Raising Awareness
News
NEWS RELEASES
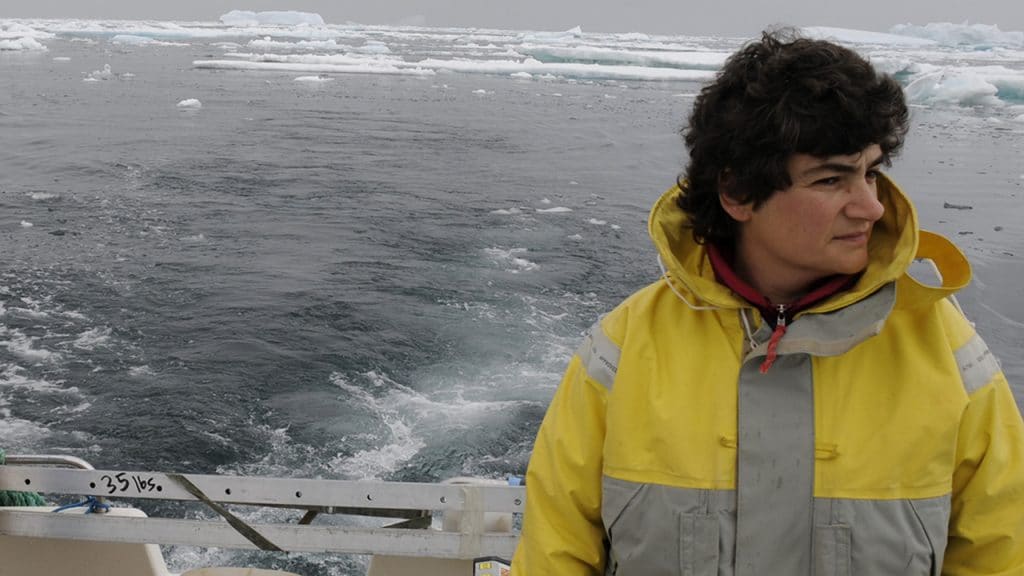
Fiamma Straneo Selected for Prestigious Sverdrup Lecture
The American Geophysical Union (AGU) has chosen Fiamma Straneo, a physical oceanographer at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), to deliver the Sverdrup Lecture at this year’s meeting of the Ocean Sciences section held in New Orleans from February 21-26, 2016. The lecture is one of the highest awards the section bestows on its members.
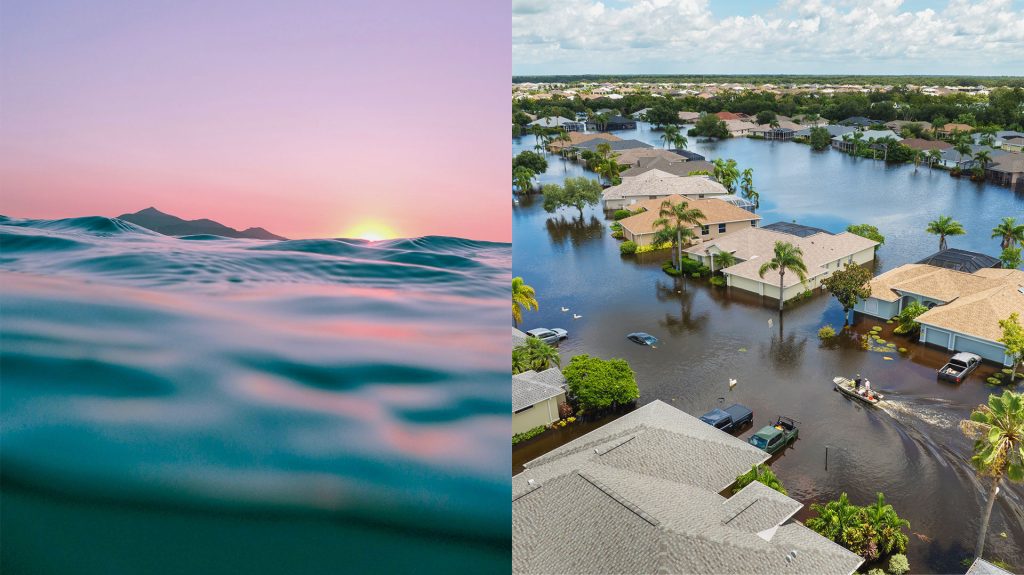
Study Reveals Climate Change Impacts on Buzzards Bay
Utilizing 22 years of data collected by a network of citizen scientists, researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and their colleagues at the Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program, the Buzzards Bay Coalition, and the Marine Biological Laboratory found that average summertime temperatures in embayments throughout Buzzards Bay warmed by almost 2 degrees Celsius—roughly 4 degrees Fahrenheit.
