Please note: You are viewing
the unstyled version of this website. Either your browser does not support CSS
(cascading style sheets) or it has been disabled. Skip
navigation.
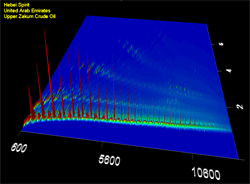
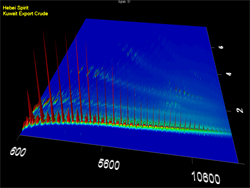
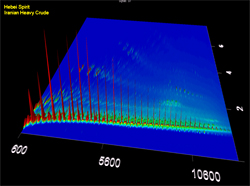
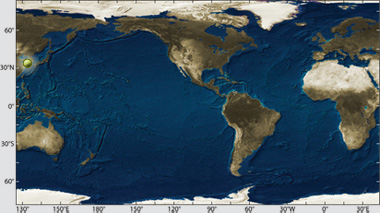 Location: Yellow Sea off Taean County, South Korea Material spilled: Light crude oil Amount spilled: est. 12,547 tons Spill extent: more than 450 miles of shoreline The ship was at anchor in the Yellow Sea approximately six miles off the coast Taean County in the province of Chungnam, which contain popular tourist destinations, important aquaculture operations and migratory bird habitats. Weather conditions immediately after the collision were poor, with gale-force winds from the northwest and 13 foot (4 meter) waves pushing the oil to the south. Eventually, more than 90 miles of coastline were identified as having been impacted ten days later. Two-dimensional gas chromatography (GCxGC) helped identify and distinguish oil from the three different tanks that leaked oil into the water. Last updated: July 28, 2014 | |||||||||||
Copyright ©2007 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, All Rights Reserved, Privacy Policy. | |||||||||||