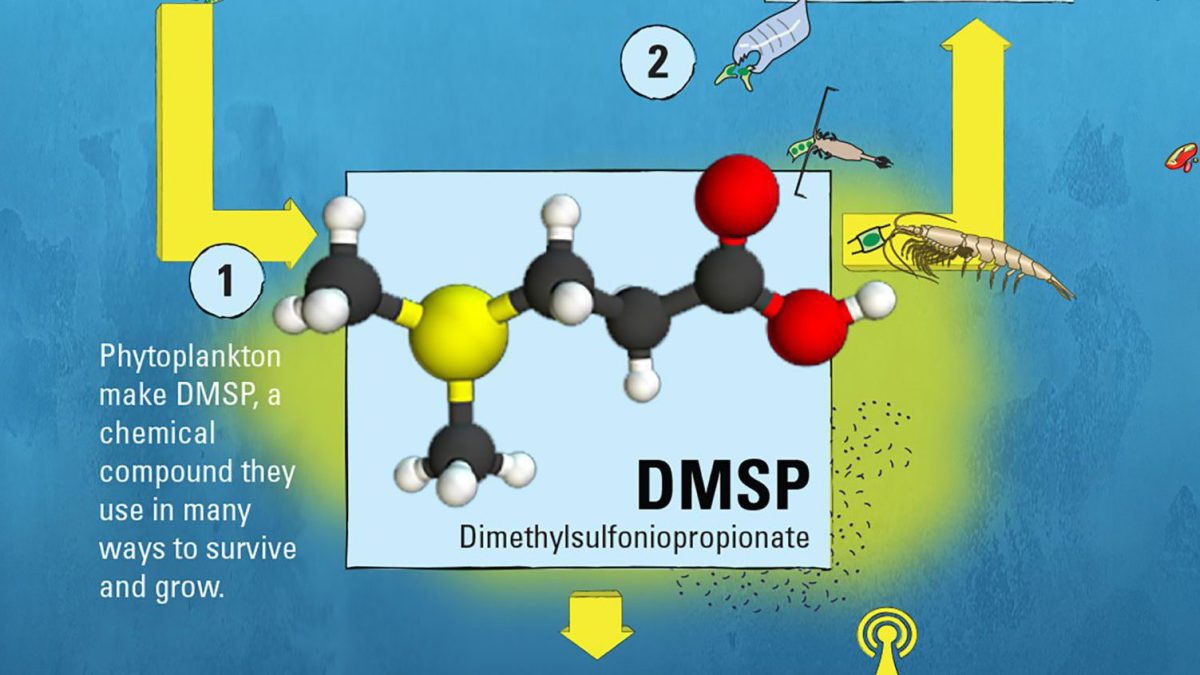
Breathe deeply when you are near the ocean and you’ll pick up the scent of the sea. That vaguely rotten aroma, accented by salt, comes from a molecule called dimethylsulfide, or DMS. But that scent offers only a hint of the fascinating far-reaching roles DMS and its precursor molecule, dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), play in the environment.
DMSP is synthesized by phytoplankton—the microscopic marine plants at the heart of the ocean food web—for a variety of beneficial uses. Scientists think DMSP acts as an antioxidant to neutralize potentially damaging chemicals generated by cellular processes and ultraviolet radiation from the sun. It may also be used to regulate the pressure inside phytoplankton cells in response to changes in seawater temperature and salinity. In addition, there is evidence that DMSP can function as a chemical signal within the marine food web.
(Illustration by Eric S. Taylor, © Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution)
Image and Visual Licensing
WHOI copyright digital assets (stills and video) contained on this website can be licensed for non-commercial use upon request and approval. Please contact WHOI Digital Assets at images@whoi.edu or (508) 289-2647.