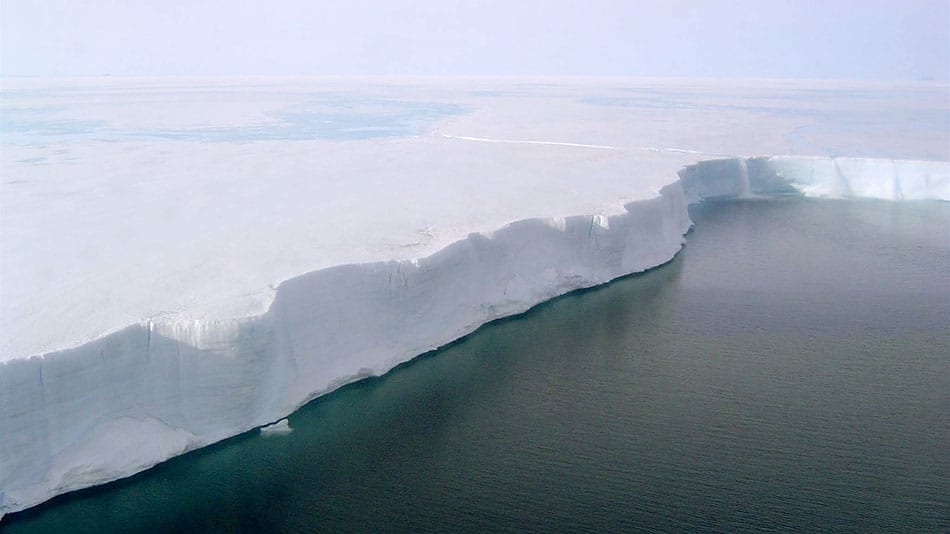
New Study Projects That Melting of Antarctic Ice Shelves Will Intensify
New research published today projects a doubling of surface melting of Antarctic ice shelves by 2050 and by 2100 may surpass intensities associated with ice shelf collapse, if greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel consumption continues at the present rate.
Ice shelves are the floating extensions of the continent’s massive land-based ice sheets. While the melting or breakup of floating ice shelves does not directly raise sea level, ice shelves do have a “door stop” effect: They slow the flow of ice from glaciers and ice sheets into the ocean, where it melts and raises sea levels.
WHOI, NEAQ Embark on Expedition to the Phoenix Islands
A research team led by the New England Aquarium (NEAQ) and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) are heading out on a 6,000-mile expedition to one of the most remote places on Earth—the Phoenix Islands in the central Pacific Ocean. Throughout the month of September and in the midst of a strengthening Pacific El Nino, researchers will investigate the combined effects of climate change and human activity on the these vast coral reef ecosystems and the diversity of life they sustain.
Shifting Winds, Ocean Currents Doubled Endangered Galapagos Penguin Population
New research suggests shifts in wind currents over the past three decades, possibly due to climate change and natural variability, have nudged the Equatorial Undercurrent north. The changing current expanded the nutrient-rich, cold water farther north along the coasts of the two islands, likely bolstering algae and fish numbers in the cold pool. This allowed the penguin population to double over the past 30 years, swelling to more than 1,000 birds by 2014, according to the new study.
WHOI | OCEANUS
Publications
IN THE NEWS - RESEARCH HIGLIGHTS
Study offers first definitive proof that Gulf Stream has weakened
“New research from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution offers the first conclusive evidence that the Gulf Stream has weakened. The powerful ocean current off the East Coast influences regional weather, climate and fisheries, and the finding could have significant implications both for New England and the global climate.”
What Happens to Marine Life When There Isn’t Enough Oxygen?
In September of 2017, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution postdoctoral scholar Maggie Johnson was conducting an experiment with a colleague in Bocas del Toro off the…
Maine’s having a lobster boom. A bust may be coming.
The waters off Maine’s coast are warming, and no one knows what that’s going to mean for the state’s half-billion-dollar-a-year lobster industry—the largest single-species fishery in North America. Some fear that continued warming could cause the lobster population to collapse. To understand what’s happening to the ecosystem of the Gulf of Maine, says Glen Gawarkiewicz, an oceanographer at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, in Massachusetts, you have to look beyond it—see how it’s affected by the atmosphere, ocean currents, and rivers that flow into it.