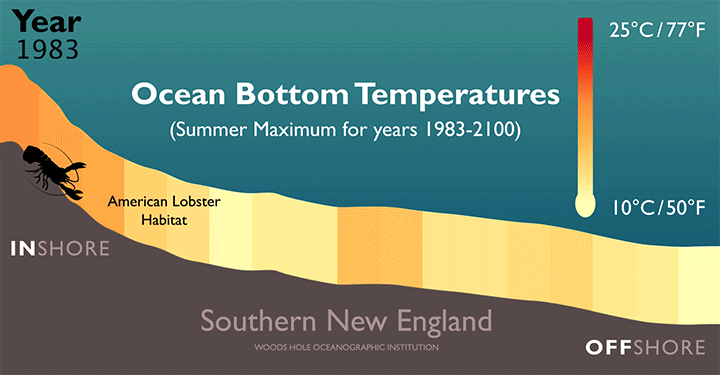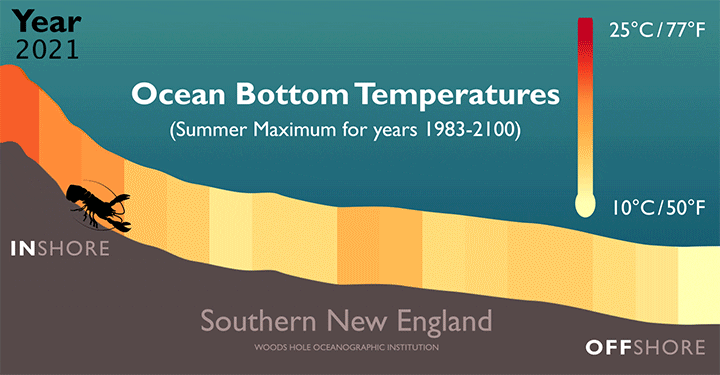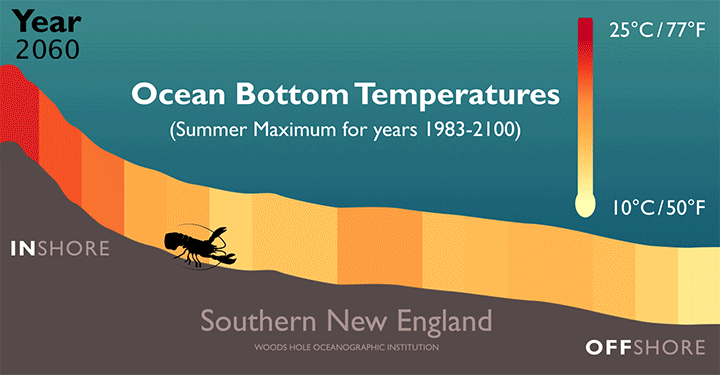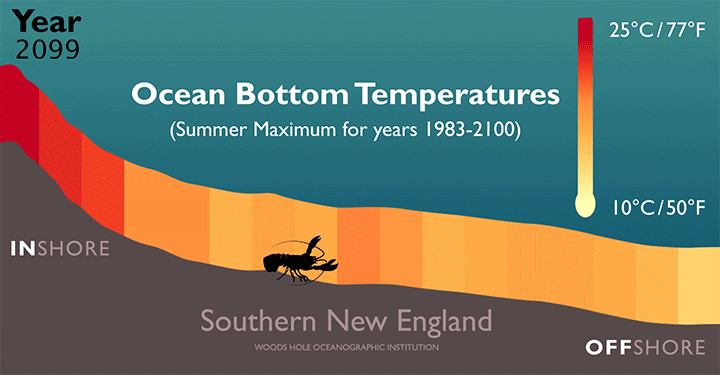
Feeling the Heat in the NW Atlantic
Rising temperatures along the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean will force American lobsters (H. americanus) farther offshore and into more northern waters, according to a new study led by researchers at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
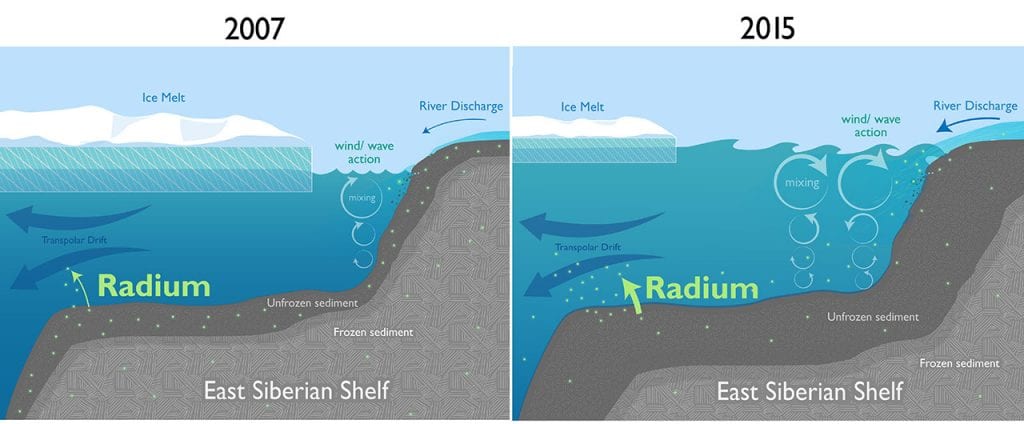
Scientists Find Surprising Evidence of Rapid Changes in the Arctic
Scientists have found surprising evidence of rapid climate change in the Arctic: In the middle of the Arctic Ocean near the North Pole, they discovered that the levels of radium-228 have almost doubled over the last decade.
WHOI | OCEANUS
Publications
IN THE NEWS - RESEARCH HIGLIGHTS
Study offers first definitive proof that Gulf Stream has weakened
“New research from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution offers the first conclusive evidence that the Gulf Stream has weakened. The powerful ocean current off the East Coast influences regional weather, climate and fisheries, and the finding could have significant implications both for New England and the global climate.”
What Happens to Marine Life When There Isn’t Enough Oxygen?
In September of 2017, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution postdoctoral scholar Maggie Johnson was conducting an experiment with a colleague in Bocas del Toro off the…
Maine’s having a lobster boom. A bust may be coming.
The waters off Maine’s coast are warming, and no one knows what that’s going to mean for the state’s half-billion-dollar-a-year lobster industry—the largest single-species fishery in North America. Some fear that continued warming could cause the lobster population to collapse. To understand what’s happening to the ecosystem of the Gulf of Maine, says Glen Gawarkiewicz, an oceanographer at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, in Massachusetts, you have to look beyond it—see how it’s affected by the atmosphere, ocean currents, and rivers that flow into it.