Who are those critters in the tide pool?
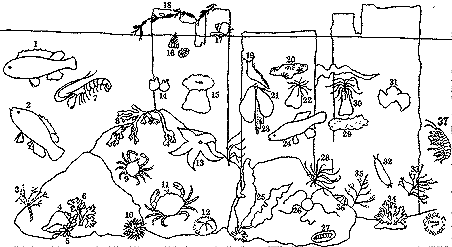
1) Tautog (Tautogo)
2) Cunner (Gadus)
3) Pink Coral Seaweed (Corallina)
4) Atlantic Dogwinkle (Nucella)
5) egg capsules of the Dogwinkle
6) Irish Moss (Chondrus)
7) Glass Shrimp (Palaemonetes)
8) Rock Weed (Fucus) with Coiled Worms (Spirorbis)
9) Spider or Decorator Crab (Libinia)
10) Purple Sea Urchin (Arbacia)
11) Rock Crab (Cancer)
12) Green Sea Urchin (Strongylocentrotus)
13) Eastern Sea Star (Asterias)
14) Sea Squirts (Molgula)
15) Northern Sea Anemone (Metridium)
16) Barnacles (Balanus)
17) Periwinkle (Littorina)
18) Knotted Wrack (Ascophyllum)
19) Nudibranch (Coryphella)
20) Eyed Tunicate (Botryllus)
21) Blue Mussels (Mytilus)
22) Striped Sea Anemone (Haliplanella or Diadumine)
23) Sea Lace (Membranipora)
24) Mummichog (Fundulus)
25) Brown Kelp (Laminaria)
26) Daisy Brittle-Star (Ophiopholis)
27) Chiton (Chaetopleura)
28) Red Seaweed (Polysiphonia)
29) Crumb of Bread Sponge (Halichondria)
30) White Sea Anemone (Sagartia)
31) Sea Lettuce (Ulva)
32) Scale Worm (Lepidonotus)
33) Pink-Hearted Hydroid (Tubularia)
34) Red Beard Sponge (Microciona)
35) Tufted Erect Bryozoan (Bugula)
36) Atlantic Plate Limpet (Acmaea)
37) Rock Amphipod (Gammarus)
Go to tide pool menu
From "Field Guide Sheet for Eastern Shore Marine Environments: Rocky Shores and Wooden
Structures." Developed in 1978 from research sponsored by the University of Massachusetts
Cooperative Extension System, Barnstable County Extension Office and funded by the Cape Cod
Sea Camps in Brewster, Ma. jointly with the Massachusetts Marine Educators. Funding support
was provided by the U.S. Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Administration, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, and Sea Grant.